
Optical proximity correction
Encyclopedia
Optical proximity correction (OPC) is a photolithography
enhancement technique commonly used to compensate for image errors due to diffraction
or process effects. The need for OPC is seen mainly in the making of semiconductor devices and is due to the limitations of light to maintain the edge placement integrity of the original design, after processing, into the etched image on the silicon wafer. These projected images appear with irregularities such as line widths that are narrower or wider than designed, these are amenable to compensation by changing the pattern on the photomask used for imaging. Other distortions such as rounded corners are driven by the resolution of the optical imaging tool and are harder to compensate for. Such distortions, if not corrected for, may significantly alter the electrical properties of what was being fabricated. Optical Proximity Correction corrects these errors by moving edges or adding extra polygons to the pattern written on the photomask. This may be driven by pre-computed look-up tables based on width and spacing between features (known as rule based OPC) or by using compact models to dynamically simulate the final pattern and thereby drive the movement of edges, typically broken into sections, to find the best solution, (this is known as model based OPC). The objective is to reproduce, as well as possible, the original layout drawn by the designer in the silicon wafer.
The two most visible benefits of OPC are correcting linewidth differences seen between features in regions of different density (e.g., center vs. edge of an array, or nested vs. isolated lines), and line end shortening (e.g., gate overlap on field oxide). For the former case, this may be used together with Resolution Enhancement Technologies
such scattering bars (sub-resolution lines placed adjacent to resolvable lines) together with linewidth adjustments. For the latter case, "dog-ear" (serif or hammerhead) features may be generated at the line end in the design. OPC has a cost impact on photomask
fabrication whereby the mask write time is related to the complexity of the mask and data-files and similarly mask inspection
for defects takes longer as the finer edge control requires a smaller spot size.
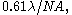 where
where  is the numerical aperture
is the numerical aperture
and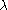 is the wavelength
is the wavelength
of the illumination source. It is often common to compare the critical feature width to this value, by defining a parameter,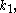 such that feature width equals
such that feature width equals 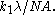 Nested features with
Nested features with  benefit less from OPC than isolated features of the same size. The reason is the spatial frequency spectrum of nested features contains fewer components than isolated features. As the feature pitch decreases, more components are truncated by the numerical aperture, resulting in greater difficulty to affect the pattern in the desired fashion.
benefit less from OPC than isolated features of the same size. The reason is the spatial frequency spectrum of nested features contains fewer components than isolated features. As the feature pitch decreases, more components are truncated by the numerical aperture, resulting in greater difficulty to affect the pattern in the desired fashion.
 . It also affects the pattern quality and hence the application of OPC. The coherence distance in the image plane is given roughly by
. It also affects the pattern quality and hence the application of OPC. The coherence distance in the image plane is given roughly by 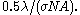 Two image points separated by more than this distance will effectively be uncorrelated, allowing a simpler OPC application. This distance is in fact close to the Rayleigh criterion for values of
Two image points separated by more than this distance will effectively be uncorrelated, allowing a simpler OPC application. This distance is in fact close to the Rayleigh criterion for values of  close to 1.
close to 1.
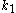 factor has been steadily shrinking over the past technology generations, the anticipated requirement of moving to multiple exposure to generate circuit patterns becomes more real. This approach will affect the application of OPC, as one will need to take into account the sum of the image intensities from each exposure. This is the case for the complementary photomask
factor has been steadily shrinking over the past technology generations, the anticipated requirement of moving to multiple exposure to generate circuit patterns becomes more real. This approach will affect the application of OPC, as one will need to take into account the sum of the image intensities from each exposure. This is the case for the complementary photomask
technique, where the images of an alternating-aperture phase-shifting mask and a conventional binary mask are added together.
film, multiple layer patterning entails repeated photoresist coating, deposition, and etching to pattern the same device layer. This gives an opportunity to use looser design rules to pattern the same layer. Depending on the lithography tool used to image at these looser design rules, the OPC will be different. Multiple-etch patterning may become a popular technique for future technology generations. A specific form of multiple-etch patterning, using sidewall sacrificial features, is currently the only demonstrated way of systematically patterning features less than 10 nm. The minimum half-pitch corresponds to the deposited thickness of the sacrificial feature.
vendors. Advances in algorithms, modeling techniques and the use of large compute farms has enabled the most critical patterning layers to be corrected overnight, starting from the 130nm design rules (when model based OPC was first used) down to the most advanced designs of today using 32nm design rules. The number of layers requiring sophisticated OPC has increased with advanced nodes, as previously non-critical layers now require compensation.
