
Ohr
Encyclopedia
Ohr is a central Kabbalistic term in the Jewish mystical tradition. The analogy of physical light is used as a way of describing metaphysical
Divine emanations. Shefa ("Flow" and its derivative, Hashpoah "Influence" ) is sometimes alternatively used in Kabbalah, a term also used in Medieval Jewish Philosophy
to mean Divine influence, while the Kabbalists favour Ohr because its numerical value
equals Raz ("mystery"). It is one of the two main metaphors in Kabbalah for understanding Divinity
, along with the other metaphor of the human soul-body relationship for the Sephirot. The metaphorical description of spiritual Divine creative-flow, using the term for physical "light" perceived with the eye, arises from analogous similarities. These include the intangible physicality of light, the delight it inspires and the illumination it gives, its apparently immediate transmission and constant connection with its source. Light can be veiled ("Tzimtzum
"-constrictions in Kabbalah) and reflected ("an ascending light from the Creations" in Kabbalah). White light divides into 7 colours, yet this plurality unites from one source. Divine light divides into the 7 emotional Sephirot, but there is no plurality in the Divine essence. The term Ohr in Kabbalah is contrasted with Ma'ohr, the "luminary", and Kli, the spiritual "vessel" for the light.
As a metaphor it also has its limitations. Divinity can only be understood from analogous comparisons to the spacial and temporal phenomena we understand. Once these images are grasped, Kabbalah stresses the need to then attempt to transcend them by understanding their deficiencies. Among the limitatations of the central metaphor of "light" are the physical inability of the luminary to withhold its radiance, the fulfilment of purpose the light gives the luminary, and the categorical differentiation between the source and its light. For God, the Creation metaphorically "arose in the Divine Will" and was not impelled. The emanation of Creation fills no lack in the perfection of God. The distinction between the Divine light (beginning with the Ohr Ein Sof - the primordial "Infinite Light", and subsequently the 10 Sephirot emanations) and the Divine Source
(the Ein Sof
"Infinite") appears only relative to Creation. From God's perspective, Scripture states "For I, the Eternal, I have not changed". From the persective of God's self knowledge, the emanations remain completely united and nullified to their source. This answers early Rabbinic criticism of dualism in Kabbalah. The term in Kabbalah
and Hasidic philosophy
for this nullification is Bittul. In daily spiritual life (Dveikus) it inspires the mystical humility of nullification of the ego.
describes 10 Sephirot (The 10 Divine emanations or attributes), that reveal the unknowable Godhead to the creations and channel the creative life-force to all levels of existence. However, these 10 attributes of God do not represent the Divine essence. The Kabbalists differentiated between the manifestations of God (forms of "light"), and their origin in the Divine essence (the "Luminary"). This difference overcame the criticism that they were introducing plurality into the pure Monotheism of Judaism. Kabbalistic texts take great care to emphasise this difference, and warn against anthropormising the subtle descriptions of Kabbalah in human terms. To avoid such heresies, the historical transmission of Kabbalah was traditionally restricted to direct teaching in close circles.
As well as the 10 "lights" of God encapsulated in the Sephirot, Kabbalah also describes a more primordial light that shines from the Ein Sof (Infinite) itself. This light, the origin of all Creation, and all lower lights, is called the "Ohr Ein Sof" ("The light of the Infinite", or alternatively, itself "The Infinite Light"). The Kabbalistic and Hasidic masters ask the question of how there can be a revelation of God, in the Ohr Ein Sof, before Creation. Surely, there can be "no king without a people". Before Creation, there could be no being to behold a revelation of Divine light. The Ohr Ein Sof is a form of Divine self knowledge, and through God knowing Himself, He created everything, with its subsequent historical unfolding, and its ultimate purpose in the innermost Divine Will.
and Seder hishtalshelus
). Any direct creations of the Infinite Light would be of infinite number, and would not be actual creations at all, as they would remain totally nullified ("bittul") to the Infinite Light, and would have no independent self awareness. Rather it is only through the restrictions of the Sephirot and the descending "Chain of Progression" (Seder hishtalshelus), that the Worlds could unfold. In the descending chain of Worlds from the Infinite to our finite realm, the creative flow of Divine light encapsulated in the Sephirot, undergoes countless restrictions, diminutions and veilings, to progressively hide Divinity. In Kabbalah these are called "Tzimtzum" ("Constrictions" - plural "tzimtzumim").
However, after the new teachings and doctrines of Isaac Luria
(The "Arizal"), in Lurianic Kabbalah, these innumerable Tzimtzumim of the descending chain of Worlds are called the "Second Tzimtzum". Isaac Luria taught the new concept of a "First Tzimtzum", based on earlier allusions in the Zohar
. As Lurianic Kabbalah became almost universally accepted in the Jewish development of Kabbalah, nowadays if the term Tzimtzum is used without qualification, it will invariably refer to the first, cosmic, ultimate Constriction taught by Luria (see Tzimtzum
).
In this radical concept of the "Ari", at the beginning of Creation the Divine "withdrew" (a complete tzimtzum) from a "Chalal" ("Vacated space"), to allow Creation to take place. The interpretation of this forms a central concern of subsequent Kabbalah (see Tzimtzum
), and the "withdrawal" of God is interpreted only as a concealment from the perspective of the Creation, and only to apply to His light, not His Essence, as that would imply heretical limitations to the Divine. In Lurianic Kabbalah, the Tzimtzum concealed the Ohr Ein Sof, which resolved the dichotomy between the Infinite Light and the possibility of creating finite Worlds. Without this radical leap of a concealment of the Ohr Ein Sof, even with the progressive, gradual concealments of the Chain of Worlds, the problem would not properly be overcome. Only a second, new light, immeasurably diminished, and of a different quality than the Ohr Ein Sof, could become the creative source of all reality. This new light, a "thin" illumination from the Ohr Ein Sof, called the "Kav" ("Ray"), shone into the "Vacated Space", and was a light that was adapted to the perspective of the subsequent creations on their own terms. It could relate to finite creation (Divine immanence), rather than the infinite Primordial light (the ultimate Divine transcendence).
Interpretations of this in Kabbalah
and Hasidic philosophy
, are careful to avoid literal, spacial, geometric understandings of the Vacated Space and the Kav, as such dimensional understandings relate only to our physical world. Nonetheless, circular diagram representations of this, strictly metaphorical, are used in Kabbalah to represent the process. In the first, a black circle is broken only by one thin, vertical, straight line that descends from the surrounding white into the centre of the black circle from the top. Here the surrounding white represents the Ein Sof, the black circle represents the Chalal vacated "space", and the thin white line represents the "thin" illumination of the Kav, derived from the Ohr Ein Sof, but able to illuminate into the Chalal on its own terms.
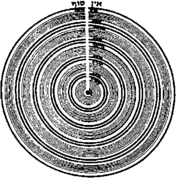 This representation is then augmented by a second, similar diagram, where the successive, unfolding Five Worlds, each with 10 successive Sephirot, are shown within the original circle as a series of concentric circles. The descending chain of Worlds proceeds in the diagram towards the centre of the circle, representing our lowest, physical realm. Each successive World and Sephirah is a successively smaller concentric circle, representing diminished, more constricted Divinity. The same Kav line is still shown connecting the outer Ein Sof to the centre of the circle, as the light of the Kav is the origin of all Creation after the Tzimtzum, though its light undergoes innumerable second tzimtzumim, toward the circle's centre. The utilisation here of concentric circles, or spheres is also significant, as with each subsequent lower step, the light encompases" (sovev - "surrounds") that level of "immanent" (mimalei"-"filled") creation. Each of the Sephirot comprises both an encompasing light vested in its immanent vessel. Each World similarly incorporates its own relative level of Divine transcendence, illuminating its own level of Divine immanence.
