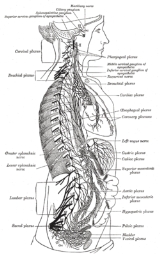
Nerve plexus
Encyclopedia
Nerve
A peripheral nerve, or simply nerve, is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of peripheral axons . A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses that are transmitted along each of the axons. Nerves are found only in the peripheral nervous system...
s. Except for the ventral rami of Th2-Th11 nerves, they combine sets of ventral rami of spinal
Vertebral column
In human anatomy, the vertebral column is a column usually consisting of 24 articulating vertebrae, and 9 fused vertebrae in the sacrum and the coccyx. It is situated in the dorsal aspect of the torso, separated by intervertebral discs...
nerves that serve the same area of the body into one large grouped nerve. There are several in the body, including:
- Cervical plexusCervical plexusThe cervical plexus is a plexus of the ventral rami of the first four cervical spinal nerves which are located from C1 to C4 cervical segment in the neck. They are located laterally to the transverse processes between prevertebral muscles from the medial side and vertebral from lateral side...
- serves the head, neck and shoulders - Brachial plexusBrachial plexusThe brachial plexus is a network of nerve fibers, running from the spine, formed by the ventral rami of the lower four cervical and first thoracic nerve roots...
- serves the chest, shoulders, arms and hands - Lumbar plexus - serves the back, abdomen, groin, thighs, knees, and calves
- Sacral plexusSacral plexus-External links:*...
- serves the pelvis, buttocks, genitals, thighs, calves, and feet - Solar plexus - serves internal organs
- Coccygeal plexusCoccygeal plexusThe coccygeal plexus is a plexus of nerves near the coccyx bone.-Structure:This plexus is formed by the fifth sacral nerve and the coccygeal nerve...
- serves a small region over the coccyx - Auerbach's plexusAuerbach's plexusA part of the enteric nervous system, Auerbach's plexus , exists between the longitudinal and circular layers of muscularis externa in the gastrointestinal tract and provides motor innervation to both layers of the mucosa, having both parasympathetic and sympathetic input, whereas Meissner's plexus...
- serves gastrointestinal tract
Cervical plexus
The Cervical plexusCervical plexus
The cervical plexus is a plexus of the ventral rami of the first four cervical spinal nerves which are located from C1 to C4 cervical segment in the neck. They are located laterally to the transverse processes between prevertebral muscles from the medial side and vertebral from lateral side...
(plexus cervicalis) is formed by the ventral rami of the upper four cervical nerves and the upper part of fifth cervical ventral ramus. The network of rami is located deep within the neck. The cervical plexus innervates muscles of the neck and areas of skin on the head, neck and chest. The deep branches innervate muscles, while the superficial branches supply areas of skin. A long branch (C4; nervus phrenicus) innervates muscles of the diaphragm
Diaphragm
-Optics and photography:* Diaphragm , a stop in the light path of a lens, having an aperture that regulates the amount of light that passes* Diaphragm shutter, a type of leaf shutter consisting of a number of thin blades in a camera-Acoustics:...
. Communications with cranial nerves vagus nerve [X.] and hypoglossal nerve [IX.] (nervus vagus et nervus hypoglossus) exist.
Brachial plexus
The Brachial plexusBrachial plexus
The brachial plexus is a network of nerve fibers, running from the spine, formed by the ventral rami of the lower four cervical and first thoracic nerve roots...
(plexus brachialis) is formed by the ventral rami of C5-C8-T1 spinal nerves, and lower and upper halves of C4 and T2 spinal nerves. The plexus extends toward the armpit (axilla). The roots of C5 and C6 form upper trunk (truncus superior), the ramus C7 forms the middle trunk (truncus medius), and the rami C8 and T1 join to form the lower trunk (tuncus inferior) of the brachial plexus. Under the clavicle, the trunks
Trunk
Trunk may refer to:In biology:*Trunk, an elephant's proboscis or nose*Trunk, torso*Trunk , a tree's central superstructureIn containers:*Trunk , a large storage compartment*Trunk...
(trunci) reorganize to form cords
Cord
Cord may refer to:* String or rope* Cord , a trimming made of multiple strands of yarn twisted together* The spinal cord* Cord Automobile, a former American car marque founded by Errett Lobban Cord* The cord , used to measure firewood...
(fasciculi) around the axillary artery
Axillary artery
In human anatomy, the axillary artery is a large blood vessel that conveys oxygenated blood to the lateral aspect of the thorax, the axilla and the upper limb...