The use of OPC is not restricted to the low features which are commonly encountered today, but can be applied to any desired image correction scheme which can be modeled accurately. For example, proximity effect
features which are commonly encountered today, but can be applied to any desired image correction scheme which can be modeled accurately. For example, proximity effect
correction in electron beam lithography
is included as an automated capability on commercial electron-beam lithography tools. Since many non-lithographic processes exhibit their own proximity effects, e.g., chemical-mechanical polishing or plasma etching
, these effects can be mixed in with the original OPC.
Photolithography
Photolithography is a process used in microfabrication to selectively remove parts of a thin film or the bulk of a substrate. It uses light to transfer a geometric pattern from a photomask to a light-sensitive chemical "photoresist", or simply "resist," on the substrate...
enhancement technique commonly used to compensate for image errors due to diffraction
Diffraction
Diffraction refers to various phenomena which occur when a wave encounters an obstacle. Italian scientist Francesco Maria Grimaldi coined the word "diffraction" and was the first to record accurate observations of the phenomenon in 1665...
or process effects. The need for OPC is seen mainly in the making of semiconductor devices and is due to the limitations of light to maintain the edge placement integrity of the original design, after processing, into the etched image on the silicon wafer. These projected images appear with irregularities such as line widths that are narrower or wider than designed, these are amenable to compensation by changing the pattern on the photomask used for imaging. Other distortions such as rounded corners are driven by the resolution of the optical imaging tool and are harder to compensate for. Such distortions, if not corrected for, may significantly alter the electrical properties of what was being fabricated. Optical Proximity Correction corrects these errors by moving edges or adding extra polygons to the pattern written on the photomask. This may be driven by pre-computed look-up tables based on width and spacing between features (known as rule based OPC) or by using compact models to dynamically simulate the final pattern and thereby drive the movement of edges, typically broken into sections, to find the best solution, (this is known as model based OPC). The objective is to reproduce, as well as possible, the original layout drawn by the designer in the silicon wafer.
The two most visible benefits of OPC are correcting linewidth differences seen between features in regions of different density (e.g., center vs. edge of an array, or nested vs. isolated lines), and line end shortening (e.g., gate overlap on field oxide). For the former case, this may be used together with Resolution Enhancement Technologies
Resolution enhancement technologies
Resolution enhancement technologies are methods used to modify photomasks for integrated circuits to compensate for limitations in the lithographic processes used to manufacture the chips....
such scattering bars (sub-resolution lines placed adjacent to resolvable lines) together with linewidth adjustments. For the latter case, "dog-ear" (serif or hammerhead) features may be generated at the line end in the design. OPC has a cost impact on photomask
Photomask
A photomask is an opaque plate with holes or transparencies that allow light to shine through in a defined pattern. They are commonly used in photolithography.-Overview:...
fabrication whereby the mask write time is related to the complexity of the mask and data-files and similarly mask inspection
Mask inspection
In microtechnology, mask inspection or photomask inspection is an operation of checking the correctness of the fabricated photomasks, used, e.g., for semiconductor device fabrication....
for defects takes longer as the finer edge control requires a smaller spot size.
Impact of resolution: the k1 factor
The conventional diffraction-limited resolution is given by the Rayleigh criterion as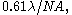 where
where  is the numerical aperture
is the numerical apertureNumerical aperture
In optics, the numerical aperture of an optical system is a dimensionless number that characterizes the range of angles over which the system can accept or emit light. By incorporating index of refraction in its definition, NA has the property that it is constant for a beam as it goes from one...
and
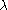 is the wavelength
is the wavelengthWavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
of the illumination source. It is often common to compare the critical feature width to this value, by defining a parameter,
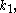 such that feature width equals
such that feature width equals 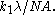 Nested features with
Nested features with  benefit less from OPC than isolated features of the same size. The reason is the spatial frequency spectrum of nested features contains fewer components than isolated features. As the feature pitch decreases, more components are truncated by the numerical aperture, resulting in greater difficulty to affect the pattern in the desired fashion.
