The
Norwegian Sea is a
marginal seaThe term marginal sea has differing meanings. In one sense the term is equivalent to territorial waters. In another sense the term indicates a partially enclosed sea adjacent to or widely open to the open ocean, but bounded by submarine ridges...
in the North Atlantic Ocean, northwest of
NorwayNorway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
. It is located between the
North SeaIn the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel connecting to the Atlantic Ocean. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively...
(i.e. north of
ScotlandScotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
) and the
Greenland SeaThe Greenland Sea is a body of water that borders Greenland to the west, the Svalbard archipelago to the east, Fram Strait and the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Norwegian Sea and Iceland to the south. The Greenland Sea is often defined as part of the Arctic Ocean, sometimes as part of the...
and adjoins the North
Atlantic OceanThe Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
to the west and the
Barents SeaThe Barents Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located north of Norway and Russia. Known in the Middle Ages as the Murman Sea, the sea takes its current name from the Dutch navigator Willem Barents...
to the northeast. In the southwest, it is separated from the Atlantic Ocean by a submarine ridge running between
IcelandIceland , described as the Republic of Iceland, is a Nordic and European island country in the North Atlantic Ocean, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Iceland also refers to the main island of the country, which contains almost all the population and almost all the land area. The country has a population...
and the
Faroe IslandsThe Faroe Islands are an island group situated between the Norwegian Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, approximately halfway between Scotland and Iceland. The Faroe Islands are a self-governing territory within the Kingdom of Denmark, along with Denmark proper and Greenland...
. To the North, the
Jan MayenJan Mayen Island is a volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean and part of the Kingdom of Norway. It is long and 373 km2 in area, partly covered by glaciers . It has two parts: larger northeast Nord-Jan and smaller Sør-Jan, linked by an isthmus wide...
Ridge separates it from the
Greenland SeaThe Greenland Sea is a body of water that borders Greenland to the west, the Svalbard archipelago to the east, Fram Strait and the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Norwegian Sea and Iceland to the south. The Greenland Sea is often defined as part of the Arctic Ocean, sometimes as part of the...
.
Unlike many other seas, most of the bottom of the Norwegian Sea is not part of a
continental shelfThe continental shelf is the extended perimeter of each continent and associated coastal plain. Much of the shelf was exposed during glacial periods, but is now submerged under relatively shallow seas and gulfs, and was similarly submerged during other interglacial periods. The continental margin,...
and therefore lies at a great depth of about two kilometres on average. Rich deposits of oil and
natural gasNatural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
are found under the sea bottom and are being explored commercially, in the areas with sea depths of up to about one kilometre. The coastal zones are rich in fish that visit the Norwegian Sea from the North Atlantic for
spawningSpawn refers to the eggs and sperm released or deposited, usually into water, by aquatic animals. As a verb, spawn refers to the process of releasing the eggs and sperm, also called spawning...
. The warm
North Atlantic CurrentThe North Atlantic Current is a powerful warm ocean current that continues the Gulf Stream northeast. West of Ireland it splits in two; one branch, the Canary Current, goes south, while the other continues north along the coast of northwestern Europe...
ensures relatively stable and high water temperatures, so that unlike the Arctic seas, the Norwegian Sea is ice-free throughout the year.
Extent
The
International Hydrographic OrganizationThe International Hydrographic Organization is the inter-governmental organisation representing the hydrographic community. It enjoys observer status at the UN and is the recognised competent authority on hydrographic surveying and nautical charting...
defines the limits of the Norwegian Sea as follows:
On the Northeast. A line joining the Southernmost point of West SpitzbergenSpitsbergen is the largest and only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in Norway. Constituting the western-most bulk of the archipelago, it borders the Arctic Ocean, the Norwegian Sea and the Greenland Sea...
to North Cape of Bear Island, through this island to Cape Bull and thence on to North CapeNorth Cape is a cape on the island of Magerøya in Northern Norway, in the municipality of Nordkapp. Its 307 m high, steep cliff is often referred to as the northernmost point of Europe, located at , 2102.3 km from the North Pole. However, the neighbouring point Knivskjellodden is actually...
in NorwayNorway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
(71°10'N 25°47'E).
On the Southeast. The West coast of Norway between North Cape and Cape Stadt (62°10′N 5°00′E).
On the South. From a point on the West coast of Norway in Latitude 61°00' NorthThe 61st parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 61 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses the Atlantic Ocean, Europe, Asia and North America....
along this parallel to Longitude 0°53' West thence a line to the NE extreme of FuglöFugloy is the eastern-most island in the Faroe Islands. The name means bird island, and refers to the large number of birds that nest on the island's cliffs.- Geography :...
(62°21′N 6°15′W) and on to the East extreme of Gerpir (65°05′N 13°30′W) in IcelandIceland , described as the Republic of Iceland, is a Nordic and European island country in the North Atlantic Ocean, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Iceland also refers to the main island of the country, which contains almost all the population and almost all the land area. The country has a population...
.
On the West. The Southeastern limit of Greenland SeaThe Greenland Sea is a body of water that borders Greenland to the west, the Svalbard archipelago to the east, Fram Strait and the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Norwegian Sea and Iceland to the south. The Greenland Sea is often defined as part of the Arctic Ocean, sometimes as part of the...
[A line joining the Southernmost point of West Spitzbergen to the Northern point of Jan MayenJan Mayen Island is a volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean and part of the Kingdom of Norway. It is long and 373 km2 in area, partly covered by glaciers . It has two parts: larger northeast Nord-Jan and smaller Sør-Jan, linked by an isthmus wide...
Island, down the West coast of that island to its Southern extreme, thence a Line to the Eastern extreme of Gerpir (65°05′N 13°30′W) in Iceland].
Formation and geography
The Norwegian Sea was formed about 250 million years ago, when the
Eurasian plateThe Eurasian Plate is a tectonic plate which includes most of the continent of Eurasia , with the notable exceptions of the Indian subcontinent, the Arabian subcontinent, and the area east of the Chersky Range in East Siberia...
of Norway and the
North American PlateThe North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Greenland, Cuba, Bahamas, and parts of Siberia, Japan and Iceland. It extends eastward to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and westward to the Chersky Range in eastern Siberia. The plate includes both continental and oceanic crust...