This representation is then augmented by a second, similar diagram, where the successive, unfolding Five Worlds, each with 10 successive Sephirot, are shown within the original circle as a series of concentric circles. The descending chain of Worlds proceeds in the diagram towards the centre of the circle, representing our lowest, physical realm. Each successive World and Sephirah is a successively smaller concentric circle, representing diminished, more constricted Divinity. The same Kav line is still shown connecting the outer Ein Sof to the centre of the circle, as the light of the Kav is the origin of all Creation after the Tzimtzum, though its light undergoes innumerable second tzimtzumim, toward the circle's centre. The utilisation here of concentric circles, or spheres is also significant, as with each subsequent lower step, the light encompases" (sovev - "surrounds") that level of "immanent" (mimalei"-"filled") creation. Each of the Sephirot comprises both an encompasing light vested in its immanent vessel. Each World similarly incorporates its own relative level of Divine transcendence, illuminating its own level of Divine immanence.
("Limitless") is the unknowable, undifferentiated, infinite Divine essence. The 10 emanations of the Sephirot enable the Creation to know God, and become God's attributes that reveal Divinity. They are also the channels through which all of Creation is continuously substained from nothing, as in the Kabbalistic scheme, Creation is continuous and God is the only true existence. A "Chain of Progression" (Seder hishtalshelus
) of descending "Worlds", including the Four Worlds
, links the Ein Sof with our physical realm.
Each of the Sephirot is said to consist of a "light" (an ohr) that is vested in a "vessel" (a kli ; plural: keilim ). Generally speaking, the light is simple and undifferentiated, as it stems originally from the Ohr Ein Sof ("The Light of the Ein Sof"), God's infinite light. It represents Divine revelation in the world. It is associated with the Kabbalistic Divine Name of Ban. The differentiation between the 10 Sephirot, each with its own particular characteristic, arises from each of their different spiritual vessels. The light adapts itself to each vessel, to express the particular nature of each vessel.
Kabbalists read their mystical teachings into exegetical
interpretations of Scripture and Rabbinic literature
. This arose from their belief that Kabbalah forms part of the Oral Torah
inherent in the revelation at Mount Sinai
. Accordingly, in Jewish tradition, each verse and concept can be interpreted in the fourfold Jewish method of Pardes
, with the metaphysical
interpretations of Kabbalah
and Hasidic philosophy
forming the Sod (secret) level of meaning. In this way, Kabbalah interprets a second meaning in Talmudic legislation and use of the term for "vessel" ("kli"). In the Halachic sense a vessel is an object that can serve a useful purpose, even if it may not resemble a physical receptacle. This term is used frequently in discussion of the laws of Shabbat
. In Jewish mysticism, typically, these narratives are given metaphysical interpretations, which relate "kli" to its Kabbalistic meaning. In Hasidic philosophy
, the plural fourfold levels of meaning are viewed as uniting in a higher essential source of explanation that describes Divinity. Jewish mysticism views such alternative, spiritual interpretations of Torah as stemming from more revealed Divine realms in the Chain of Worlds.
The purpose of Creation was not for the sake of the higher spiritual Worlds. In relation to the infinite Ein Sof
, their great revelations of Divinity are a concealment, and have no comparison. Instead, the ultimate purpose of Creation in Kabbalah is for the sake of the lowest World, our physical realm. The Divine Will was to have a dwelling place in this World, made by man, which will be achieved in the Messianic Age. In higher spiritual Worlds (Seder hishtalshelus
), the souls and angels sense this, and seek to channel Divine flow down the chain of Worlds. Therefore Shuv, even though it is an exile for the light to descend into the vessel, is the ultimate purpose of Creation. The terms "Ratzo" and "Shuv" come from the Biblical description of the angels in the vision of Ezekiel
(1:4-26), when he beheld the Divine chariot (Merkavah). These angels "ran and returned". In this explanation, they desired to ascend to God, but returned down to their station, to fulfil their purpose. In daily spiritual life too, man seeks dveikus (cleaving) with God, and then returns with this inspiration to fulfil his or her tasks in the World. Here the human soul is the "ohr", the body the "kli", and this realm presently an exile for the soul.
The dynamics of Ratzo and Shuv are felt by the angels and man, but also apply to any spiritual emanation. The "Seder Histalshelus" describes the continuous descending chain from the Infinite to our finite World. In each World, the 10 Sephirot shine. Each World unfolds from the previous, with the lowest Sephirah (Malchut-"Kingship"-fulfilment of the plan in reality) of one World, becoming the highest Sephirah (Keter
-"Crown"-the supernal Will of the plan in that World) of the next, lower World. Within each World too, the spiritual chain descends down the 10 Sephirot, with the illumination of one giving birth to the next, lower Sephirah.
(parable) given to explain this relationship, is the relationship between the sun and the light that it gives off. However, technically speaking, the light that comes from the sun is not the perfect example for the Ohr, since it has already passed through a "Nartik" ("Sheath/Shield"), a level that reduces the intensity of the revelation of the sun. In truth, the Ohr that exists in the parable of the sun is the light of the sun that exists in the sun itself. The light that we see from the sun has already been limited in its quality and therefore lacks the "Bittul" ("nullification") of the true Ohr to its origin. Rather, this Ohr, being that it has been limited by the Nartik, is called Ohr HaNartik (the light of the sheath), for although it does not actually come from the Nartik, since the Nartik limited it in such a way that it no longer possesses a connection with its ultimate source, we associate it with the Nartik.
In Kabbalah, the level of the Ma'ohr is represented by the higher Hebrew name of God, the Tetragrammaton
, and the Ohr is the revelation of that level. Similarly, the lower name of God, Elokim (Here the "h" has been replaced with a "k" in traditional deference to avoid writing the names of God), represents the Nartik, and the light that stems thereof is the Ohr HaNartik, and as such, it lacks a higher level of nullification, enabling it to create the Worlds. If the light of the Tetragrammaton were to create the Worlds, they would not exist as creations with independent self awareness. The immense revelation of the Divine would nullify them in their source, as the light of the sun inside the sun itself.
In the second section of the Tanya
by Schneur Zalman of Liadi, the Hasidic Panentheism
of the Baal Shem Tov, the founder of Hasidism, is systematically explained in philosophical terms. Two levels of Divine Unity are explained, that paradoxically are both true perspectives. From God's perspective, in comparison to the unchanging Divine Infinity, all of Creation is literally as if it did not exist (Acosmism
). This is represented by a Higher Bittul-"Bittul Hametsiyas" ("Nullification of Essence") of the light of the sun inside the orb of the sun itself. This is called the "Upper Divine Unity". The "Lower Divine Unity" describes the Unity of God from the illusiory self independent perspective of the Creations. From this perspective, Creation does exist, but is continuously dependent on receiving its Divine lifeforce that constantly brings it into being from nothing. In our World, this constant, total dependence for the existence of everything on the Divine creative light is hidden. In the spiritual Worlds of Creation, it is revealed, but they still lack true "Bittul" (nullification), as the souls and angels in those realms have some self awareness, albeit totally nullified to God. This Lower Bittul-"Bittul Hayesh" ("Nullification of Ego") is represented by a light of a candle on a sunny day. In the Chain of Four Worlds
, the first realm, the World of Atzilus, is not yet considered a Creation, but rather an emanation of supernal Divinity. It is characterised by the higher Nullification of Essence. The three lower realms of Beriah
, Yetzirah
and Asiyah
are considered created realms as they only possess different levels of the lower Nullification of Ego.
