
Note value
Encyclopedia

Note head
In music, a note head is the elliptical part of a note. Noteheads may be coloured completely black or white, indicating the note value . In a whole note, the note head is the only component of the note. Shorter note values attach a stem to the note head, and possibly beams or flags...
, the presence or absence of a stem
Stem (music)
Stems can refer to two things in music, relating to music notation and production.-Notation:Stems are the lines which extend from the notehead. Stems may point up or down. Different-facing stems indicate the voice for polyphonic music written on the same staff...
, and the presence or absence of flags/beams
Beam (music)
A beam in musical notation is a thick line frequently used to connect multiple consecutive eighth notes , or notes of shorter value , and occasionally rests...
/hooks/tails.
A rest
Rest (music)
A rest is an interval of silence in a piece of music, marked by a sign indicating the length of the pause. Each rest symbol corresponds with a particular note value:The quarter rest may also be found as a form in older music....
indicates a silence of an equivalent duration.
| Note | Rest | American name | British name |
|---|---|---|---|
| longa Longa (music) A longa is a musical note that could be either twice or three times as long as a breve, four or six times as long as a semibreve/whole note, that appears in early music... |
longa | ||
| double whole note Double whole note In music, a double whole note or breve is a note lasting twice as long as a whole note... |
breve | ||
| whole note Whole note thumb|right|250px|Figure 1. A whole note and a whole rest.In music, a whole note or semibreve is a note represented by a hollow oval note head, like a half note , and no note stem . Its length is equal to four beats in 4/4 time... |
semibreve | ||
| half note Half note In music, a half note or minim is a note played for half the duration of a whole note and twice the duration of a quarter note... |
minim | ||
| or | quarter note Quarter note A quarter note or crotchet is a note played for one quarter of the duration of a whole note . Often people will say that a crotchet is one beat, however, this is not always correct, as the beat is indicated by the time signature of the music; a quarter note may or may not be the beat... |
crotchet | |
| eighth note Eighth note thumb|180px|right|Figure 1. An eighth note with stem facing up, an eighth note with stem facing down, and an eighth rest.thumb|right|180px|Figure 2. Four eighth notes beamed together.... |
quaver | ||
| sixteenth note Sixteenth note thumb|right|Figure 1. A sixteenth note with stem facing up, a sixteenth note with stem facing down, and a sixteenth rest.thumb|right|Figure 2. Four sixteenth notes beamed together.... |
semiquaver | ||
| thirty-second note Thirty-second note In music, a thirty-second note or demisemiquaver is a note played for 1/32 of the duration of a whole note... |
demisemiquaver | ||
| sixty-fourth note Sixty-fourth note In music notation, a sixty-fourth note or hemidemisemiquaver is a note played for 1/64 of the duration of a whole note . It lasts half as long as a thirty-second note .... |
hemidemisemiquaver | ||
| hundred twenty-eighth note Hundred twenty-eighth note In music, a hundred twenty-eighth note or semihemidemisemiquaver or quasihemidemisemiquaver is a note played for 1/128 of the duration of a whole note . It lasts half as long as a sixty-fourth note . It has a total of five flags or beams.Notes this short are very rare in printed music, but not... |
Quasihemidemisemiquaver / Semihemidemisemiquaver |
Variations

Sometimes the longa is used to indicate a very long note of indefinite duration, as at the end of a piece.
When a stem is present, it can go either up (from the right side of the note head) or down (from the left side, except in the case of the longa). In most cases, the stem goes down if the notehead is on the center line or above, and up otherwise. Any flags always go to the right of the stem.
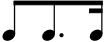
Eighth note
thumb|180px|right|Figure 1. An eighth note with stem facing up, an eighth note with stem facing down, and an eighth rest.thumb|right|180px|Figure 2. Four eighth notes beamed together....
s or shorter) appear successively, the flags may be replaced by beams
Beam (music)
A beam in musical notation is a thick line frequently used to connect multiple consecutive eighth notes , or notes of shorter value , and occasionally rests...
, as shown at right. Notes are typically beamed only if they appear in the same beat within the bar
Bar (music)
In musical notation, a bar is a segment of time defined by a given number of beats of a given duration. Typically, a piece consists of several bars of the same length, and in modern musical notation the number of beats in each bar is specified at the beginning of the score by the top number of a...
.
Modifiers
A note value may be augmentedAugmentation (music)
In Western music and music theory, the word augmentation has three distinct meanings. Augmentation is a compositional device where a melody, theme or motif is presented in longer note-values than were previously used...
by adding a dot after it. This dot
Dotted note
In Western musical notation, a dotted note is a note with a small dot written after it. The dot increases the duration of the basic note by half of its original value. If the basic note lasts 2 beats, the corresponding dotted note lasts 3 beats...
adds the next lower note value, making it one and a half times its original duration. A number of dots (n) lengthen the note value by
 its value, so Two dots
its value, so Two dotsDotted note
In Western musical notation, a dotted note is a note with a small dot written after it. The dot increases the duration of the basic note by half of its original value. If the basic note lasts 2 beats, the corresponding dotted note lasts 3 beats...
add two lower note values, making a total of one and three quarters times its original duration. The rare three dots
Dotted note
In Western musical notation, a dotted note is a note with a small dot written after it. The dot increases the duration of the basic note by half of its original value. If the basic note lasts 2 beats, the corresponding dotted note lasts 3 beats...
make it one and seven eighths the duration, and so on.