benefit less from OPC than isolated features of the same size. The reason is the spatial frequency spectrum of nested features contains fewer components than isolated features. As the feature pitch decreases, more components are truncated by the numerical aperture, resulting in greater difficulty to affect the pattern in the desired fashion.Impact of spatial coherence
The degree of coherence of the illumination source is determined by the ratio of its angular extent to the numerical aperture. This ratio is often called the partial coherence factor, or . It also affects the pattern quality and hence the application of OPC. The coherence distance in the image plane is given roughly by
. It also affects the pattern quality and hence the application of OPC. The coherence distance in the image plane is given roughly by 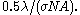 Two image points separated by more than this distance will effectively be uncorrelated, allowing a simpler OPC application. This distance is in fact close to the Rayleigh criterion for values of
Two image points separated by more than this distance will effectively be uncorrelated, allowing a simpler OPC application. This distance is in fact close to the Rayleigh criterion for values of  close to 1.
close to 1.Impact of multiple exposure
As the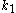 factor has been steadily shrinking over the past technology generations, the anticipated requirement of moving to multiple exposure to generate circuit patterns becomes more real. This approach will affect the application of OPC, as one will need to take into account the sum of the image intensities from each exposure. This is the case for the complementary photomask
factor has been steadily shrinking over the past technology generations, the anticipated requirement of moving to multiple exposure to generate circuit patterns becomes more real. This approach will affect the application of OPC, as one will need to take into account the sum of the image intensities from each exposure. This is the case for the complementary photomaskPhotomask
A photomask is an opaque plate with holes or transparencies that allow light to shine through in a defined pattern. They are commonly used in photolithography.-Overview:...
technique, where the images of an alternating-aperture phase-shifting mask and a conventional binary mask are added together.
Impact of multiple-etch patterning
In contrast to multiple exposure of the same photoresistPhotoresist
A photoresist is a light-sensitive material used in several industrial processes, such as photolithography and photoengraving to form a patterned coating on a surface.-Tone:Photoresists are classified into two groups: positive resists and negative resists....
film, multiple layer patterning entails repeated photoresist coating, deposition, and etching to pattern the same device layer. This gives an opportunity to use looser design rules to pattern the same layer. Depending on the lithography tool used to image at these looser design rules, the OPC will be different. Multiple-etch patterning may become a popular technique for future technology generations. A specific form of multiple-etch patterning, using sidewall sacrificial features, is currently the only demonstrated way of systematically patterning features less than 10 nm. The minimum half-pitch corresponds to the deposited thickness of the sacrificial feature.
OPC application today
Today, OPC is rarely practiced without the use of commercial packages from EDAElectronic design automation
Electronic design automation is a category of software tools for designing electronic systems such as printed circuit boards and integrated circuits...
vendors. Advances in algorithms, modeling techniques and the use of large compute farms has enabled the most critical patterning layers to be corrected overnight, starting from the 130nm design rules (when model based OPC was first used) down to the most advanced designs of today using 32nm design rules. The number of layers requiring sophisticated OPC has increased with advanced nodes, as previously non-critical layers now require compensation.
The use of OPC is not restricted to the low
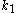 features which are commonly encountered today, but can be applied to any desired image correction scheme which can be modeled accurately. For example, proximity effect
features which are commonly encountered today, but can be applied to any desired image correction scheme which can be modeled accurately. For example, proximity effectProximity effect (electron beam lithography)
The proximity effect in electron beam lithography is the phenomenon that the exposure dose distribution, and hence the developed pattern, is wider than the scanned pattern, due to the interactions of the primary beam electrons with the resist and substrate...
correction in electron beam lithography
Electron beam lithography
Electron beam lithography is the practice of emitting a beam of electrons in a patterned fashion across a surface covered with a film , and of selectively removing either exposed or non-exposed regions of the resist...
is included as an automated capability on commercial electron-beam lithography tools. Since many non-lithographic processes exhibit their own proximity effects, e.g., chemical-mechanical polishing or plasma etching
Plasma etching
Plasma etching is a form of plasma processing used to fabricate integrated circuits. It involves a high-speed stream of glow discharge of an appropriate gas mixture being shot at a sample. The plasma source, known as etch species, can be either charged or neutral...
, these effects can be mixed in with the original OPC.

