
Pieter van Musschenbroek
Encyclopedia
Pieter van Musschenbroek (14 March 1692 – 19 September 1761) was a Dutch
scientist
. He was a professor in Duisburg
, Utrecht
, and Leiden, where he held positions in mathematics
, philosophy
, medicine
, and astrology
. He is credited with the invention of the first capacitor
in 1746: the Leyden jar
. He performed pioneering work on the buckling of compressed struts. Musschenbroek was also one of the first scientists (1729) to provide detailed descriptions of testing machines for tension, compression, and flexure testing. An early example of a problem in dynamic plasticity was described in the 1739 paper (in the form of the penetration of butter by a wooden stick subjected to impact by a wooden sphere).
 Pieter van Musschenbroek was born on 14 March 1692 in Leiden, Holland, Dutch Republic
Pieter van Musschenbroek was born on 14 March 1692 in Leiden, Holland, Dutch Republic
. His father was Johannes van Musschenbroek and his mother was Margaretha van Straaten. The Van Musschenbroeks, originally from Flanders
, lived in the city of Leiden since circa 1600. His father was an instrument maker, who made scientific instrument
s such as air pump
s, microscope
s, and telescope
s.
Van Musschenbroek attended Latin school
until 1708, where he studied Greek
, Latin
, French
, English
, High German
, Italian
, and Spanish
. He studied medicine
at Leiden University
and received his doctorate in 1715. He also attended lectures by John Theophilus Desaguliers
and Isaac Newton
in London
. He finished his study in philosophy
in 1719.
and philosophy at the University of Duisburg
. In 1721, he also became professor of medicine.
.
Musschenbroek's Elementa Physica (1726) played an important part in the transmission of Isaac Newton
's ideas in physics to Europe. In November 1734 he was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society.
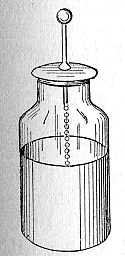 In 1739, he returned to Leiden, where he succeeded Jacobus Wittichius
In 1739, he returned to Leiden, where he succeeded Jacobus Wittichius
as professor.
Already during his studies at Leiden University Van Musschenbroek became interested in electrostatics
. At that time, transient electrical energy could be generated by friction machine
s but there was no way to store it. Musschenbroek and his student Andreas Cunaeus discovered that the energy could be stored, in work that also involved Jean-Nicolas-Sébastien Allamand
as collaborator. The apparatus was a glass jar filled with water into which a brass rod had been placed; and the stored energy could be released only by completing an external circuit between the brass rod and another conductor, originally a hand, placed in contact with the outside of the jar. Van Musschenbroek communicated this discovery to René Réaumur in January 1746, and it was Abbé Nollet, the translator of Musschenbroek's letter from Latin, who named the invention the 'Leyden jar
'.
Soon afterwards, it transpired that a German scientist, Ewald von Kleist
, had independently constructed a similar device in late 1745, shortly before Musschenbroek.
In 1754, he became an honorary professor at the Imperial Academy of Science in Saint Petersburg
. He was also elected a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences
in 1747.
Van Musschenbroek died on 19 September 1761 in Leiden.
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
scientist
Scientist
A scientist in a broad sense is one engaging in a systematic activity to acquire knowledge. In a more restricted sense, a scientist is an individual who uses the scientific method. The person may be an expert in one or more areas of science. This article focuses on the more restricted use of the word...
. He was a professor in Duisburg
Duisburg
- History :A legend recorded by Johannes Aventinus holds that Duisburg, was built by the eponymous Tuisto, mythical progenitor of Germans, ca. 2395 BC...
, Utrecht
Utrecht (city)
Utrecht city and municipality is the capital and most populous city of the Dutch province of Utrecht. It is located in the eastern corner of the Randstad conurbation, and is the fourth largest city of the Netherlands with a population of 312,634 on 1 Jan 2011.Utrecht's ancient city centre features...
, and Leiden, where he held positions in mathematics
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, philosophy
Philosophy
Philosophy is the study of general and fundamental problems, such as those connected with existence, knowledge, values, reason, mind, and language. Philosophy is distinguished from other ways of addressing such problems by its critical, generally systematic approach and its reliance on rational...