This explanation of the spiritual meanings of the different Hebrew names of God of the Tetragrammaton and Elokim, gives the Kabbalistic reason why the lower name "Elokim" (Divine immanence) is universally used in the Creation account in the beginning of Genesis, with the multiple phrases on each day:
In Kabbalah, going back to the Scriptural commentary
of Nachmanides, the 7 Days of Creation are understood to symbolically refer to the 7 Emotional revelations of the Sefirot, each one called a "day". These Hebrew sayings themselves, are explained in Kabbalah to be the creative channels of the Sephirot in activating Creation. Only after Genesis recounts its first narrative of Creation, with the beginning of its second account, does it use the higher, essential, Divine name of the Tetragrammaton (Divine transcendence). Here it combines both names, as both are involved in Creation. Later on, when God speaks to Moses, the name of God used is only the transcendent Tetragrammaton. In the second account of Creation:
According to the Kabbalistic and Hasidic explanation, the ability to Create Ex nihilo
(something from nothing) can only come from the Divine essence (Ein Sof
), which is referred to by the Tetragrammaton. Nonetheless, the light to create existence must be constricted through the name Elokim. This process is referred to in this second account of Creation.
 Sovev means "surrounding" and Mimalei means "filling". The geometric associations of these adjectives are metaphorical. Kabbalah describes two types of light that emanate in Creation. One, called "Sovev Kol Olmin" ("Surrounding All Worlds"), is the Divine light of transcendence, rooted in the Ohr Ein Sof (primordial "Infinite Light") before the Tzimtzum of Lurianic Kabbalah. It descends through the Seder hishtalshelut (Chain of Worlds), representing Divine transcendence in each level. It could be revealed in a blessing or miracle above the vessels and limitations of that realm. Souls in their essence transcend the body and all the Worlds. Similarly, as the Zohar
Sovev means "surrounding" and Mimalei means "filling". The geometric associations of these adjectives are metaphorical. Kabbalah describes two types of light that emanate in Creation. One, called "Sovev Kol Olmin" ("Surrounding All Worlds"), is the Divine light of transcendence, rooted in the Ohr Ein Sof (primordial "Infinite Light") before the Tzimtzum of Lurianic Kabbalah. It descends through the Seder hishtalshelut (Chain of Worlds), representing Divine transcendence in each level. It could be revealed in a blessing or miracle above the vessels and limitations of that realm. Souls in their essence transcend the body and all the Worlds. Similarly, as the Zohar
states that God is totally united with his Torah
, the Torah is inherently transcendent in all Worlds, and each World studies it according to their mystical level of perception.
The other light, called Mimalei Kol Olmin ("Filling All Worlds") is the Divine light of immanence, rooted in the Kav (first "Ray" of light) after the Tzimtzum in Lurianic Kabbalah. This is the light that descends immanently to every level of the Chain of Worlds, itself creating every spiritual and, ultimately, physical vessel of each World. It undergoes the innumerable concealments and contractions of the second Tzimtzumim. Hasidic thought sees the ultimate advantage of this lower light, because the ultimate purpose of Creation lies in this lowest realm. Hasidism therefore rejected Jewish asceticism, seeking to utilise and mystically transform the physical into spirituality, through dveikus cleaving to God. Hasidic thought likewise describes another, higher type of miracle that is immanently invested within the physical laws of this World, without breaking them. Only a higher source rooted in the Divine essence
, beyond infinite-finite duality, could unite the infinite encompassing light of Sovev within the limited invested light of Mimalei.
These terms are also related to the parallel notions of Makif ("Outer") and Pnimi ("Inner"), taught in Hasidic philosophy
. Hasidism relates the esoteric spiritual structures of Kabbalah to their inner dimensions in the consciousness and perception of man. This is found in the Hasidic idea of dveikus (mystical fervour). It seeks an inner response to the Jewish mystical tradition. In the Sephirot, for example, Hasidic thought focuses on the inner motivational soul within each Sephirah, and its parallel in the spiritual psychology of man.
The descent of masculine waters can be a free expression of the Sephirah of Hesed (Kindness), which has the essential nature to give Divine blessing in an unlimited way, without considering whether the vessels of the Creation are worthy. Hesed is counterbalanced by Gevurah (Judgement), that measures and withholds the blessing according to the worth and capacity of the vessel.
More commonly, the descent of direct light is in response to the ascent from below of reflected light. This "arousal from below", the ascent of "feminine waters", is the spiritual illumination created by each person through meritorious ethical or ritual mitzvot (Jewish observances). While Kabbalah
offered radical theosophical cosmic explanations of Judaism
, it remained inherently conservative. The metaphysical
doctrines of Kabbalah support and deepen normative Jewish observance. Kabbalah, especially the new teachings of Isaac Luria
in the 16th Century, taught the cosmic power of each person to affect and rectify the Divine scheme of Creation. In Lurianic Kabbalah, the ultimate Tikkun
is dependent on each individual fulfilling their own unique tasks in Creation, through the mitzvot. This affect would occur whether the person was aware of the deeper meanings or not. The great delight the illumination of the ascending feminine waters causes in the Heavenly realms (Four Worlds
), leads to the reciprocal Divine response of descending blessing and light in the Masculine waters. This gives the inherent metaphysical Kabbalistic structure of the traditional Jewish belief of "Reward and Punishment", incorporated in Maimonides
' Jewish Principles of Faith
. The Kabbalistic explanation puts these external categories in an inner scheme of Divine loving-kindness.

 An example given in Kabbalah of the dynamics of "masculine" and "feminine" waters, is found in the yartzheit (date of passing) and birthdays of three central figures in the Jewish mystical tradition. Judah Loew ben Bezalel
An example given in Kabbalah of the dynamics of "masculine" and "feminine" waters, is found in the yartzheit (date of passing) and birthdays of three central figures in the Jewish mystical tradition. Judah Loew ben Bezalel
(the Maharal) died on the 18th day (18 means "Hai"-"life" in Gematria
) of the Hebrew month
of Elul
in the year 1609 (17 September). The 18th of Elul, 12 days before Rosh Hashanah
, is a central mystical date in the personal preparations of teshuvah (return to God) for the upcoming "Days of Awe". A central component of the teachings of the Maharal was the concept of Divine paradox, above intellect. This prepared the way for the Hasidic movement, that sought the inner expression in Hasidic philosophy
of the Kabbalistic tradition. The founder of Hasidism, Israel Baal Shem Tov was born on the 18th of Elul in 1698 (August 27), and the founder of Habad intellectual expression of Hasidism, Schneur Zalman of Liadi, was born on the 18th day of Elul in 1745 (September 4). Kabbalah teaches that the yarthzeit of a Tzaddik (righteous person) causes the spiritual revelation and ascent of their life's spiritual service, the ascent of the "feminine waters" the Tzaddik illuminated. Anyone who attaches themselves to the teachings and influence of the Tzaddik receives from their illumination and blessing on the yartzheit. In the Kabbalistic scheme, this "arousal from below" ellicited the "arousal of God from above" to descend "masculine waters" by the descent of the souls on this date, later on, of the Baal Shem Tov and Schneur Zalman of Liadi. Kabbalah finds an allusion to the deeper aspects of this structure, including the essence of the different spiritual teachings of these three figures, in a Scriptural verse that relates to the mystical meaning of the 18th of Elul.
