Nuclear energy in the European Union
Encyclopedia
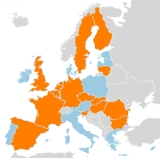
Nuclear power in the European Union accounted for approximately 15% of total energy consumption in 2005. The energy policies of the European Union
(EU) member countries vary significantly. As of January 2010, 14 out of 27 countries have nuclear reactor
s. The countries with reactors are: Belgium, Bulgaria
, Czech Republic
, Finland
, France
, Germany
, Hungary, Netherlands, Romania
, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain
, Sweden
, and the United Kingdom
. France and Finland embrace nuclear technology
, new EPR reactors are being built there. In the wake of the Fukushima disaster, Switzerland and Germany decided that they will phase out
nuclear energy in the first years of the 2020s.
provided the largest source (29.5%) of electricity with a production of 990 TWh, and an installed capacity of 134 GWe (17,6% of all installed capacity). It was the leading electric power source in Belgium, France, Hungary, Lithuania and Slovakia. France, where nuclear is also the largest primary energy source, produced 450 TWh
in 2006 – 45% of the EU's total. Denmark, Estonia, Ireland, Greece, Italy, Cyprus, Latvia, Luxembourg, Malta, Austria, Poland and Portugal did not produce any nuclear energy. As of September 2008 there are 146 nuclear reactors in the European Union. 125 units of these are located in eight of the western EU countries. Total nuclear energy generation from EU power plants increased by 25% from 1995 to 2005. The majority of this growth occurred in the 1990s. Installed capacities decreased by 2.6% since 1990 and relative contribution to the overall electricity mix decreased from 30,8% in 1990 to 30,2% in 2005.
used in European nuclear reactors was mined
in Europe. Australia, Russia, Canada and Niger were the largest suppliers of nuclear materials to the EU, supplying more than 70% of the total needs in 2009
or the market does not apply to issues in the nuclear field. The nuclear policy is mainly in the competence of the member states. In the EU level, DG ENER is the main authority for EU nuclear issues.
The European Council
is the locus for intergovernmental decisions. The European Parliament
does not have authority in the field of nuclear other than the right to ask questions to the European Commission.
In case of a radiological emergency, the EU will trigger its ECURIE
alert system, which immediately notifies all national authorities of an impending nuclear hazard. This system was installed after the experience with the Chernobyl disaster
.
The FP7 research program has a special branch which is governed under the EURATOM treaty, which deals with community research into nuclear issues. The European Commission is owner of the high flux reactor
(HFR) in Petten
, NL.
In November 2007 the European Nuclear Energy Forum (ENEF), or the Bratislava/Prague forum, was launched to bring the policy on nuclear issues in the EU forward. The forum has working groups on "Risks
", "Transparency
" and "Opportunities". Policymakers, industry and NGOs are participating.
At present, the European Commission is investigating the issue of Nuclear liability, and is seeking how to harmonise the Vienna Convention on Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage
and the Paris Convention on Third Party Liability in the Field of Nuclear Energy
, as the differing caps on liability constitute a distortion of competition between operators in members states.
The Commisisons's SET plan mentions the "sustainable nuclear fission initiative" to develop Generation IV reactors as one of the research priorities of the European Union.
The European Commission is proposing a stress test for all nuclear power plants in Europe, to prove the nuclear fleet can withstand incidents like those in Fukushima. The European Commission is also proposing tests for countries near the EU who make use of nuclear.
per year. Eighty percent of that is short-lived low-level radioactive waste. France and the United Kingdom are currently the only EU countries that reprocess waste
. However, the reprocessing of spent fuel in the UK is being phased out but is expected to continue in France. The countries that currently use this reprocessed fuel (MOX
) include Germany
, Belgium, France
and Switzerland
. Reprocessing spent fuel significantly decreases its volume and extracts plutonium
from it. Although plutonium is commonly associated with nuclear weapons, the plutonium extracted with reprocessing is not suitable for 'classic' nuclear weapons.
The EBRD
is financing the decommissioning
of old nuclear plants in Bulgaria
, Lithuania and Slovakia.
EU memberstates Austria, Ireland, Netherlands, Poland, Slovakia, Bulgaria, Italy, Lithuania, Romania, and Slovenia are working since January 2009 together in the European Repository Development Organisation (ERDO) to address common issues on nuclear waste storage. This working group is led by ARiUS
from Switzerland and facilitated by COVRA
, waste management organisation, from the Netherlands.
ERDO was working early 2010 on a plan to dump European nuclear waste somewhere in Eastern Europe.
