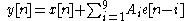Noise shaping
Encyclopedia
Noise shaping is a technique typically used in digital audio, image, and video processing, usually in combination with dithering, as part of the process of quantization
or bit-depth reduction of a digital signal. Its purpose is to increase the apparent signal to noise ratio of the resultant signal by altering the spectral shape of the error that is introduced by dithering and quantization such that the noise power is at a lower level in frequency bands at which noise is perceived to be more undesirable and at a correspondingly higher level in bands where it is perceived to be less undesirable. A popular noise shaping algorithm used in image processing is known as ‘Floyd Steinberg dithering’; many noise shaping algorithm used in audio processing are based on an ‘Absolute threshold of hearing
’ model.
loop. Any feedback loop functions as a filter
, so by creating a feedback loop for the error itself, the error can be filtered as desired. The simplest example would be
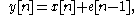
where y is the output sample value that is to be quantized
, x is the input sample value, n is the sample number, and e is the quantization error made at sample n (error when quantizing y[n]). This formula can also be read: The output sample is equal to the input sample plus the quantization error on previous sample.
Essentially, when any sample's bit depth is reduced, the quantization error between the rounded (truncated) value and the original value is measured and stored. That "error value" is then added to the next sample prior to its quantization. The effect here is that the quantization error itself (and not the valid signal) is put into a feedback loop. This simple example gives a single-pole
filter (a first-order Butterworth filter
), or a filter that rolls off 6 dB per octave. The cutoff frequency of the filter can be controlled by the amount of the error from the previous sample that is fed back. For example, changing the value for A1 in the formula
will change the frequency at which the feedback loop is centered.
More complex algorithms can be used which use more samples' errors' worth of feedback in order to create more complex curves. The formula
is that of a ninth order noise shaper, and can allow very complex noise shaping.
Noise shaping must also always involve an appropriate amount of dither within the process itself so as to prevent determinable and correlated errors to the signal itself. If dither is not used then noise shaping effectively functions merely as distortion shaping — pushing the distortion energy around to different frequency bands, but it is still distortion. If dither is added to the process as
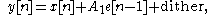
then the quantization error truly becomes noise, and the process indeed yields noise shaping.
s have been used in analog to digital converters. This involves sampling the audio at a very high rate (2.8224 million samples per second, for example) but only using a single bit. Because only 1 bit is used, this converter only has 6.02 dB of dynamic range
. The noise floor
, however, is spread throughout the entire "legal" frequency range below the Nyquist frequency
of 1.4112 MHz. Noise shaping is used to lower the noise present in the audible range (20 Hz to 20 kHz) and increase the noise above the audible range. This results in a broadband dynamic range of only 7.78 dB, but it is not consistent amongst frequency bands, and in the lowest frequencies (the audible range) the dynamic range is much greater — over 100 dB. Noise Shaping is inherently built into the delta-sigma modulators.
The 1 bit converter is the basis of the DSD
format by Sony. One criticism of the 1 bit converter (and thus the DSD system) is that because only 1 bit is used in both the signal and the feedback loop, adequate amounts of dither cannot be used in the feedback loop and distortion can be heard under some conditions. Most A/D converters made since 2000 use multi-bit or multi-level delta sigma modulators that yield more than 1 bit output so that proper dither can be added in the feedback loop. For traditional PCM
sampling the signal is then decimate
d to 44.1 ks/s or other appropriate sample rates.
Quantization (signal processing)
Quantization, in mathematics and digital signal processing, is the process of mapping a large set of input values to a smaller set – such as rounding values to some unit of precision. A device or algorithmic function that performs quantization is called a quantizer. The error introduced by...
or bit-depth reduction of a digital signal. Its purpose is to increase the apparent signal to noise ratio of the resultant signal by altering the spectral shape of the error that is introduced by dithering and quantization such that the noise power is at a lower level in frequency bands at which noise is perceived to be more undesirable and at a correspondingly higher level in bands where it is perceived to be less undesirable. A popular noise shaping algorithm used in image processing is known as ‘Floyd Steinberg dithering’; many noise shaping algorithm used in audio processing are based on an ‘Absolute threshold of hearing
Absolute threshold of hearing
The absolute threshold of hearing is the minimum sound level of a pure tone that an average ear with normal hearing can hear with no other sound present. The absolute threshold relates to the sound that can just be heard by the organism...
’ model.
How noise shaping works
Noise shaping works by putting the quantization error in a feedbackFeedback
Feedback describes the situation when output from an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or occurrences of the same Feedback describes the situation when output from (or information about the result of) an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or...
loop. Any feedback loop functions as a filter
Filter (signal processing)
In signal processing, a filter is a device or process that removes from a signal some unwanted component or feature. Filtering is a class of signal processing, the defining feature of filters being the complete or partial suppression of some aspect of the signal...
, so by creating a feedback loop for the error itself, the error can be filtered as desired. The simplest example would be
where y is the output sample value that is to be quantized
Quantization (signal processing)
Quantization, in mathematics and digital signal processing, is the process of mapping a large set of input values to a smaller set – such as rounding values to some unit of precision. A device or algorithmic function that performs quantization is called a quantizer. The error introduced by...