(arteria axillaris). The lateral cord (fasciculus lateralis) is formed by the upper and middle trunk, all three trunks join to form the posterior cord (fasciculus posterior) , the lower trunk continues to the medial trunk (fasciculus medialis). The peripheral nerves (motor
Motor
Motor is a device that creates motion. It usually refers to an engine of some kind. It may also specifically refer to:*Electric motor, a machine that converts electricity into a mechanical motion...
and sensory
Sensory
Sensory may refer to:relating to senses or smellIn biology:* Sensory preference* Sensory system, part of the nervous system of organisms* Sensory neuron, nerve cell responsible for transmitting information about external stimuli...
fibers) to the shoulder
Shoulder
The human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle , the scapula , and the humerus as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons. The articulations between the bones of the shoulder make up the shoulder joints. The major joint of the shoulder is the glenohumeral joint, which...
and to the upper limb
Upper limb
The upper limb or upper extremity is the region in an animal extending from the deltoid region to the hand, including the arm, axilla and shoulder.-Definition:...
emerge from the brachial plexus.
Lumbar plexus
Since the Lumbar plexus and Sacral plexusSacral plexus
-External links:*...
are interconnected, they are sometimes referred to as the Lumbosacral plexus
Lumbosacral plexus
The anterior divisions of the lumbar nerves, sacral nerves, and coccygeal nerve form the lumbosacral plexus, the first lumbar nerve being frequently joined by a branch from the twelfth thoracic. For descriptive purposes this plexus is usually divided into three parts:* lumbar plexus* sacral plexus*...
. The intercostal nerves
Intercostal nerves
The intercostal nerves are the anterior divisions of the thoracic spinal nerves from T1 to T11.Each nerve is connected with the adjoining ganglion of the sympathetic trunk by a gray and a white ramus communicans...
that give rami to the chest and to the upper parts of the abdominal wall efferent
Efferent
Efferent is an anatomical term with the following meanings:*Conveying away from a center, for example the efferent arterioles conveying blood away from the Bowman's capsule in the kidney. Opposite to afferent....
motor
Motor
Motor is a device that creates motion. It usually refers to an engine of some kind. It may also specifically refer to:*Electric motor, a machine that converts electricity into a mechanical motion...
innervation and to the pleura and peritoneum
Peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane that forms the lining of the abdominal cavity or the coelom — it covers most of the intra-abdominal organs — in amniotes and some invertebrates...
afferent
Afferent
Afferent is an anatomical term with the following meanings:*Conveying towards a center, for example the afferent arterioles conveying blood towards the Bowman's capsule in the Kidney. Opposite to Efferent.*Something that so conducts, see Afferent nerve fiber...
sensory
Sensory
Sensory may refer to:relating to senses or smellIn biology:* Sensory preference* Sensory system, part of the nervous system of organisms* Sensory neuron, nerve cell responsible for transmitting information about external stimuli...
innervation are the only ones that do not originate from a plexus.
The ventral rami of L1-L5 spinal nerves with a contribution of T12 form Lumbar plexus. This plexus lies within the psoas major muscle
Psoas major muscle
-External links: - "Posterior Abdominal Wall: Muscles of the Posterior Abdominal Wall"* *...
. Nervi of the plexus serve the skin and the muscles of the lower abdominal wall, the tight
Tight
*High and tight, a hairstyle typical in the U.S. military*Tight end, a position in American football on the offensive team*Tight your black belt hard!, a popular judo manga in Japan*TighT, a psychedelic trance live act from KohPhangan, Thailand...
and external genitals. The largest nerve of the plexus is the femoral nerve
Femoral nerve
The femoral nerve, the largest branch of the lumbar plexus, arises from the dorsal divisions of the ventral rami of the second, third, and fourth lumbar nerves...
. It supplies anterior muscles of the tight and a part of skin distal to the inguinal ligament
Inguinal ligament
The inguinal ligament is a band running from the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine. Its anatomy is very important for operating on hernia patients.-Anatomy:...
.
Sacral plexus
Ventral rami of L4-S3 with parts of L4 and S4 spinal nerves form the Sacral plexusSacral plexus
-External links:*...
. It is located on the posterior wall of pelvic cavity
Pelvic cavity
-External links:* * *...
(pelvis minor). Nervi of the plexus innervate the perineal region, buttocks
Buttocks
The buttocks are two rounded portions of the anatomy, located on the posterior of the pelvic region of apes and humans, and many other bipeds or quadrupeds, and comprise a layer of fat superimposed on the gluteus maximus and gluteus medius muscles. Physiologically, the buttocks enable weight to...
and the lower limb
Lower limb
The lower limb is a limb of the body.According to Terminologia Anatomica, it includes the pelvic girdle, buttocks, hip, and thigh, as well as the components distal to the knee.-References:...