"Some 7,000 cubic meters of high-level nuclear waste are produced across the EU each year. Most Member States store spent fuel and other highly radioactive wastes in above-ground storage facilities that need continuous maintenance and oversight and are at risk of accidents, such as airplane crashes, fires or earthquakes. Hungary and Bulgaria currently ship nuclear waste to Russia."
In 2007 a "High level group on safety and waste management", a body with nuclear regulators from all EU member states, discussed if and how nuclear regulation in the European Union could be harmonised.
On July 19, 2011, the European Commission adopted a Directive for regulating and handling nuclear waste in the EU.
"Exports to countries outside the EU is allowed under very strict and binding conditions: The third country needs to have a final repository in operation, when the waste is being shipped. Such a repository for highly radioactive waste is internationally defined to be a deep geological repository. At present, such deep geological repositories do not exist anywhere in the world nor is a repository in construction outside of the EU. It takes currently a minimum of 40 years to develop and build one."
Along with companies and trade organizations like Foratom, General Electric
, Hitachi
, and Toshiba
are all partners in the European Nuclear Industry. Other partners may include TEPCO from Japan and KEPCO from South Korea. The nuclear industry is regulated by governments and financing is often provided to private contractors who do the work.
Nuclear Safety is an ongoing discussion in the EU. The Western European Nuclear Regulators Association has members from 17 states or European countries. Nuclear safety faces many challenges. WENR addresses these challenges and commits itself to objective reporting. An example of a report is the publication, "Stress Test" specifications, Proposal by the WENRA Task Force, 21 April 2011.
) and launched a citizen' initiative for a pan-EU ban on nuclear power.
Power companies are building nuclear reactors in Finland and France and the French state continues to fund nuclear power, with a €1 billion added to help research for fourth-generation technology and nuclear safety. GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy
won a bid to build the Visaginas Nuclear Power Plant
in Lithuania.
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
(EU) member countries vary significantly. As of January 2010, 14 out of 27 countries have nuclear reactor
Nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device to initiate and control a sustained nuclear chain reaction. Most commonly they are used for generating electricity and for the propulsion of ships. Usually heat from nuclear fission is passed to a working fluid , which runs through turbines that power either ship's...
s. The countries with reactors are: Belgium, Bulgaria
Nuclear power in Bulgaria
The Bulgarian government has favored nuclear power for the generation of electricity since 1956, and Bulgaria's first commercial nuclear reactor began to operate in 1974.. The government plans to build two new units at the Belene Nuclear Power Plant...
, Czech Republic
Nuclear power in the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic currently operates two nuclear power stations: Temelín and Dukovany. As of 2010 there have been government and corporate moves to expand Czech nuclear power generation capacity...
, Finland
Nuclear power in Finland
As of 2008, Finland's nuclear power program has four nuclear reactors in two power plants. The first of these came into operation in 1977. In 2007 they provided 28.4% of Finland's electricity. They are among the world's most productive, with average capacity factors of 94% in the 1990s...
, France
Nuclear power in France
Nuclear power is the primary source of electric power in France. In 2004, 425.8 TWh out of the country's total production of 540.6 TWh of electricity was from nuclear power , the highest percentage in the world....
, Germany
Nuclear power in Germany
Nuclear power in Germany accounted for 23% of national electricity consumption, before the permanent shutdown of 8 plants in March 2011. German nuclear power began with research reactors in the 1950s and 1960s with the first commercial plant coming online in 1969...
, Hungary, Netherlands, Romania
Nuclear power in Romania
Romania currently has 1,400 MW of nuclear power capacity by means of one active nuclear power plant with 2 reactors, which constitutes around 18% of the national power generation capacity of the country...
, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain
Nuclear power in Spain
Currently, Spain has eight nuclear reactors producing 20% of the country’s electricity or 7,448 net megawatts . Spain imports approximately 2% of its energy from France but exports the same amount to Portugal....
, Sweden
Nuclear power in Sweden
Sweden has an energy policy focused on hydroelectricity, which has been supplemented by nuclear power starting in 1965.The country began research into nuclear energy in 1947 with the establishment of the Atomic Energy Research Organization. In 1964, the country built its first small heavy water...
, and the United Kingdom
Nuclear power in the United Kingdom
Nuclear power currently generates around a sixth of the United Kingdom's electricity. As of 2011, the United Kingdom operates 19 nuclear reactors at nine locations...
. France and Finland embrace nuclear technology
Nuclear technology
Nuclear technology is technology that involves the reactions of atomic nuclei. Among the notable nuclear technologies are nuclear power, nuclear medicine, and nuclear weapons...
