
Network-attached storage
Encyclopedia
Network-attached storage (NAS) is file-level computer data storage connected to a computer network
providing data access to heterogeneous
clients. NAS not only operates as a file server
, but is specialized for this task either by its hardware, software, or configuration of those elements. NAS is often made as a computer appliance
– a specialized computer built from the ground up for storing and serving files – rather than simply a general purpose computer being used for the role.In this article "file server" is generally used as the term contrasting to NAS, referring to general-purpose computer used for serving files.
NAS devices are gaining popularity, as a convenient method of sharing files among multiple computers. Potential benefits of network-attached storage, compared to file servers, include faster data access, easier administration, and simple configuration.
NAS systems are networked appliances which contain one or more hard drives, often arranged into logical, redundant storage containers or RAID
arrays. Network-attached storage removes the responsibility of file serving from other servers on the network. They typically provide access to files using network file sharing protocols such as NFS, SMB
/CIFS, or AFP
.
A fully featured operating system is not needed on a NAS device, so often a stripped-down operating system is used. For example, FreeNAS
, an open source
NAS solution designed for commodity PC hardware, is implemented as a stripped-down version of FreeBSD
.
NAS systems contain one or more hard disks, often arranged into logical, redundant storage containers or RAID
arrays. NAS removes the responsibility of file serving from other servers on the network.
NAS uses file-based protocols such as NFS (popular on UNIX
systems), SMB/CIFS (Server Message Block/Common Internet File System) (used with MS Windows systems), or AFP
(used with Apple Macintosh
computers). NAS units rarely limit clients to a single protocol.
Both DAS and NAS can potentially increase availability of data by using RAID
or clustering
.
When both are served over the network, NAS could have better performance than DAS, because the NAS device can be tuned precisely for file serving which is less likely to happen on a server responsible for other processing. Both NAS and DAS can have various amount of cache memory, which greatly affects performance. When comparing use of NAS with use of local (non-networked) DAS, the performance of NAS depends mainly on the speed of and congestion on the network.
NAS is generally not as customizable in terms of hardware (CPU, memory, storage components) or software (extensions, plug-ins, additional protocols) as a general-purpose server supplied with DAS.
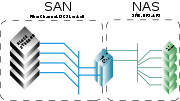 NAS provides both storage and a file system
NAS provides both storage and a file system
. This is often contrasted with SAN (Storage Area Network
), which provides only block-based storage and leaves file system concerns on the "client" side. SAN protocols are SCSI
, Fibre Channel
, iSCSI
, ATA over Ethernet
(AoE), or HyperSCSI
.
One way to loosely conceptualise the difference between a NAS and a SAN is that a NAS appears to the client OS (operating system) as a file server (the client can map network drives to shares on that server) whereas a disk available through a SAN still appears to the client OS as a disk, visible in disk and volume management utilities (along with client's local disks), and available to be formatted with a file system and mounted
.
Despite their differences, SAN and NAS are not mutually exclusive, and may be combined as a SAN-NAS hybrid, offering both file-level protocols (NAS) and block-level protocols (SAN) from the same system. An example of this is Openfiler
, a free software product running on Linux-based systems.
and his colleagues at Newcastle University demonstrated and developed remote file access across a set of UNIX machines. Novell
's NetWare server operating system and NCP
protocol was released in 1983. Following the Newcastle Connection, Sun Microsystems
' 1984 release of NFS allowed network servers to share their storage space with networked clients. 3Com and Microsoft
would develop the LAN Manager
software and protocol to further this new market. 3Com
's 3Server
and 3+Share
software was the first purpose-built server (including proprietary hardware, software, and multiple disks) for open systems servers.
Inspired by the success of file server
s from Novell, IBM
, and Sun, several firms developed dedicated file servers. While 3Com was among the first firms to build a dedicated NAS for desktop operating systems, Auspex Systems was one of the first to develop a dedicated NFS server for use in the UNIX market. A group of Auspex engineers split away in the early 1990s to create the integrated NetApp filer
, which supported both the Windows CIFS and the UNIX NFS protocols, and had superior scalability
and ease of deployment. This started the market for proprietary
NAS devices now led by NetApp and EMC Celerra.
