
National parks of England and Wales
Encyclopedia
National Parks and Access to the Countryside Act 1949
The National Parks and Access to the Countryside Act 1949 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which created the National Parks Commission which later became the Countryside Commission and then the Countryside Agency, which became Natural England when it merged with English Nature in...
. Despite their similar name, national parks in England and Wales
Wales
Wales is a country that is part of the United Kingdom and the island of Great Britain, bordered by England to its east and the Atlantic Ocean and Irish Sea to its west. It has a population of three million, and a total area of 20,779 km²...
are quite different from national park
National park
A national park is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state declares or owns. Although individual nations designate their own national parks differently A national park is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state declares or...
s in many other countries, which are usually owned and managed by the government as a protected community resource, and which do not usually include permanent human communities. In England and Wales, designation as a national park may include substantial settlements and human land uses which are often integral parts of the landscape, and land within a national park remains largely in private ownership.
There are currently thirteen national parks in England and Wales. Each park is operated by its own national park authority
National Park Authority
A national park authority is a special term used in the United Kingdom for the legal body in charge of a national park. The powers and duties of the authorities are all similar, but do vary somewhat depending on the country in which they are situated....
, with two "statutory purposes":
- to conserve and enhance the natural beauty, wildlifeWildlifeWildlife includes all non-domesticated plants, animals and other organisms. Domesticating wild plant and animal species for human benefit has occurred many times all over the planet, and has a major impact on the environment, both positive and negative....
and cultural heritage of the area, and - to promote opportunities for the understanding and enjoyment of the park's special qualities by the public.
An estimated 110 million people visit the national parks of England and Wales each year. Recreation and tourism bring visitors and funds into the parks, to sustain their conservation
Conservation ethic
Conservation is an ethic of resource use, allocation, and protection. Its primary focus is upon maintaining the health of the natural world: its, fisheries, habitats, and biological diversity. Secondary focus is on materials conservation and energy conservation, which are seen as important to...
efforts and support the local population through jobs and businesses. These visitors also bring problems, such as erosion
Erosion
Erosion is when materials are removed from the surface and changed into something else. It only works by hydraulic actions and transport of solids in the natural environment, and leads to the deposition of these materials elsewhere...
and traffic congestion
Traffic congestion
Traffic congestion is a condition on road networks that occurs as use increases, and is characterized by slower speeds, longer trip times, and increased vehicular queueing. The most common example is the physical use of roads by vehicles. When traffic demand is great enough that the interaction...
, and conflicts over the use of the parks' resources. Access to cultivated land is restricted to bridleways, public footpaths, and permissive paths, with most (but not all) uncultivated areas in England and Wales having right of access for walking under the Countryside and Rights of Way Act 2000
Countryside and Rights of Way Act 2000
The Countryside and Rights of Way Act 2000 is a UK Act of Parliament which came into force on 30 November 2000.As of September 2007, not all sections of the Countryside and Rights of Way Act have yet come into force...
.
Untamed countryside
ArchaeologicalArchaeology
Archaeology, or archeology , is the study of human society, primarily through the recovery and analysis of the material culture and environmental data that they have left behind, which includes artifacts, architecture, biofacts and cultural landscapes...
evidence from prehistoric Britain
Prehistoric Britain
For the purposes of this article, Prehistoric Britain is that period of time between the first arrival of humans on the land mass now known as Great Britain and the start of recorded British history...
shows that the areas now designated as national parks have been occupied by humans since the Stone Age
Stone Age
The Stone Age is a broad prehistoric period, lasting about 2.5 million years , during which humans and their predecessor species in the genus Homo, as well as the earlier partly contemporary genera Australopithecus and Paranthropus, widely used exclusively stone as their hard material in the...
, at least 5,000 years ago and in some cases much earlier.