Metaphysics
Metaphysics is a branch of philosophy concerned with explaining the fundamental nature of being and the world, although the term is not easily defined. Traditionally, metaphysics attempts to answer two basic questions in the broadest possible terms:...
Divine emanations. Shefa ("Flow" and its derivative, Hashpoah "Influence" ) is sometimes alternatively used in Kabbalah, a term also used in Medieval Jewish Philosophy
Jewish philosophy
Jewish philosophy , includes all philosophy carried out by Jews, or, in relation to the religion of Judaism. Jewish philosophy, until modern Enlightenment and Emancipation, was pre-occupied with attempts to reconcile coherent new ideas into the tradition of Rabbinic Judaism; thus organizing...
to mean Divine influence, while the Kabbalists favour Ohr because its numerical value
Gematria
Gematria or gimatria is a system of assigning numerical value to a word or phrase, in the belief that words or phrases with identical numerical values bear some relation to each other, or bear some relation to the number itself as it may apply to a person's age, the calendar year, or the like...
equals Raz ("mystery"). It is one of the two main metaphors in Kabbalah for understanding Divinity
God in Judaism
The conception of God in Judaism is strictly monotheistic. God is an absolute one indivisible incomparable being who is the ultimate cause of all existence. Jewish tradition teaches that the true aspect of God is incomprehensible and unknowable, and that it is only God's revealed aspect that...
, along with the other metaphor of the human soul-body relationship for the Sephirot. The metaphorical description of spiritual Divine creative-flow, using the term for physical "light" perceived with the eye, arises from analogous similarities. These include the intangible physicality of light, the delight it inspires and the illumination it gives, its apparently immediate transmission and constant connection with its source. Light can be veiled ("Tzimtzum
Tzimtzum
Tzimtzum is a term used in the kabbalistic teaching of Isaac Luria, explaining his concept that God began the process of creation by "contracting" his infinite light in order to allow for a "conceptual space" in which a finite and seemingly independent world could exist...
"-constrictions in Kabbalah) and reflected ("an ascending light from the Creations" in Kabbalah). White light divides into 7 colours, yet this plurality unites from one source. Divine light divides into the 7 emotional Sephirot, but there is no plurality in the Divine essence. The term Ohr in Kabbalah is contrasted with Ma'ohr, the "luminary", and Kli, the spiritual "vessel" for the light.
As a metaphor it also has its limitations. Divinity can only be understood from analogous comparisons to the spacial and temporal phenomena we understand. Once these images are grasped, Kabbalah stresses the need to then attempt to transcend them by understanding their deficiencies. Among the limitatations of the central metaphor of "light" are the physical inability of the luminary to withhold its radiance, the fulfilment of purpose the light gives the luminary, and the categorical differentiation between the source and its light. For God, the Creation metaphorically "arose in the Divine Will" and was not impelled. The emanation of Creation fills no lack in the perfection of God. The distinction between the Divine light (beginning with the Ohr Ein Sof - the primordial "Infinite Light", and subsequently the 10 Sephirot emanations) and the Divine Source
Godhead (Judaism)
Godhead is used to refer to "God as He is in Himself." This is the aspect or substratum of God that lies behind His actions or properties, i.e., the essence of God, and its nature has been the subject of long debate in every major religion.-Terminology:...
(the Ein Sof
Ein Sof
Ein Sof , in Kabbalah, is understood as God prior to His self-manifestation in the production of any spiritual Realm, probably derived from Ibn Gabirol's term, "the Endless One"...
"Infinite") appears only relative to Creation. From God's perspective, Scripture states "For I, the Eternal, I have not changed". From the persective of God's self knowledge, the emanations remain completely united and nullified to their source. This answers early Rabbinic criticism of dualism in Kabbalah. The term in Kabbalah
Kabbalah
Kabbalah/Kabala is a discipline and school of thought concerned with the esoteric aspect of Rabbinic Judaism. It was systematized in 11th-13th century Hachmei Provence and Spain, and again after the Expulsion from Spain, in 16th century Ottoman Palestine...
and Hasidic philosophy
Hasidic philosophy
Hasidic philosophy or Hasidus , alternatively transliterated as Hassidism, Chassidism, Chassidut etc. is the teachings, interpretations of Judaism, and mysticism articulated by the modern Hasidic movement...
for this nullification is Bittul. In daily spiritual life (Dveikus) it inspires the mystical humility of nullification of the ego.
The Ohr Ein Sof - The Infinite Light
The Ein Sof (literally: "Without End"/Limitless/Infinite) is the Kabbalistic term for the Divine essence. KabbalahKabbalah
Kabbalah/Kabala is a discipline and school of thought concerned with the esoteric aspect of Rabbinic Judaism. It was systematized in 11th-13th century Hachmei Provence and Spain, and again after the Expulsion from Spain, in 16th century Ottoman Palestine...
describes 10 Sephirot (The 10 Divine emanations or attributes), that reveal the unknowable Godhead to the creations and channel the creative life-force to all levels of existence. However, these 10 attributes of God do not represent the Divine essence. The Kabbalists differentiated between the manifestations of God (forms of "light"), and their origin in the Divine essence (the "Luminary"). This difference overcame the criticism that they were introducing plurality into the pure Monotheism of Judaism. Kabbalistic texts take great care to emphasise this difference, and warn against anthropormising the subtle descriptions of Kabbalah in human terms. To avoid such heresies, the historical transmission of Kabbalah was traditionally restricted to direct teaching in close circles.
As well as the 10 "lights" of God encapsulated in the Sephirot, Kabbalah also describes a more primordial light that shines from the Ein Sof (Infinite) itself. This light, the origin of all Creation, and all lower lights, is called the "Ohr Ein Sof" ("The light of the Infinite", or alternatively, itself "The Infinite Light"). The Kabbalistic and Hasidic masters ask the question of how there can be a revelation of God, in the Ohr Ein Sof, before Creation. Surely, there can be "no king without a people". Before Creation, there could be no being to behold a revelation of Divine light. The Ohr Ein Sof is a form of Divine self knowledge, and through God knowing Himself, He created everything, with its subsequent historical unfolding, and its ultimate purpose in the innermost Divine Will.
Tzimtzum – Restrictions of Divine Light
As the Ohr Ein Sof is itself infinite, it could not itself directly be the source for the creation of Worlds (Four WorldsFour Worlds
The Four Worlds , sometimes counted with a prior stage to make Five Worlds, are the comprehensive categories of spiritual realms in Kabbalah in the descending chain of Existence....
and Seder hishtalshelus
Seder hishtalshelus
Seder hishtalshelus means the "order of development" or "order of evolution", where the word Hishtalshelus is derived from the reduplicated quadriliteral root ŠLŠL "to chain", and so literally means "the chain-like process"...
