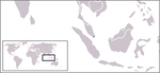
Outline of Singapore
Encyclopedia

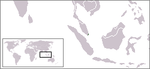
Singapore
Singapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the...
is a sovereign republic
Republic
A republic is a form of government in which the people, or some significant portion of them, have supreme control over the government and where offices of state are elected or chosen by elected people. In modern times, a common simplified definition of a republic is a government where the head of...
comprising the main island of Singapore and smaller outlying islands which are located at the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula
Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula or Thai-Malay Peninsula is a peninsula in Southeast Asia. The land mass runs approximately north-south and, at its terminus, is the southern-most point of the Asian mainland...
in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
. Singapore lies 137 kilometres (85.1 mi) north of the equator
Equator
An equator is the intersection of a sphere's surface with the plane perpendicular to the sphere's axis of rotation and containing the sphere's center of mass....
, south of the Malaysian state of Johor
Johor
Johor is a Malaysian state, located in the southern portion of Peninsular Malaysia. It is one of the most developed states in Malaysia. The state capital city and royal city of Johor is Johor Bahru, formerly known as Tanjung Puteri...
and north of Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
's Riau Islands. Singapore is one of three remaining true city-state
City-state
A city-state is an independent or autonomous entity whose territory consists of a city which is not administered as a part of another local government.-Historical city-states:...
s in the world. It is the second smallest nation in Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
.
Prior to European settlement, the island now known as Singapore was the site of a Malay
Malays in Singapore
Malays in Singapore are defined by the Singaporean government using the broader and antiquated "Malay race" concept, rather than modern-day Malay ethnic group. Although Malays have inhabited the area that is now Singapore since the 17th century, most of the Malays in Singapore today are immigrants...
fishing village at the mouth of the Singapore River
Singapore River
The Singapore River is a river in Singapore with great historical importance. The Singapore River flows from the Central Area, which lies in the Central Region in the southern part of Singapore before emptying into the ocean...
. Several hundred indigenous Orang Laut
Orang Laut
The Orang Laut, or Bajau Laut are a group of Malay people living in the Riau Islands of Indonesia. It also may refer to any Malay origin people living on coastal islands, including those of Andaman Sea islands in Thailand and Burma, commonly known as Moken.-Etymology:The Malay term orang laut...
people also lived along the nearby coast, rivers and on smaller islands. In 1819 the British East India Company
British East India Company
The East India Company was an early English joint-stock company that was formed initially for pursuing trade with the East Indies, but that ended up trading mainly with the Indian subcontinent and China...
established a trading post on the island, which was used thereafter as a strategic trading post along the spice route. Singapore would become one of the most important commercial and military centres of the British Empire, and the hub of British power in Southeast Asia. The city was occupied by the Japanese
Japanese Occupation of Singapore
The Japanese occupation of Singapore in World War II occurred between about 1942 and 1945 after the fall of Singapore on 15 February 1942. Military forces of the Empire of Japan occupied Singapore after defeating the combined Australian, British, Indian and Malayan garrison in the Battle of Singapore...
during World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, which Winston Churchill
Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer-Churchill, was a predominantly Conservative British politician and statesman known for his leadership of the United Kingdom during the Second World War. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest wartime leaders of the century and served as Prime Minister twice...
called "Britain's greatest defeat". Singapore reverted to British rule immediately postwar, in 1945. Eighteen years later the city, having achieved independence from Britain, merged with Malaya
Federation of Malaya
The Federation of Malaya is the name given to a federation of 11 states that existed from 31 January 1948 until 16 September 1963. The Federation became independent on 31 August 1957...
, Sabah
Sabah
Sabah is one of 13 member states of Malaysia. It is located on the northern portion of the island of Borneo. It is the second largest state in the country after Sarawak, which it borders on its southwest. It also shares a border with the province of East Kalimantan of Indonesia in the south...
and Sarawak
Sarawak
Sarawak is one of two Malaysian states on the island of Borneo. Known as Bumi Kenyalang , Sarawak is situated on the north-west of the island. It is the largest state in Malaysia followed by Sabah, the second largest state located to the North- East.The administrative capital is Kuching, which...
to form Malaysia. However, less than two years later it seceded from the federation and became an independent republic
Republic
A republic is a form of government in which the people, or some significant portion of them, have supreme control over the government and where offices of state are elected or chosen by elected people. In modern times, a common simplified definition of a republic is a government where the head of...
on 9 August 1965. Singapore joined the United Nations
United Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
on 21 September that same year.
Since independence, Singapore's standard of living
Standard of living
Standard of living is generally measured by standards such as real income per person and poverty rate. Other measures such as access and quality of health care, income growth inequality and educational standards are also used. Examples are access to certain goods , or measures of health such as...
has been on the rise. Foreign direct investment
Foreign direct investment
Foreign direct investment or foreign investment refers to the net inflows of investment to acquire a lasting management interest in an enterprise operating in an economy other than that of the investor.. It is the sum of equity capital,other long-term capital, and short-term capital as shown in...
and a state-led drive to industrialization based on plans drawn up by the Dutch economist Albert Winsemius
Albert Winsemius
Albert Winsemius , a Dutch economist, was Singapore's long-time economic advisor from 1961 to 1984. He led the United Nations Survey Mission to Singapore, and was to play a major role in the formulation of Singapore's national economic development strategy.In 1960, Dr Winsemius led the United...
have created a modern economy focused on electronics manufacturing, petrochemicals, tourism and financial services alongside traditional entrepôt
Entrepôt
An entrepôt is a trading post where merchandise can be imported and exported without paying import duties, often at a profit. This profit is possible because of trade conditions, for example, the reluctance of ships to travel the entire length of a long trading route, and selling to the entrepôt...
trade. Singapore is the 6th wealthiest country in the world in terms of GDP per capita. The small nation has foreign exchange reserves
Foreign exchange reserves
Foreign-exchange reserves in a strict sense are 'only' the foreign currency deposits and bonds held by central banks and monetary authorities. However, the term in popular usage commonly includes foreign exchange and gold, Special Drawing Rights and International Monetary Fund reserve positions...
of US$171.7353 billion.
The population of Singapore is approximately 4.59 million. Though Singapore is highly cosmopolitan and diverse, ethnic Chinese form the majority of the population. English is the administrative language of the country.
The Constitution of the Republic of Singapore
Constitution of Singapore
The Constitution of Singapore is the supreme law of Singapore and it is a codified constitution.The constitution cannot be amended without the support of more than two-thirds of the members of parliament on the second and third readings . The president may seek opinion on constitutional issues...
established the nation's political system as a representative democracy
Representative democracy
Representative democracy is a form of government founded on the principle of elected individuals representing the people, as opposed to autocracy and direct democracy...
, while the country is recognized as a parliamentary republic
Parliamentary republic
A parliamentary republic or parliamentary constitutional republic is a type of republic which operates under a parliamentary system of government - meaning a system with no clear-cut separation of powers between the executive and legislative branches. There are a number of variations of...
. The People's Action Party
People's Action Party
The People's Action Party is the leading political party in Singapore. It has been the city-state's ruling political party since 1959....