Starting in the early 2000s, a series of startups emerged offering alternative solutions to single filer solutions in the form of clustered NAS – Spinnaker Networks (acquired by NetApp in February 2004), Exanet
(acquired by Dell
in February 2010), Gluster
(acquired by RedHat in 2011), ONStor (acquired by LSI in 2009), IBRIX (acquired by HP), Isilon (acquired by EMC), PolyServe (acquired by HP in 2007), and Panasas
, to name a few.
In 2009, NAS vendors (notably CTERA Networks and NETGEAR
) began to introduce Online Backup solutions integrated in their NAS appliances, for online disaster recovery.
, PowerPC
or MIPS
processors running an embedded Linux
operating system
.
NAS-oriented distributions of Linux
and FreeBSD
are available, including FreeNAS
, CryptoNAS, NASLite
, Gluster
, Openfiler
, OpenMediaVault
and the Ubuntu-based TurnKey File Server. These are designed to be easy to set up on commodity PC hardware, and are typically configured using a web browser.
They can run from a virtual machine
, Live CD
, bootable USB flash drive (Live USB
), or from one of the mounted hard drives. They run Samba
(an SMB
daemon), NFS daemon, and FTP
daemons which are freely available for those operating systems.
NexentaStor
, built on the Nexenta Core Platform, is similar in that it is built on open source foundations; however, NexentaStor requires more memory than consumer-oriented open source NAS solutions and also contains most of the features of enterprise class NAS solutions, such as snapshots, management utilities, tiering services, mirroring, and end-to-end checksumming due, in part, to the use of ZFS
.
across the cluster nodes or storage devices. Clustered NAS, like a traditional one, still provides unified access to the files from any of the cluster nodes, unrelated to the actual location of the data.
Computer network
A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information....
providing data access to heterogeneous
Heterogeneous computing
Heterogeneous computing systems refer to electronic systems that use a variety of different types of computational units. A computational unit could be a general-purpose processor , a special-purpose processor Heterogeneous computing systems refer to electronic systems that use a variety of...
clients. NAS not only operates as a file server
File server
In computing, a file server is a computer attached to a network that has the primary purpose of providing a location for shared disk access, i.e. shared storage of computer files that can be accessed by the workstations that are attached to the computer network...
, but is specialized for this task either by its hardware, software, or configuration of those elements. NAS is often made as a computer appliance
Computer appliance
A computer appliance is generally a separate and discrete hardware device with integrated software , specifically designed to provide a specific computing resource. These devices became known as "appliances" because of their similarity to home appliances, which are generally "closed and sealed" –...
– a specialized computer built from the ground up for storing and serving files – rather than simply a general purpose computer being used for the role.In this article "file server" is generally used as the term contrasting to NAS, referring to general-purpose computer used for serving files.
NAS devices are gaining popularity, as a convenient method of sharing files among multiple computers. Potential benefits of network-attached storage, compared to file servers, include faster data access, easier administration, and simple configuration.
NAS systems are networked appliances which contain one or more hard drives, often arranged into logical, redundant storage containers or RAID
RAID
RAID is a storage technology that combines multiple disk drive components into a logical unit...
arrays. Network-attached storage removes the responsibility of file serving from other servers on the network. They typically provide access to files using network file sharing protocols such as NFS, SMB
Server Message Block
In computer networking, Server Message Block , also known as Common Internet File System operates as an application-layer network protocol mainly used to provide shared access to files, printers, serial ports, and miscellaneous communications between nodes on a network. It also provides an...
/CIFS, or AFP
Apple Filing Protocol
The Apple Filing Protocol is a network protocol that offers file services for Mac OS X and original Mac OS. In Mac OS X, AFP is one of several file services supported including Server Message Block , Network File System , File Transfer Protocol , and WebDAV...
.