). Any direct creations of the Infinite Light would be of infinite number, and would not be actual creations at all, as they would remain totally nullified ("bittul") to the Infinite Light, and would have no independent self awareness. Rather it is only through the restrictions of the Sephirot and the descending "Chain of Progression" (Seder hishtalshelus), that the Worlds could unfold. In the descending chain of Worlds from the Infinite to our finite realm, the creative flow of Divine light encapsulated in the Sephirot, undergoes countless restrictions, diminutions and veilings, to progressively hide Divinity. In Kabbalah these are called "Tzimtzum" ("Constrictions" - plural "tzimtzumim").
However, after the new teachings and doctrines of Isaac Luria
Isaac Luria
Isaac Luria , also called Yitzhak Ben Shlomo Ashkenazi acronym "The Ari" "Ari-Hakadosh", or "Arizal", meaning "The Lion", was a foremost rabbi and Jewish mystic in the community of Safed in the Galilee region of Ottoman Palestine...
(The "Arizal"), in Lurianic Kabbalah, these innumerable Tzimtzumim of the descending chain of Worlds are called the "Second Tzimtzum". Isaac Luria taught the new concept of a "First Tzimtzum", based on earlier allusions in the Zohar
Zohar
The Zohar is the foundational work in the literature of Jewish mystical thought known as Kabbalah. It is a group of books including commentary on the mystical aspects of the Torah and scriptural interpretations as well as material on Mysticism, mythical cosmogony, and mystical psychology...
. As Lurianic Kabbalah became almost universally accepted in the Jewish development of Kabbalah, nowadays if the term Tzimtzum is used without qualification, it will invariably refer to the first, cosmic, ultimate Constriction taught by Luria (see Tzimtzum
Tzimtzum
Tzimtzum is a term used in the kabbalistic teaching of Isaac Luria, explaining his concept that God began the process of creation by "contracting" his infinite light in order to allow for a "conceptual space" in which a finite and seemingly independent world could exist...
).
In this radical concept of the "Ari", at the beginning of Creation the Divine "withdrew" (a complete tzimtzum) from a "Chalal" ("Vacated space"), to allow Creation to take place. The interpretation of this forms a central concern of subsequent Kabbalah (see Tzimtzum
Tzimtzum
Tzimtzum is a term used in the kabbalistic teaching of Isaac Luria, explaining his concept that God began the process of creation by "contracting" his infinite light in order to allow for a "conceptual space" in which a finite and seemingly independent world could exist...
), and the "withdrawal" of God is interpreted only as a concealment from the perspective of the Creation, and only to apply to His light, not His Essence, as that would imply heretical limitations to the Divine. In Lurianic Kabbalah, the Tzimtzum concealed the Ohr Ein Sof, which resolved the dichotomy between the Infinite Light and the possibility of creating finite Worlds. Without this radical leap of a concealment of the Ohr Ein Sof, even with the progressive, gradual concealments of the Chain of Worlds, the problem would not properly be overcome. Only a second, new light, immeasurably diminished, and of a different quality than the Ohr Ein Sof, could become the creative source of all reality. This new light, a "thin" illumination from the Ohr Ein Sof, called the "Kav" ("Ray"), shone into the "Vacated Space", and was a light that was adapted to the perspective of the subsequent creations on their own terms. It could relate to finite creation (Divine immanence), rather than the infinite Primordial light (the ultimate Divine transcendence).
Interpretations of this in Kabbalah
Kabbalah
Kabbalah/Kabala is a discipline and school of thought concerned with the esoteric aspect of Rabbinic Judaism. It was systematized in 11th-13th century Hachmei Provence and Spain, and again after the Expulsion from Spain, in 16th century Ottoman Palestine...
and Hasidic philosophy
Hasidic philosophy
Hasidic philosophy or Hasidus , alternatively transliterated as Hassidism, Chassidism, Chassidut etc. is the teachings, interpretations of Judaism, and mysticism articulated by the modern Hasidic movement...
, are careful to avoid literal, spacial, geometric understandings of the Vacated Space and the Kav, as such dimensional understandings relate only to our physical world. Nonetheless, circular diagram representations of this, strictly metaphorical, are used in Kabbalah to represent the process. In the first, a black circle is broken only by one thin, vertical, straight line that descends from the surrounding white into the centre of the black circle from the top. Here the surrounding white represents the Ein Sof, the black circle represents the Chalal vacated "space", and the thin white line represents the "thin" illumination of the Kav, derived from the Ohr Ein Sof, but able to illuminate into the Chalal on its own terms.

In the 10 Sefirot: Ohrot and Keilim - Lights and Vessels
The 10 Sephirot describe the emanations, or attributes of God in Kabbalah. The Ein SofEin Sof
Ein Sof , in Kabbalah, is understood as God prior to His self-manifestation in the production of any spiritual Realm, probably derived from Ibn Gabirol's term, "the Endless One"...
("Limitless") is the unknowable, undifferentiated, infinite Divine essence. The 10 emanations of the Sephirot enable the Creation to know God, and become God's attributes that reveal Divinity. They are also the channels through which all of Creation is continuously substained from nothing, as in the Kabbalistic scheme, Creation is continuous and God is the only true existence. A "Chain of Progression" (Seder hishtalshelus
Seder hishtalshelus
Seder hishtalshelus means the "order of development" or "order of evolution", where the word Hishtalshelus is derived from the reduplicated quadriliteral root ŠLŠL "to chain", and so literally means "the chain-like process"...
) of descending "Worlds", including the Four Worlds
Four Worlds
The Four Worlds , sometimes counted with a prior stage to make Five Worlds, are the comprehensive categories of spiritual realms in Kabbalah in the descending chain of Existence....
, links the Ein Sof with our physical realm.
Each of the Sephirot is said to consist of a "light" (an ohr) that is vested in a "vessel" (a kli ; plural: keilim ). Generally speaking, the light is simple and undifferentiated, as it stems originally from the Ohr Ein Sof ("The Light of the Ein Sof"), God's infinite light. It represents Divine revelation in the world. It is associated with the Kabbalistic Divine Name of Ban. The differentiation between the 10 Sephirot, each with its own particular characteristic, arises from each of their different spiritual vessels. The light adapts itself to each vessel, to express the particular nature of each vessel.
Kabbalists read their mystical teachings into exegetical
Exegesis
Exegesis is a critical explanation or interpretation of a text, especially a religious text. Traditionally the term was used primarily for exegesis of the Bible; however, in contemporary usage it has broadened to mean a critical explanation of any text, and the term "Biblical exegesis" is used...
interpretations of Scripture and Rabbinic literature
Rabbinic literature
Rabbinic literature, in its broadest sense, can mean the entire spectrum of rabbinic writings throughout Jewish history. However, the term often refers specifically to literature from the Talmudic era, as opposed to medieval and modern rabbinic writing, and thus corresponds with the Hebrew term...
. This arose from their belief that Kabbalah forms part of the Oral Torah
Oral Torah
The Oral Torah comprises the legal and interpretative traditions that, according to tradition, were transmitted orally from Mount Sinai, and were not written in the Torah...
inherent in the revelation at Mount Sinai
Biblical Mount Sinai
The Biblical Mount Sinai is the mountain at which the Book of Exodus states that the Ten Commandments were given to Moses by God...
. Accordingly, in Jewish tradition, each verse and concept can be interpreted in the fourfold Jewish method of Pardes
Pardes (Jewish exegesis)
Pardes refers to approaches to biblical exegesis in rabbinic Judaism . The term, sometimes also spelled PaRDeS, is an acronym formed from the name initials of the following four approaches:...