. The largest nerve of the human body, the sciatic nerve
Sciatic nerve
The sciatic nerve is a large nerve fiber in humans and other animals. It begins in the lower back and runs through the buttock and down the lower limb...
is the main branch, that give rami to the motor
Motor
Motor is a device that creates motion. It usually refers to an engine of some kind. It may also specifically refer to:*Electric motor, a machine that converts electricity into a mechanical motion...
innervation of the muscles of the foot
Foot
The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws...
, the leg
Leg
Łęg may refer to the following places in Poland:*A former name for the town of Ełk *Part of the Czyżyny district of Kraków*Łęg, Pleszew County in Greater Poland Voivodeship...
and the thigh
Thigh
In humans the thigh is the area between the pelvis and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb.The single bone in the thigh is called the femur...
. Common peroneal nerve and its branches innervate some part of the skin of the foot, the peroneal muscles of the leg and the dorsal muscles of the foot.
Coccygeal plexus
Coccygeal plexusCoccygeal plexus
The coccygeal plexus is a plexus of nerves near the coccyx bone.-Structure:This plexus is formed by the fifth sacral nerve and the coccygeal nerve...
originate from S4, S5, Co1 spinal nerves. (It is interconnected with the lower part of Sacral plexus). The only nerve of the plexus is the coccygeal nerve
Coccygeal nerve
-Structure:The coccygeal nerve is the 31st spinal nerve. It arises from the sacral plexus, and its ventral ramus helps form the coccygeal plexus. It does not divide into a medial and lateral branch...
, that serves sensory innervation of the skin in the coccygeal region.
See also:
- Autonomic plexusesAutonomic nervous systemThe autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils,...
- Autonomic nervous systemAutonomic nervous systemThe autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils,...
- Solar (celiac) plexusAutonomic nervous systemThe autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils,...
- Auerbach's plexusAutonomic nervous systemThe autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils,...
- Meissner's plexusAutonomic nervous systemThe autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils,...
Sources
- Henry Gray: Anatomy of the human body (Bartleby.com; Great Books Online)
- Richard S. Snell: Clinical neuroanatomy (Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Ed.6th 2006) Philadelphia, Baltimore, New York, London. ISBN 978 963 226 293 2
- Eldra P. Solomon - Richard R. Schmidt - Peter J. Adragna : Human anatomy & physiology ed. 2nd 1990 (Sunders College Publishing, Philadelphia) ISBN 0 03 011914 6
- Jochen Staubesand (Ed.); R. Putz, R. Pabst, Johannes Sobotta: Sobotta Atlas of Human Anatomy I-II. (Urban & Schwarzenberg, München 1982) ISBN 3-541-72710-1
Gallery

Nerve
A peripheral nerve, or simply nerve, is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of peripheral axons . A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses that are transmitted along each of the axons. Nerves are found only in the peripheral nervous system...
s. Except for the ventral rami of Th2-Th11 nerves, they combine sets of ventral rami of spinal
Vertebral column
In human anatomy, the vertebral column is a column usually consisting of 24 articulating vertebrae, and 9 fused vertebrae in the sacrum and the coccyx. It is situated in the dorsal aspect of the torso, separated by intervertebral discs...
nerves that serve the same area of the body into one large grouped nerve. There are several in the body, including:
- Cervical plexusCervical plexusThe cervical plexus is a plexus of the ventral rami of the first four cervical spinal nerves which are located from C1 to C4 cervical segment in the neck. They are located laterally to the transverse processes between prevertebral muscles from the medial side and vertebral from lateral side...
- serves the head, neck and shoulders - Brachial plexusBrachial plexusThe brachial plexus is a network of nerve fibers, running from the spine, formed by the ventral rami of the lower four cervical and first thoracic nerve roots...
- serves the chest, shoulders, arms and hands - Lumbar plexus - serves the back, abdomen, groin, thighs, knees, and calves
- Sacral plexusSacral plexus-External links:*...
- serves the pelvis, buttocks, genitals, thighs, calves, and feet - Solar plexus - serves internal organs
- Coccygeal plexusCoccygeal plexusThe coccygeal plexus is a plexus of nerves near the coccyx bone.-Structure:This plexus is formed by the fifth sacral nerve and the coccygeal nerve...
- serves a small region over the coccyx - Auerbach's plexusAuerbach's plexusA part of the enteric nervous system, Auerbach's plexus , exists between the longitudinal and circular layers of muscularis externa in the gastrointestinal tract and provides motor innervation to both layers of the mucosa, having both parasympathetic and sympathetic input, whereas Meissner's plexus...
