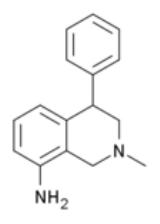
Nomifensine
Encyclopedia
Nomifensine is a norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor
developed by a team at Hoechst AG in the 1960s.. The drug was test-marketed in the United States
by Hoechst AG
(now Sanofi-Aventis
), i.e. a drug that increases the amount of synaptic norepinephrine and dopamine available to receptors by blocking the dopamine and norepinephrine reuptake transporters. This is a mechanism of action shared by some recreational drugs like cocaine
(see DRI
), and currently-available antidepressants (e.g. Bupropion
).
Nomifensine was investigated for use as an antidepressant in the 1970s, and was found to be a useful antidepressant at doses of 50-225 mg per day, both motivating and anxiolytic. There were relatively few adverse effects (mainly dry mouth, headache, nausea), the drug was not sedating, did not interact significantly with alcohol and lacked anticholinergic effects. No withdrawal symptoms were seen after 6 months treatment. The drug was however considered not suitable for agitated patients as it presumably made agitation worse.
Some case reports in the 1980s suggested that there was potential for psychological dependence on nomifensine, typically in patients with a history of stimulant addiction, or when the drug was used in very high doses (400-600mg per day).
In a 1989 study it has been investigated for use in treating adult ADHD and proven successful. In a 1977 study it has not proven of benefit in advanced parkinsonism, except for depression associated with the parkinsonism.
Nomifensine was withdrawn in the US, Canada and the UK for a risk of haemolytic anaemia.Some deaths were linked to immunohaemolytic anemia caused by this compound although the mechanism remained unclear.
Nomifensine is now mainly used in scientific research, particularly in studies involving dopamine release in response to addiction. This is because typically different areas of the brain have different amounts of dopamine transporter, but when Nomifensine is administered, a sufficient basal dopamine level is reached to allow comparison of dopamine release from drugs of abuse in different areas of the brain without the results being skewed by re-uptake speed variation.
Norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor
A norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor is a drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor for the neurotransmitters norepinephrine and dopamine by blocking the action of the norepinephrine transporter and the dopamine transporter , respectively...
developed by a team at Hoechst AG in the 1960s.. The drug was test-marketed in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
by Hoechst AG
Hoechst AG
Hoechst AG was a German chemicals then life-sciences company that became Aventis Deutschland after its merger with France's Rhône-Poulenc S.A. in 1999...
(now Sanofi-Aventis
Sanofi-Aventis
Sanofi S.A. is a multinational pharmaceutical company headquartered in Paris, France, the world's fourth-largest by prescription sales. Sanofi engages in the research and development, manufacturing and marketing of pharmaceutical products for sale principally in the prescription market, but the...
), i.e. a drug that increases the amount of synaptic norepinephrine and dopamine available to receptors by blocking the dopamine and norepinephrine reuptake transporters. This is a mechanism of action shared by some recreational drugs like cocaine
Cocaine
Cocaine is a crystalline tropane alkaloid that is obtained from the leaves of the coca plant. The name comes from "coca" in addition to the alkaloid suffix -ine, forming cocaine. It is a stimulant of the central nervous system, an appetite suppressant, and a topical anesthetic...
(see DRI
Dopamine reuptake inhibitor
A dopamine reuptake inhibitor is a type of drug that acts as a reuptake inhibitor for the neurotransmitter dopamine by blocking the action of the dopamine transporter...
), and currently-available antidepressants (e.g. Bupropion
Bupropion
Bupropion is an atypical antidepressant and smoking cessation aid. The drug is a non-tricyclic antidepressant and differs from most commonly prescribed antidepressants such as SSRIs, as its primary pharmacological action is thought to be norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibition...
).
Nomifensine was investigated for use as an antidepressant in the 1970s, and was found to be a useful antidepressant at doses of 50-225 mg per day, both motivating and anxiolytic. There were relatively few adverse effects (mainly dry mouth, headache, nausea), the drug was not sedating, did not interact significantly with alcohol and lacked anticholinergic effects. No withdrawal symptoms were seen after 6 months treatment. The drug was however considered not suitable for agitated patients as it presumably made agitation worse.
Some case reports in the 1980s suggested that there was potential for psychological dependence on nomifensine, typically in patients with a history of stimulant addiction, or when the drug was used in very high doses (400-600mg per day).
In a 1989 study it has been investigated for use in treating adult ADHD and proven successful. In a 1977 study it has not proven of benefit in advanced parkinsonism, except for depression associated with the parkinsonism.
Nomifensine was withdrawn in the US, Canada and the UK for a risk of haemolytic anaemia.Some deaths were linked to immunohaemolytic anemia caused by this compound although the mechanism remained unclear.
Nomifensine is now mainly used in scientific research, particularly in studies involving dopamine release in response to addiction. This is because typically different areas of the brain have different amounts of dopamine transporter, but when Nomifensine is administered, a sufficient basal dopamine level is reached to allow comparison of dopamine release from drugs of abuse in different areas of the brain without the results being skewed by re-uptake speed variation.