, with the metaphysical
Metaphysics
Metaphysics is a branch of philosophy concerned with explaining the fundamental nature of being and the world, although the term is not easily defined. Traditionally, metaphysics attempts to answer two basic questions in the broadest possible terms:...
interpretations of Kabbalah
Kabbalah
Kabbalah/Kabala is a discipline and school of thought concerned with the esoteric aspect of Rabbinic Judaism. It was systematized in 11th-13th century Hachmei Provence and Spain, and again after the Expulsion from Spain, in 16th century Ottoman Palestine...
and Hasidic philosophy
Hasidic philosophy
Hasidic philosophy or Hasidus , alternatively transliterated as Hassidism, Chassidism, Chassidut etc. is the teachings, interpretations of Judaism, and mysticism articulated by the modern Hasidic movement...
forming the Sod (secret) level of meaning. In this way, Kabbalah interprets a second meaning in Talmudic legislation and use of the term for "vessel" ("kli"). In the Halachic sense a vessel is an object that can serve a useful purpose, even if it may not resemble a physical receptacle. This term is used frequently in discussion of the laws of Shabbat
Shabbat
Shabbat is the seventh day of the Jewish week and a day of rest in Judaism. Shabbat is observed from a few minutes before sunset on Friday evening until a few minutes after when one would expect to be able to see three stars in the sky on Saturday night. The exact times, therefore, differ from...
. In Jewish mysticism, typically, these narratives are given metaphysical interpretations, which relate "kli" to its Kabbalistic meaning. In Hasidic philosophy
Hasidic philosophy
Hasidic philosophy or Hasidus , alternatively transliterated as Hassidism, Chassidism, Chassidut etc. is the teachings, interpretations of Judaism, and mysticism articulated by the modern Hasidic movement...
, the plural fourfold levels of meaning are viewed as uniting in a higher essential source of explanation that describes Divinity. Jewish mysticism views such alternative, spiritual interpretations of Torah as stemming from more revealed Divine realms in the Chain of Worlds.
Ratzo and Shuv - Run and Return of emanations and Creations
More generally, Ohr also refers to the revelation and expression of any particular spiritual level which descends from that level and enclothes itself in a vessel (Kli). This Ohr is typically in a state of "Bittul" ("nullification") vis-a-vis the level from which it stems. Therefore, even when it descends to lower realms, it possesses a characteristic of "Ratzo" ("Run"), the desire to ascend and return to its source. Correspondingly, the Kli persuades the Ohr to descend through impressing upon it the need for Shuv ("Return"), the acknowledgment of the necessity of descent in order to fulfill the ultimate supernal will.The purpose of Creation was not for the sake of the higher spiritual Worlds. In relation to the infinite Ein Sof
Ein Sof
Ein Sof , in Kabbalah, is understood as God prior to His self-manifestation in the production of any spiritual Realm, probably derived from Ibn Gabirol's term, "the Endless One"...
, their great revelations of Divinity are a concealment, and have no comparison. Instead, the ultimate purpose of Creation in Kabbalah is for the sake of the lowest World, our physical realm. The Divine Will was to have a dwelling place in this World, made by man, which will be achieved in the Messianic Age. In higher spiritual Worlds (Seder hishtalshelus
Seder hishtalshelus
Seder hishtalshelus means the "order of development" or "order of evolution", where the word Hishtalshelus is derived from the reduplicated quadriliteral root ŠLŠL "to chain", and so literally means "the chain-like process"...
), the souls and angels sense this, and seek to channel Divine flow down the chain of Worlds. Therefore Shuv, even though it is an exile for the light to descend into the vessel, is the ultimate purpose of Creation. The terms "Ratzo" and "Shuv" come from the Biblical description of the angels in the vision of Ezekiel
Ezekiel
Ezekiel , "God will strengthen" , is the central protagonist of the Book of Ezekiel in the Hebrew Bible. In Judaism, Christianity and Islam, Ezekiel is acknowledged as a Hebrew prophet...
(1:4-26), when he beheld the Divine chariot (Merkavah). These angels "ran and returned". In this explanation, they desired to ascend to God, but returned down to their station, to fulfil their purpose. In daily spiritual life too, man seeks dveikus (cleaving) with God, and then returns with this inspiration to fulfil his or her tasks in the World. Here the human soul is the "ohr", the body the "kli", and this realm presently an exile for the soul.
The dynamics of Ratzo and Shuv are felt by the angels and man, but also apply to any spiritual emanation. The "Seder Histalshelus" describes the continuous descending chain from the Infinite to our finite World. In each World, the 10 Sephirot shine. Each World unfolds from the previous, with the lowest Sephirah (Malchut-"Kingship"-fulfilment of the plan in reality) of one World, becoming the highest Sephirah (Keter
Keter
*Keter in Kabbalah, is one of the ten Sephirot *Keter or kether כתר is the Hebrew word for "Crown ", as worn by a king or queen* Keter Publishing House is a book publisher based in Israel...
-"Crown"-the supernal Will of the plan in that World) of the next, lower World. Within each World too, the spiritual chain descends down the 10 Sephirot, with the illumination of one giving birth to the next, lower Sephirah.
Ohr and Ma'ohr - Two levels of Nullification of the Light to the Luminary
The "Ohr" ("Light") stems from the "Ma'ohr" ("Luminary"), the source of the light. Traditionally, the MashalMashal
A Mashal is a short parable with a moral lesson or religious allegory, called a nimshal. "Mashal" is used also to designate other forms in rhetoric, such as the fable and apothegm.-Biblical Parables:...
(parable) given to explain this relationship, is the relationship between the sun and the light that it gives off. However, technically speaking, the light that comes from the sun is not the perfect example for the Ohr, since it has already passed through a "Nartik" ("Sheath/Shield"), a level that reduces the intensity of the revelation of the sun. In truth, the Ohr that exists in the parable of the sun is the light of the sun that exists in the sun itself. The light that we see from the sun has already been limited in its quality and therefore lacks the "Bittul" ("nullification") of the true Ohr to its origin. Rather, this Ohr, being that it has been limited by the Nartik, is called Ohr HaNartik (the light of the sheath), for although it does not actually come from the Nartik, since the Nartik limited it in such a way that it no longer possesses a connection with its ultimate source, we associate it with the Nartik.
In Kabbalah, the level of the Ma'ohr is represented by the higher Hebrew name of God, the Tetragrammaton
Tetragrammaton
The term Tetragrammaton refers to the name of the God of Israel YHWH used in the Hebrew Bible.-Hebrew Bible:...
, and the Ohr is the revelation of that level. Similarly, the lower name of God, Elokim (Here the "h" has been replaced with a "k" in traditional deference to avoid writing the names of God), represents the Nartik, and the light that stems thereof is the Ohr HaNartik, and as such, it lacks a higher level of nullification, enabling it to create the Worlds. If the light of the Tetragrammaton were to create the Worlds, they would not exist as creations with independent self awareness. The immense revelation of the Divine would nullify them in their source, as the light of the sun inside the sun itself.