Description
A Network Attached Storage (NAS) unit is a computer connected to a network that only provides file-based data storage services to other devices on the network. Although it may technically be possible to run other software on a NAS unit, it is not designed to be a general purpose server. For example, NAS units usually do not have a keyboard or display, and are controlled and configured over the network, often using a browser.A fully featured operating system is not needed on a NAS device, so often a stripped-down operating system is used. For example, FreeNAS
FreeNAS
FreeNAS is a free network-attached storage server, supporting: CIFS , FTP, NFS, rsync, AFP protocols, iSCSI, S.M.A.R.T., local user authentication, and software RAID , with a web-based configuration interface. FreeNAS takes less than 64 MB once installed on CompactFlash, hard drive or USB flash...
, an open source
Open source
The term open source describes practices in production and development that promote access to the end product's source materials. Some consider open source a philosophy, others consider it a pragmatic methodology...
NAS solution designed for commodity PC hardware, is implemented as a stripped-down version of FreeBSD
FreeBSD
FreeBSD is a free Unix-like operating system descended from AT&T UNIX via BSD UNIX. Although for legal reasons FreeBSD cannot be called “UNIX”, as the direct descendant of BSD UNIX , FreeBSD’s internals and system APIs are UNIX-compliant...
.
NAS systems contain one or more hard disks, often arranged into logical, redundant storage containers or RAID
RAID
RAID is a storage technology that combines multiple disk drive components into a logical unit...
arrays. NAS removes the responsibility of file serving from other servers on the network.
NAS uses file-based protocols such as NFS (popular on UNIX
Unix
Unix is a multitasking, multi-user computer operating system originally developed in 1969 by a group of AT&T employees at Bell Labs, including Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, Brian Kernighan, Douglas McIlroy, and Joe Ossanna...
systems), SMB/CIFS (Server Message Block/Common Internet File System) (used with MS Windows systems), or AFP
Apple Filing Protocol
The Apple Filing Protocol is a network protocol that offers file services for Mac OS X and original Mac OS. In Mac OS X, AFP is one of several file services supported including Server Message Block , Network File System , File Transfer Protocol , and WebDAV...
(used with Apple Macintosh
Macintosh
The Macintosh , or Mac, is a series of several lines of personal computers designed, developed, and marketed by Apple Inc. The first Macintosh was introduced by Apple's then-chairman Steve Jobs on January 24, 1984; it was the first commercially successful personal computer to feature a mouse and a...
computers). NAS units rarely limit clients to a single protocol.
NAS vs DAS
The key difference between direct-attached storage (DAS) and NAS is that DAS is simply an extension to an existing server and is not necessarily networked. NAS is designed as an easy and self-contained solution for sharing files over the network.Both DAS and NAS can potentially increase availability of data by using RAID
RAID
RAID is a storage technology that combines multiple disk drive components into a logical unit...
or clustering
Cluster (computing)
A computer cluster is a group of linked computers, working together closely thus in many respects forming a single computer. The components of a cluster are commonly, but not always, connected to each other through fast local area networks...
.
When both are served over the network, NAS could have better performance than DAS, because the NAS device can be tuned precisely for file serving which is less likely to happen on a server responsible for other processing. Both NAS and DAS can have various amount of cache memory, which greatly affects performance. When comparing use of NAS with use of local (non-networked) DAS, the performance of NAS depends mainly on the speed of and congestion on the network.
NAS is generally not as customizable in terms of hardware (CPU, memory, storage components) or software (extensions, plug-ins, additional protocols) as a general-purpose server supplied with DAS.
NAS vs SAN

File system
A file system is a means to organize data expected to be retained after a program terminates by providing procedures to store, retrieve and update data, as well as manage the available space on the device which contain it. A file system organizes data in an efficient manner and is tuned to the...
. This is often contrasted with SAN (Storage Area Network
Storage area network
A storage area network is a dedicated network that provides access to consolidated, block level data storage. SANs are primarily used to make storage devices, such as disk arrays, tape libraries, and optical jukeboxes, accessible to servers so that the devices appear like locally attached devices...
), which provides only block-based storage and leaves file system concerns on the "client" side. SAN protocols are SCSI
SCSI
Small Computer System Interface is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, and electrical and optical interfaces. SCSI is most commonly used for hard disks and tape drives, but it...
, Fibre Channel
Fibre Channel
Fibre Channel, or FC, is a gigabit-speed network technology primarily used for storage networking. Fibre Channel is standardized in the T11 Technical Committee of the InterNational Committee for Information Technology Standards , an American National Standards Institute –accredited standards...