- serves gastrointestinal tract
Cervical plexus
The Cervical plexusCervical plexus
The cervical plexus is a plexus of the ventral rami of the first four cervical spinal nerves which are located from C1 to C4 cervical segment in the neck. They are located laterally to the transverse processes between prevertebral muscles from the medial side and vertebral from lateral side...
(plexus cervicalis) is formed by the ventral rami of the upper four cervical nerves and the upper part of fifth cervical ventral ramus. The network of rami is located deep within the neck. The cervical plexus innervates muscles of the neck and areas of skin on the head, neck and chest. The deep branches innervate muscles, while the superficial branches supply areas of skin. A long branch (C4; nervus phrenicus) innervates muscles of the diaphragm
Diaphragm
-Optics and photography:* Diaphragm , a stop in the light path of a lens, having an aperture that regulates the amount of light that passes* Diaphragm shutter, a type of leaf shutter consisting of a number of thin blades in a camera-Acoustics:...
. Communications with cranial nerves vagus nerve [X.] and hypoglossal nerve [IX.] (nervus vagus et nervus hypoglossus) exist.
Brachial plexus
The Brachial plexusBrachial plexus
The brachial plexus is a network of nerve fibers, running from the spine, formed by the ventral rami of the lower four cervical and first thoracic nerve roots...
(plexus brachialis) is formed by the ventral rami of C5-C8-T1 spinal nerves, and lower and upper halves of C4 and T2 spinal nerves. The plexus extends toward the armpit (axilla). The roots of C5 and C6 form upper trunk (truncus superior), the ramus C7 forms the middle trunk (truncus medius), and the rami C8 and T1 join to form the lower trunk (tuncus inferior) of the brachial plexus. Under the clavicle, the trunks
Trunk
Trunk may refer to:In biology:*Trunk, an elephant's proboscis or nose*Trunk, torso*Trunk , a tree's central superstructureIn containers:*Trunk , a large storage compartment*Trunk...
(trunci) reorganize to form cords
Cord
Cord may refer to:* String or rope* Cord , a trimming made of multiple strands of yarn twisted together* The spinal cord* Cord Automobile, a former American car marque founded by Errett Lobban Cord* The cord , used to measure firewood...
(fasciculi) around the axillary artery
Axillary artery
In human anatomy, the axillary artery is a large blood vessel that conveys oxygenated blood to the lateral aspect of the thorax, the axilla and the upper limb...
(arteria axillaris). The lateral cord (fasciculus lateralis) is formed by the upper and middle trunk, all three trunks join to form the posterior cord (fasciculus posterior) , the lower trunk continues to the medial trunk (fasciculus medialis). The peripheral nerves (motor
Motor
Motor is a device that creates motion. It usually refers to an engine of some kind. It may also specifically refer to:*Electric motor, a machine that converts electricity into a mechanical motion...
and sensory
Sensory
Sensory may refer to:relating to senses or smellIn biology:* Sensory preference* Sensory system, part of the nervous system of organisms* Sensory neuron, nerve cell responsible for transmitting information about external stimuli...
fibers) to the shoulder
Shoulder
The human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle , the scapula , and the humerus as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons. The articulations between the bones of the shoulder make up the shoulder joints. The major joint of the shoulder is the glenohumeral joint, which...
and to the upper limb
Upper limb
The upper limb or upper extremity is the region in an animal extending from the deltoid region to the hand, including the arm, axilla and shoulder.-Definition:...
emerge from the brachial plexus.
Lumbar plexus
Since the Lumbar plexus and Sacral plexusSacral plexus
-External links:*...
are interconnected, they are sometimes referred to as the Lumbosacral plexus
Lumbosacral plexus
The anterior divisions of the lumbar nerves, sacral nerves, and coccygeal nerve form the lumbosacral plexus, the first lumbar nerve being frequently joined by a branch from the twelfth thoracic. For descriptive purposes this plexus is usually divided into three parts:* lumbar plexus* sacral plexus*...