In the second section of the Tanya
Tanya
The Tanya is an early work of Hasidic philosophy, by Rabbi Shneur Zalman of Liadi, the founder of Chabad Hasidism, first published in 1797. Its formal title is Likkutei Amarim , but is more commonly known by its opening word, Tanya, which means "it was taught in a beraita"...
by Schneur Zalman of Liadi, the Hasidic Panentheism
Panentheism
Panentheism is a belief system which posits that God exists, interpenetrates every part of nature and timelessly extends beyond it...
of the Baal Shem Tov, the founder of Hasidism, is systematically explained in philosophical terms. Two levels of Divine Unity are explained, that paradoxically are both true perspectives. From God's perspective, in comparison to the unchanging Divine Infinity, all of Creation is literally as if it did not exist (Acosmism
Acosmism
Acosmism, in contrast to pantheism, denies the reality of the universe, seeing it as ultimately illusory, , and only the infinite unmanifest Absolute as real....
). This is represented by a Higher Bittul-"Bittul Hametsiyas" ("Nullification of Essence") of the light of the sun inside the orb of the sun itself. This is called the "Upper Divine Unity". The "Lower Divine Unity" describes the Unity of God from the illusiory self independent perspective of the Creations. From this perspective, Creation does exist, but is continuously dependent on receiving its Divine lifeforce that constantly brings it into being from nothing. In our World, this constant, total dependence for the existence of everything on the Divine creative light is hidden. In the spiritual Worlds of Creation, it is revealed, but they still lack true "Bittul" (nullification), as the souls and angels in those realms have some self awareness, albeit totally nullified to God. This Lower Bittul-"Bittul Hayesh" ("Nullification of Ego") is represented by a light of a candle on a sunny day. In the Chain of Four Worlds
Four Worlds
The Four Worlds , sometimes counted with a prior stage to make Five Worlds, are the comprehensive categories of spiritual realms in Kabbalah in the descending chain of Existence....
, the first realm, the World of Atzilus, is not yet considered a Creation, but rather an emanation of supernal Divinity. It is characterised by the higher Nullification of Essence. The three lower realms of Beriah
Beri'ah
Beri'ah , or Briyah , is the second of the four celestial worlds in the Tree of Life of the Kabbalah, intermediate between the World of Emanation and the World of Formation , the third world, that of the angels...
, Yetzirah
Yetzirah
Yetzirah is the third of four worlds in the Kabbalistic Tree of Life, following Atziluth and Briah...
and Asiyah
Assiah
Assiah is the last of the four spiritual worlds of the Kabbalah—Atziluth, Beri'ah, Yetzirah, 'Asiyah—based on the passage in . According to the Maseket Aẓilut, it is the region where the Ofanim rule and where they promote the hearing of prayers, support human endeavor, and combat evil...
are considered created realms as they only possess different levels of the lower Nullification of Ego.
This explanation of the spiritual meanings of the different Hebrew names of God of the Tetragrammaton and Elokim, gives the Kabbalistic reason why the lower name "Elokim" (Divine immanence) is universally used in the Creation account in the beginning of Genesis, with the multiple phrases on each day:
"And God (Elokim) said, 'Let there be..'"
In Kabbalah, going back to the Scriptural commentary
Jewish commentaries on the Bible
This article describes the first printing of the Hebrew Bible with major Jewish commentaries, notes concerning translations into Aramaic and English, lists some universally accepted Jewish commentaries with notes on their method of approach and lists modern translations into English with notes.-...
of Nachmanides, the 7 Days of Creation are understood to symbolically refer to the 7 Emotional revelations of the Sefirot, each one called a "day". These Hebrew sayings themselves, are explained in Kabbalah to be the creative channels of the Sephirot in activating Creation. Only after Genesis recounts its first narrative of Creation, with the beginning of its second account, does it use the higher, essential, Divine name of the Tetragrammaton (Divine transcendence). Here it combines both names, as both are involved in Creation. Later on, when God speaks to Moses, the name of God used is only the transcendent Tetragrammaton. In the second account of Creation:
"This is the account of the Heavens and the Earth when they were created, when the Lord (Tetragrammaton) God (Elokim) made the Earth and Heavens."
According to the Kabbalistic and Hasidic explanation, the ability to Create Ex nihilo
Ex nihilo
Ex nihilo is a Latin phrase meaning "out of nothing". It often appears in conjunction with the concept of creation, as in creatio ex nihilo, meaning "creation out of nothing"—chiefly in philosophical or theological contexts, but also occurs in other fields.In theology, the common phrase creatio ex...
(something from nothing) can only come from the Divine essence (Ein Sof
Ein Sof
Ein Sof , in Kabbalah, is understood as God prior to His self-manifestation in the production of any spiritual Realm, probably derived from Ibn Gabirol's term, "the Endless One"...
), which is referred to by the Tetragrammaton. Nonetheless, the light to create existence must be constricted through the name Elokim. This process is referred to in this second account of Creation.
Sovev/Makif and Mimalei/Pnimi - Surrounding/Transcendent light and Filling/Inner light

Zohar
The Zohar is the foundational work in the literature of Jewish mystical thought known as Kabbalah. It is a group of books including commentary on the mystical aspects of the Torah and scriptural interpretations as well as material on Mysticism, mythical cosmogony, and mystical psychology...
states that God is totally united with his Torah
Torah
Torah- A scroll containing the first five books of the BibleThe Torah , is name given by Jews to the first five books of the bible—Genesis , Exodus , Leviticus , Numbers and Deuteronomy Torah- A scroll containing the first five books of the BibleThe Torah , is name given by Jews to the first five...
, the Torah is inherently transcendent in all Worlds, and each World studies it according to their mystical level of perception.
The other light, called Mimalei Kol Olmin ("Filling All Worlds") is the Divine light of immanence, rooted in the Kav (first "Ray" of light) after the Tzimtzum in Lurianic Kabbalah. This is the light that descends immanently to every level of the Chain of Worlds, itself creating every spiritual and, ultimately, physical vessel of each World. It undergoes the innumerable concealments and contractions of the second Tzimtzumim. Hasidic thought sees the ultimate advantage of this lower light, because the ultimate purpose of Creation lies in this lowest realm. Hasidism therefore rejected Jewish asceticism, seeking to utilise and mystically transform the physical into spirituality, through dveikus cleaving to God. Hasidic thought likewise describes another, higher type of miracle that is immanently invested within the physical laws of this World, without breaking them. Only a higher source rooted in the Divine essence
Atzmus
Atzmus/Atzmut meaning "essence", is the descriptive term referred to in Kabbalah, and explored in Hasidic thought, for the Divine essence....
, beyond infinite-finite duality, could unite the infinite encompassing light of Sovev within the limited invested light of Mimalei.
These terms are also related to the parallel notions of Makif ("Outer") and Pnimi ("Inner"), taught in Hasidic philosophy
Hasidic philosophy
Hasidic philosophy or Hasidus , alternatively transliterated as Hassidism, Chassidism, Chassidut etc. is the teachings, interpretations of Judaism, and mysticism articulated by the modern Hasidic movement...
. Hasidism relates the esoteric spiritual structures of Kabbalah to their inner dimensions in the consciousness and perception of man. This is found in the Hasidic idea of dveikus (mystical fervour). It seeks an inner response to the Jewish mystical tradition. In the Sephirot, for example, Hasidic thought focuses on the inner motivational soul within each Sephirah, and its parallel in the spiritual psychology of man.
