
Nucleotide sugar
Encyclopedia
Nucleotide sugars are the activated forms of monosaccharides. Nucleotide sugars act as glycosyl donors in glycosylation
reactions. Those reactions are catalyzed by a group of enzymes called glycosyltransferase
s.

In plants and bacteria many other sugars are used and various donors are utilized for them. Specifically, CDP-glucose and TDP-glucose are found in nature and give rise to various other forms of CDP and TDP-sugar donor nucleotides.
Glycosylation
Glycosylation is the reaction in which a carbohydrate, i.e. a glycosyl donor, is attached to a hydroxyl or other functional group of another molecule . In biology glycosylation refers to the enzymatic process that attaches glycans to proteins, lipids, or other organic molecules...
reactions. Those reactions are catalyzed by a group of enzymes called glycosyltransferase
Glycosyltransferase
Glycosyltransferases are enzymes that act as a catalyst for the transfer of a monosaccharide unit from an activated nucleotide sugar to a glycosyl acceptor molecule, usually an alcohol....
s.
History
The anabolism of oligosaccharides - and, hence, the role of nucleotide sugars - was not clear until 1950s when Leloir and his coworkers found that the key enzymes in this process are the glycosyltranserases. These enzymes transfer a glycosyl group from a sugar nucleotide to an acceptor.Biological Importance
To act as glycosyl donors, those monosaccharides should exist in a highly energetic form. This occurs as a result of a reaction between nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) and glycosyl monophosphate (phosphate at anomeric carbon).
Types
There are nine sugar nucleotides in complex animals which act as glycosyl donors and they can be classified depending on the type of the nucleoside forming them :- Uridine Diphosphate: UDP-Glc, UDP-Gal, UDP-GalNAc, UDP-GlcNAcUDP-N-acetylglucosamineUridine diphosphate N-acetylglucosamine or UDP-GlcNAc is a nucleotide sugar and a coenzyme in metabolism. It is used by glycosyltransferases to transfer N-acetylglucosamine residues to substrates. D-Glucosamine is made naturally in the form of glucosamine-6-phosphate, and is the biochemical...
, UDP-GlcUAUridine diphosphate glucuronic acidUDP glucuronic acid is a sugar used in the creation of polysaccharides and is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of ascorbic acid ....
, UDP-Xyl - Guanine Diphosphate: GDP-Man, GDP-Fuc.
- Cytosine Monophosphate: CMP-Neu5Ac, it is the only nucleotide sugar in the form of nucleotide monophosphate.
In plants and bacteria many other sugars are used and various donors are utilized for them. Specifically, CDP-glucose and TDP-glucose are found in nature and give rise to various other forms of CDP and TDP-sugar donor nucleotides.
Structures
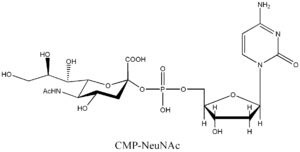
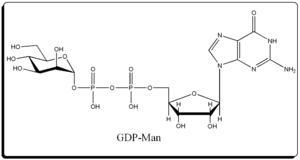
listed below are the structures of some nucleotide sugars (example from each type).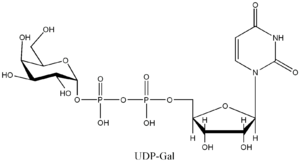 |
 |
 |
| UDP-Gal Uridine diphosphate galactose Uridine diphosphate galactose is an intermediate in the production of polysaccharides. It is important in nucleotide sugars metabolism, and is the substrate for the transferase B4GALT5.... |
CMP-NeuNAc | GDP-Man |
Relationship between glycosylation pathways and different diseases
Normal metabolism of nucleotide sugars is very important. Any malfunction in any contributing enzyme will lead to a certain disease for example:- Inclusion body myopathy: is a congenital disease resulted from altered function of UDP-GlcNAc epimerase .
- Macular corneal dystrophy: is a congenital disease resulted from malfunction of GlcNAc-6-sulfotransferase.
- Congenital disorder in α-1,3 mannosyl transferase will result in a variety of clinical symptoms, e.g. hypotonia, psychomotor retardation, liver fibrosis and various feeding problems.