. The intercostal nerves
Intercostal nerves
The intercostal nerves are the anterior divisions of the thoracic spinal nerves from T1 to T11.Each nerve is connected with the adjoining ganglion of the sympathetic trunk by a gray and a white ramus communicans...
that give rami to the chest and to the upper parts of the abdominal wall efferent
Efferent
Efferent is an anatomical term with the following meanings:*Conveying away from a center, for example the efferent arterioles conveying blood away from the Bowman's capsule in the kidney. Opposite to afferent....
motor
Motor
Motor is a device that creates motion. It usually refers to an engine of some kind. It may also specifically refer to:*Electric motor, a machine that converts electricity into a mechanical motion...
innervation and to the pleura and peritoneum
Peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane that forms the lining of the abdominal cavity or the coelom — it covers most of the intra-abdominal organs — in amniotes and some invertebrates...
afferent
Afferent
Afferent is an anatomical term with the following meanings:*Conveying towards a center, for example the afferent arterioles conveying blood towards the Bowman's capsule in the Kidney. Opposite to Efferent.*Something that so conducts, see Afferent nerve fiber...
sensory
Sensory
Sensory may refer to:relating to senses or smellIn biology:* Sensory preference* Sensory system, part of the nervous system of organisms* Sensory neuron, nerve cell responsible for transmitting information about external stimuli...
innervation are the only ones that do not originate from a plexus.
The ventral rami of L1-L5 spinal nerves with a contribution of T12 form Lumbar plexus. This plexus lies within the psoas major muscle
Psoas major muscle
-External links: - "Posterior Abdominal Wall: Muscles of the Posterior Abdominal Wall"* *...
. Nervi of the plexus serve the skin and the muscles of the lower abdominal wall, the tight
Tight
*High and tight, a hairstyle typical in the U.S. military*Tight end, a position in American football on the offensive team*Tight your black belt hard!, a popular judo manga in Japan*TighT, a psychedelic trance live act from KohPhangan, Thailand...
and external genitals. The largest nerve of the plexus is the femoral nerve
Femoral nerve
The femoral nerve, the largest branch of the lumbar plexus, arises from the dorsal divisions of the ventral rami of the second, third, and fourth lumbar nerves...
. It supplies anterior muscles of the tight and a part of skin distal to the inguinal ligament
Inguinal ligament
The inguinal ligament is a band running from the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine. Its anatomy is very important for operating on hernia patients.-Anatomy:...
.
Sacral plexus
Ventral rami of L4-S3 with parts of L4 and S4 spinal nerves form the Sacral plexusSacral plexus
-External links:*...
. It is located on the posterior wall of pelvic cavity
Pelvic cavity
-External links:* * *...
(pelvis minor). Nervi of the plexus innervate the perineal region, buttocks
Buttocks
The buttocks are two rounded portions of the anatomy, located on the posterior of the pelvic region of apes and humans, and many other bipeds or quadrupeds, and comprise a layer of fat superimposed on the gluteus maximus and gluteus medius muscles. Physiologically, the buttocks enable weight to...
and the lower limb
Lower limb
The lower limb is a limb of the body.According to Terminologia Anatomica, it includes the pelvic girdle, buttocks, hip, and thigh, as well as the components distal to the knee.-References:...
. The largest nerve of the human body, the sciatic nerve
Sciatic nerve
The sciatic nerve is a large nerve fiber in humans and other animals. It begins in the lower back and runs through the buttock and down the lower limb...
is the main branch, that give rami to the motor
Motor
Motor is a device that creates motion. It usually refers to an engine of some kind. It may also specifically refer to:*Electric motor, a machine that converts electricity into a mechanical motion...
innervation of the muscles of the foot
Foot
The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws...
, the leg
Leg
Łęg may refer to the following places in Poland:*A former name for the town of Ełk *Part of the Czyżyny district of Kraków*Łęg, Pleszew County in Greater Poland Voivodeship...
and the thigh
Thigh
In humans the thigh is the area between the pelvis and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb.The single bone in the thigh is called the femur...
. Common peroneal nerve and its branches innervate some part of the skin of the foot, the peroneal muscles of the leg and the dorsal muscles of the foot.
Coccygeal plexus
Coccygeal plexusCoccygeal plexus
The coccygeal plexus is a plexus of nerves near the coccyx bone.-Structure:This plexus is formed by the fifth sacral nerve and the coccygeal nerve...
originate from S4, S5, Co1 spinal nerves. (It is interconnected with the lower part of Sacral plexus). The only nerve of the plexus is the coccygeal nerve
Coccygeal nerve
-Structure:The coccygeal nerve is the 31st spinal nerve. It arises from the sacral plexus, and its ventral ramus helps form the coccygeal plexus. It does not divide into a medial and lateral branch...
, that serves sensory innervation of the skin in the coccygeal region.
See also:
- Autonomic plexusesAutonomic nervous systemThe autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils,...
- Autonomic nervous systemAutonomic nervous systemThe autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils,...
- Solar (celiac) plexusAutonomic nervous systemThe autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils,...
- Auerbach's plexusAutonomic nervous systemThe autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils,...
- Meissner's plexusAutonomic nervous systemThe autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils,...