(PAP) dominates the political process and has won control of Parliament
Parliament of Singapore
The Parliament of the Republic of Singapore and the President jointly make up the legislature of Singapore. Parliament is unicameral and is made up of Members of Parliament who are elected, as well as Non-constituency Members of Parliament and Nominated Members of Parliament who are appointed...
in every election since self-government in 1959.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Singapore:
General reference
- PronunciationInternational Phonetic AlphabetThe International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic...
: ˈsɪŋəpɔr or ˈsɪŋɡəpɔr - Common English country name: SingaporeSingaporeSingapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the...
- Official English country name: The Republic of Singapore
- Official endonymsExonym and endonymIn ethnolinguistics, an endonym or autonym is a local name for a geographical feature, and an exonym or xenonym is a foreign language name for it...
: Singapore (English), Singapura (MalayMalay languageMalay is a major language of the Austronesian family. It is the official language of Malaysia , Indonesia , Brunei and Singapore...
), (PinyinPinyinPinyin is the official system to transcribe Chinese characters into the Roman alphabet in China, Malaysia, Singapore and Taiwan. It is also often used to teach Mandarin Chinese and spell Chinese names in foreign publications and used as an input method to enter Chinese characters into...
: Xīnjiāpō, MandarinStandard MandarinStandard Chinese or Modern Standard Chinese, also known as Mandarin or Putonghua, is the official language of the People's Republic of China and Republic of China , and is one of the four official languages of Singapore....
), (Ciŋkappūr, TamilTamil languageTamil is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by Tamil people of the Indian subcontinent. It has official status in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu and in the Indian union territory of Pondicherry. Tamil is also an official language of Sri Lanka and Singapore...
) - Common endonyms: Lion City, Little red dotLittle red dot"Little red dot" is an epithet for the nation of Singapore. It describes the manner in which the main and subsidiary islands comprising the Republic, with a total land area of no more than 704 km2 , are marked on many world maps. Originally, it was apparently used to refer to Singapore in a...
, TemasekTemasekTemasek was the name of an early city on the site of modern Singapore. From the 14th century, the island has also been known as Singapura, which is derived from Sanskrit and means "Lion City"... - ExonymExonym and endonymIn ethnolinguistics, an endonym or autonym is a local name for a geographical feature, and an exonym or xenonym is a foreign language name for it...
: Disneyland with the death penaltyDisneyland with the Death Penalty"Disneyland with the Death Penalty" is an article about Singapore written by William Gibson, his first major piece of non-fiction, first published as the cover story for Wired magazine's September/October 1993 issue .... - Adjectival(s): SingaporeSingaporeSingapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the...
an - Demonym(s): SingaporeSingaporeSingapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the...
an - EtymologyEtymologyEtymology is the study of the history of words, their origins, and how their form and meaning have changed over time.For languages with a long written history, etymologists make use of texts in these languages and texts about the languages to gather knowledge about how words were used during...
: Name of Singapore - International rankings of SingaporeInternational rankings of SingaporeThe following are international rankings of Singapore.-Cities:Singapore is a city-state.*Most livable cities —**Economist Intelligence Unit: World's Most Livable Cities survey 2011: Singapore is ranked 4th on the Economist Intelligence Unit's Asia Most Livable City survey**Singapore is ranked 1st...
- ISO country codes: SG, SGP, 702
- ISO region codes: See ISO 3166-2:SGISO 3166-2:SGISO 3166-2:SG is the entry for Singapore in ISO 3166-2, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization , which defines codes for the names of the principal subdivisions of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1.Currently for Singapore, ISO 3166-2 codes are...
- InternetInternetThe Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
country code top-level domainCountry code top-level domainA country code top-level domain is an Internet top-level domain generally used or reserved for a country, a sovereign state, or a dependent territory....
: .sg.sg.sg is the Internet country code top-level domain for Singapore. It is administered by the Singapore Network Information Centre. Registrations are processed via accredited registrars....
Geography of Singapore
- Singapore is: a country
- Location:
- Northern HemisphereNorthern HemisphereThe Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
and Eastern HemisphereEastern HemisphereThe Eastern Hemisphere, also Eastern hemisphere or eastern hemisphere, is a geographical term for the half of the Earth that is east of the Prime Meridian and west of 180° longitude. It is also used to refer to Europe, Asia, Africa, and Australasia, vis-à-vis the Western Hemisphere, which includes... - EurasiaEurasiaEurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
- AsiaAsiaAsia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
- Southeast AsiaSoutheast AsiaSoutheast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
- IndochinaIndochinaThe Indochinese peninsula, is a region in Southeast Asia. It lies roughly southwest of China, and east of India. The name has its origins in the French, Indochine, as a combination of the names of "China" and "India", and was adopted when French colonizers in Vietnam began expanding their territory...
- Maritime Southeast AsiaMaritime Southeast AsiaMaritime Southeast Asia refers to the maritime region of Southeast Asia as opposed to mainland Southeast Asia and includes the modern countries of Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Brunei, East Timor and Singapore....
- Indochina
- Southeast Asia
- Asia
- Time zoneTime zoneA time zone is a region on Earth that has a uniform standard time for legal, commercial, and social purposes. In order for the same clock time to always correspond to the same portion of the day as the Earth rotates , different places on the Earth need to have different clock times...
: Singapore Standard TimeSingapore Standard TimeSingapore Standard Time or Singapore Time based in Singapore uses a time zone eight hours in advance of UTC .- History :...
= ASEAN Common TimeASEAN Common TimeASEAN Common Time is an idea by ASEAN to adopt a standard time of UTC+08 for all member countries. Some businesses with a local or regional reach have already adopted the use of the "ASEAN Common Time", and can be seen using the abbreviation '"ACT"' in their Press Releases, communications, and...
(UTC+08) - Extreme points of SingaporeExtreme points of SingaporeThis is a list of the extreme points of Singapore, the points that are farther north, south, east, or west than any other location in the country. Also included are extreme points in elevation...
:- High: Bukit TimahBukit TimahBukit Timah is an area in Singapore and a hill in that area. Bukit Timah is located near the centre of the Singapore main island. The hill stands at an altitude of 163.63 metres and is the highest point in the city-state of Singapore...
163.63 m (537 ft) - Low: Singapore StraitSingapore StraitThe Singapore Strait is a 105-kilometer long, 16-kilometer wide strait between the Strait of Malacca in the west and the South China Sea in the east. Singapore is on the north of the channel and the Riau Islands are on the south...
0 m
- High: Bukit Timah
- Land boundaries: none (two causeways to Malaysia)
- Coastline: 193 km (119.9 mi)
- Northern Hemisphere
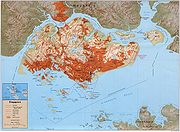
- Area of Singapore: 707.1 km² (273 sq mi)
- Atlas of Singapore
Environment of Singapore

- Astronomical phenomenaAstronomyAstronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
- Next total solar eclipseSolar eclipseAs seen from the Earth, a solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth, and the Moon fully or partially blocks the Sun as viewed from a location on Earth. This can happen only during a new moon, when the Sun and the Moon are in conjunction as seen from Earth. At least...
visible in Singapore: 5 July 2168
- Next total solar eclipse
- Biosphere reserves in Singapore
- Bukit Timah Nature ReserveBukit Timah Nature ReserveThe Bukit Timah Nature Reserve is a small 1.64 square kilometer nature reserve near the geographic centre of the city-state of Singapore, located on the slopes of Bukit Timah Hill, Singapore's highest hill standing at a height of 163.63 metres, and parts of the surrounding area...
