
Normalized frequency (fiber optics)
Encyclopedia
In an optical fiber
, the normalized frequency, V (also called the V number), is given by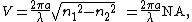
where a is the core radius, λ is the wavelength
in vacuum, n1 is the maximum refractive index
of the core, n2 is the refractive index of the homogeneous cladding, and applying the usual definition of the numerical aperture
NA.
In multimode operation of an optical fiber having a power-law refractive index profile, the approximate number of bound modes (the mode volume), is given by
where g is the profile parameter, and V is the normalized frequency, which must be greater than 5 for the approximation to be valid.
For a step index fiber, the mode volume is given by 4V2/π2. For single-mode operation is required that V < 2.405, which is the first root of the Bessel function
J0.
Optical fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
, the normalized frequency, V (also called the V number), is given by
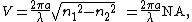
where a is the core radius, λ is the wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
in vacuum, n1 is the maximum refractive index
Refractive index
In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
of the core, n2 is the refractive index of the homogeneous cladding, and applying the usual definition of the numerical aperture
Numerical aperture
In optics, the numerical aperture of an optical system is a dimensionless number that characterizes the range of angles over which the system can accept or emit light. By incorporating index of refraction in its definition, NA has the property that it is constant for a beam as it goes from one...
NA.
In multimode operation of an optical fiber having a power-law refractive index profile, the approximate number of bound modes (the mode volume), is given by

where g is the profile parameter, and V is the normalized frequency, which must be greater than 5 for the approximation to be valid.
For a step index fiber, the mode volume is given by 4V2/π2. For single-mode operation is required that V < 2.405, which is the first root of the Bessel function
Bessel function
In mathematics, Bessel functions, first defined by the mathematician Daniel Bernoulli and generalized by Friedrich Bessel, are canonical solutions y of Bessel's differential equation:...
J0.