Sources
- Henry Gray: Anatomy of the human body (Bartleby.com; Great Books Online)
- Richard S. Snell: Clinical neuroanatomy (Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Ed.6th 2006) Philadelphia, Baltimore, New York, London. ISBN 978 963 226 293 2
- Eldra P. Solomon - Richard R. Schmidt - Peter J. Adragna : Human anatomy & physiology ed. 2nd 1990 (Sunders College Publishing, Philadelphia) ISBN 0 03 011914 6
- Jochen Staubesand (Ed.); R. Putz, R. Pabst, Johannes Sobotta: Sobotta Atlas of Human Anatomy I-II. (Urban & Schwarzenberg, München 1982) ISBN 3-541-72710-1
Gallery

Nerve
A peripheral nerve, or simply nerve, is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of peripheral axons . A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses that are transmitted along each of the axons. Nerves are found only in the peripheral nervous system...
s. Except for the ventral rami of Th2-Th11 nerves, they combine sets of ventral rami of spinal
Vertebral column
In human anatomy, the vertebral column is a column usually consisting of 24 articulating vertebrae, and 9 fused vertebrae in the sacrum and the coccyx. It is situated in the dorsal aspect of the torso, separated by intervertebral discs...
nerves that serve the same area of the body into one large grouped nerve. There are several in the body, including:
- Cervical plexusCervical plexusThe cervical plexus is a plexus of the ventral rami of the first four cervical spinal nerves which are located from C1 to C4 cervical segment in the neck. They are located laterally to the transverse processes between prevertebral muscles from the medial side and vertebral from lateral side...
- serves the head, neck and shoulders - Brachial plexusBrachial plexusThe brachial plexus is a network of nerve fibers, running from the spine, formed by the ventral rami of the lower four cervical and first thoracic nerve roots...
- serves the chest, shoulders, arms and hands - Lumbar plexus - serves the back, abdomen, groin, thighs, knees, and calves
- Sacral plexusSacral plexus-External links:*...
- serves the pelvis, buttocks, genitals, thighs, calves, and feet - Solar plexus - serves internal organs
- Coccygeal plexusCoccygeal plexusThe coccygeal plexus is a plexus of nerves near the coccyx bone.-Structure:This plexus is formed by the fifth sacral nerve and the coccygeal nerve...
- serves a small region over the coccyx - Auerbach's plexusAuerbach's plexusA part of the enteric nervous system, Auerbach's plexus , exists between the longitudinal and circular layers of muscularis externa in the gastrointestinal tract and provides motor innervation to both layers of the mucosa, having both parasympathetic and sympathetic input, whereas Meissner's plexus...
- serves gastrointestinal tract
Cervical plexus
The Cervical plexusCervical plexus
The cervical plexus is a plexus of the ventral rami of the first four cervical spinal nerves which are located from C1 to C4 cervical segment in the neck. They are located laterally to the transverse processes between prevertebral muscles from the medial side and vertebral from lateral side...
(plexus cervicalis) is formed by the ventral rami of the upper four cervical nerves and the upper part of fifth cervical ventral ramus. The network of rami is located deep within the neck. The cervical plexus innervates muscles of the neck and areas of skin on the head, neck and chest. The deep branches innervate muscles, while the superficial branches supply areas of skin. A long branch (C4; nervus phrenicus) innervates muscles of the diaphragm
Diaphragm
-Optics and photography:* Diaphragm , a stop in the light path of a lens, having an aperture that regulates the amount of light that passes* Diaphragm shutter, a type of leaf shutter consisting of a number of thin blades in a camera-Acoustics:...
. Communications with cranial nerves vagus nerve [X.] and hypoglossal nerve [IX.] (nervus vagus et nervus hypoglossus) exist.
Brachial plexus
The Brachial plexusBrachial plexus
The brachial plexus is a network of nerve fibers, running from the spine, formed by the ventral rami of the lower four cervical and first thoracic nerve roots...
(plexus brachialis) is formed by the ventral rami of C5-C8-T1 spinal nerves, and lower and upper halves of C4 and T2 spinal nerves. The plexus extends toward the armpit (axilla). The roots of C5 and C6 form upper trunk (truncus superior), the ramus C7 forms the middle trunk (truncus medius), and the rami C8 and T1 join to form the lower trunk (tuncus inferior) of the brachial plexus. Under the clavicle, the trunks
Trunk
Trunk may refer to:In biology:*Trunk, an elephant's proboscis or nose*Trunk, torso*Trunk , a tree's central superstructureIn containers:*Trunk , a large storage compartment*Trunk...