- Central Catchment Nature ReserveCentral Catchment Nature ReserveThe Central Catchment Nature Reserve is the largest nature reserve in Singapore, occupying 2889 hectares Forming a large green lung in the geographical centre of the city, it houses several recreational sites, including the Singapore Zoo and the Night Safari, as well as several newer facilities...
- Chek JawaChek JawaTanjong Chek Jawa is a cape and the name of its 100-hectare wetlands located on the south-eastern tip of Pulau Ubin, an island off the north-eastern coast of the main island of Singapore...
- Labrador Nature ReserveLabrador Nature ReserveLabrador Nature Reserve , also locally known as Labrador Park , is located in the southern part of the main island of Singapore. It contains the only rocky sea-cliff on the mainland that is accessible to the public...
- Sungei Buloh Wetland ReserveSungei Buloh Wetland ReserveThe Sungei Buloh Wetland Reserve is a nature reserve located in the Northwest area of Singapore. It is the first wetlands reserve to be gazetted in Singapore in the year 2002, and its global importance as a stop-over point for migratory birds was also recognised by the Wetlands International's...
- Bukit Timah Nature Reserve
- Climate of Singapore
- Tropical climateTropical climateA tropical climate is a climate of the tropics. In the Köppen climate classification it is a non-arid climate in which all twelve months have mean temperatures above...
- Long-term average annual rainRainRain is liquid precipitation, as opposed to non-liquid kinds of precipitation such as snow, hail and sleet. Rain requires the presence of a thick layer of the atmosphere to have temperatures above the melting point of water near and above the Earth's surface...
fall: 2,346 mm - Average monthly number of thunderstormThunderstormA thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm, a lightning storm, thundershower or simply a storm is a form of weather characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere known as thunder. The meteorologically assigned cloud type associated with the...
days over the last 50 years up to 2008: 14 (about 3.8% of the year) - Average annual number of wet days (more than 0.2 mm of rainfall recorded) over the last 50 years up to 2008: 169 (about 46.3% of the year)
- Driest month since 1869: February 2010 (6.3 mm of rain)
- Longest period without rain since 1869: 42 days (5 January – 15 February 2009)
- Tropical climate
- Environmental issues in Singapore
- Ecoregions in Singapore
- Renewable energy in Singapore
- Geology of SingaporeGeology of SingaporeSingapore is a heavily built up society. Not much is shown among the natives about the types of rocks found on the islands, because its physical environment has changed a lot. Igneous rocks are found in Bukit Timah, Woodlands, and Pulau Ubin island. Granite makes up the bulk of the igneous rock...
- Wildlife of SingaporeWildlife of SingaporeSingapore has a surprisingly diverse wildlife despite its rapid urbanisation. Most of the fauna that has remained exists in various nature reserves such as the Bukit Timah Nature Reserve and the Sungei Buloh Wetland Reserve.-History:...
- Flora of SingaporeFlora of SingaporeSingapore has a wide variety of flora. Plants are mainly used to beautify the landscape of Singapore. The national flower is a variety of orchid, Vanda Miss Joaquim.- Places exhibiting the flora of Singapore :*Singapore Botanic Gardens...
- Fauna of SingaporeFauna of SingaporeSingapore has about 60 species of mammals, 365 species of birds, 107 species of reptiles, and 28 species of amphibians.The Central Catchment Nature Reserve and the nearby Bukit Timah Nature Reserve are the stronghold of the remaining forest animals on the mainland...
- Birds of Singapore
- Mammals of Singapore
- Flora of Singapore
Natural geographic features of Singapore

- Hills of Singapore
- Bukit TimahBukit TimahBukit Timah is an area in Singapore and a hill in that area. Bukit Timah is located near the centre of the Singapore main island. The hill stands at an altitude of 163.63 metres and is the highest point in the city-state of Singapore...
- Fort CanningFort CanningFort Canning is a small hill slightly more than 60 metres high in the southeast portion of the island city-state of Singapore, within the Central Area that forms Singapore's central business district...
- Mount FaberMount FaberMount Faber is a hill about 105 metres in height in Singapore, located near the Bukit Merah planning area in the Central Region. It overlooks the Telok Blangah area, and the western parts of the Central Area...
- Bukit Timah
- Islands of Singapore
- Jurong IslandJurong IslandJurong Island is an artificial island located to the southwest of the main island of Singapore, off Jurong Industrial Estate. It was formed from the amalgamation of seven offshore islands, the islands of Pulau Ayer Chawan, Pulau Ayer Merbau, Pulau Merlimau, Pulau Pesek, Pulau Pesek Kechil , Pulau...
- Kusu IslandKusu IslandKusu Island is one of the Southern Islands in Singapore, located about 5.6 kilometres to the south of the main island of Singapore, off the Straits of Singapore. The name means "Tortoise Island" or "Turtle Island" in Chinese; the island is also known as Peak Island or Pulau Tembakul in Malay...
- Pedra Branca
- Pulau BraniPulau BraniPulau Brani is an island located off the southern coast of Singapore, near Keppel Harbour. The island is situated between the main island of Singapore and the resort island of Sentosa, and is linked to the mainland via Brani Terminal Avenue...
- Pulau BukomPulau BukomPulau Bukom, also known as Pulau Bukum, is a small island located about five kilometres to the south of the main island of Singapore, off the Straits of Singapore. The size of Pulau Bukom is about 1.45 km²....
- Pulau HantuPulau HantuPulau Hantu is located to the south of the main island of Singapore, off the Straits of Singapore. Pulau Hantu is actually made up of two islets: Pulau Hantu Besar and Pulau Hantu Kechil , with a total area of 12.6 hectares...
- Pulau TekongPulau TekongPulau Tekong is the second largest of Singapore's outlying islands with an area of 24.43 km², and the island is still expanding due to land reclamation works on its southern and northwestern coasts which will eventually subsume many of its surrounding small islets, including Pulau Tekong...
- Pulau UbinPulau UbinPulau Ubin is a small island situated in the north east of Singapore, to the west of Pulau Tekong. Granite quarrying supported a few thousand settlers on Pulau Ubin in the 1960s, but only about a hundred villagers live there today...
- Saint John's IslandSaint John's IslandSaint John's Island, previously known as Pulau Sakijang Bendera, is one of the Southern Islands in Singapore. It is located approximately 6.5 km to the south of the main island of Singapore, off the Straits of Singapore....
- SentosaSentosaSentosa, which translates to peace and tranquility in Malay , is a popular island resort in Singapore, visited by some five million people a year...
- Sisters' IslandsSisters' IslandsThe Sisters' Islands are two of the Southern Islands in Singapore and are located to the south of the main island of Singapore, off the Straits of Singapore...