, including Greenland, started to move apart. The existing narrow shelf sea between Norway and Greenland began to widen and deepen. The present continental slope in the Norwegian Sea marks the border between Norway and Greenland as it stood approximately 250 million years ago. In the north it extends east from
SvalbardSvalbard is an archipelago in the Arctic, constituting the northernmost part of Norway. It is located north of mainland Europe, midway between mainland Norway and the North Pole. The group of islands range from 74° to 81° north latitude , and from 10° to 35° east longitude. Spitsbergen is the...
and on the southwest between Britain and the Faroes. This continental slope contains rich fishing grounds and numerous
coral reefCoral reefs are underwater structures made from calcium carbonate secreted by corals. Coral reefs are colonies of tiny living animals found in marine waters that contain few nutrients. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, which in turn consist of polyps that cluster in groups. The polyps...
s. Settling of the shelf after the separation of the continents has resulted in
landslideA landslide or landslip is a geological phenomenon which includes a wide range of ground movement, such as rockfalls, deep failure of slopes and shallow debris flows, which can occur in offshore, coastal and onshore environments...
s, such as the
Storegga SlideThe three Storegga Slides are considered to be amongst the largest known landslides. They occurred under water, at the edge of Norway's continental shelf , in the Norwegian Sea, 100 km north-west of the Møre coast, causing a very large tsunami in the North Atlantic Ocean...
about 8,000 years ago that induced a major
tsunamiA tsunami is a series of water waves caused by the displacement of a large volume of a body of water, typically an ocean or a large lake...
.
The coasts of the Norwegian Sea were shaped during the last
Ice AgeAn ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
. Large
glacierA glacier is a large persistent body of ice that forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. At least 0.1 km² in area and 50 m thick, but often much larger, a glacier slowly deforms and flows due to stresses induced by its weight...
s several kilometres high pushed into the land, forming fjords, removing the crust into the sea, and thereby extending the continental slopes. This is particularly clear off the Norwegian coast along
HelgelandHelgeland is the most southerly district in Northern Norway. Generally speaking, Helgeland refers to the part of Nordland county that is located south of the Arctic Circle. The district covers an area of about , with nearly 79,000 inhabitants...
and north to the Lofoten Islands. The
Norwegian continental shelfThe Norwegian continental shelf is the continental shelf over which Norway exercises sovereign rights as defined by the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea...
is between 40 and 200 kilometres wide, and has a different shape from the shelves in the North Sea and Barents Sea. It contains numerous trenches and irregular peaks, which usually have an amplitude of less than 100 metres, but can reach up to 400 metres. They are covered with a mixture of gravel, sand, and mud, and the trenches are used by fish as spawning grounds. Deeper into the sea, there are two deep basins separated by a low ridge (its deepest point at 3,000 m) between the Vøring Plateau and
Jan MayenJan Mayen Island is a volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean and part of the Kingdom of Norway. It is long and 373 km2 in area, partly covered by glaciers . It has two parts: larger northeast Nord-Jan and smaller Sør-Jan, linked by an isthmus wide...
island. The southern basin is larger and deeper, with large areas between 3,500 and 4,000 metres deep. The northern basin is shallower at 3,200–3,300 metres, but contains many individual sites going down to 3,500 metres. Submarine thresholds and continental slopes mark the borders of these basins with the adjacent seas. To the south lies the European
continental shelfThe continental shelf is the extended perimeter of each continent and associated coastal plain. Much of the shelf was exposed during glacial periods, but is now submerged under relatively shallow seas and gulfs, and was similarly submerged during other interglacial periods. The continental margin,...
and the North Sea, to the east is the Eurasian continental shelf with the Barents Sea. To the west, the Scotland-Greenland Ridge separates the Norwegian Sea from the North Atlantic. This ridge is on average only 500 metres deep, only in a few places reaching the depth of 850 metres. To the north lie the Jan Mayen Ridge and Mohns Ridge, which lie at a depth of 2,000 metres, with some trenches reaching depths of about 2,600 meters.
Hydrology
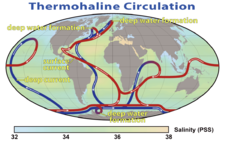
Four major water masses originating in the Atlantic and Arctic oceans meet in the Norwegian Sea, and the associated currents are of fundamental importance for the global climate. The warm, salty
North Atlantic CurrentThe North Atlantic Current is a powerful warm ocean current that continues the Gulf Stream northeast. West of Ireland it splits in two; one branch, the Canary Current, goes south, while the other continues north along the coast of northwestern Europe...
flows in from the Atlantic Ocean, and the colder and less saline
Norwegian CurrentThe Norwegian Current is a water current that flows north-easterly along the Atlantic coast of Norway at depths of between 50 and 100 meters...
originates in the North Sea. The so-called East Iceland Current transports cold water south from the Norwegian Sea toward Iceland and then east, along the
Arctic CircleThe Arctic Circle is one of the five major circles of latitude that mark maps of the Earth. For Epoch 2011, it is the parallel of latitude that runs north of the Equator....
; this current occurs in the middle water layer. Deep water flows into the Norwegian Sea from the Greenland Sea. The tides in the sea are semi-diurnal; that is, they rise twice a day, to a height of about 3.3 metres.
Surface currents
The hydrology of the upper water layers is largely determined by the flow from the North Atlantic. It reaches a speed of 10
SvThe sverdrup, named in honour of the pioneering oceanographer Harald Sverdrup, is a unit of measure of volume transport. It is used almost exclusively in oceanography, to measure the transport of ocean currents. Its symbol is Sv. Note that the sverdrup is not an SI unit, and that its symbol...
(1 Sv = million m
3/s) and its maximum depth is 700 metres at the Lofoten Islands, but normally it is within 500 metres. Part of it comes through the Faroe-Shetland Channel and has a comparatively high
salinitySalinity is the saltiness or dissolved salt content of a body of water. It is a general term used to describe the levels of different salts such as sodium chloride, magnesium and calcium sulfates, and bicarbonates...
of 35.3‰ (parts per thousand). This current originates in the North Atlantic Current and passes along the European continental slope; increased evaporation due to the warm European climate results in the elevated salinity. Another part passes through the Greenland-Scotland trench between the Faroe Islands and
IcelandIceland , described as the Republic of Iceland, is a Nordic and European island country in the North Atlantic Ocean, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Iceland also refers to the main island of the country, which contains almost all the population and almost all the land area. The country has a population...
; this water has a mean salinity between 35 and 35.2‰. The flow shows strong seasonal variations and can be twice as high in winter as in summer. While at the Faroe-Shetland Channel it has a temperature of about 9.5 °C; it cools to about 5 °C at Svalbard and releases this energy (about 250 terawatts) to the environment.