, iSCSI
ISCSI
In computing, iSCSI , is an abbreviation of Internet Small Computer System Interface, an Internet Protocol -based storage networking standard for linking data storage facilities. By carrying SCSI commands over IP networks, iSCSI is used to facilitate data transfers over intranets and to manage...
, ATA over Ethernet
ATA over Ethernet
ATA over Ethernet is a network protocol developed by the Brantley Coile Company, designed for simple, high-performance access of SATA storage devices over Ethernet networks. It is used to build storage area networks with low-cost, standard technologies.- Protocol description :AoE runs on layer 2...
(AoE), or HyperSCSI
HyperSCSI
HyperSCSI was a computer network protocol for accessing storage by sending and receiving SCSI commands.It was developed by researchers at the Data Storage Institute in Singapore in 2000 to 2003....
.
One way to loosely conceptualise the difference between a NAS and a SAN is that a NAS appears to the client OS (operating system) as a file server (the client can map network drives to shares on that server) whereas a disk available through a SAN still appears to the client OS as a disk, visible in disk and volume management utilities (along with client's local disks), and available to be formatted with a file system and mounted
Mount (computing)
Mounting takes place before a computer can use any kind of storage device . The user or their operating system must make it accessible through the computer's file system. A user can access only files on mounted media.- Mount point :A mount point is a physical location in the partition used as a...
.
Despite their differences, SAN and NAS are not mutually exclusive, and may be combined as a SAN-NAS hybrid, offering both file-level protocols (NAS) and block-level protocols (SAN) from the same system. An example of this is Openfiler
Openfiler
Openfiler is an operating system that provides file-based network-attached storage and block-based storage area network. It was created by Xinit Systems, and is based on the rPath Linux distribution. It is free software licensed under the GNU General Public License version 2...
, a free software product running on Linux-based systems.
History
In the early 1980s, the "Newcastle Connection" by Brian RandellBrian Randell
Brian Randell is a British computer scientist, and Emeritus Professor at the School of Computing Science, Newcastle University, U.K. He specializes in research in software fault tolerance and dependability, and is a noted authority on the early prior to 1950 history of computers.- Biography...
and his colleagues at Newcastle University demonstrated and developed remote file access across a set of UNIX machines. Novell
Novell
Novell, Inc. is a multinational software and services company. It is a wholly owned subsidiary of The Attachmate Group. It specializes in network operating systems, such as Novell NetWare; systems management solutions, such as Novell ZENworks; and collaboration solutions, such as Novell Groupwise...
's NetWare server operating system and NCP
NetWare Core Protocol
The NetWare Core Protocol is a network protocol used in some products from Novell, Inc. It is usually associated with the NetWare operating system, but parts of it have been implemented on other platforms such as Linux, Windows NT and various flavors of Unix.It is used to access file, print,...
protocol was released in 1983. Following the Newcastle Connection, Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc. was a company that sold :computers, computer components, :computer software, and :information technology services. Sun was founded on February 24, 1982...
' 1984 release of NFS allowed network servers to share their storage space with networked clients. 3Com and Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American public multinational corporation headquartered in Redmond, Washington, USA that develops, manufactures, licenses, and supports a wide range of products and services predominantly related to computing through its various product divisions...
would develop the LAN Manager
LAN Manager
LAN Manager was a Network Operating System available from multiple vendors and developed by Microsoft in cooperation with 3Com Corporation. It was designed to succeed 3Com's 3+Share network server software which ran atop a heavily modified version of MS-DOS.-Development history:LAN Manager was...
software and protocol to further this new market. 3Com
3Com
3Com was a pioneering digital electronics manufacturer best known for its computer network infrastructure products. The company was co-founded in 1979 by Robert Metcalfe, Howard Charney, Bruce Borden, and Greg Shaw...
's 3Server
3Server
The 3Com 3Server was a headless dedicated network attached storage machine designed to run 3Com LAN server software.The companion product was the diskless 3Station network workstation, a dedicated client machine. However, 3Servers could also network with standard PC-compatibles and were commonly...
and 3+Share
3+Share
3+Share was a pioneering file and print sharing product from 3Com. Introduced in the early 1980s, 3+Share was competitive with Novell's NetWare in the open systems network server business throughout the 1980s....
software was the first purpose-built server (including proprietary hardware, software, and multiple disks) for open systems servers.
