
Planckian locus
Encyclopedia
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
and color science, the Planckian locus or black body locus is the path or locus
Locus (mathematics)
In geometry, a locus is a collection of points which share a property. For example a circle may be defined as the locus of points in a plane at a fixed distance from a given point....
that the color of an incandescent black body
Black body
A black body is an idealized physical body that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation. Because of this perfect absorptivity at all wavelengths, a black body is also the best possible emitter of thermal radiation, which it radiates incandescently in a characteristic, continuous spectrum...
would take in a particular chromaticity space as the blackbody temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
changes. It goes from deep red
Red
Red is any of a number of similar colors evoked by light consisting predominantly of the longest wavelengths of light discernible by the human eye, in the wavelength range of roughly 630–740 nm. Longer wavelengths than this are called infrared , and cannot be seen by the naked eye...
at low temperatures through orange, yellow
Yellow
Yellow is the color evoked by light that stimulates both the L and M cone cells of the retina about equally, with no significant stimulation of the S cone cells. Light with a wavelength of 570–590 nm is yellow, as is light with a suitable mixture of red and green...
ish white, white
White
White is a color, the perception of which is evoked by light that stimulates all three types of color sensitive cone cells in the human eye in nearly equal amounts and with high brightness compared to the surroundings. A white visual stimulation will be void of hue and grayness.White light can be...
, and finally bluish
Blue
Blue is a colour, the perception of which is evoked by light having a spectrum dominated by energy with a wavelength of roughly 440–490 nm. It is considered one of the additive primary colours. On the HSV Colour Wheel, the complement of blue is yellow; that is, a colour corresponding to an equal...
white at very high temperatures.
A color space
Color space
A color model is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples of numbers, typically as three or four values or color components...
is a three-dimensional space
Three-dimensional space
Three-dimensional space is a geometric 3-parameters model of the physical universe in which we live. These three dimensions are commonly called length, width, and depth , although any three directions can be chosen, provided that they do not lie in the same plane.In physics and mathematics, a...
; that is, a color is specified by a set of three numbers (for example, either the CIE
CIE 1931 color space
In the study of color perception, one of the first mathematically defined color spaces is the CIE 1931 XYZ color space, created by the International Commission on Illumination in 1931....
coordinates X, Y, and Z, or other values such as hue
Hue
Hue is one of the main properties of a color, defined technically , as "the degree to which a stimulus can be describedas similar to or different from stimuli that are described as red, green, blue, and yellow,"...
, colorfulness, and luminance
Luminance
Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle. The SI unit for luminance is candela per square...
) which specify the color and brightness of a particular homogeneous visual stimulus. A chromaticity is a color projected into a two-dimensional space
Two-dimensional space
- Details :Bi-dimensional space is a geometric model of the planar projection of the physical universe in which we live.The two dimensions are commonly called length and width .Both directions lies in the same plane....
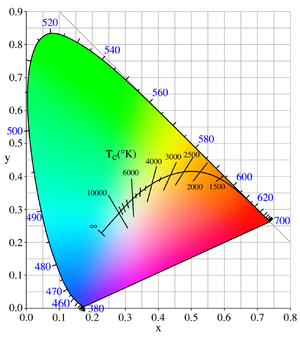
that ignores brightness. For example, the standard CIE XYZ color space projects directly to the corresponding chromaticity space specified by the two chromaticity coordinates known as x and y, making the familiar chromaticity diagram shown in the figure. The Planckian locus, the path that the color of a black body takes as the blackbody temperature changes, is often shown in this standard chromaticity space.
The Planckian locus in the XYZ color space

CIE 1931 color space
In the study of color perception, one of the first mathematically defined color spaces is the CIE 1931 XYZ color space, created by the International Commission on Illumination in 1931....
, the three coordinates defining a color are given by X, Y, and Z:



where I(λ,T) is the spectral radiance
Radiance
Radiance and spectral radiance are radiometric measures that describe the amount of radiation such as light or radiant heat that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle in a specified direction. They are used to characterize both emission from...
of the light being viewed, and X(λ), Y(λ) and Z(λ) are the color matching functions of the CIE standard colorimetric observer, shown in the diagram on the right, and λ is the wavelength. The Planckian locus is determined by substituting into the above equations the black body spectral radiance, which is given by Planck's law:

where:
- I is the black body spectral radiance (power per unit area per unit solid angle per unit wavelength)
- T is the temperatureTemperatureTemperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
of the black body - h is Planck's constant
- c is the speed of lightSpeed of lightThe speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
- k is Boltzmann's constant
This will give the Planckian locus in CIE XYZ color space. If these coordinates are XT, YT, ZT where T is the temperature, then in the CIE chromaticity coordinates will be