The current flowing from the
North SeaIn the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel connecting to the Atlantic Ocean. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively...
originates in the Baltic Sea and thus collects most of the drainage from northern Europe; this contribution is however relatively small. The temperature and salinity of this current show strong seasonal and annual fluctuations. Long-term measurements within the top 50 metres near the coast show a maximum temperature of 11.2 °C at the 63° N
parallelA circle of latitude, on the Earth, is an imaginary east-west circle connecting all locations that share a given latitude...
in September and a minimum of 3.9 °C at the North Cape in March. The salinity varies between 34.3 and 34.6‰ and is lowest in spring owing to the inflow of melted snow from rivers. The largest rivers discharging into the sea are
NamsenNamsen is the biggest river in Nord-Trøndelag county, in the central part of Norway. The long river flows through the municipalities of Røyrvik, Namsskogan, Grong, Overhalla, and Namsos. It traditionally has been used for floating timber down from the forests to the town of Namsos, where the...
,
RanelvaRanelva is a 130 km long river in the municipality of Rana, and is one of the longest rivers in the county of Nordland, Norway. The river begins on Saltfjellet, in the borders between Norway and Sweden, and flows northwestwards under the name Randalselv . Ranelva begins where Randalselva and the...
and
VefsnaThe river Vefsna is the largest river in Nordland county, Norway. It is long and drains a watershed of . Its headwaters lie in the mountains of Børgefjell National Park at the lake Simskardvatnet. The river runs through the municipalities of Hattfjelldal, Grane, and Vefsn. The southern parts of...
. They are all relatively short, but have a high discharge rate owing to their steep mountainous nature.
A portion of the warm surface water flows directly, within the
West Spitsbergen CurrentThe West Spitsbergen Current is a warm, salty current that runs poleward just west of Spitsbergen, , in the Arctic Ocean. The WSC branches off the Norwegian Atlantic Current in the Norwegian Sea. The WSC is of importance because it drives warm and salty Atlantic Water into the interior Arctic...
, from the Atlantic Ocean, off the Greenland Sea, to the Arctic Ocean. This current has a speed of 3–5 Sv and has a large impact on the climate. Other surface water (~1 Sv) flows along the Norwegian coast in the direction of the
Barents SeaThe Barents Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located north of Norway and Russia. Known in the Middle Ages as the Murman Sea, the sea takes its current name from the Dutch navigator Willem Barents...
. This water may cool enough in the Norwegian Sea to submerge into the deeper layers; there it displaces water that flows back into the North Atlantic.
Arctic water from the East Iceland Current is mostly found in the southwestern part of the sea, near Greenland. Its properties also show significant annual fluctuations, with long-term average temperature being below 3 °C and salinity between 34.7 and 34.9‰. The fraction of this water on the sea surface depends on the strength of the current, which in turn depends on the pressure difference between the
Icelandic LowThe Icelandic Low is a semi-permanent centre of low atmospheric pressure found between Iceland and southern Greenland and extending in the Northern Hemisphere winter into the Barents Sea. In summer it weakens and splits into two centres, one near Davis Strait and the other west of Iceland...
and
Azores HighThe Azores High is a large subtropical semi-permanent centre of high atmospheric pressure found near the Azores in the Atlantic Ocean, at the Horse latitudes...
: the larger the difference, the stronger the current.
Deep-sea currents
The Norwegian Sea is connected with the Greenland Sea and the Arctic Ocean by the 2,600-metre deep
Fram StraitThe Fram Strait is a passage from the Arctic Ocean to the Greenland Sea and Norwegian Sea, between Greenland and Spitsbergen. It is named after the Norwegian ship Fram. The Fram Strait is the major connection between the Arctic Ocean and the world ocean....
. The Norwegian Sea Deep Water (NSDW) occurs at depths exceeding 2,000 metres; this homogeneous layer with a salinity of 34.91‰ experiences little exchange with the adjacent seas. Its temperature is below 0 °C and drops to −1 °C at the ocean floor. Compared with the deep waters of the surrounding seas, NSDW has more nutrients but less oxygen and is relatively old.
The weak deep-water exchange with the Atlantic Ocean is due to the small depth of the relatively flat Greenland-Scotland Ridge between Scotland and Greenland, an offshoot of the
Mid-Atlantic RidgeThe Mid-Atlantic Ridge is a mid-ocean ridge, a divergent tectonic plate boundary located along the floor of the Atlantic Ocean, and part of the longest mountain range in the world. It separates the Eurasian Plate and North American Plate in the North Atlantic, and the African Plate from the South...
. Only four areas of the Greenland-Scotland Ridge are deeper than 500 metres: the Faroe Bank Channel (about 850 metres), some parts of the Iceland-Faroe Ridge (about 600 metres), the
Wyville-Thomson RidgeThe Wyville-Thomson Ridge is a bathymetric feature of the North Atlantic ocean floor ca. 200 km in length, located between the Faroe Islands and Scotland. The ridge separates the Faroe-Shetland Channel to the north from the Rockall Trough to the south...
(620 metres), and areas between
GreenlandGreenland is an autonomous country within the Kingdom of Denmark, located between the Arctic and Atlantic Oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Though physiographically a part of the continent of North America, Greenland has been politically and culturally associated with Europe for...
and the
Denmark StraitThe Denmark Strait or Greenland Strait |Sound]]) is an oceanic strait between Greenland and Iceland...
(850 meters) – this is much shallower than the Norwegian Sea. Cold deep water flows into the Atlantic through various channels: about 1.9 Sv through the Faroe Bank channel, 1.1 Sv through the Iceland-Faroe channel, and 0.1 Sv via the Wyville-Thomson Ridge. The turbulence that occurs when the deep water falls behind the Greenland-Scotland Ridge into the deep Atlantic basin mixes the adjacent water layers and forms the
North Atlantic Deep WaterNorth Atlantic Deep Water is a water mass that forms in the North Atlantic Ocean. It is largely formed in the Labrador Sea and in the Greenland Sea by the sinking of highly saline, dense overflow water from the Greenland Sea...
, one of two major deep-sea currents providing the deep ocean with oxygen.
Climate
The thermohaline circulation affects the climate in the Norwegian Sea, and the regional climate can significantly deviate from average. There is also a difference of about 10 °C between the sea and the coastline. Temperatures rose between 1920 and 1960, and the frequency of storms decreased in this period. The storminess was relatively high between 1880 and 1910, decreased significantly in 1910–1960, and then recovered to the original level.