Inspired by the success of file server
File server
In computing, a file server is a computer attached to a network that has the primary purpose of providing a location for shared disk access, i.e. shared storage of computer files that can be accessed by the workstations that are attached to the computer network...
s from Novell, IBM
IBM
International Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas...
, and Sun, several firms developed dedicated file servers. While 3Com was among the first firms to build a dedicated NAS for desktop operating systems, Auspex Systems was one of the first to develop a dedicated NFS server for use in the UNIX market. A group of Auspex engineers split away in the early 1990s to create the integrated NetApp filer
NetApp filer
In computer storage, NetApp filer, known also as NetApp Fabric-Attached Storage , or NetApp's network attached storage device are NetApp's offering in the area of Storage Systems. A FAS functions in an enterprise-class Storage area network as well as a networked storage appliance...
, which supported both the Windows CIFS and the UNIX NFS protocols, and had superior scalability
Scalability
In electronics scalability is the ability of a system, network, or process, to handle growing amount of work in a graceful manner or its ability to be enlarged to accommodate that growth...
and ease of deployment. This started the market for proprietary
Proprietary hardware
Proprietary hardware is computer hardware which is owned by the proprietor.Historically, most early computer hardware was designed as proprietary until the 1980s, when IBM PC changed this paradigm...
NAS devices now led by NetApp and EMC Celerra.
Starting in the early 2000s, a series of startups emerged offering alternative solutions to single filer solutions in the form of clustered NAS – Spinnaker Networks (acquired by NetApp in February 2004), Exanet
Exanet
Exanet Ltd., was a software company which provides scalable network-attached storage software solutions to OEM partners....
(acquired by Dell
Dell
Dell, Inc. is an American multinational information technology corporation based in 1 Dell Way, Round Rock, Texas, United States, that develops, sells and supports computers and related products and services. Bearing the name of its founder, Michael Dell, the company is one of the largest...
in February 2010), Gluster
Gluster
Gluster Inc. is a software company that provides an open source platform for scale-out Public and Private Cloud Storage. The company is privately funded and headquartered in Sunnyvale, California with an engineering center in Bangalore, India. Gluster is funded by Nexus Venture Partners and Index...
(acquired by RedHat in 2011), ONStor (acquired by LSI in 2009), IBRIX (acquired by HP), Isilon (acquired by EMC), PolyServe (acquired by HP in 2007), and Panasas
Panasas
Panasas, Inc., is a private, multinational computer storage company based in Sunnyvale, California. It specializes in high-performance scale-out network-attached storage optimized for Linux clusters.- History :...
, to name a few.
In 2009, NAS vendors (notably CTERA Networks and NETGEAR
Netgear
Netgear is a U.S. manufacturer of computer networking equipment and other computer hardware....
) began to introduce Online Backup solutions integrated in their NAS appliances, for online disaster recovery.
Uses
NAS is useful for more than just general centralized storage provided to client computers in environments with large amounts of data. NAS can enable simpler and lower cost systems such as load-balancing and fault-tolerant email and web server systems by providing storage services. The potential emerging market for NAS is the consumer market where there is a large amount of multi-media data. Such consumer market appliances are now commonly available. Unlike their rackmounted counterparts, they are generally packaged in smaller form factors. The price of NAS appliances has plummeted in recent years, offering flexible network-based storage to the home consumer market for little more than the cost of a regular USB or FireWire external hard disk. Many of these home consumer devices are built around ARMARM architecture
ARM is a 32-bit reduced instruction set computer instruction set architecture developed by ARM Holdings. It was named the Advanced RISC Machine, and before that, the Acorn RISC Machine. The ARM architecture is the most widely used 32-bit ISA in numbers produced...