- Jurong Island
- Lakes of Singapore
- Rivers of Singapore
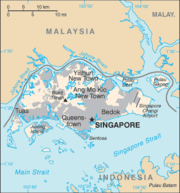
Administrative divisions of Singapore
- Singapore, being a city itself, has no administrative divisionAdministrative divisionAn administrative division, subnational entity, or country subdivision is a portion of a country or other political division, established for the purpose of government. Administrative divisions are each granted a certain degree of autonomy, and are required to manage themselves through their own...
s- It does, however, have subdivisionsSubdivisions of SingaporeWhile the small physical size of Singapore does not justify the creation of national subdivisions in the form of provinces, states, and other national political divisions found in larger countries, the city-state is nonetheless subdivided in various ways throughout its history for the purpose of...
- It does, however, have subdivisions
Municipalities
- Being a city-stateCity-stateA city-state is an independent or autonomous entity whose territory consists of a city which is not administered as a part of another local government.-Historical city-states:...
, Singapore is both a cityCityA city is a relatively large and permanent settlement. Although there is no agreement on how a city is distinguished from a town within general English language meanings, many cities have a particular administrative, legal, or historical status based on local law.For example, in the U.S...
and a nation state- Singapore is its own only municipality
- Capital of Singapore: Singapore is its own capital
Population structure
- Population (end June 2009): 4,987,600
- Resident population: 3,733,900 (74.9%).
- Singapore citizensSingaporean nationality lawSingaporean nationality law is derived from the Constitution of Singapore and is based on jus sanguinis and a modified form of jus soli...
: 3,200,700 (64.2%) - Singapore permanent residents: 533,200 (10.7%)
- Singapore citizens
- Non-resident population: 1,253,700 (25.1%)
- Resident population: 3,733,900 (74.9%).
- Population densityPopulation densityPopulation density is a measurement of population per unit area or unit volume. It is frequently applied to living organisms, and particularly to humans...
(2008): 6,814 per km2 - Sex ratioSex ratioSex ratio is the ratio of males to females in a population. The primary sex ratio is the ratio at the time of conception, secondary sex ratio is the ratio at time of birth, and tertiary sex ratio is the ratio of mature organisms....
of residents (end June 2009): 976 males per 1,000 females - Median agePopulation pyramidA population pyramid, also called an age structure diagram, is a graphical illustration that shows the distribution of various age groups in a population , which forms the shape of a pyramid when the population is growing...
of residents (2008): 36.7 years - Age composition of residents (2009): 0–14 years – 17.9%, 15–64 years – 73.3%, 65 years and above – 8.8%
- Ethnic composition of residents (June 2009): ChineseChinese in SingaporeChinese Singaporeans are people of Chinese ethnicity who hold Singaporean nationality. As of 2010, Chinese Singaporeans constitute 74.1% of Singapore's resident population, or approximately three out of four Singaporeans, making them the largest ethnic group in Singapore...
– 2,770,300 (74.2%), MalaysMalays in SingaporeMalays in Singapore are defined by the Singaporean government using the broader and antiquated "Malay race" concept, rather than modern-day Malay ethnic group. Although Malays have inhabited the area that is now Singapore since the 17th century, most of the Malays in Singapore today are immigrants...
– 500,100 (13.4%), Indians – 343,500 (9.2%), others – 120,000 (3.2%) - Proportion single among residents aged 35–39 years (2008): men – 19.4%, women – 15.2%
- Average resident household size (2008): 3.5 people
Family formation and dissolution
- Total marriages (2008): 24,596
- MedianMedianIn probability theory and statistics, a median is described as the numerical value separating the higher half of a sample, a population, or a probability distribution, from the lower half. The median of a finite list of numbers can be found by arranging all the observations from lowest value to...
age at first marriage (2008): men – 29.8 years, women – 27.3 years
- Median
- Total divorces and annulments (2008): 7,220
Fertility rate
- Crude birth rateBirth rateCrude birth rate is the nativity or childbirths per 1,000 people per year . Another word used interchangeably with "birth rate" is "natality". When the crude birth rate is subtracted from the crude death rate, it reveals the rate of natural increase...
per 1,000 residents (2008): 10.2 - Total fertility rateTotal Fertility RateThe total fertility rate of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if she were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates through her lifetime, and she...
(TFR) of residents (2008): 1.28
Mortality
- Crude death rateMortality rateMortality rate is a measure of the number of deaths in a population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit time...
per 1,000 residents (2008): 4.4 - Life expectancy at birthLife expectancyLife expectancy is the expected number of years of life remaining at a given age. It is denoted by ex, which means the average number of subsequent years of life for someone now aged x, according to a particular mortality experience...
of residents (2008): men – 78.4 years, women – 83.2 years
Government and politics of Singapore
- Form of governmentForm of governmentA form of government, or form of state governance, refers to the set of political institutions by which a government of a state is organized. Synonyms include "regime type" and "system of government".-Empirical and conceptual problems:...
: Unitary stateUnitary stateA unitary state is a state governed as one single unit in which the central government is supreme and any administrative divisions exercise only powers that their central government chooses to delegate...
under a Parliamentary democracy
- Elections in SingaporeElections in SingaporeThere are currently two types of elections in Singapore: parliamentary and presidential elections.While the Constitution of Singapore does not specify exactly when elections need to be held, Parliamentary or General Elections are generally 5 years apart, while Presidential elections are generally...
- Political parties in Singapore
- Taxation in Singapore
Executive branch of the government of Singapore
- Head of stateHead of StateA head of state is the individual that serves as the chief public representative of a monarchy, republic, federation, commonwealth or other kind of state. His or her role generally includes legitimizing the state and exercising the political powers, functions, and duties granted to the head of...
: President of SingaporePresident of SingaporeThe President of the Republic of Singapore is Singapore's head of state. In a Westminster parliamentary system, as which Singapore governs itself, the prime minister is the head of the government while the position of president is largely ceremonial. Before 1993, the President of Singapore was...
, Sellapan Ramanathan - Head of governmentHead of governmentHead of government is the chief officer of the executive branch of a government, often presiding over a cabinet. In a parliamentary system, the head of government is often styled prime minister, chief minister, premier, etc...
: Prime Minister of SingaporePrime Minister of SingaporeThe Prime Minister of the Republic of Singapore is the head of the government of the Republic of Singapore. The President of Singapore appoints as Prime Minister a Member of Parliament who, in his opinion, is most likely to command the confidence of a majority of MPs.The office of Prime Minister...
, Lee Hsien LoongLee Hsien LoongLee Hsien Loong is the third and current Prime Minister of Singapore. He is married to Ho Ching, who is the Executive Director and Chief Executive Officer of Temasek Holdings. He is the eldest son of Singapore's first Prime Minister Lee Kuan Yew.... - Cabinet of SingaporeCabinet of SingaporeThe Cabinet of Singapore forms the Government of Singapore together with the President of Singapore. It is led by the Prime Minister of Singapore who is the head of government...
Legislative branch of the government of Singapore
- Parliament of SingaporeParliament of SingaporeThe Parliament of the Republic of Singapore and the President jointly make up the legislature of Singapore. Parliament is unicameral and is made up of Members of Parliament who are elected, as well as Non-constituency Members of Parliament and Nominated Members of Parliament who are appointed...
(unicameral)
Judicial branch of the government of Singapore
- Judicial officers of the Republic of SingaporeJudicial officers of the Republic of SingaporeThe judicial officers of the Republic of Singapore work in the Supreme Court and the Subordinate Courts to hear and determine disputes between litigants in civil cases and, in criminal matters, to determine the liability of accused persons and their sentences if they are convicted.In the Supreme...