, medicine
Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
, and astrology
Astrology
Astrology consists of a number of belief systems which hold that there is a relationship between astronomical phenomena and events in the human world...
. He is credited with the invention of the first capacitor
Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
in 1746: the Leyden jar
Leyden jar
A Leyden jar, or Leiden jar, is a device that "stores" static electricity between two electrodes on the inside and outside of a jar. It was invented independently by German cleric Ewald Georg von Kleist on 11 October 1745 and by Dutch scientist Pieter van Musschenbroek of Leiden in 1745–1746. The...
. He performed pioneering work on the buckling of compressed struts. Musschenbroek was also one of the first scientists (1729) to provide detailed descriptions of testing machines for tension, compression, and flexure testing. An early example of a problem in dynamic plasticity was described in the 1739 paper (in the form of the penetration of butter by a wooden stick subjected to impact by a wooden sphere).
Early life and studies

Dutch Republic
The Dutch Republic — officially known as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands , the Republic of the United Netherlands, or the Republic of the Seven United Provinces — was a republic in Europe existing from 1581 to 1795, preceding the Batavian Republic and ultimately...
. His father was Johannes van Musschenbroek and his mother was Margaretha van Straaten. The Van Musschenbroeks, originally from Flanders
Flanders
Flanders is the community of the Flemings but also one of the institutions in Belgium, and a geographical region located in parts of present-day Belgium, France and the Netherlands. "Flanders" can also refer to the northern part of Belgium that contains Brussels, Bruges, Ghent and Antwerp...
, lived in the city of Leiden since circa 1600. His father was an instrument maker, who made scientific instrument
Scientific instrument
A scientific instrument can be any type of equipment, machine, apparatus or device as is specifically designed, constructed and often, through trial and error, ingeniously refined to apply utmost efficiency in the utilization of well proven physical principle, relationship or technology to...
s such as air pump
Air pump
An air pump is a device for pushing air. Examples include a bicycle pump, pumps that are used to aerate an aquarium or a pond via an airstone; a gas compressor used to power a pneumatic tool, air horn or pipe organ; a bellows used to encourage a fire; and a vacuum pump.The first effective air pump...
s, microscope
Microscope
A microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small for the naked eye. The science of investigating small objects using such an instrument is called microscopy...
s, and telescope
Telescope
A telescope is an instrument that aids in the observation of remote objects by collecting electromagnetic radiation . The first known practical telescopes were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 1600s , using glass lenses...
s.
Van Musschenbroek attended Latin school
Latin School
Latin School may refer to:* Latin schools of Medieval Europe* These schools in the United States:** Boston Latin School, Boston, MA** Brooklyn Latin School, New York, NY** Brother Joseph C. Fox Latin School, Long Island, NY...
until 1708, where he studied Greek
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek is the stage of the Greek language in the periods spanning the times c. 9th–6th centuries BC, , c. 5th–4th centuries BC , and the c. 3rd century BC – 6th century AD of ancient Greece and the ancient world; being predated in the 2nd millennium BC by Mycenaean Greek...
, Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
, French
French language
French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
, English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
, High German
Standard German
Standard German is the standard variety of the German language used as a written language, in formal contexts, and for communication between different dialect areas...
, Italian
Italian language
Italian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia...
, and Spanish
Spanish language
Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the...
. He studied medicine
Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
at Leiden University
Leiden University
Leiden University , located in the city of Leiden, is the oldest university in the Netherlands. The university was founded in 1575 by William, Prince of Orange, leader of the Dutch Revolt in the Eighty Years' War. The royal Dutch House of Orange-Nassau and Leiden University still have a close...
and received his doctorate in 1715. He also attended lectures by John Theophilus Desaguliers
John Theophilus Desaguliers
John Theophilus Desaguliers was a natural philosopher born in France. He was a member of the Royal Society of London beginning 29 July 1714. He was presented with the Royal Society's highest honour, the Copley Medal, in 1734, 1736 and 1741, with the 1741 award being for his discovery of the...
and Isaac Newton
Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton PRS was an English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, natural philosopher, alchemist, and theologian, who has been "considered by many to be the greatest and most influential scientist who ever lived."...
in London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
. He finished his study in philosophy
Philosophy
Philosophy is the study of general and fundamental problems, such as those connected with existence, knowledge, values, reason, mind, and language. Philosophy is distinguished from other ways of addressing such problems by its critical, generally systematic approach and its reliance on rational...
in 1719.