, PowerPC
PowerPC
PowerPC is a RISC architecture created by the 1991 Apple–IBM–Motorola alliance, known as AIM...
or MIPS
MIPS architecture
MIPS is a reduced instruction set computer instruction set architecture developed by MIPS Technologies . The early MIPS architectures were 32-bit, and later versions were 64-bit...
processors running an embedded Linux
Embedded Linux
Embedded Linux is the use of Linux in embedded computer systems such as mobile phones, personal digital assistants, media players, set-top boxes, and other consumer electronics devices, networking equipment, machine control, industrial automation, navigation equipment and medical instruments...
operating system
Operating system
An operating system is a set of programs that manage computer hardware resources and provide common services for application software. The operating system is the most important type of system software in a computer system...
.
Open source implementations
Open sourceOpen source
The term open source describes practices in production and development that promote access to the end product's source materials. Some consider open source a philosophy, others consider it a pragmatic methodology...
NAS-oriented distributions of Linux
Linux
Linux is a Unix-like computer operating system assembled under the model of free and open source software development and distribution. The defining component of any Linux system is the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released October 5, 1991 by Linus Torvalds...
and FreeBSD
FreeBSD
FreeBSD is a free Unix-like operating system descended from AT&T UNIX via BSD UNIX. Although for legal reasons FreeBSD cannot be called “UNIX”, as the direct descendant of BSD UNIX , FreeBSD’s internals and system APIs are UNIX-compliant...
are available, including FreeNAS
FreeNAS
FreeNAS is a free network-attached storage server, supporting: CIFS , FTP, NFS, rsync, AFP protocols, iSCSI, S.M.A.R.T., local user authentication, and software RAID , with a web-based configuration interface. FreeNAS takes less than 64 MB once installed on CompactFlash, hard drive or USB flash...
, CryptoNAS, NASLite
NASLite
NASLite is a commercial Linux distribution designed to turn conventional x86-based computers with PCI interface into a simple network-attached storage device. It fits onto a single 3½-inch High Density floppy disk formatted to 1.72MB. NASLite boots from the floppy disk and runs in a 4MB RAM disk...
, Gluster
Gluster
Gluster Inc. is a software company that provides an open source platform for scale-out Public and Private Cloud Storage. The company is privately funded and headquartered in Sunnyvale, California with an engineering center in Bangalore, India. Gluster is funded by Nexus Venture Partners and Index...
, Openfiler
Openfiler
Openfiler is an operating system that provides file-based network-attached storage and block-based storage area network. It was created by Xinit Systems, and is based on the rPath Linux distribution. It is free software licensed under the GNU General Public License version 2...
, OpenMediaVault
OpenMediaVault
OpenMediaVault is a free network-attached storage server, supporting: CIFS , FTP, NFS, rsync, AFP protocols, iSCSI, S.M.A.R.T., local user authentication, and software RAID , with a web-based configuration interface. OpenMediaVault is currently distributed as an ISO image and in source form...
and the Ubuntu-based TurnKey File Server. These are designed to be easy to set up on commodity PC hardware, and are typically configured using a web browser.
They can run from a virtual machine
Virtual machine
A virtual machine is a "completely isolated guest operating system installation within a normal host operating system". Modern virtual machines are implemented with either software emulation or hardware virtualization or both together.-VM Definitions:A virtual machine is a software...
, Live CD
Live CD
A live CD, live DVD, or live disc is a CD or DVD containing a bootable computer operating system. Live CDs are unique in that they have the ability to run a complete, modern operating system on a computer lacking mutable secondary storage, such as a hard disk drive...
, bootable USB flash drive (Live USB
Live USB
A live USB is a USB flash drive or a USB external hard disk drive containing a full operating system that can be booted. Live USBs are closely related to live CDs, but sometimes have the ability to persistently save settings and permanently install software packages back onto the USB device...
), or from one of the mounted hard drives. They run Samba
Samba (software)
Samba is a free software re-implementation, originally developed by Andrew Tridgell, of the SMB/CIFS networking protocol. As of version 3, Samba provides file and print services for various Microsoft Windows clients and can integrate with a Windows Server domain, either as a Primary Domain...
