Normal good
Overview
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
, normal goods are any goods for which demand
Demand (economics)
In economics, demand is the desire to own anything, the ability to pay for it, and the willingness to pay . The term demand signifies the ability or the willingness to buy a particular commodity at a given point of time....
increases when income increases and falls when income decreases but price remains constant, i.e. with a positive income elasticity of demand. The term does not necessarily refer to the quality of the good.
Depending on the indifference curve
Indifference curve
In microeconomic theory, an indifference curve is a graph showing different bundles of goods between which a consumer is indifferent. That is, at each point on the curve, the consumer has no preference for one bundle over another. One can equivalently refer to each point on the indifference curve...
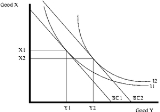
s, the amount of a good bought can either increase, decrease, or stay the same when income increases. In the diagram below, good Y is a normal good since the amount purchased increases from Y1 to Y2 as the budget constraint
Budget constraint
A budget constraint represents the combinations of goods and services that a consumer can purchase given current prices with his or her income. Consumer theory uses the concepts of a budget constraint and a preference map to analyze consumer choices...
shifts from BC1 to the higher income BC2.