In contrast to the Greenland Sea and Arctic seas, the Norwegian Sea is ice-free year round, owing to its warm currents. The convection between the relatively warm water and cold air in the winter plays an important role in the Arctic climate. The 10-degree July isotherm (air temperature line) runs through the northern boundary of the Norwegian Sea and is often taken as the southern boundary of the Arctic. In winter, the Norwegian Sea generally has the lowest air pressure in the entire Arctic and where most
Icelandic LowThe Icelandic Low is a semi-permanent centre of low atmospheric pressure found between Iceland and southern Greenland and extending in the Northern Hemisphere winter into the Barents Sea. In summer it weakens and splits into two centres, one near Davis Strait and the other west of Iceland...
depressions form. The water temperature in most parts of the sea is 2–7 °C in February and 8–12 °C in August.
Flora and fauna
The Norwegian Sea is a transition zone between
borealThe term boreal is usually applied to ecosystems localized in subarctic and subantarctic zones, although Austral is also used for the latter....
and Arctic conditions, and thus contains flora and fauna characteristic of both climatic regions. The southern limit of many Arctic species runs through the North Cape, Iceland, and the center of the Norwegian Sea, while the northern limit of boreal species lies near the borders of the Greenland Sea with the Norwegian Sea and Barents Sea; that is, these areas overlap. Some species like the
scallopA scallop is a marine bivalve mollusk of the family Pectinidae. Scallops are a cosmopolitan family, found in all of the world's oceans. Many scallops are highly prized as a food source...
Chlamys islandicaChlamys islandica, or the Iceland scallop, is a species of bivalve mollusc in the family Pectinidae. It can be found along the Atlantic coast of North America, ranging from Greenland to Massachusetts....
and
capelinThe capelin or caplin, Mallotus villosus, is a small forage fish of the smelt family found in the Atlantic and Arctic oceans. In summer, it grazes on dense swarms of plankton at the edge of the ice shelf. Larger capelin also eat a great deal of krill and other crustaceans...
tend to occupy this area between the Atlantic and Arctic Oceans.
Plankton and sea bottom organisms
Most of the aquatic life in the Norwegian Sea is concentrated in the upper layers. Estimates for the entire North Atlantic are that only 2% of biomass is produced at depths below 1,000 metres and only 1.2% occurs near the sea floor.
The blooming of the
phytoplanktonPhytoplankton are the autotrophic component of the plankton community. The name comes from the Greek words φυτόν , meaning "plant", and πλαγκτός , meaning "wanderer" or "drifter". Most phytoplankton are too small to be individually seen with the unaided eye...
is dominated by
chlorophyllChlorophyll is a green pigment found in almost all plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. Its name is derived from the Greek words χλωρος, chloros and φύλλον, phyllon . Chlorophyll is an extremely important biomolecule, critical in photosynthesis, which allows plants to obtain energy from light...
and peaks around 20 May. The major phytoplankton forms are diatoms, in particular the genus
Thalassiosira and
ChaetocerosChaetoceros is probably the largest genus of marine planktonic diatoms with approximately 400 species described. Although a large number of these descriptions are no longer valid. It is often very difficult to distinguish between different Chaetoceros species...
. After the spring bloom the haptophytes of the genus
Phaecocystis pouchetti become dominant.
Zooplankton is mostly represented by the copepods
Calanus finmarchicus and
Calanus hyperboreus, where the former occurs about four times more often than the latter and is mostly found in the Atlantic streams, whereas
C. hyperboreus dominates the Arctic waters; they are the main diet of most marine predators. The most important krill species are
Meganyctiphanes norvegicaNorthern krill, Meganyctiphanes norvegica, is a species of krill that lives in the North Atlantic Ocean. It is an important component of the zooplankton, providing food for whales, fish and birds. M...
,
Thyssanoessa inermis, and
Thyssanoessa longicaudata. In contrast to the Greenland Sea, there is a significant presence of
calcareousCalcareous is an adjective meaning mostly or partly composed of calcium carbonate, in other words, containing lime or being chalky. The term is used in a wide variety of scientific disciplines.-In zoology:...
plankton (
CoccolithophoreCoccolithophores are single-celled algae, protists, and phytoplankton belonging to the division of haptophytes. They are distinguished by special calcium carbonate plates of uncertain function called coccoliths , which are important microfossils...
and
GlobigerinidaThe Globigerinida are a common group of foraminiferans that are found as marine plankton . They produce hyaline calcareous tests, and are known as fossils from the Jurassic period onwards. The group has included more than 100 genera and over 400 species, of which about 30 species are extant...
) in the Norwegian Sea. Plankton production strongly fluctuates between years. For example,
C. finmarchicus yield was 28 g/m² (dry weight) in 1995 and only 8 g/m² in 1997; this correspondingly affected the population of all its predators.
Shrimp of the species
Pandalus borealisPandalus borealis is a species of shrimp found in cold parts of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Many different common names are used, including pink shrimp, deepwater prawn, deep-sea prawn, great northern prawn, and northern shrimp.-Distribution:P...
play an important role in the diet of fish, particularly cod and
blue whitingThe blue whiting, Micromesistius poutassou, is one of the two species in the genus Micromesistius in the cod family, common in the North-East Atlantic ocean, from Morocco to Iceland and Spitsbergen. Blue whiting also occur in the North-West Atlantic ocean between Canada and Greenland. It has a...
, and mostly occur at depths between 200 and 300 metres. A special feature of the Norwegian Sea is extensive coral reefs of
Lophelia pertusaLophelia pertusa is a species of cold-water coral which grows in the deep waters throughout the North Atlantic ocean, as well as parts of the Caribbean Sea and Alboran Sea. L...
, which provide shelter to various fish species. Although these corals are widespread in many peripheral areas of the North Atlantic, they never reach such amounts and concentrations as at the Norwegian continental slopes. However, they are at risk due to increasing
trawlingTrawling is a method of fishing that involves pulling a fishing net through the water behind one or more boats. The net that is used for trawling is called a trawl....
, which mechanically destroys the coral reefs.
Fish
The Norwegian coastal waters are the most important spawning ground of the
herring populationsAtlantic herring is a fish in the family Clupeidae. It is one of the most abundant fish species on earth. Herring can be found on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean, congregating in large schools. They can grow up to in length and weigh more than...
of the North Atlantic, and the hatching occurs in March. The eggs float to the surface and are washed off the coast by the northward current. Whereas a small herring population remains in the fjords and along the northern Norwegian coast, the majority spends the summer in the Barents Sea, where it feeds on the rich plankton. Upon reaching puberty, herring returns to the Norwegian Sea. The herring stock varies greatly between years. It increased in the 1920s owing to the milder climate and then collapsed in the following decades until 1970; the decrease was, however, at least partly caused by overfishing. The biomass of young hatched herring declined from 11 million tonnes in 1956 to almost zero in 1970; that affected the ecosystem not only of the Norwegian Sea but also of the Barents Sea.