(an SMB
Server Message Block
In computer networking, Server Message Block , also known as Common Internet File System operates as an application-layer network protocol mainly used to provide shared access to files, printers, serial ports, and miscellaneous communications between nodes on a network. It also provides an...
daemon), NFS daemon, and FTP
File Transfer Protocol
File Transfer Protocol is a standard network protocol used to transfer files from one host to another host over a TCP-based network, such as the Internet. FTP is built on a client-server architecture and utilizes separate control and data connections between the client and server...
daemons which are freely available for those operating systems.
NexentaStor
NexentaStor
NexentaStor is a proprietary derivative operating system built by the developers of the open-source Nexenta OpenSolaris-distribution that has been optimized for use virtualized server environments NAS and iSCSI and Fibre Channel applications built around the ZFS file system...
, built on the Nexenta Core Platform, is similar in that it is built on open source foundations; however, NexentaStor requires more memory than consumer-oriented open source NAS solutions and also contains most of the features of enterprise class NAS solutions, such as snapshots, management utilities, tiering services, mirroring, and end-to-end checksumming due, in part, to the use of ZFS
ZFS
In computing, ZFS is a combined file system and logical volume manager designed by Sun Microsystems. The features of ZFS include data integrity verification against data corruption modes , support for high storage capacities, integration of the concepts of filesystem and volume management,...
.
Clustered NAS
A clustered NAS is a NAS that is using a distributed file system running simultaneously on multiple servers. The key difference between a clustered and traditional NAS is the ability to distribute (e.g. stripe) data and metadataMetadata
The term metadata is an ambiguous term which is used for two fundamentally different concepts . Although the expression "data about data" is often used, it does not apply to both in the same way. Structural metadata, the design and specification of data structures, cannot be about data, because at...
across the cluster nodes or storage devices. Clustered NAS, like a traditional one, still provides unified access to the files from any of the cluster nodes, unrelated to the actual location of the data.
List of network protocols used to serve NAS
- CIFS
- NFS
- FTP
- SFTPSSH file transfer protocolIn computing, the SSH File Transfer Protocol is a network protocol that provides file access, file transfer, and file management functionality over any reliable data stream...
- HTTP
- UPnP
- Apple Filing ProtocolApple Filing ProtocolThe Apple Filing Protocol is a network protocol that offers file services for Mac OS X and original Mac OS. In Mac OS X, AFP is one of several file services supported including Server Message Block , Network File System , File Transfer Protocol , and WebDAV...
(AFP) - rsyncRsyncrsync is a software application and network protocol for Unix-like and Windows systems which synchronizes files and directories from one location to another while minimizing data transfer using delta encoding when appropriate. An important feature of rsync not found in most similar...
- Andrew file systemAndrew file systemThe Andrew File System is a distributed networked file system which uses a set of trusted servers to present a homogeneous, location-transparent file name space to all the client workstations. It was developed by Carnegie Mellon University as part of the Andrew Project. It is named after Andrew...
(AFS)
See also
- List of NAS manufacturers
- File area network
- Storage area networkStorage area networkA storage area network is a dedicated network that provides access to consolidated, block level data storage. SANs are primarily used to make storage devices, such as disk arrays, tape libraries, and optical jukeboxes, accessible to servers so that the devices appear like locally attached devices...
(SAN) - Shared disk file system
- Disk enclosureDisk enclosureA disk enclosure is essentially a specialized chassis designed to hold and power disk drives while providing a mechanism to allow them to communicate to one or more separate computers. Drive enclosures provide power to the drives therein and convert the data sent across their native data bus into a...
- Network architectureNetwork architectureNetwork architecture is the design of a communications network. It is a framework for the specification of a network's physical components and their functional organization and configuration, its operational principles and procedures, as well as data formats used in its operation.In...
- Network File ControlNetwork File ControlNetwork File Control is a common point of "command and control" for file data—delivering a common set of network resident services, centrally defined and managed via policy, then applied across a heterogeneous file storage infrastructure. NFC's associated services are delivered "within the...
- Global NamespaceGlobal NamespaceA Global Namespace is a heterogeneous, enterprise-wide abstraction of all file information, open to dynamic customization based on user-defined parameters...
- Server (computing)Server (computing)In the context of client-server architecture, a server is a computer program running to serve the requests of other programs, the "clients". Thus, the "server" performs some computational task on behalf of "clients"...

