
Pen Huo Qi
Encyclopedia
Chinese language
The Chinese language is a language or language family consisting of varieties which are mutually intelligible to varying degrees. Originally the indigenous languages spoken by the Han Chinese in China, it forms one of the branches of Sino-Tibetan family of languages...
: 噴火器; Pinyin
Pinyin
Pinyin is the official system to transcribe Chinese characters into the Roman alphabet in China, Malaysia, Singapore and Taiwan. It is also often used to teach Mandarin Chinese and spell Chinese names in foreign publications and used as an input method to enter Chinese characters into...
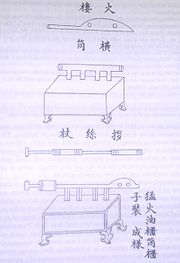
: pen huo qi, "spray fire device") is a double-piston pump naphtha
Naphtha
Naphtha normally refers to a number of different flammable liquid mixtures of hydrocarbons, i.e., a component of natural gas condensate or a distillation product from petroleum, coal tar or peat boiling in a certain range and containing certain hydrocarbons. It is a broad term covering among the...
flamethrower
Flamethrower
A flamethrower is a mechanical device designed to project a long controllable stream of fire.Some flamethrowers project a stream of ignited flammable liquid; some project a long gas flame. Most military flamethrowers use liquids, but commercial flamethrowers tend to use high-pressure propane and...
used in 919 AD in China, during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. The flamethrower was carefully documented and illustrated in the Chinese military manual known as the Wujing Zongyao
Wujing Zongyao
The Wujing Zongyao was a Chinese military compendium written in 1044 AD, during the Northern Song Dynasty. Its authors were the prominent scholars Zeng Gongliang , Ding Du , and Yang Weide , whose writing influenced many later Chinese military writers. The book covered a wide range of subjects,...
, compiled in the year 1044 AD during the Song Dynasty
Song Dynasty
The Song Dynasty was a ruling dynasty in China between 960 and 1279; it succeeded the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period, and was followed by the Yuan Dynasty. It was the first government in world history to issue banknotes or paper money, and the first Chinese government to establish a...
. Among various descriptions of equipment and components of the device, the book also provided instructions for how to keep up maintenance and repair of double-piston flamethrowers.
Advances in military technology aided the Song Dynasty
Song Dynasty
The Song Dynasty was a ruling dynasty in China between 960 and 1279; it succeeded the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period, and was followed by the Yuan Dynasty. It was the first government in world history to issue banknotes or paper money, and the first Chinese government to establish a...
in its defense against hostile neighbors to the north, including the Mongols. The earliest reference to the flamethrower in China was made in 917 AD, written by the author Wu Ren-chen in his Shi Guo Chun Qiu (十國春秋, "Ten States"). In 919 AD, the siphon projector-pump was used to spread the 'fierce fire oil' that could not be doused with water, as recorded by Lin Yu (林禹) in his Wu Yue Bei Shi (吳越備史, "The History of Wu and Yue"), hence the first credible Chinese reference to the flamethrower employing the chemical solution of Greek fire
Greek fire
Greek fire was an incendiary weapon used by the Byzantine Empire. The Byzantines typically used it in naval battles to great effect as it could continue burning while floating on water....
Lin Yu mentioned also that the 'fierce fire oil' derived ultimately from China's contact in the 'southern seas', Arabia (Dashiguo, 大食國, "Great Food Country"). In the Battle of Langshan Jiang (Wolf Mountain River, 狼山江) in 932, the naval fleet of the Wenmu King of Wuyue defeated the fleet of the Kingdom of Wu because he had used 'fire oil' (huo yóu, 火油) to burn his fleet; this signified the first Chinese use of gunpowder in warfare, since a slow-burning match fuse was required to ignite the flames. The Chinese applied the use of double-piston bellows to pump petrol out of a single cylinder (with an upstroke and downstroke), lit at the end by a slow-burning gunpowder match to fire a continuous stream of flame (as referred to in the Wujing Zongyao manuscript of 1044 AD). In the suppression of the Southern Tang state by 976 AD, early Song naval forces confronted them on the Yangtze River in 975 AD. Southern Tang forces attempted to use flamethrowers against the Song navy, but were accidentally consumed by their own fire when violent winds swept in their direction. Documented also in later Chinese publications, illustrations and descriptions of mobile flamethrowers on four-wheel push carts appear in the Wujing Zongyao, written in 1044 AD (its illustration redrawn in 1601 as well).

