
Peierls bracket
Encyclopedia
In theoretical physics
, the Peierls bracket is an equivalent description of the Poisson bracket
. It directly follows from the action
and does not require the canonical coordinates and their canonical momenta to be defined in advance.
The bracket
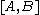
is defined as
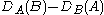 ,
,
as the difference between some kind of action of one quantity on the other, minus the flipped term.
In quantum mechanics
, the Peierls bracket becomes a commutator
i.e. a Lie bracket
.
Theoretical physics
Theoretical physics is a branch of physics which employs mathematical models and abstractions of physics to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena...
, the Peierls bracket is an equivalent description of the Poisson bracket
Poisson bracket
In mathematics and classical mechanics, the Poisson bracket is an important binary operation in Hamiltonian mechanics, playing a central role in Hamilton's equations of motion, which govern the time-evolution of a Hamiltonian dynamical system...
. It directly follows from the action
Action (physics)
In physics, action is an attribute of the dynamics of a physical system. It is a mathematical functional which takes the trajectory, also called path or history, of the system as its argument and has a real number as its result. Action has the dimension of energy × time, and its unit is...
and does not require the canonical coordinates and their canonical momenta to be defined in advance.
The bracket
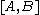
is defined as
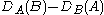 ,
,as the difference between some kind of action of one quantity on the other, minus the flipped term.
In quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
, the Peierls bracket becomes a commutator
Commutator
In mathematics, the commutator gives an indication of the extent to which a certain binary operation fails to be commutative. There are different definitions used in group theory and ring theory.-Group theory:...
i.e. a Lie bracket
Lie bracket of vector fields
In the mathematical field of differential topology, the Lie bracket of vector fields, Jacobi–Lie bracket, or commutator of vector fields is a bilinear differential operator which assigns, to any two vector fields X and Y on a smooth manifold M, a third vector field denoted [X, Y]...
.