Enforcement of environmental and fishing regulations has resulted in partial recovery of the herring populations since 1987. This recovery was accompanied by a decline of capelin and cod stocks. While the capelin benefited from the reduced fishing, the temperature rise in the 1980s and competition for food with the herring resulted in a near disappearance of young capelin from the Norwegian Sea. Meanwhile, the elderly capelin population was quickly fished out. This also reduced the population of cod – a major predator of capelin – as the herring was still too small in numbers to replace the capelin in the cod's diet.
Blue whitingThe blue whiting, Micromesistius poutassou, is one of the two species in the genus Micromesistius in the cod family, common in the North-East Atlantic ocean, from Morocco to Iceland and Spitsbergen. Blue whiting also occur in the North-West Atlantic ocean between Canada and Greenland. It has a...
(
Micromesistius poutassou) has benefited from the decline of the herring and capelin stocks as it assumed the role of major predator of plankton. The blue whiting spawns near the British Isles. The sea currents carry their eggs to the Norwegian Sea, and the adults also swim there in order to benefit from the food supply. The young spend the summer and the winter until February in Norwegian coastal waters and then return to the warmer waters west of Scotland. The Norwegian Arctic cod mostly occurs in the Barents Sea and at the
SvalbardSvalbard is an archipelago in the Arctic, constituting the northernmost part of Norway. It is located north of mainland Europe, midway between mainland Norway and the North Pole. The group of islands range from 74° to 81° north latitude , and from 10° to 35° east longitude. Spitsbergen is the...
Archipelago. In the rest of the Norwegian Sea, it is found only during the reproduction season, at the Lofoten Islands, whereas
Pollachius virensPollachius virens is a species of marine fish in the Pollachius genus. Together with Pollachius pollachius it is generally referred to in the U.S. as Pollock. Other names include the Boston blues , coalfish and saithe in the UK.This species can be separated from P...
and
haddockThe haddock , also known as the offshore hake, is a marine fish distributed on both sides of the North Atlantic. Haddock is a popular food fish and is widely fished commercially....
spawn in the coastal waters.
MackerelMackerel is a common name applied to a number of different species of fish, mostly, but not exclusively, from the family Scombridae. They may be found in all tropical and temperate seas. Most live offshore in the oceanic environment but a few, like the Spanish mackerel , enter bays and can be...
is an important commercial fish. The coral reefs are populated by different species of the genus
SebastesSebastes is a genus of fish in the family Sebastidae , most of which have the common name of rockfish. Most of the world's almost 110 Sebastes species live in the north Pacific, although two live in the south Pacific/Atlantic and four Sebastes is a genus of fish in the family Sebastidae (though...
.
Mammals and birds
Significant numbers of
minkeMinke whale , or lesser rorqual, is a name given to two species of marine mammal belonging to a clade within the suborder of baleen whales. The minke whale was given its official designation by Lacepède in 1804, who described a dwarf form of Balænoptera acuto-rostrata...
,
humpbackThe humpback whale is a species of baleen whale. One of the larger rorqual species, adults range in length from and weigh approximately . The humpback has a distinctive body shape, with unusually long pectoral fins and a knobbly head. It is an acrobatic animal, often breaching and slapping the...
,
seiThe sei whale , Balaenoptera borealis, is a baleen whale, the third-largest rorqual after the blue whale and the fin whale. It inhabits most oceans and adjoining seas, and prefers deep offshore waters. It avoids polar and tropical waters and semi-enclosed bodies of water...
, and orca whales are present in the Norwegian Sea, and
white-beaked dolphinThe White-beaked dolphin is a marine mammal belonging to the family Delphinidae in the suborder Odontoceti .-Taxonomy:...
s occur in the coastal waters. Orcas and some other whales visit the sea in the summer months for feeding; their population is closely related to the herring stocks, and they follow the herring schools within the sea. With a total population of about 110,000, minke whales are by far the most common whales in the sea. They are hunted by Norway and Iceland, with a quota of about 1,000 per year in Norway. In contrast to the past, nowadays primarily their meat is consumed, rather than fat and oil.
The
bowhead whaleThe bowhead whale is a baleen whale of the right whale family Balaenidae in suborder Mysticeti. A stocky dark-colored whale without a dorsal fin, it can grow to in length. This thick-bodied species can weigh to , second only to the blue whale, although the bowhead's maximum length is less than...
used to be a major plankton predator, but it almost disappeared from the Norwegian Sea after intense whaling in the 19th century, and was temporarily extinct in the entire North Atlantic. Similarly, the
blue whaleThe blue whale is a marine mammal belonging to the suborder of baleen whales . At in length and or more in weight, it is the largest known animal to have ever existed....
used to form large groups between Jan Mayen and Spitsbergen, but is hardly present nowadays. Observations of northern bottlenose whales in the Norwegian Sea are rare.
[Klinowska, 1991, p. 320] Other large animals of the sea are
hoodedThe hooded seal is an arctic pinniped found only in the central and western North Atlantic ranging from Svalbard in the east to the Gulf of St...
and
harp sealThe harp seal or saddleback seal is a species of earless seal native to the northernmost Atlantic Ocean and adjacent parts of the Arctic Ocean. It now belongs to the monotypic genus Pagophilus. Its scientific name, Pagophilus groenlandicus, means "ice-lover from Greenland", and its synonym, Phoca...
s and
squidSquid are cephalopods of the order Teuthida, which comprises around 300 species. Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, bilateral symmetry, a mantle, and arms. Squid, like cuttlefish, have eight arms arranged in pairs and two, usually longer, tentacles...
.
Important waterfowl species of the Norwegian Sea are
puffinPuffins are any of three small species of auk in the bird genus Fratercula with a brightly coloured beak during the breeding season. These are pelagic seabirds that feed primarily by diving in the water. They breed in large colonies on coastal cliffs or offshore islands, nesting in crevices among...
,
kittiwakeThe kittiwakes are two closely related seabird species in the gull family Laridae, the Black-legged Kittiwake and the Red-legged Kittiwake . The epithets "Black-legged" and "Red-legged" are used to distinguish the two species in North America, but in Europe, where R...
and
guillemotGuillemots is the common name for several species of seabird in the auk family . In British use, the term comprises two genera: Uria and Cepphus. In North America the Uria species are called "murres" and only the Cepphus species are called "guillemots"...
. Puffins and guillemots also suffered from the collapse of the herring population, especially the puffins on the Lofoten Islands. The latter hardly had an alternative to herring and their population was approximately halved between 1969 and 1987.