, new EPR reactors are being built there. In the wake of the Fukushima disaster, Switzerland and Germany decided that they will phase out
Nuclear power phase-out
A nuclear power phase-out is the discontinuation of usage of nuclear power for energy production. Often initiated because of concerns about nuclear power, phase-outs usually include shutting down nuclear power plants and looking towards renewable energy and other fuels.Austria was the first country...
nuclear energy in the first years of the 2020s.
Energy mix
The EU-27 in 2005 satisfied its primary energy consumption with 36.7% oil, 24.6% gas, 17.7% coal, 14.2% nuclear, 6.7% renewables and 0.1% industrial waste. In 2006, nuclear energyNuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity...
provided the largest source (29.5%) of electricity with a production of 990 TWh, and an installed capacity of 134 GWe (17,6% of all installed capacity). It was the leading electric power source in Belgium, France, Hungary, Lithuania and Slovakia. France, where nuclear is also the largest primary energy source, produced 450 TWh
TWH
TWH or twh could refer to:*Tennessee Walking Horse, a breed of horse* Toronto Western Hospital, a hospital in Toronto, Canada* TWH Bus & Coach, a bus company in Romford, England* Terrawatt-hour, measure of electrical energy, 1012 watt-hours...
in 2006 – 45% of the EU's total. Denmark, Estonia, Ireland, Greece, Italy, Cyprus, Latvia, Luxembourg, Malta, Austria, Poland and Portugal did not produce any nuclear energy. As of September 2008 there are 146 nuclear reactors in the European Union. 125 units of these are located in eight of the western EU countries. Total nuclear energy generation from EU power plants increased by 25% from 1995 to 2005. The majority of this growth occurred in the 1990s. Installed capacities decreased by 2.6% since 1990 and relative contribution to the overall electricity mix decreased from 30,8% in 1990 to 30,2% in 2005.
Uranium resources
In 2009, only 3% of the uraniumUranium
Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons...
used in European nuclear reactors was mined
Uranium mining
Uranium mining is the process of extraction of uranium ore from the ground. The worldwide production of uranium in 2009 amounted to 50,572 tonnes, of which 27% was mined in Kazakhstan. Kazakhstan, Canada, and Australia are the top three producers and together account for 63% of world uranium...
in Europe. Australia, Russia, Canada and Niger were the largest suppliers of nuclear materials to the EU, supplying more than 70% of the total needs in 2009
EU-level policy
European nuclear policy is governed by the EURATOM treaty. Therefore regular EU policy, on for example environmentDirectorate-General for the Environment (European Commission)
The Directorate-General for the Environment is a Directorate-General of the European Commission, responsible for the European Union policy area of the environment....
or the market does not apply to issues in the nuclear field. The nuclear policy is mainly in the competence of the member states. In the EU level, DG ENER is the main authority for EU nuclear issues.
The European Council
European Council
The European Council is an institution of the European Union. It comprises the heads of state or government of the EU member states, along with the President of the European Commission and the President of the European Council, currently Herman Van Rompuy...
is the locus for intergovernmental decisions. The European Parliament
European Parliament
The European Parliament is the directly elected parliamentary institution of the European Union . Together with the Council of the European Union and the Commission, it exercises the legislative function of the EU and it has been described as one of the most powerful legislatures in the world...
does not have authority in the field of nuclear other than the right to ask questions to the European Commission.
In case of a radiological emergency, the EU will trigger its ECURIE
Écurie
Écurie is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Nord-Pas-de-Calais region of France.-Geography:A farming village situated north of Arras at the junction of the N17 and D60 roads.-Population:-Places of interest:...
alert system, which immediately notifies all national authorities of an impending nuclear hazard. This system was installed after the experience with the Chernobyl disaster
Chernobyl disaster
The Chernobyl disaster was a nuclear accident that occurred on 26 April 1986 at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in Ukraine , which was under the direct jurisdiction of the central authorities in Moscow...
.
The FP7 research program has a special branch which is governed under the EURATOM treaty, which deals with community research into nuclear issues. The European Commission is owner of the high flux reactor
Petten nuclear reactor
The Petten nuclear reactors are nuclear research reactors in Petten, Netherlands. There are two reactors on the premises of the Petten research centre: a high flux reactor and a low flux reactor....
(HFR) in Petten
Petten
Petten is a town in the Dutch province of North Holland. It is a part of the municipality of Zijpe, and lies about 15 km northwest of Alkmaar, on the North Sea. The population is ca. 1900....
, NL.