, x is the input sample value, n is the sample number, and e is the quantization error made at sample n (error when quantizing y[n]). This formula can also be read: The output sample is equal to the input sample plus the quantization error on previous sample.
Essentially, when any sample's bit depth is reduced, the quantization error between the rounded (truncated) value and the original value is measured and stored. That "error value" is then added to the next sample prior to its quantization. The effect here is that the quantization error itself (and not the valid signal) is put into a feedback loop. This simple example gives a single-pole
Complex analysis
Complex analysis, traditionally known as the theory of functions of a complex variable, is the branch of mathematical analysis that investigates functions of complex numbers. It is useful in many branches of mathematics, including number theory and applied mathematics; as well as in physics,...
filter (a first-order Butterworth filter
Butterworth filter
The Butterworth filter is a type of signal processing filter designed to have as flat a frequency response as possible in the passband so that it is also termed a maximally flat magnitude filter...
), or a filter that rolls off 6 dB per octave. The cutoff frequency of the filter can be controlled by the amount of the error from the previous sample that is fed back. For example, changing the value for A1 in the formula
will change the frequency at which the feedback loop is centered.
More complex algorithms can be used which use more samples' errors' worth of feedback in order to create more complex curves. The formula
is that of a ninth order noise shaper, and can allow very complex noise shaping.
Noise shaping must also always involve an appropriate amount of dither within the process itself so as to prevent determinable and correlated errors to the signal itself. If dither is not used then noise shaping effectively functions merely as distortion shaping — pushing the distortion energy around to different frequency bands, but it is still distortion. If dither is added to the process as
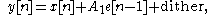
then the quantization error truly becomes noise, and the process indeed yields noise shaping.
Noise shaping in digital audio
Noise shaping in audio is most commonly done as a bit-reduction scheme. The quantization error from straight dither is flat, white noise. The ear, however, is less sensitive to certain frequencies than others at low levels (see Fletcher-Munson curves). By using noise shaping we can effectively spread the quantization error around so that more of it is focused on frequencies that we can't hear as well and less of it is focused on frequencies that we can hear. The result is that where the ear is most critical the quantization error can be reduced greatly and where our ears are less sensitive the noise is much greater. This can give a perceived noise reduction of 4 bits compared to straight dither.Noise shaping and 1-bit converters
Since around 1989, 1 bit delta-sigma modulatorDelta-sigma modulation
Delta-sigma modulation is a method for encoding high-resolution or analog signals into lower-resolution digital signals. The conversion is done using error feedback, where the difference between the two signals is measured and used to improve the conversion...
s have been used in analog to digital converters. This involves sampling the audio at a very high rate (2.8224 million samples per second, for example) but only using a single bit. Because only 1 bit is used, this converter only has 6.02 dB of dynamic range
Dynamic range
Dynamic range, abbreviated DR or DNR, is the ratio between the largest and smallest possible values of a changeable quantity, such as in sound and light. It is measured as a ratio, or as a base-10 or base-2 logarithmic value.-Dynamic range and human perception:The human senses of sight and...
. The noise floor
Noise floor
In signal theory, the noise floor is the measure of the signal created from the sum of all the noise sources and unwanted signals within a measurement system, where the noise is defined as any signal other than the one being monitored....
, however, is spread throughout the entire "legal" frequency range below the Nyquist frequency
Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem
The Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem, after Harry Nyquist and Claude Shannon, is a fundamental result in the field of information theory, in particular telecommunications and signal processing. Sampling is the process of converting a signal into a numeric sequence...
of 1.4112 MHz. Noise shaping is used to lower the noise present in the audible range (20 Hz to 20 kHz) and increase the noise above the audible range. This results in a broadband dynamic range of only 7.78 dB, but it is not consistent amongst frequency bands, and in the lowest frequencies (the audible range) the dynamic range is much greater — over 100 dB. Noise Shaping is inherently built into the delta-sigma modulators.
The 1 bit converter is the basis of the DSD
Direct Stream Digital
Direct-Stream Digital is the trademark name used by Sony and Philips for their system of recreating audible signals which uses pulse-density modulation encoding, a technology to store audio signals on digital storage media which is used for the Super Audio CD .The signal is stored as delta-sigma...
format by Sony. One criticism of the 1 bit converter (and thus the DSD system) is that because only 1 bit is used in both the signal and the feedback loop, adequate amounts of dither cannot be used in the feedback loop and distortion can be heard under some conditions. Most A/D converters made since 2000 use multi-bit or multi-level delta sigma modulators that yield more than 1 bit output so that proper dither can be added in the feedback loop. For traditional PCM
Pulse-code modulation
Pulse-code modulation is a method used to digitally represent sampled analog signals. It is the standard form for digital audio in computers and various Blu-ray, Compact Disc and DVD formats, as well as other uses such as digital telephone systems...
sampling the signal is then decimate
Decimation (signal processing)
In digital signal processing, decimation is a technique for reducing the number of samples in a discrete-time signal. The element which implements this technique is referred to as a decimator.Decimation is a two-step process:...
d to 44.1 ks/s or other appropriate sample rates.