Direct/Descending light and Reflected/Ascending light
A descending light is a Divine emanation "from above". It is metaphorically called "masculine waters" and "an arousal from Above" in Kabbalah, based on the verses in Genesis 1:6-8 about the Upper and Lower Waters:
6 And God said, Let there be a firmament in the midst of the waters, and let it divide the waters from the waters. 7 And God made the firmament, and divided the waters which were under the firmament from the waters which were above the firmament: and it was so. 8 And God called the firmament Heaven. And the evening and the morning were the second day.
The descent of masculine waters can be a free expression of the Sephirah of Hesed (Kindness), which has the essential nature to give Divine blessing in an unlimited way, without considering whether the vessels of the Creation are worthy. Hesed is counterbalanced by Gevurah (Judgement), that measures and withholds the blessing according to the worth and capacity of the vessel.
More commonly, the descent of direct light is in response to the ascent from below of reflected light. This "arousal from below", the ascent of "feminine waters", is the spiritual illumination created by each person through meritorious ethical or ritual mitzvot (Jewish observances). While Kabbalah
Kabbalah
Kabbalah/Kabala is a discipline and school of thought concerned with the esoteric aspect of Rabbinic Judaism. It was systematized in 11th-13th century Hachmei Provence and Spain, and again after the Expulsion from Spain, in 16th century Ottoman Palestine...
offered radical theosophical cosmic explanations of Judaism
Judaism
Judaism ) is the "religion, philosophy, and way of life" of the Jewish people...
, it remained inherently conservative. The metaphysical
Metaphysics
Metaphysics is a branch of philosophy concerned with explaining the fundamental nature of being and the world, although the term is not easily defined. Traditionally, metaphysics attempts to answer two basic questions in the broadest possible terms:...
doctrines of Kabbalah support and deepen normative Jewish observance. Kabbalah, especially the new teachings of Isaac Luria
Isaac Luria
Isaac Luria , also called Yitzhak Ben Shlomo Ashkenazi acronym "The Ari" "Ari-Hakadosh", or "Arizal", meaning "The Lion", was a foremost rabbi and Jewish mystic in the community of Safed in the Galilee region of Ottoman Palestine...
in the 16th Century, taught the cosmic power of each person to affect and rectify the Divine scheme of Creation. In Lurianic Kabbalah, the ultimate Tikkun
Tikkun olam
Tikkun olam is a Hebrew phrase that means "repairing the world." In Judaism, the concept of tikkun olam originated in the early rabbinic period...
is dependent on each individual fulfilling their own unique tasks in Creation, through the mitzvot. This affect would occur whether the person was aware of the deeper meanings or not. The great delight the illumination of the ascending feminine waters causes in the Heavenly realms (Four Worlds
Four Worlds
The Four Worlds , sometimes counted with a prior stage to make Five Worlds, are the comprehensive categories of spiritual realms in Kabbalah in the descending chain of Existence....
), leads to the reciprocal Divine response of descending blessing and light in the Masculine waters. This gives the inherent metaphysical Kabbalistic structure of the traditional Jewish belief of "Reward and Punishment", incorporated in Maimonides
Maimonides
Moses ben-Maimon, called Maimonides and also known as Mūsā ibn Maymūn in Arabic, or Rambam , was a preeminent medieval Jewish philosopher and one of the greatest Torah scholars and physicians of the Middle Ages...
' Jewish Principles of Faith
Jewish principles of faith
The concept of an explicit, paramount definition of faith does not exist in Judaism as it does in other monotheistic religions such as Christianity. Although Jews and religious leaders share a core of monotheistic principles, and there are many fundamental principles quoted in the Talmud to define...
. The Kabbalistic explanation puts these external categories in an inner scheme of Divine loving-kindness.

Judah Loew ben Bezalel
Judah Loew ben Bezalel, alt. Loewe, Löwe, or Levai, widely known to scholars of Judaism as the Maharal of Prague, or simply The MaHaRaL, the Hebrew acronym of "Moreinu ha-Rav Loew," was an important Talmudic scholar, Jewish mystic, and philosopher who served as a leading rabbi in the city of...
(the Maharal) died on the 18th day (18 means "Hai"-"life" in Gematria
Gematria
Gematria or gimatria is a system of assigning numerical value to a word or phrase, in the belief that words or phrases with identical numerical values bear some relation to each other, or bear some relation to the number itself as it may apply to a person's age, the calendar year, or the like...
) of the Hebrew month
Hebrew calendar
The Hebrew calendar , or Jewish calendar, is a lunisolar calendar used today predominantly for Jewish religious observances. It determines the dates for Jewish holidays and the appropriate public reading of Torah portions, yahrzeits , and daily Psalm reading, among many ceremonial uses...
of Elul
Elul
Elul is the twelfth month of the Jewish civil year and the sixth month of the ecclesiastical year on the Hebrew calendar. It is a summer month of 29 days...
in the year 1609 (17 September). The 18th of Elul, 12 days before Rosh Hashanah
Rosh Hashanah
Rosh Hashanah , , is the Jewish New Year. It is the first of the High Holy Days or Yamim Nora'im which occur in the autumn...
, is a central mystical date in the personal preparations of teshuvah (return to God) for the upcoming "Days of Awe". A central component of the teachings of the Maharal was the concept of Divine paradox, above intellect. This prepared the way for the Hasidic movement, that sought the inner expression in Hasidic philosophy
Hasidic philosophy
Hasidic philosophy or Hasidus , alternatively transliterated as Hassidism, Chassidism, Chassidut etc. is the teachings, interpretations of Judaism, and mysticism articulated by the modern Hasidic movement...
of the Kabbalistic tradition. The founder of Hasidism, Israel Baal Shem Tov was born on the 18th of Elul in 1698 (August 27), and the founder of Habad intellectual expression of Hasidism, Schneur Zalman of Liadi, was born on the 18th day of Elul in 1745 (September 4). Kabbalah teaches that the yarthzeit of a Tzaddik (righteous person) causes the spiritual revelation and ascent of their life's spiritual service, the ascent of the "feminine waters" the Tzaddik illuminated. Anyone who attaches themselves to the teachings and influence of the Tzaddik receives from their illumination and blessing on the yartzheit. In the Kabbalistic scheme, this "arousal from below" ellicited the "arousal of God from above" to descend "masculine waters" by the descent of the souls on this date, later on, of the Baal Shem Tov and Schneur Zalman of Liadi. Kabbalah finds an allusion to the deeper aspects of this structure, including the essence of the different spiritual teachings of these three figures, in a Scriptural verse that relates to the mystical meaning of the 18th of Elul.
See also
- TzimtzumTzimtzumTzimtzum is a term used in the kabbalistic teaching of Isaac Luria, explaining his concept that God began the process of creation by "contracting" his infinite light in order to allow for a "conceptual space" in which a finite and seemingly independent world could exist...
- Ayin and YeshAyin and YeshAyin is an important concept in Kabbalah and Hasidic philosophy. It is contrasted with the term Yesh...
- Sephirot
- Deveikut
- Light (theology)Light (theology)In theology, light or divine light is a term used to refer to an aspect of divine presence, specifically an unknown and mysterious ability of God, angels, or human beings to express themselves communicatively through spiritual means, rather than through physical capacities...
- EmanationismEmanationismEmanationism is an idea in the cosmology or cosmogony of certain religious or philosophical systems. Emanation, from the Latin emanare meaning "to flow from" or "to pour forth or out of", is the mode by which all things are derived from the First Reality, or Principle...