- Supreme Court of Singapore
- Subordinate Courts of SingaporeSubordinate Courts of SingaporeThe Subordinate Courts of Singapore is one of the two tiers of the court system in Singapore, the other tier being the Supreme Court. The Subordinate Courts comprise the District and Magistrate Courts—both of which oversee civil and criminal matters—as well as specialised family, juvenile,...
Foreign relations of Singapore
- Diplomatic missions in Singapore
- Diplomatic missions of Singapore
- Malaysia-Singapore relationsMalaysia-Singapore relationsMalaysia-Singapore relations refers to bilateral foreign relations between the two countries Malaysia and Singapore, after the separation of Singapore from the Federation of Malaysia in 1965. Singapore has a high commission in Kuala Lumpur, and Malaysia has a high commission in Singapore...
- Singapore – United States relations
International organization membership
The Republic of Singapore is a member of the:- Asian Development BankAsian Development BankThe Asian Development Bank is a regional development bank established on 22 August 1966 to facilitate economic development of countries in Asia...
(ADB) - Asia-Pacific Economic CooperationAsia-Pacific Economic CooperationAsia-Pacific Economic Cooperation is a forum for 21 Pacific Rim countries that seeks to promote free trade and economic cooperation throughout the Asia-Pacific region...
(APEC) - Asia-Pacific TelecommunityAsia-Pacific Telecommunity-Introduction:The Asia Pacific Telecommunity was founded on the joint initiatives of the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific and the International Telecommunication Union ....
(APT) - Association of Southeast Asian NationsAssociation of Southeast Asian NationsThe Association of Southeast Asian Nations, commonly abbreviated ASEAN rarely ), is a geo-political and economic organization of ten countries located in Southeast Asia, which was formed on 8 August 1967 by Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore and Thailand. Since then, membership has...
(ASEAN) - Association of Southeast Asian Nations Regional Forum (ARF)
- Bank for International SettlementsBank for International SettlementsThe Bank for International Settlements is an intergovernmental organization of central banks which "fosters international monetary and financial cooperation and serves as a bank for central banks." It is not accountable to any national government...
(BIS) - Colombo PlanColombo PlanThe Colombo Plan is a regional organization that embodies the concept of collective inter-governmental effort to strengthen economic and social development of member countries in the Asia-Pacific Region...
(CP) - Commonwealth of NationsCommonwealth of NationsThe Commonwealth of Nations, normally referred to as the Commonwealth and formerly known as the British Commonwealth, is an intergovernmental organisation of fifty-four independent member states...
- East Asia SummitEast Asia SummitThe East Asia Summit is a forum held annually by leaders of, initially, 16 countries in the East Asian region. Membership will expand to 18 countries including the United States and Russia at the Sixth EAS in 2011. EAS meetings are held after annual ASEAN leaders’ meetings...
(EAS) - Group of 77Group of 77The Group of 77 at the United Nations is a loose coalition of developing nations, designed to promote its members' collective economic interests and create an enhanced joint negotiating capacity in the United Nations. There were 77 founding members of the organization, but the organization has...
(G77) - International Atomic Energy AgencyInternational Atomic Energy AgencyThe International Atomic Energy Agency is an international organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy, and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. The IAEA was established as an autonomous organization on 29 July 1957...
(IAEA) - International Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentInternational Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentThe International Bank for Reconstruction and Development is one of five institutions that compose the World Bank Group. The IBRD is an international organization whose original mission was to finance the reconstruction of nations devastated by World War II. Now, its mission has expanded to fight...
(IBRD) - International Chamber of CommerceInternational Chamber of CommerceThe International Chamber of Commerce is the largest, most representative business organization in the world. Its hundreds of thousands of member companies in over 130 countries have interests spanning every sector of private enterprise....
(ICC) - International Civil Aviation OrganizationInternational Civil Aviation OrganizationThe International Civil Aviation Organization , pronounced , , is a specialized agency of the United Nations. It codifies the principles and techniques of international air navigation and fosters the planning and development of international air transport to ensure safe and orderly growth...
(ICAO) - International Criminal Police Organization (Interpol)
- International Development AssociationInternational Development AssociationThe International Development Association , is the part of the World Bank that helps the world’s poorest countries. It complements the World Bank's other lending arm — the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development — which serves middle-income countries with capital investment and...
(IDA) - International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent SocietiesInternational Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent SocietiesThe International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies is a humanitarian institution that is part of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement along with the ICRC and 186 distinct National Societies...
(IFRCS) - International Finance CorporationInternational Finance CorporationThe International Finance Corporation promotes sustainable private sector investment in developing countries.IFC is a member of the World Bank Group and is headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States....
(IFC) - International Hydrographic OrganizationInternational Hydrographic OrganizationThe International Hydrographic Organization is the inter-governmental organisation representing the hydrographic community. It enjoys observer status at the UN and is the recognised competent authority on hydrographic surveying and nautical charting...
(IHO) - International Labour OrganizationInternational Labour OrganizationThe International Labour Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that deals with labour issues pertaining to international labour standards. Its headquarters are in Geneva, Switzerland. Its secretariat — the people who are employed by it throughout the world — is known as the...
(ILO) - International Maritime OrganizationInternational Maritime OrganizationThe International Maritime Organization , formerly known as the Inter-Governmental Maritime Consultative Organization , was established in Geneva in 1948, and came into force ten years later, meeting for the first time in 1959...
(IMO) - International Mobile Satellite OrganizationInternational Mobile Satellite OrganizationThe International Mobile Satellite Organization is the intergovernmental organization that oversees certain public satellite safety and security communication services provided via the Inmarsat satellites...
(IMSO) - International Monetary FundInternational Monetary FundThe International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
(IMF) - International Olympic CommitteeInternational Olympic CommitteeThe International Olympic Committee is an international corporation based in Lausanne, Switzerland, created by Pierre de Coubertin on 23 June 1894 with Demetrios Vikelas as its first president...
(IOC)
- International Organization for StandardizationInternational Organization for StandardizationThe International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
(ISO) - International Red Cross and Red Crescent MovementInternational Red Cross and Red Crescent MovementThe International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is an international humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide which was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, and to prevent and alleviate human...
(ICRM) - International Telecommunication UnionInternational Telecommunication UnionThe International Telecommunication Union is the specialized agency of the United Nations which is responsible for information and communication technologies...
(ITU) - International Telecommunications Satellite OrganizationInternational Telecommunications Satellite OrganizationThe International Telecommunications Satellite Organization is an intergovernmental organisation charged with overseeing the public service obligations of Intelsat.-External links:*...
(ITSO) - International Trade Union ConfederationInternational Trade Union ConfederationThe International Trade Union Confederation is the world's largest trade union federation. It was formed on November 1, 2006 out of the merger of the International Confederation of Free Trade Unions and the World Confederation of Labour...
(ITUC) - Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU)
- Multilateral Investment Guarantee AgencyMultilateral Investment Guarantee AgencyThe Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency is a member organization of the World Bank Group that offers political risk insurance. It was established to promote foreign direct investment into developing countries. MIGA was founded in 1988 with a capital base of $1 billion and is headquartered in...