(trunci) reorganize to form cords
Cord
Cord may refer to:* String or rope* Cord , a trimming made of multiple strands of yarn twisted together* The spinal cord* Cord Automobile, a former American car marque founded by Errett Lobban Cord* The cord , used to measure firewood...
(fasciculi) around the axillary artery
Axillary artery
In human anatomy, the axillary artery is a large blood vessel that conveys oxygenated blood to the lateral aspect of the thorax, the axilla and the upper limb...
(arteria axillaris). The lateral cord (fasciculus lateralis) is formed by the upper and middle trunk, all three trunks join to form the posterior cord (fasciculus posterior) , the lower trunk continues to the medial trunk (fasciculus medialis). The peripheral nerves (motor
Motor
Motor is a device that creates motion. It usually refers to an engine of some kind. It may also specifically refer to:*Electric motor, a machine that converts electricity into a mechanical motion...
and sensory
Sensory
Sensory may refer to:relating to senses or smellIn biology:* Sensory preference* Sensory system, part of the nervous system of organisms* Sensory neuron, nerve cell responsible for transmitting information about external stimuli...
fibers) to the shoulder
Shoulder
The human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle , the scapula , and the humerus as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons. The articulations between the bones of the shoulder make up the shoulder joints. The major joint of the shoulder is the glenohumeral joint, which...
and to the upper limb
Upper limb
The upper limb or upper extremity is the region in an animal extending from the deltoid region to the hand, including the arm, axilla and shoulder.-Definition:...
emerge from the brachial plexus.
Lumbar plexus
Since the Lumbar plexus and Sacral plexusSacral plexus
-External links:*...
are interconnected, they are sometimes referred to as the Lumbosacral plexus
Lumbosacral plexus
The anterior divisions of the lumbar nerves, sacral nerves, and coccygeal nerve form the lumbosacral plexus, the first lumbar nerve being frequently joined by a branch from the twelfth thoracic. For descriptive purposes this plexus is usually divided into three parts:* lumbar plexus* sacral plexus*...
. The intercostal nerves
Intercostal nerves
The intercostal nerves are the anterior divisions of the thoracic spinal nerves from T1 to T11.Each nerve is connected with the adjoining ganglion of the sympathetic trunk by a gray and a white ramus communicans...
that give rami to the chest and to the upper parts of the abdominal wall efferent
Efferent
Efferent is an anatomical term with the following meanings:*Conveying away from a center, for example the efferent arterioles conveying blood away from the Bowman's capsule in the kidney. Opposite to afferent....
motor
Motor
Motor is a device that creates motion. It usually refers to an engine of some kind. It may also specifically refer to:*Electric motor, a machine that converts electricity into a mechanical motion...
innervation and to the pleura and peritoneum
Peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane that forms the lining of the abdominal cavity or the coelom — it covers most of the intra-abdominal organs — in amniotes and some invertebrates...
afferent
Afferent
Afferent is an anatomical term with the following meanings:*Conveying towards a center, for example the afferent arterioles conveying blood towards the Bowman's capsule in the Kidney. Opposite to Efferent.*Something that so conducts, see Afferent nerve fiber...
sensory
Sensory
Sensory may refer to:relating to senses or smellIn biology:* Sensory preference* Sensory system, part of the nervous system of organisms* Sensory neuron, nerve cell responsible for transmitting information about external stimuli...
innervation are the only ones that do not originate from a plexus.
The ventral rami of L1-L5 spinal nerves with a contribution of T12 form Lumbar plexus. This plexus lies within the psoas major muscle
Psoas major muscle
-External links: - "Posterior Abdominal Wall: Muscles of the Posterior Abdominal Wall"* *...
. Nervi of the plexus serve the skin and the muscles of the lower abdominal wall, the tight
Tight
*High and tight, a hairstyle typical in the U.S. military*Tight end, a position in American football on the offensive team*Tight your black belt hard!, a popular judo manga in Japan*TighT, a psychedelic trance live act from KohPhangan, Thailand...
and external genitals. The largest nerve of the plexus is the femoral nerve
Femoral nerve
The femoral nerve, the largest branch of the lumbar plexus, arises from the dorsal divisions of the ventral rami of the second, third, and fourth lumbar nerves...
. It supplies anterior muscles of the tight and a part of skin distal to the inguinal ligament
Inguinal ligament
The inguinal ligament is a band running from the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine. Its anatomy is very important for operating on hernia patients.-Anatomy:...
.
Sacral plexus
Ventral rami of L4-S3 with parts of L4 and S4 spinal nerves form the Sacral plexusSacral plexus
-External links:*...