In November 2007 the European Nuclear Energy Forum (ENEF), or the Bratislava/Prague forum, was launched to bring the policy on nuclear issues in the EU forward. The forum has working groups on "Risks
Nuclear safety
Nuclear safety covers the actions taken to prevent nuclear and radiation accidents or to limit their consequences. This covers nuclear power plants as well as all other nuclear facilities, the transportation of nuclear materials, and the use and storage of nuclear materials for medical, power,...
", "Transparency
Freedom of information legislation
Freedom of information legislation comprises laws that guarantee access to data held by the state. They establish a "right-to-know" legal process by which requests may be made for government-held information, to be received freely or at minimal cost, barring standard exceptions...
" and "Opportunities". Policymakers, industry and NGOs are participating.
At present, the European Commission is investigating the issue of Nuclear liability, and is seeking how to harmonise the Vienna Convention on Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage
Vienna Convention on Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage
Vienna Convention on Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage-Background:In September 1997, many of the world's governments took a significant step forward in improving the liability regime for nuclear damage...
and the Paris Convention on Third Party Liability in the Field of Nuclear Energy
Paris Convention on Third Party Liability in the Field of Nuclear Energy
The Paris Convention on Third Party Liability in the Field of Nuclear Energy is an OECD Convention on liability and compensation for damage caused by accidents occurring while producing nuclear energy.The convention:...
, as the differing caps on liability constitute a distortion of competition between operators in members states.
The Commisisons's SET plan mentions the "sustainable nuclear fission initiative" to develop Generation IV reactors as one of the research priorities of the European Union.
The European Commission is proposing a stress test for all nuclear power plants in Europe, to prove the nuclear fleet can withstand incidents like those in Fukushima. The European Commission is also proposing tests for countries near the EU who make use of nuclear.
Nuclear waste
On average, the EU creates about 40,000 cubic meters of radioactive wasteRadioactive waste
Radioactive wastes are wastes that contain radioactive material. Radioactive wastes are usually by-products of nuclear power generation and other applications of nuclear fission or nuclear technology, such as research and medicine...
per year. Eighty percent of that is short-lived low-level radioactive waste. France and the United Kingdom are currently the only EU countries that reprocess waste
Nuclear reprocessing
Nuclear reprocessing technology was developed to chemically separate and recover fissionable plutonium from irradiated nuclear fuel. Reprocessing serves multiple purposes, whose relative importance has changed over time. Originally reprocessing was used solely to extract plutonium for producing...
. However, the reprocessing of spent fuel in the UK is being phased out but is expected to continue in France. The countries that currently use this reprocessed fuel (MOX
Mox
MOX might be a name or acronym for:*Malaysian Oxygen Berhad - A Malaysian company that is specializes in providing total gas solutions.*Mixed Oxide Fuel, from nuclear reprocessing*An alien race in the TimeSplitters 2 video game, the Mox...
) include Germany
Nuclear power in Germany
Nuclear power in Germany accounted for 23% of national electricity consumption, before the permanent shutdown of 8 plants in March 2011. German nuclear power began with research reactors in the 1950s and 1960s with the first commercial plant coming online in 1969...
, Belgium, France
Nuclear power in France
Nuclear power is the primary source of electric power in France. In 2004, 425.8 TWh out of the country's total production of 540.6 TWh of electricity was from nuclear power , the highest percentage in the world....
and Switzerland
Nuclear power in Switzerland
Switzerland has four nuclear power plants, with five reactors in operation as of 2008. These plants produced 26.3 TWh in 2007...
. Reprocessing spent fuel significantly decreases its volume and extracts plutonium
Plutonium
Plutonium is a transuranic radioactive chemical element with the chemical symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, forming a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation...
from it. Although plutonium is commonly associated with nuclear weapons, the plutonium extracted with reprocessing is not suitable for 'classic' nuclear weapons.
The EBRD
European Bank for Reconstruction and Development
Founded in 1991, the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development uses the tools of investment to help build market economies and democracies in 30 countries from central Europe to central Asia. Its mission was to support the formerly communist countries in the process of establishing their...
is financing the decommissioning
Nuclear decommissioning
Nuclear decommissioning is the dismantling of a nuclear power plant and decontamination of the site to a state no longer requiring protection from radiation for the general public...
of old nuclear plants in Bulgaria
Nuclear power in Bulgaria
The Bulgarian government has favored nuclear power for the generation of electricity since 1956, and Bulgaria's first commercial nuclear reactor began to operate in 1974.. The government plans to build two new units at the Belene Nuclear Power Plant...
, Lithuania and Slovakia.