(MIGA) - Nonaligned Movement (NAM)
- Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW)
- Pacific Economic Cooperation CouncilPacific Economic Cooperation CouncilThe Pacific Economic Cooperation Council is a network of member committees composed of individuals and institutions dedicated to promoting cooperation across the Asia Pacific region...
(PECC) - Permanent Court of ArbitrationPermanent Court of ArbitrationThe Permanent Court of Arbitration , is an international organization based in The Hague in the Netherlands.-History:The court was established in 1899 as one of the acts of the first Hague Peace Conference, which makes it the oldest institution for international dispute resolution.The creation of...
(PCA) - United NationsUnited NationsThe United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
(UN) - United Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentUnited Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentThe United Nations Conference on Trade and Development was established in 1964 as a permanent intergovernmental body. It is the principal organ of the United Nations General Assembly dealing with trade, investment, and development issues....
(UNCTAD) - United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
- United Nations Integrated Mission in Timor-LesteUnited Nations Integrated Mission in Timor-LesteThe United Nations Integrated Mission in East Timor was established on August 25, 2006 by UN Security Council Resolution 1704. Its objectives are "to support the Government in consolidating stability, enhancing a culture of democratic governance, and facilitating political dialogue among Timorese...
(UNMIT) - Universal Postal UnionUniversal Postal UnionThe Universal Postal Union is an international organization that coordinates postal policies among member nations, in addition to the worldwide postal system. The UPU contains four bodies consisting of the Congress, the Council of Administration , the Postal Operations Council and the...
(UPU) - World Confederation of LabourWorld Confederation of LabourThe World Confederation of Labour was an international labour organization founded in 1920 and based in Europe. Totalitarian governments of the 1930s repressed the federation and imprisoned many of its leaders, limiting operations until the end of World War II...
(WCL) - World Customs OrganizationWorld Customs OrganizationThe World Customs Organization is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. With its worldwide membership, the WCO is recognized as the voice of the global customs community...
(WCO) - World Federation of Trade UnionsWorld Federation of Trade UnionsThe World Federation of Trade Unions was established in 1945 to replace the International Federation of Trade Unions. Its mission was to bring together trade unions across the world in a single international organization, much like the United Nations...
(WFTU) - World Health OrganizationWorld Health OrganizationThe World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
(WHO) - World Intellectual Property OrganizationWorld Intellectual Property OrganizationThe World Intellectual Property Organization is one of the 17 specialized agencies of the United Nations. WIPO was created in 1967 "to encourage creative activity, to promote the protection of intellectual property throughout the world"....
(WIPO) - World Meteorological OrganizationWorld Meteorological OrganizationThe World Meteorological Organization is an intergovernmental organization with a membership of 189 Member States and Territories. It originated from the International Meteorological Organization , which was founded in 1873...
(WMO) - World Trade OrganizationWorld Trade OrganizationThe World Trade Organization is an organization that intends to supervise and liberalize international trade. The organization officially commenced on January 1, 1995 under the Marrakech Agreement, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade , which commenced in 1948...
(WTO)
Law and order in Singapore

- Criminal law of SingaporeCriminal law of SingaporeAlthough the legal system of Singapore is a common law system, the criminal law of Singapore is largely statutory in nature. The general principles of criminal law, as well as the elements and penalties of common criminal offences such as homicide, theft and cheating, are set out in the Penal Code...
- Capital punishment in SingaporeCapital punishment in SingaporeCapital punishment is a legal form of punishment in Singapore. The city-state had the highest per-capita execution rate in the world between 1994 and 1999, estimated by the United Nations to be 1.357 executions per hundred thousand of population during that period. The next highest was Turkmenistan...
- Crime in SingaporeCrime in SingaporeThe crime rate in Singapore is one of the lowest in the world although Singapore does have a very high incarceration rate, and sends criminals guilty of drug related crimes to drug rehabilitation centers which arguably conceals their true crime rate...
- Capital punishment in Singapore
- Constitution of SingaporeConstitution of SingaporeThe Constitution of Singapore is the supreme law of Singapore and it is a codified constitution.The constitution cannot be amended without the support of more than two-thirds of the members of parliament on the second and third readings . The president may seek opinion on constitutional issues...
- Human rights in SingaporeHuman rights in SingaporeAccording to U.S. Department of State Country Reports on Human Rights Practices, there have been no reports of human rights abuses by security forces in Singapore. The Singapore government maintains effective control over all security activities, and generally respects the human rights of its...
- LGBT rights in Singapore
- Freedom of religion in SingaporeFreedom of religion in SingaporeFreedom of religion in Singapore is guaranteed under the Constitution. However, the Government of Singapore restricts this right in some circumstances. The Government has banned the Jehovah's Witnesses and the Unification Church...
- Law enforcement in SingaporeLaw enforcement in SingaporeGenerally, law enforcement in Singapore comes under the direct purview of the Singapore Police Force, the main government agency entrusted with the maintenance of law and order in Singapore...
- Sources of Singapore lawSources of Singapore lawThere are generally regarded to be three sources of Singapore law: legislation, judicial precedents and custom.Legislation can be divided into statutes and subsidiary legislation. Statutes are written laws enacted by the Singapore Parliament, as well as by other bodies which had power to pass laws...
Military of Singapore
- Command
- Chief of Defence Force: Lieutenant GeneralLieutenant GeneralLieutenant General is a military rank used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages where the title of Lieutenant General was held by the second in command on the battlefield, who was normally subordinate to a Captain General....
Desmond Kuek Bak ChyeDesmond Kuek Bak ChyeLieutenant General Desmond Kuek Bak Chye was the 6th Chief of Defence Force of the Singapore Armed Forces. He relinquished his appointment to Major General Neo Kian Hong on 31 Mar 2010.He received his then-appointment as Chief of Defense Force on 23 March 2007, taking over from Lieutenant...
- Ministry of Defence of SingaporeMinistry of Defence (Singapore)The Ministry of Defence is a ministry of the Government of Singapore entrusted with overseeing the national defence needs of the Republic of Singapore. It is the headquarters of the Singapore Armed Forces...
- Ministry of Defence of Singapore
- Chief of Defence Force: Lieutenant General
- Forces
- Army of Singapore
- Navy of Singapore
- Air Force of Singapore
- Special forces of Singapore
- Military history of SingaporeMilitary history of Singapore-World War II:* Battle of Bukit Timah* Battle of Kranji* Battle of Sarimbun Beach* Battle of Singapore* Japanese Occupation of Singapore* The Battle Box-Konfrontasi:...
- Military ranks of Singapore
History of Singapore
- Main article: History of SingaporeHistory of SingaporeThe history of Singapore dates to the 11th century. The island rose in importance during the 14th century under the rule of Srivijayan prince Parameswara and became an important port until it was destroyed by Acehnese raiders in 1613. The modern history of Singapore began in 1819 when Englishman...
, Timeline of the history of Singapore, and Current events of Singapore
- Economic history of Singapore
- Military history of SingaporeMilitary history of Singapore-World War II:* Battle of Bukit Timah* Battle of Kranji* Battle of Sarimbun Beach* Battle of Singapore* Japanese Occupation of Singapore* The Battle Box-Konfrontasi:...