Approximation
The Planckian locus in xy space is depicted as a curve in the chromaticity diagram above. While it is possible to compute the CIE xy co-ordinates exactly given the above formulas, it is faster to use approximations. Since the mired scale changes more evenly along the locus than the temperature itself, it is common for such approximations to be functions of the reciprocal temperature. Kim et al. uses a cubic spline:

The Planckian locus can also be approximated in the CIE 1960 UCS, which is used to compute CCT and CRI, using the following expressions:


This approximation is accurate to within
 and
and  for
for 
Correlated color temperature
The mathematical procedure for determining the correlated color temperature involves finding the closest point to the light source's white pointWhite point
A white point is a set of tristimulus values or chromaticity coordinates that serve to define the color "white" in image capture, encoding, or reproduction. Depending on the application, different definitions of white are needed to give acceptable results...
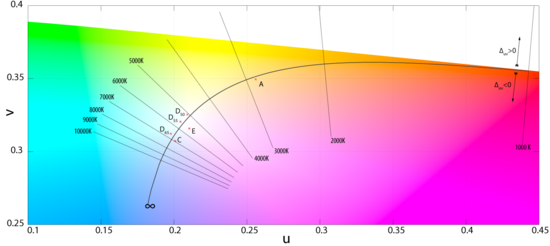
on the Planckian locus. Since the CIE's 1959 meeting in Brussels, the Planckian locus has been computed using the CIE 1960 color space
CIE 1960 color space
The CIE 1960 color space is another name for the chromaticity space devised by David MacAdam....
, also known as MacAdam's (u,v) diagram. Today, the CIE 1960 color space is deprecated for other purposes:
Owing to the perceptual inaccuracy inherent to the concept, it suffices to calculate to within 2K at lower CCTs and 10K at higher CCTs to reach the threshold of imperceptibility.
International Temperature Scale
The Planckian locus is derived by the determining the chromaticity values of a Planckian radiator using the standard colorimetric observer. The relative SPD of Planckian radiator follows Planck's law, and depends on the second radiation constant, . As measuring techniques have improved, the General Conference on Weights and Measures
. As measuring techniques have improved, the General Conference on Weights and MeasuresGeneral Conference on Weights and Measures
The General Conference on Weights and Measures is the English name of the Conférence générale des poids et mesures . It is one of the three organizations established to maintain the International System of Units under the terms of the Convention du Mètre of 1875...
has revised its estimate of this constant, with the International Temperature Scale (and briefly, the International Practical Temperature Scale). These successive revisions caused a shift in the Planckian locus and, as a result, the correlated color temperature scale. Before ceasing publication of standard illuminant
Standard illuminant
A standard illuminant is a theoretical source of visible light with a profile which is published. Standard illuminants provide a basis for comparing images or colors recorded under different lighting.-CIE illuminants:...
s, the CIE worked around this problem by explicitly specifying the form of the SPD, rather than making references to black bodies and a color temperature. Nevertheless, it is useful to be aware of previous revisions in order to be able to verify calculations made in older texts:
-
 (ITS-27). Note: Was in effect during the standardization of Illuminants A, B, C (1931), however the CIE used the value recommended by the U.S. National Bureau of Standards, 1.435 × 10-2
(ITS-27). Note: Was in effect during the standardization of Illuminants A, B, C (1931), however the CIE used the value recommended by the U.S. National Bureau of Standards, 1.435 × 10-2 -
 (IPTS-48). In effect for Illuminant series D (formalized in 1967).
(IPTS-48). In effect for Illuminant series D (formalized in 1967). -
 (ITS-68), (ITS-90). Often used in recent papers.
(ITS-68), (ITS-90). Often used in recent papers. -
 (CODATA, 2006). Current value, as of 2008.
(CODATA, 2006). Current value, as of 2008.