Human activities
Norway, Iceland, and Denmark/Faroe Islands share the territorial waters of the Norwegian Sea, with the largest part belonging to the first. Norway has claimed
twelve-mile limitTerritorial waters, or a territorial sea, as defined by the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, is a belt of coastal waters extending at most from the baseline of a coastal state...
as territorial waters since 2004 and an exclusive economic zone of 200 miles since 1976. Consequently, due to the Norwegian islands of Svalbard and Jan Mayen, the southeast, northeast and northwest edge of the sea fall within Norway. The southwest border is shared between Iceland and Denmark/Faroe Islands.
The largest damage to the Norwegian Sea was caused by extensive fishing, whaling, and pollution. The British nuclear complex of
SellafieldSellafield is a nuclear reprocessing site, close to the village of Seascale on the coast of the Irish Sea in Cumbria, England. The site is served by Sellafield railway station. Sellafield is an off-shoot from the original nuclear reactor site at Windscale which is currently undergoing...
is one of the greatest polluters, discharging radioactive waste into the sea. Other contamination is mostly by oil and toxic substances, but also from the great number of ships sunk during the two world wars. The environmental protection of the Norwegian Sea is mainly regulated by the
OSPARThe or OSPAR Convention is the current legislative instrument regulating international cooperation on environmental protection in the North-East Atlantic. It combines and up-dates the 1972 Oslo Convention on dumping waste at sea and the 1974 Paris Convention on land-based sources of marine pollution...
Convention.
Fishing and whaling
Fishing has been practised near the Lofoten archipelago for hundreds of years. The coastal waters of the remote Lofoten islands are one of the richest fishing areas in Europe, as most of the Atlantic cod swims to the coastal waters of Lofoten in the winter to spawn. So in the 19th century, dried cod was one of Norway's main exports and by far the most important industry in northern Norway. Strong sea currents,
maelstromA maelstrom is a very powerful whirlpool; a large, swirling body of water. A free vortex, it has considerable downdraft. The power of tidal whirlpools tends to be exaggerated by laymen. There are virtually no stories of large ships ever being sucked into a maelstrom, although smaller craft are in...
s, and especially frequent storms made fishing a dangerous occupation: several hundred men died on the "Fatal Monday" in March 1821, 300 of them from a single
parishA parish is a territorial unit historically under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of one parish priest, who might be assisted in his pastoral duties by a curate or curates - also priests but not the parish priest - from a more or less central parish church with its associated organization...
, and about a hundred boats with their crews were lost within a short time in April 1875.
Whaling was also important for the Norwegian Sea. In the early 1600s, the Englishman Stephen Bennet started hunting
walrusThe walrus is a large flippered marine mammal with a discontinuous circumpolar distribution in the Arctic Ocean and sub-Arctic seas of the Northern Hemisphere. The walrus is the only living species in the Odobenidae family and Odobenus genus. It is subdivided into three subspecies: the Atlantic...
at Bear Island. In May 1607 the
Muscovy CompanyThe Muscovy Company , was a trading company chartered in 1555. It was the first major chartered joint stock company, the precursor of the type of business that would soon flourish in England, and became closely associated with such famous names as Henry Hudson and William Baffin...
, while looking for the
Northwest PassageThe Northwest Passage is a sea route through the Arctic Ocean, along the northern coast of North America via waterways amidst the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans...
and exploring the sea, discovered the large populations of walrus and whales in the Norwegian Sea and started hunting them in 1610 near
SpitsbergenSpitsbergen is the largest and only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in Norway. Constituting the western-most bulk of the archipelago, it borders the Arctic Ocean, the Norwegian Sea and the Greenland Sea...
. Later in the 17th century, Dutch ships started hunting bowhead whales near
Jan MayenJan Mayen Island is a volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean and part of the Kingdom of Norway. It is long and 373 km2 in area, partly covered by glaciers . It has two parts: larger northeast Nord-Jan and smaller Sør-Jan, linked by an isthmus wide...
; the bowhead population between Svalbard and Jan Mayen was then about 25,000 individuals. Britons and Dutch were then joined by Germans,
DanesDenmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
, and Norwegians. Between 1615 and 1820, the waters between Jan Mayen, Svalbard, Bear Island, and Greenland, between the Norwegian, Greenland, and Barents Seas, were the most productive whaling area in the world. However, extensive hunting had wiped out the whales in that region by the early 20th century.
Sea monsters and maelstroms
For many centuries, the Norwegian Sea was regarded as the edge of the known world. The disappearance of ships there, due to the natural disasters, induced legends of monsters that stopped and sank ships (
krakenKraken are legendary sea monsters of giant proportions said to have dwelt off the coasts of Norway and Iceland.In modern German, Krake means octopus but can also refer to the legendary Kraken...
). As late as in 1845, the
Encyclopædia metropolitana contained a multi-page review by
Erik PontoppidanErik Pontoppidan was a Danish author, bishop, historian and antiquary, born in Aarhus August 24, 1698; died in Copenhagen December 20, 1764. He was educated in Fredericia , after which he was a private tutor in Norway, and then studied in Holland, and in London and Oxford, England...
(1698–1764) on ship-sinking sea monsters half a mile in size. Many legends might be based on the work
Historia de gentibus septentrionalibus of 1539 by
Olaus MagnusOlaus Magnus was a Swedish ecclesiastic and writer, who did pioneering work for the interest of Nordic people. He was reported as born in October 1490 in Östergötland, and died on August 1, 1557. Magnus, Latin for the Swedish Stor “great”, is a Latin family name taken personally, and not a...
, which described the kraken and maelstroms of the Norwegian Sea. The kraken also appears in Alfred Tennyson's poem of the same name, in Herman Melville's
Moby Dick, and in
Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the SeaTwenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea is a classic science fiction novel by French writer Jules Verne published in 1870. It tells the story of Captain Nemo and his submarine Nautilus as seen from the perspective of Professor Pierre Aronnax...
by
Jules VerneJules Gabriel Verne was a French author who pioneered the science fiction genre. He is best known for his novels Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea , A Journey to the Center of the Earth , and Around the World in Eighty Days...
.
Between the Lofoten islands of
MoskenesøyaMoskenesøya is an island in Lofoten in Nordland county of Norway. The island consists of an agglomeration of glaciated hills with the highest peak at . It is elongated from south-west to north east, is about 40 km long and 10 km wide, and has a very uneven shoreline...
and
VærøyVærøy is an island and municipality in Nordland county, Norway. It is part of the Lofoten traditional region. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Sørland. Værøy was established as a municipality on 1 January 1838...
