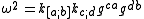Optical scalars
Encyclopedia
In general relativity
, optical scalars are a set of scalars
that describe various properties of null geodesic congruence
s. The three optical scalars used in general relativity are expansion, shear and twist (vorticity) and were first defined and used by Sachs (1961). Given a vector field
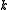 tangent to the null geodesic, the optical scalars are defined as follows.
tangent to the null geodesic, the optical scalars are defined as follows.

General relativity
General relativity or the general theory of relativity is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1916. It is the current description of gravitation in modern physics...
, optical scalars are a set of scalars
Scalar (physics)
In physics, a scalar is a simple physical quantity that is not changed by coordinate system rotations or translations , or by Lorentz transformations or space-time translations . This is in contrast to a vector...
that describe various properties of null geodesic congruence
Congruence (general relativity)
In general relativity, a congruence is the set of integral curves of a vector field in a four-dimensional Lorentzian manifold which is interpreted physically as a model of spacetime...
s. The three optical scalars used in general relativity are expansion, shear and twist (vorticity) and were first defined and used by Sachs (1961). Given a vector field
Vector field
In vector calculus, a vector field is an assignmentof a vector to each point in a subset of Euclidean space. A vector field in the plane for instance can be visualized as an arrow, with a given magnitude and direction, attached to each point in the plane...
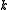 tangent to the null geodesic, the optical scalars are defined as follows.
tangent to the null geodesic, the optical scalars are defined as follows.Expansion
The expansion of the null ray is defined as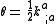
Shear
The shear of the null ray is defined as
Twist
The twist of the null ray is defined as