Duisburg
In 1719, he became professor of mathematicsMathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
and philosophy at the University of Duisburg
University of Duisburg
-History:Its origins date back to the 1555 decision to create a university for the unified duchies at the Lower Rhine that were later to be merged into Prussia. After the foundation of an academic college in 1559, a university was founded in 1655 by Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg, the...
. In 1721, he also became professor of medicine.
Utrecht
In 1723, he left his posts in Duisburg and became professor at the University of Utrecht. In 1732 he also became professor in astrologyAstrology
Astrology consists of a number of belief systems which hold that there is a relationship between astronomical phenomena and events in the human world...
.
Musschenbroek's Elementa Physica (1726) played an important part in the transmission of Isaac Newton
Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton PRS was an English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, natural philosopher, alchemist, and theologian, who has been "considered by many to be the greatest and most influential scientist who ever lived."...
's ideas in physics to Europe. In November 1734 he was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society.
Leiden

Jacobus Wittichius
Jacobus Wittichius was a German-Dutch philosopher, a Cartesian and follower of Burchard de Volder, and holder of controversial views on the nature of God.-Life:...
as professor.
Already during his studies at Leiden University Van Musschenbroek became interested in electrostatics
Electrostatics
Electrostatics is the branch of physics that deals with the phenomena and properties of stationary or slow-moving electric charges....
. At that time, transient electrical energy could be generated by friction machine
Electrostatic generator
An electrostatic generator, or electrostatic machine, is a mechanical device that produces static electricity, or electricity at high voltage and low continuous current...
s but there was no way to store it. Musschenbroek and his student Andreas Cunaeus discovered that the energy could be stored, in work that also involved Jean-Nicolas-Sébastien Allamand
Jean-Nicolas-Sébastien Allamand
-Life:He was born in Lausanne. At first he specialized in theology, and subsequently he came to the Netherlands, where he practised mathematics, physics, chemistry, and natural history, in Leiden. He met Willem 'sGravesande, who entrusted him with the education of his two sons and made him his...
as collaborator. The apparatus was a glass jar filled with water into which a brass rod had been placed; and the stored energy could be released only by completing an external circuit between the brass rod and another conductor, originally a hand, placed in contact with the outside of the jar. Van Musschenbroek communicated this discovery to René Réaumur in January 1746, and it was Abbé Nollet, the translator of Musschenbroek's letter from Latin, who named the invention the 'Leyden jar
Leyden jar
A Leyden jar, or Leiden jar, is a device that "stores" static electricity between two electrodes on the inside and outside of a jar. It was invented independently by German cleric Ewald Georg von Kleist on 11 October 1745 and by Dutch scientist Pieter van Musschenbroek of Leiden in 1745–1746. The...
'.
Soon afterwards, it transpired that a German scientist, Ewald von Kleist
Ewald Jürgen Georg von Kleist
Ewald Georg von Kleist was a German jurist, Lutheran cleric, and physicist.A member of the von Kleist family, Ewald was born in Vietzow in Farther Pomerania...
, had independently constructed a similar device in late 1745, shortly before Musschenbroek.
In 1754, he became an honorary professor at the Imperial Academy of Science in Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg is a city and a federal subject of Russia located on the Neva River at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea...
. He was also elected a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences
Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences
The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences or Kungliga Vetenskapsakademien is one of the Royal Academies of Sweden. The Academy is an independent, non-governmental scientific organization which acts to promote the sciences, primarily the natural sciences and mathematics.The Academy was founded on 2...
in 1747.
Van Musschenbroek died on 19 September 1761 in Leiden.