. It is located on the posterior wall of pelvic cavity
Pelvic cavity
-External links:* * *...
(pelvis minor). Nervi of the plexus innervate the perineal region, buttocks
Buttocks
The buttocks are two rounded portions of the anatomy, located on the posterior of the pelvic region of apes and humans, and many other bipeds or quadrupeds, and comprise a layer of fat superimposed on the gluteus maximus and gluteus medius muscles. Physiologically, the buttocks enable weight to...
and the lower limb
Lower limb
The lower limb is a limb of the body.According to Terminologia Anatomica, it includes the pelvic girdle, buttocks, hip, and thigh, as well as the components distal to the knee.-References:...
. The largest nerve of the human body, the sciatic nerve
Sciatic nerve
The sciatic nerve is a large nerve fiber in humans and other animals. It begins in the lower back and runs through the buttock and down the lower limb...
is the main branch, that give rami to the motor
Motor
Motor is a device that creates motion. It usually refers to an engine of some kind. It may also specifically refer to:*Electric motor, a machine that converts electricity into a mechanical motion...
innervation of the muscles of the foot
Foot
The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws...
, the leg
Leg
Łęg may refer to the following places in Poland:*A former name for the town of Ełk *Part of the Czyżyny district of Kraków*Łęg, Pleszew County in Greater Poland Voivodeship...
and the thigh
Thigh
In humans the thigh is the area between the pelvis and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb.The single bone in the thigh is called the femur...
. Common peroneal nerve and its branches innervate some part of the skin of the foot, the peroneal muscles of the leg and the dorsal muscles of the foot.
Coccygeal plexus
Coccygeal plexusCoccygeal plexus
The coccygeal plexus is a plexus of nerves near the coccyx bone.-Structure:This plexus is formed by the fifth sacral nerve and the coccygeal nerve...
originate from S4, S5, Co1 spinal nerves. (It is interconnected with the lower part of Sacral plexus). The only nerve of the plexus is the coccygeal nerve
Coccygeal nerve
-Structure:The coccygeal nerve is the 31st spinal nerve. It arises from the sacral plexus, and its ventral ramus helps form the coccygeal plexus. It does not divide into a medial and lateral branch...
, that serves sensory innervation of the skin in the coccygeal region.
See also:
- Autonomic plexusesAutonomic nervous systemThe autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils,...
- Autonomic nervous systemAutonomic nervous systemThe autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils,...
- Solar (celiac) plexusAutonomic nervous systemThe autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils,...
- Auerbach's plexusAutonomic nervous systemThe autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils,...
- Meissner's plexusAutonomic nervous systemThe autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils,...
Sources
- Henry Gray: Anatomy of the human body (Bartleby.com; Great Books Online)
- Richard S. Snell: Clinical neuroanatomy (Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Ed.6th 2006) Philadelphia, Baltimore, New York, London. ISBN 978 963 226 293 2
- Eldra P. Solomon - Richard R. Schmidt - Peter J. Adragna : Human anatomy & physiology ed. 2nd 1990 (Sunders College Publishing, Philadelphia) ISBN 0 03 011914 6
- Jochen Staubesand (Ed.); R. Putz, R. Pabst, Johannes Sobotta: Sobotta Atlas of Human Anatomy I-II. (Urban & Schwarzenberg, München 1982) ISBN 3-541-72710-1
Gallery
Image:Spinal nerve CAT.svg|Spinal nerve
Spinal nerve
The term spinal nerve generally refers to a mixed spinal nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body...
Image:Gray804.png|Cervical plexus
Cervical plexus
The cervical plexus is a plexus of the ventral rami of the first four cervical spinal nerves which are located from C1 to C4 cervical segment in the neck. They are located laterally to the transverse processes between prevertebral muscles from the medial side and vertebral from lateral side...
Image:Brachial plexus 2.svg|Anatomical illustration of the Brachial plexus
Brachial plexus
The brachial plexus is a network of nerve fibers, running from the spine, formed by the ventral rami of the lower four cervical and first thoracic nerve roots...
with areas of roots, trunks, divisions and cords marked. Clicking on names of branches will link to their Wikipedia entry.
Image:Lumbar_plexus.svg|The Lumbar plexus and its branches
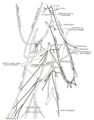
Image:Gray828.png|Plan of Sacral and Coccygeal plexuses
Plexus
A plexus is a part of nervous system. Plexus has a slightly different definition in vertebrates and in invertebrates.- In vertebrates :In vertebrates, a plexus is an area where nerves branch and rejoin. The electrical signals do not mix; rather, the fibres travel together with their electrical...
.