, at the tiny
MoskenMosken is a small uninhabited rocky island in Lofoten archipelago in the Nordland county of Norway. It is located between the Værøy island to the south and Moskenesøy island to the north. The Moskenstraumen maelstrom – one of the most powerful in the world – is located at Mosken.-See also:* List of...
island, lies the Moskenstraumen – a system of
tidalTides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the moon and the sun and the rotation of the Earth....
eddiesIn fluid dynamics, an eddy is the swirling of a fluid and the reverse current created when the fluid flows past an obstacle. The moving fluid creates a space devoid of downstream-flowing fluid on the downstream side of the object...
and a
whirlpoolA whirlpool is a swirling body of water usually produced by ocean tides. The vast majority of whirlpools are not very powerful. More powerful ones are more properly termed maelstroms. Vortex is the proper term for any whirlpool that has a downdraft...
called a
maelstromA maelstrom is a very powerful whirlpool; a large, swirling body of water. A free vortex, it has considerable downdraft. The power of tidal whirlpools tends to be exaggerated by laymen. There are virtually no stories of large ships ever being sucked into a maelstrom, although smaller craft are in...
. With a speed on the order of 15 km/h (the value strongly varies between sources), it is one of the strongest maelstroms in the world. It was described in the 13th century in the
Old NorseOld Norse is a North Germanic language that was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and inhabitants of their overseas settlements during the Viking Age, until about 1300....
Poetic EddaThe Poetic Edda is a collection of Old Norse poems primarily preserved in the Icelandic mediaeval manuscript Codex Regius. Along with Snorri Sturluson's Prose Edda, the Poetic Edda is the most important extant source on Norse mythology and Germanic heroic legends, and from the early 19th century...
and remained an attractive subject for painters and writers, including
Edgar Allan PoeEdgar Allan Poe was an American author, poet, editor and literary critic, considered part of the American Romantic Movement. Best known for his tales of mystery and the macabre, Poe was one of the earliest American practitioners of the short story and is considered the inventor of the detective...
,
Walter MoersWalter Moers is one of the best-known and commercially most successful German comic creators and authors.-Life and work:...
and
Jules VerneJules Gabriel Verne was a French author who pioneered the science fiction genre. He is best known for his novels Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea , A Journey to the Center of the Earth , and Around the World in Eighty Days...
. The term maelstrom originates from the combination of Dutch words
malen (to grind) and
strom (stream); it was introduced into the English language by Poe in his story "
A Descent into the Maelström"A Descent into the Maelström" is a short story by Edgar Allan Poe. In the tale, a man recounts how he survived a shipwreck and a whirlpool. It has been grouped with Poe's tales of ratiocination and also labeled an early form of science fiction.-Plot:...
" (1841) describing the Moskenstraumen. The Moskenstraumen is created as a result of a combination of several factors, including the tides, the position of the Lofoten, and the underwater topography; unlike most other whirlpools, it is located in the open sea rather than in a channel or bay. With a diameter of 40–50 metres, it can be dangerous even in modern times to small fishing vessels that might be attracted by the abundant cod feeding on the microorganisms sucked in by the whirlpool.
Exploration
The fish-rich coastal waters of northern Norway have long been known and attracted skilled sailors from Iceland and Greenland. Thus most settlements in Iceland and Greenland were on the west coasts of the islands, which were also warmer due to the Atlantic currents. The first reasonably reliable map of northern Europe, the
Carta marinaThe Carta marina , created by Olaus Magnus in the 16th century, is the earliest map of the Nordic countries that gives details and placenames...
of 1539, represents the Norwegian Sea as coastal waters and shows nothing north of the North Cape. The Norwegian Sea off the coast regions appeared on the maps in the 17th century as an important part of the then sought
Northern Sea RouteThe Northern Sea Route is a shipping lane officially defined by Russian legislation from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean specifically running along the Russian Arctic coast from Murmansk on the Barents Sea, along Siberia, to the Bering Strait and Far East. The entire route lies in Arctic...
and a rich whaling ground.
Jan Mayen island was discovered in 1607 and become an important base of Dutch whalers. The Dutchman
Willem BarentsWillem Barentsz was a Dutch navigator, cartographer, explorer, and a leader of early expeditions to the far north....
discovered Bear Island and
SvalbardSvalbard is an archipelago in the Arctic, constituting the northernmost part of Norway. It is located north of mainland Europe, midway between mainland Norway and the North Pole. The group of islands range from 74° to 81° north latitude , and from 10° to 35° east longitude. Spitsbergen is the...
, which was then used by Russian whalers called
pomorsPomors or Pomory are Russian settlers and their descendants on the White Sea coast. It is also term of self-identification for the descendants of Russian, primarily Novgorod, settlers of Pomorye , living on the White Sea coasts and the territory whose southern border lies on a watershed which...
. The islands on the edge of the Norwegian Sea have been rapidly divided between nations. During the peaks of whaling, some 300 ships with 12,000 crew members were yearly visiting Svalbard.
The first
depth measurementsA sounding line or lead line is a length of thin rope with a plummet, generally of lead, at its end. Regardless of the actual composition of the plummet, it is still called a "lead."...
of the Norwegian Sea were performed in 1773 by
Constantine PhippsConstantine Phipps may refer to:*Constantine Phipps, 1st Baron Mulgrave *Constantine John Phipps, 2nd Baron Mulgrave, PC *Constantine Henry Phipps, 1st Marquess of Normanby, KG GCB GCH...
aboard HMS
Racehorse, as a part of his North Pole expedition. Systematic
oceanographic researchOceanography , also called oceanology or marine science, is the branch of Earth science that studies the ocean...
in the Norwegian Sea started in the late 19th century, when declines in the yields of cod and herring off the Lofoten prompted the Norwegian government to investigate the matter. The zoologist Georg Ossian Sars and meteorologist
Henrik MohnHenrik Mohn was a Norwegian astronomer and meteorologist. Although he enrolled in theology studies after finishing school, he is credited with founding meteorological research in Norway, being a professor at the Royal Frederick University and director of the Norwegian Meteorological Institute from...
persuaded the government in 1874 to send out a scientific expedition, and between 1876 and 1878 they explored much of the sea aboard
Vøringen. The data obtained allowed Mohn to establish the first dynamic model of ocean currents, which incorporated winds, pressure differences, sea water temperature, and salinity and agreed well with later measurements.