To divide a note value to three equal parts, or some other value than two, tuplet
Tuplet
In music a tuplet is "any rhythm that involves dividing the beat into a different number of equal subdivisions from that usually permitted by the...
s may be used. However, see swung note and notes inégales
Notes inégales
In music, notes inégales refers to a performance practice, mainly from the Baroque and Classical music eras, in which some notes with equal written time values are performed with unequal durations, usually as alternating long and short...
.
Gregorian chant
Although note heads of various shapes, and notes with and without stems appear in early Gregorian chantGregorian chant
Gregorian chant is the central tradition of Western plainchant, a form of monophonic liturgical music within Western Christianity that accompanied the celebration of Mass and other ritual services...
manuscripts, most scholars agree that these symbols do not indicate different durations, although the dot is used for augmentation. See neume
Neume
A neume is the basic element of Western and Eastern systems of musical notation prior to the invention of five-line staff notation. The word is a Middle English corruption of the ultimately Ancient Greek word for breath ....
.
In the 13th century, chant was sometimes performed according to rhythmic modes, roughly equivalent to meters
Metre (music)
Meter or metre is a term that music has inherited from the rhythmic element of poetry where it means the number of lines in a verse, the number of syllables in each line and the arrangement of those syllables as long or short, accented or unaccented...
; however, the note shapes still did not indicate duration in the same way as modern note values.
Mensural notation
Around 1250, Franco of CologneFranco of Cologne
Franco of Cologne was a German music theorist and possibly composer. He was one of the most influential theorists of the late Medieval era, and was the first to propose an idea which was to transform musical notation permanently: that the duration of any note should be determined by its...
invented different symbols for different durations, although the relation between different note values could vary; three was the most common ratio. Philippe de Vitry
Philippe de Vitry
Philippe de Vitry was a French composer, music theorist and poet. He was an accomplished, innovative, and influential composer, and may also have been the author of the Ars Nova treatise...
's treatise Ars nova (1320) described a system in which the ratios of different note values could be 2:1 or 3:1, with a system of mensural time signature
Time signature
The time signature is a notational convention used in Western musical notation to specify how many beats are in each measure and which note value constitutes one beat....
s to distinguish between them.
This black mensural notation
Mensural notation
Mensural notation is the musical notation system which was used in European music from the later part of the 13th century until about 1600."Mensural" refers to the ability of this system to notate complex rhythms with great exactness and flexibility...
gave way to white mensural notation around 1450, in which all note values were written with white (outline) noteheads. In white notation the use of triplets
Tuplet
In music a tuplet is "any rhythm that involves dividing the beat into a different number of equal subdivisions from that usually permitted by the...
was indicated by coloration, i.e. filling in the noteheads to make them black (or sometimes red). Both black and white notation periodically made use of ligatures
Ligature (music)
In music notation, a ligature is a graphic symbol representing two or more notes performed in a single gesture, and on a single syllable, primarily in use ca. 800–1650 AD. They are characteristic of neumatic and mensural notation...
, a holdover from the clivis and porrectus neume
Neume
A neume is the basic element of Western and Eastern systems of musical notation prior to the invention of five-line staff notation. The word is a Middle English corruption of the ultimately Ancient Greek word for breath ....
s used in chant
Gregorian chant
Gregorian chant is the central tradition of Western plainchant, a form of monophonic liturgical music within Western Christianity that accompanied the celebration of Mass and other ritual services...
.
Around 1600 the modern notational system was generally adopted, along with barlines and the practice of writing multipart music in scores rather than only individual parts. In the 17th century, however, old usages came up occasionally.
Origins of the names
The British names go back at least to English renaissance music, and the terms of Latin origin had international currency at that time. Obviously, longa means 'long', and the rest mostly indicate relative shortness. Breve is from Latin brevis, 'short', minim is from minimus, 'very small', and quaver refers to the quivering effect of very fast notes. The elements semi-, demi- and hemi- mean 'half' in Latin, French and Greek respectively, while quasi- means 'almost'. The chain semantic shift whereby notes which were originally perceived as short came progressively to be long notes is interesting both linguistically and musically. However, the crotchet is named after the shape of the note, from the Old French for a 'little hook', and it is possible to argue that the same is true of the minim, since the word is also used in palaeography to mean a vertical stroke in mediaeval handwriting.The American names are loan translations of the German terms; when American orchestras were first established in the 19th century they were populated to a significant degree by German emigrants.