Culture of Singapore
- Built heritage of Singapore
- Architecture of SingaporeArchitecture of SingaporeThe architecture of Singapore displays a range of influences and styles from different places and periods. These range from the eclectic styles and hybrid forms of the colonial period to the tendency of more contemporary architecture to incorporate trends from around the world...
- National Monuments of SingaporeNational Monuments of SingaporeNational Monuments of Singapore are buildings and structures in Singapore that have been designated by the Preservation of Monuments Board as being of special historic, traditional, archaeological, architectural or artistic value....
- Protected areas of Singapore
- World Heritage Sites: none
- Architecture of Singapore
- Cuisine of SingaporeCuisine of SingaporeSingaporean cuisine is indicative of the ethnic diversity of the culture of Singapore, as a product of centuries of cultural interaction owing to Singapore's strategic location...
- Ethnic minorities in Singapore
- Eurasians in Singapore
- Indians in Singapore
- Malays in SingaporeMalays in SingaporeMalays in Singapore are defined by the Singaporean government using the broader and antiquated "Malay race" concept, rather than modern-day Malay ethnic group. Although Malays have inhabited the area that is now Singapore since the 17th century, most of the Malays in Singapore today are immigrants...
- Festivals in Singapore
- Holidays in SingaporeHolidays in SingaporeThe 11 major public holidays in Singapore reflect the cultural and religious diversity of the country. They include the Chinese New Year, the Buddhist holiday Vesak Day, the Muslim holidays Hari Raya Puasa and Hari Raya Haji, the Hindu holiday Deepavali, and the Christian holidays of Good Friday...
- Humor in Singapore
- Languages of Singapore
- EnglishEnglish languageEnglish is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
- MalayMalay languageMalay is a major language of the Austronesian family. It is the official language of Malaysia , Indonesia , Brunei and Singapore...
- MandarinStandard MandarinStandard Chinese or Modern Standard Chinese, also known as Mandarin or Putonghua, is the official language of the People's Republic of China and Republic of China , and is one of the four official languages of Singapore....
- TamilTamil languageTamil is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by Tamil people of the Indian subcontinent. It has official status in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu and in the Indian union territory of Pondicherry. Tamil is also an official language of Sri Lanka and Singapore...
- English
- Media in Singapore
- InternetInternet in SingaporeIn Singapore, there are 6,791,000 broadband Internet subscribers . and household broadband penetration was at 82% the same year. There are four major Internet Service Providers in Singapore, namely, SingNet, StarHub, Pacnet and M1...
- Newspapers
- Berita HarianBerita Harian (Singapore)Berita Harian is a Malay language newspaper and the only one to be published in Singapore. The Sunday edition is called Berita Minggu also the only Malay language weekly newspaper in the country. This newspaper is published in the general daily broadsheet format. It was founded on 1 July 1957...
and Berita Minggu (Malay) - Business TimesBusiness Times (Singapore)The Business Times of Singapore is an English-language newspaper published since 1 October 1976 . In 1 January 1994, it became the first English-language newspaper in Asia to launch an online news service called Business Times Online. It is part of the Singapore Press Holdings group.-External links:*...
- Lianhe ZaobaoLianhe ZaobaoNanyang Sin-Chew Lianhe Zaobao , commonly abbreviated as Lianhe Zaobao , is the largest Singapore based Chinese-language newspaper with a daily circulation of about 176,000. Published by Singapore Press Holdings , it was formed on March 16, 1983 as a result of a merger between Nanyang Siang Pau and...
and Lianhe Wanbao (ChineseChinese languageThe Chinese language is a language or language family consisting of varieties which are mutually intelligible to varying degrees. Originally the indigenous languages spoken by the Han Chinese in China, it forms one of the branches of Sino-Tibetan family of languages...
) - my paperMy paperMy Paper is a free, bilingual newspaper in Singapore published by the Singapore Press Holdings....
(English and Chinese) - The New PaperThe New PaperThe New Paper is Singapore's second-highest circulating paid English-language newspaper, first launched on July 26, 1988, by Singapore Press Holdings . According to SPH, its average daily circulation for August 2010 was 101600....
and The New Paper Sunday - Shin Min Daily NewsShin Min Daily NewsShin Min Daily News is a Singapore Chinese-language afternoon newspaper currently published by Singapore Press Holdings...
(Chinese) - The Straits TimesThe Straits TimesThe Straits Times is an English language daily broadsheet newspaper based in Singapore currently owned by Singapore Press Holdings . It is the country's highest-selling paper, with a current daily circulation of nearly 400,000...
and The Sunday Times - tabla!
- Tamil MurasuTamil MurasuTamil Murasu is a Singapore based Tamil language newspaper. Launched in 1935 by Thamizhavel G. Sarangapani, Tamil Murasu is Singapore's only Tamil language newspaper...
(Tamil) - Thumbs UpThumbs Up (newspaper)Thumbs Up is a Chinese newspaper published in Singapore for school children. It was launched by Deputy Prime Minister Mr Lee Hsien Loong on 15 January 2000. Most primary schools in Singapore subscribe to the newspaper for their Chinese students, to improve their Chinese language.The newspaper...
(Chinese) - TodayToday (Singapore newspaper)Today is a free English-language compact in Singapore published by government-owned MediaCorp print media arm. It is distributed from Monday to Sunday....
and Weekend Today - zbCOMMA (Chinese)
- Berita Harian
- Radio
- Television
- Internet
- National symbols of Singapore
- Coat of arms of SingaporeCoat of arms of SingaporeThe coat of arms of Singapore was adopted in 1959, the year Singapore became self-governing within the British Empire. The committee that created it, headed by then Deputy Prime Minister Toh Chin Chye, was also responsible for the national flag and the national anthem...
- Lion head symbolSymbol of SingaporeThe lion head symbol was introduced in 1986 as an alternative national symbol of Singapore. The lion head was chosen as a logo, as it best captures the characteristics of Singapore's reputation as a Lion City...
- MerlionMerlionThe Merlion is a mythical creature with the head of a lion and the body of a fish, used as a mascot of Singapore. Its name combines "mer" meaning the sea and "lion". The fish body represents Singapore's origin as a fishing village when it was called Temasek, which means "sea town" in Javanese...
- National anthem of Singapore
- National flag of SingaporeFlag of SingaporeThe national flag of Singapore was first adopted in 1959, the year Singapore became self-governing within the British Empire. It was reconfirmed as the national flag when the Republic gained independence on 9 August 1965...
- National flower of Singapore (Vanda Miss JoaquimVanda Miss JoaquimVanda Miss Joaquim , also known as the Singapore Orchid and the Princess Aloha Orchid is a hybrid orchid cultivar that is Singapore's national flower....
) - National pledge of SingaporeSingapore National PledgeThe Singapore National Pledge is an oath of allegiance to Singapore. It is commonly recited by Singaporeans in unison at public events, especially in schools, in the Singapore Armed Forces and during the National Day Parade.-Origin:...
- Coat of arms of Singapore
- People of Singapore
- Prostitution in SingaporeProstitution in SingaporeProstitution in Singapore is legal, but various prostitution-related activities are not. This includes public solicitation, living on the earnings of a prostitute and maintaining a brothel. In practice, police unofficially tolerate and monitor a limited number of brothels. Prostitutes in such...