Navigation
Until the 20th century, the coasts of the Norwegian Sea were sparsely populated and therefore shipping in the sea was mostly focused on fishing, whaling, and occasional coastal transportation. Since the late 19th century, the
Norwegian Coastal ExpressHurtigruten or Hurtigruta is a Norwegian passenger and freight line with daily sailings along Norway's western and northern coast. Sometimes referred to in English as Norwegian Coastal Express, Hurtigruten ships sail almost the entire length of the country, completing the roundtrip journey in 11...
sea line has been established, connecting the more densely populated south with the north of Norway by at least one trip a day. The importance of shipping in the Norwegian Sea also increased with the expansion of the Russian and Soviet navies in the Barents Sea and development of international routes to the Atlantic through the
Baltic SeaThe Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
,
KattegatThe Kattegat , or Kattegatt is a sea area bounded by the Jutland peninsula and the Straits islands of Denmark on the west and south, and the provinces of Västergötland, Scania, Halland and Bohuslän in Sweden on the east. The Baltic Sea drains into the Kattegat through the Øresund and the Danish...
,
SkagerrakThe Skagerrak is a strait running between Norway and the southwest coast of Sweden and the Jutland peninsula of Denmark, connecting the North Sea and the Kattegat sea area, which leads to the Baltic Sea.-Name:...
, and
North SeaIn the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel connecting to the Atlantic Ocean. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively...
.
The Norwegian Sea is ice-free and provides a direct route from the Atlantic to the Russian ports in the Arctic (
MurmanskMurmansk is a city and the administrative center of Murmansk Oblast, Russia. It serves as a seaport and is located in the extreme northwest part of Russia, on the Kola Bay, from the Barents Sea on the northern shore of the Kola Peninsula, not far from Russia's borders with Norway and Finland...
,
ArchangelAn archangel is an angel of high rank. Archangels are found in a number of religious traditions, including Judaism, Christianity and Islam. Michael and Gabriel are recognized as archangels in Judaism and by most Christians. Michael is the only archangel specifically named in the Protestant Bible...
, and
KandalakshaKandalaksha is a town in Kandalakshsky District of Murmansk Oblast, Russia, located at the head of Kandalaksha Gulf on the White Sea, beyond the Arctic Circle. Population: 40,564 ; -History:The settlement has existed since the 11th century...
), which are directly linked to central Russia. This route was extensively used for supplies during World War II – of 811 US ships, 720 reached Russian ports, bringing some 4 million tonnes of cargo that included about 5,000 tanks and 7,000 aircraft. The Allies lost 18 convoys and 89 merchant ships on this route. The major operations of the German Navy against the convoys included PQ 17 in July 1942, the
Battle of the Barents SeaThe Battle of the Barents Sea took place on 31 December 1942 between German surface raiders and British ships escorting convoy JW 51B to Kola Inlet in the USSR. The action took place in the Barents Sea north of North Cape, Norway...
in December 1942, and the Battle of the North Cape in December 1943 and were carried out around the border between the Norwegian Sea and Barents Sea, near the North Cape.
Navigation across the Norwegian Sea declined after World War II and intensified only in the 1960s–70s with the expansion of the Soviet Northern Fleet, which was reflected in major joint naval exercises of the Soviet Northern Baltic fleets in the Norwegian Sea. The sea was the gateway for the Soviet Navy to the Atlantic Ocean and thus to the United States, and the major Soviet port of
MurmanskMurmansk is a city and the administrative center of Murmansk Oblast, Russia. It serves as a seaport and is located in the extreme northwest part of Russia, on the Kola Bay, from the Barents Sea on the northern shore of the Kola Peninsula, not far from Russia's borders with Norway and Finland...
was just behind the border of the Norwegian and Barents Sea. The countermeasures by the NATO countries resulted in a significant naval presence in the Norwegian Sea and intense cat-and-mouse games between Soviet and NATO aircraft, ships, and especially submarines. A relic of the Cold War in the Norwegian Sea, the Soviet nuclear submarine K-278 Komsomolets, sank in 1989 southwest of Bear Island, at the border of the Norwegian and Barents seas, with radioactive material onboard that poses potential danger to flora and fauna.
The Norwegian Sea is part of the
Northern Sea RouteThe Northern Sea Route is a shipping lane officially defined by Russian legislation from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean specifically running along the Russian Arctic coast from Murmansk on the Barents Sea, along Siberia, to the Bering Strait and Far East. The entire route lies in Arctic...
for ships from European ports to Asia. The travel distance from
RotterdamRotterdam is the second-largest city in the Netherlands and one of the largest ports in the world. Starting as a dam on the Rotte river, Rotterdam has grown into a major international commercial centre...
to
Tokyo, ; officially , is one of the 47 prefectures of Japan. Tokyo is the capital of Japan, the center of the Greater Tokyo Area, and the largest metropolitan area of Japan. It is the seat of the Japanese government and the Imperial Palace, and the home of the Japanese Imperial Family...
is 21,100 km via the
Suez CanalThe Suez Canal , also known by the nickname "The Highway to India", is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea. Opened in November 1869 after 10 years of construction work, it allows water transportation between Europe and Asia without navigation...
and only 14,100 km through the Norwegian Sea. Sea ice is a common problem in the Arctic seas, but ice-free conditions along the entire northern route wwere observed at the end of August 2008. Russia is planning to expand its offshore oil production in the Arctic , which should increase the traffic of tankers through the Norwegian Sea to markets in Europe and America; it is expected that the number of oil shipments through the northern Norwegian Sea will increase from 166 in 2002 to 615 in 2015.
Oil and gas
The most important products of the Norwegian Sea are no longer fish, but oil and especially gas found under the Norwegian Sea. Norway started undersea oil production in 1993, followed by development of the Huldra gas field in 2001. The large depth and harsh waters of the Norwegian Sea pose significant technical challenges for offshore drilling. Whereas drilling at depths exceeding 500 meters has been conducted since 1995, only a few deep gas fields have been explored commercially. The most important current project is Ormen Lange (depth 800-1,100 m), where gas production started in 2007. With reserves of 1.4 cubic feet, it is the major Norwegian gas field. It is connected to the Langeled pipeline, currently the world's longest underwater pipeline, and thus to a major European gas pipeline network. Several other gas fields are being developed. A particular challenge is the Kristin field, where the temperature is as high as 170 °C and the gas pressure exceeds 900 bar (900 times the normal pressure).
Further north are Norne and
SnøhvitSnøhvit is the name of a natural gas field in the Norwegian Sea, situated northwest of Hammerfest, Norway. The northern part of the Norwegian Sea is often described as the Barents Sea by offshore petroleum companies...
.
External links
The source of this article is
wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. The text of this article is licensed under the
GFDL.