EU memberstates Austria, Ireland, Netherlands, Poland, Slovakia, Bulgaria, Italy, Lithuania, Romania, and Slovenia are working since January 2009 together in the European Repository Development Organisation (ERDO) to address common issues on nuclear waste storage. This working group is led by ARiUS
Arius
Arius was a Christian presbyter in Alexandria, Egypt of Libyan origins. His teachings about the nature of the Godhead, which emphasized the Father's divinity over the Son , and his opposition to the Athanasian or Trinitarian Christology, made him a controversial figure in the First Council of...
from Switzerland and facilitated by COVRA
COVRA
COVRA is a Dutch nuclear waste processing and storage company in Vlissingen,, which stores the waste produced in the Borssele nuclear power plant after it is reprocessed by Areva NC in La Hague, Manche, Basse-Normandie, France. Until the Dutch government decides where to eventually do with the...
, waste management organisation, from the Netherlands.
ERDO was working early 2010 on a plan to dump European nuclear waste somewhere in Eastern Europe.
"Some 7,000 cubic meters of high-level nuclear waste are produced across the EU each year. Most Member States store spent fuel and other highly radioactive wastes in above-ground storage facilities that need continuous maintenance and oversight and are at risk of accidents, such as airplane crashes, fires or earthquakes. Hungary and Bulgaria currently ship nuclear waste to Russia."
In 2007 a "High level group on safety and waste management", a body with nuclear regulators from all EU member states, discussed if and how nuclear regulation in the European Union could be harmonised.
On July 19, 2011, the European Commission adopted a Directive for regulating and handling nuclear waste in the EU.
"Exports to countries outside the EU is allowed under very strict and binding conditions: The third country needs to have a final repository in operation, when the waste is being shipped. Such a repository for highly radioactive waste is internationally defined to be a deep geological repository. At present, such deep geological repositories do not exist anywhere in the world nor is a repository in construction outside of the EU. It takes currently a minimum of 40 years to develop and build one."
European nuclear industry
The European nuclear industry is working to develop Generation IV nuclear reactors. Foratom is a Brussells based trade organization that bills itself as the "voice of the nuclear industry".Along with companies and trade organizations like Foratom, General Electric
General Electric
General Electric Company , or GE, is an American multinational conglomerate corporation incorporated in Schenectady, New York and headquartered in Fairfield, Connecticut, United States...
, Hitachi
Hitachi
Hitachi is a multinational corporation specializing in high-technology.Hitachi may also refer to:*Hitachi, Ibaraki, Japan*Hitachi province, former province of Japan*Prince Hitachi and Princess Hitachi, members of the Japanese imperial family...
, and Toshiba
Toshiba
is a multinational electronics and electrical equipment corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. It is a diversified manufacturer and marketer of electrical products, spanning information & communications equipment and systems, Internet-based solutions and services, electronic components and...
are all partners in the European Nuclear Industry. Other partners may include TEPCO from Japan and KEPCO from South Korea. The nuclear industry is regulated by governments and financing is often provided to private contractors who do the work.
Nuclear Safety is an ongoing discussion in the EU. The Western European Nuclear Regulators Association has members from 17 states or European countries. Nuclear safety faces many challenges. WENR addresses these challenges and commits itself to objective reporting. An example of a report is the publication, "Stress Test" specifications, Proposal by the WENRA Task Force, 21 April 2011.
Future plans
Germany, Italy, and Switzerland have decided to phase out nuclear power plants. According to FutureChallenges.org, Chancellor of Austria Werner Feymann plans to eliminate the usage of nuclear power by 2015 (nuclear power is already banned in AustriaNuclear energy in Austria
In the 1960s the Austrian government started a nuclear energy program and parliament unanimously ordered a nuclear power plant built. In 1972, the German company KWU began construction of the Zwentendorf Nuclear Power Plant boiling water 700 MWe reactor...
) and launched a citizen' initiative for a pan-EU ban on nuclear power.
Power companies are building nuclear reactors in Finland and France and the French state continues to fund nuclear power, with a €1 billion added to help research for fourth-generation technology and nuclear safety. GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy
GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy
GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy is a provider of advanced reactors and nuclear services. It is located in Wilmington, N.C.. Established in June 2007, GEH is a global nuclear alliance created by General Electric and Hitachi...
won a bid to build the Visaginas Nuclear Power Plant
Visaginas nuclear power plant
Visaginas nuclear power plant is a planned nuclear power plant project in Lithuania. It is proposed to be built at the site of the closed Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant which was shut-down on 31 December 2009 in accordance with Lithuania's accession agreement to the European Union...
in Lithuania.
See also
- Nuclear energy policy by country#Europe