- Records of Singapore
- Religion in SingaporeReligion in SingaporeSingapore is a secular multi-religious country due to its diverse ethnic mix of peoples originating from various countries. Most major religious denominations are present in Singapore....
- Buddhism in SingaporeBuddhism in SingaporeAs of 2010, 33.6% of Singaporeans identified themselves as Buddhist. Adherents of Buddhism are mostly of the Chinese majority ethnic group, although small minorities of Sinhalese and Thai Buddhists do exist as well....
- Christianity in SingaporeChristianity in SingaporeChristians in Singapore constitute approximately 17.5% of the population. In the 2000 Census, 4.8% of residents aged 15 years and older, identified as Catholic and 9.8% as 'Other Christians'.-History:...
- Hinduism in SingaporeHinduism in Singapore-Beginnings of Hinduism in Singapore:The early 19th century saw a wave of immigrants to Singapore from southern India, mostly Tamils, to work as coolies and labourers for the British East India Company in Singapore. These immigrants brought along their religion and culture from their homeland as well...
- Islam in SingaporeIslam in SingaporeAbout 15% of Singapore's population are Muslims. A majority of Malays are Sunni Muslims. Other adherents include Indian and Pakistani communities as well as a small number of Chinese, Myanmar Muslims, Arabs and Eurasians. 17 per cent of Muslims in Singapore are of Indian origin...
- Judaism in Singapore
- Sikhism in SingaporeSikhism in SingaporeSikhism in Singapore has its roots in the military and policing forces of the British Empire. Currently, there are 12,000-15,000 Sikhs in Singapore-Early Sikh Pioneers:...
- Buddhism in Singapore
Art in Singapore
- Art in Singapore
- Cinema of SingaporeCinema of SingaporeDespite having a flourishing Chinese and Malay film industry in the 1950s and 1960s, Singapore's film industry declined after independence in 1965. There were a few films that featured Singaporean actors and were set in Singapore, including Saint Jack and They Call Her Cleopatra Wong...
- Literature of SingaporeLiterature of SingaporeThe literature of Singapore comprises a collection of literary works by Singaporeans in any of the country's four main languages: English, Chinese, Malay and Tamil....
- Music of SingaporeMusic of SingaporeSingapore has an urban musical scene, and is a center for rock, punk and other genres in the region. The 1960s produced bands like The Crecendos with hit songs like Mr Twister. The Quests, who had hits like "Shanty", "Don't Play That Song", "Jesamine" and "Mr Rainbow"...
- Television in Singapore
- Theatre in Singapore
Sports in Singapore
- Football in Singapore
- Singapore at the OlympicsSingapore at the OlympicsSingapore has sent athletes to most Summer Olympic Games held since 1948, when it was established as a separate British Crown Colony from the Straits Settlements just over three months before the commencement of the 1948 Summer Olympics. It continued to send a team to the Games until 1964 when...
Economy and infrastructure of Singapore
- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 45th (forty-fifth)
- Agriculture in Singapore
- Banking in SingaporeBanking in SingaporeBanking in Singapore is a service industry that has grown significantly in recent years. Total banking assets under management in Singapore rose from about $92 billion in 1998 to about $350 billion in 2004....
- Monetary Authority of SingaporeMonetary Authority of SingaporeThe Monetary Authority of Singapore is Singapore's central bank and financial regulatory authority...
- Monetary Authority of Singapore
- Communications in SingaporeCommunications in SingaporeThe telecommunication infrastructure of Singapore spans the entire city-state. Its development level is high, with close accessibility to the infrastructure from nearly all inhabited parts of the island and for all of the population, with exceptions...
- Internet in SingaporeInternet in SingaporeIn Singapore, there are 6,791,000 broadband Internet subscribers . and household broadband penetration was at 82% the same year. There are four major Internet Service Providers in Singapore, namely, SingNet, StarHub, Pacnet and M1...
- Internet in Singapore
- Companies of Singapore
- Currency of SingaporeCurrencyIn economics, currency refers to a generally accepted medium of exchange. These are usually the coins and banknotes of a particular government, which comprise the physical aspects of a nation's money supply...
: DollarSingapore dollarThe Singapore dollar or Dollar is the official currency of Singapore. It is normally abbreviated with the dollar sign $, or alternatively S$ to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies...
- ISO 4217ISO 4217ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Standards Organization, which delineates currency designators, country codes , and references to minor units in three tables:* Table A.1 – Current currency & funds code list...
: SGD
- ISO 4217
- Economic history of Singapore
- Energy in SingaporeEnergy in SingaporeEnergy in Singapore describes energy related issues in Singapore. Singapore is in East Asia. Energy import is about three times the primary energy. Oil import in relation to population is high. Owner of the biggest palm oil company Wilmar International is in Singapore...
- Energy policy of Singapore
- Oil industry in Singapore
- Health care in SingaporeHealth care in SingaporeHealthcare in Singapore is mainly under the responsibility of the Singapore Government's Ministry of Health. Singapore generally has an efficient and widespread system of healthcare...
- Mining in Singapore
- Singapore Stock Exchange
- Tourism in SingaporeTourism in SingaporeTourism in Singapore is a major industry and contributor to the Singaporean economy, attracting 11,638,663 tourists in 2010, over twice Singapore's total population. Its cultural attraction can be attributed to its cultural diversity that reflects its colonial history and Chinese, Malay, Indian and...
- Transport in SingaporeTransport in SingaporeTransport within Singapore is mainly land-based. Many parts of Singapore are accessible by road, including islands such as Sentosa and Jurong Island. The other major form of transportation within Singapore is rail: the Mass Rapid Transit which runs the length and width of Singapore, and the Light...
- Airports in Singapore
- Rail transport in SingaporeRail transport in SingaporeRail transport in Singapore exists in three main types, namely an international rail connection operated by Malaysian company Keretapi Tanah Melayu , a rapid transit system collectively known as the Mass Rapid Transit system operated by the two biggest public transport operators SMRT Corporation...
- Road transport in Singapore
- Water supply and sanitation in Singapore
See also
- Index of Singapore-related articles
- International rankings of SingaporeInternational rankings of SingaporeThe following are international rankings of Singapore.-Cities:Singapore is a city-state.*Most livable cities —**Economist Intelligence Unit: World's Most Livable Cities survey 2011: Singapore is ranked 4th on the Economist Intelligence Unit's Asia Most Livable City survey**Singapore is ranked 1st...
- List of Singapore-related topics
- Member state of the Commonwealth of Nations
- Member state of the United Nations
- Outline of AsiaOutline of AsiaThe following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Asia:Asia – world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
- Outline of geographyOutline of geographyThe following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geography:Geography – science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth.- Geography is :...
External links
General Information- Singapore Infomap
- Singapore Government Directory Interactive
- Singapore Government Online Portal
- Gateway To All Government Services
- Singapore National Service Portal
- Singapore Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority
- Amnesty International's 2005 report on Singapore
- CIA World Factbook Entry for Singapore
- Singapore Department of Statistics Annual Data
- Memories of Asia
Travel
Maps