Before the 19th century, relatively wild, remote areas were often seen simply as uncivilised and dangerous. In 1725 Daniel Defoe
Daniel Defoe
Daniel Defoe , born Daniel Foe, was an English trader, writer, journalist, and pamphleteer, who gained fame for his novel Robinson Crusoe. Defoe is notable for being one of the earliest proponents of the novel, as he helped to popularise the form in Britain and along with others such as Richardson,...
described the High Peak
Peak District
The Peak District is an upland area in central and northern England, lying mainly in northern Derbyshire, but also covering parts of Cheshire, Greater Manchester, Staffordshire, and South and West Yorkshire....
as "the most desolate, wild and abandoned country in all England". However, by the early 19th century, romantic poets
Romantic poetry
Romanticism, a philosophical, literary, artistic and cultural era which began in the mid/late-1700s as a reaction against the prevailing Enlightenment ideals of the day , also influenced poetry...
such as Byron
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron, later George Gordon Noel, 6th Baron Byron, FRS , commonly known simply as Lord Byron, was a British poet and a leading figure in the Romantic movement...
, Coleridge
Samuel Taylor Coleridge
Samuel Taylor Coleridge was an English poet, Romantic, literary critic and philosopher who, with his friend William Wordsworth, was a founder of the Romantic Movement in England and a member of the Lake Poets. He is probably best known for his poems The Rime of the Ancient Mariner and Kubla...
and Wordsworth
William Wordsworth
William Wordsworth was a major English Romantic poet who, with Samuel Taylor Coleridge, helped to launch the Romantic Age in English literature with the 1798 joint publication Lyrical Ballads....
wrote about the inspirational beauty of the "untamed" countryside. Wordsworth described the Lake District
Lake District
The Lake District, also commonly known as The Lakes or Lakeland, is a mountainous region in North West England. A popular holiday destination, it is famous not only for its lakes and its mountains but also for its associations with the early 19th century poetry and writings of William Wordsworth...
as a "sort of national property in which every man has a right and interest who has an eye to perceive and a heart to enjoy" in 1810. This early vision, based in the Picturesque
Picturesque
Picturesque is an aesthetic ideal introduced into English cultural debate in 1782 by William Gilpin in Observations on the River Wye, and Several Parts of South Wales, etc. Relative Chiefly to Picturesque Beauty; made in the Summer of the Year 1770, a practical book which instructed England's...
movement, took over a century, and much controversy, to take legal form in the UK with the National Parks and Access to the Countryside Act 1949.
The idea for a form of national parks was first proposed in the United States in the 1860s, where National Parks were established to protect wilderness
Wilderness
Wilderness or wildland is a natural environment on Earth that has not been significantly modified by human activity. It may also be defined as: "The most intact, undisturbed wild natural areas left on our planet—those last truly wild places that humans do not control and have not developed with...
areas such as Yosemite
Yosemite National Park
Yosemite National Park is a United States National Park spanning eastern portions of Tuolumne, Mariposa and Madera counties in east central California, United States. The park covers an area of and reaches across the western slopes of the Sierra Nevada mountain chain...
. This model has been used in many other countries since, but not in the United Kingdom.
After thousands of years of human integration into the landscape, Britain lacks any substantial areas of wilderness. Furthermore, those areas of natural beauty so cherished by the romantic poets were often only maintained and managed in their existing state by human activity, usually agriculture.
Government support is established
By the early 1930s, increasing public interest in the countryside, coupled with the growing and newly mobile urban population, was generating increasing friction between those seeking access to the countryside and landowners. Alongside of direct action trespasses, such as the mass trespass of Kinder ScoutMass trespass of Kinder Scout
thumb|left|North flank of Kinder ScoutThe mass trespass of Kinder Scout was a notable act of willful trespass by ramblers. It was undertaken at Kinder Scout, Derbyshire, in the Peak District of England, on 24 April 1932, to highlight that walkers in England and Wales were denied access to areas of...
, several voluntary bodies took up the cause of public access in the political arena.
In 1931, Christopher Addison
Christopher Addison, 1st Viscount Addison
Sir Christopher Addison, 1st Viscount Addison KG, PC was a British medical doctor and politician. By turns a liberal and a socialist, he served as Minister of Munitions during the first World War, and was later Minister of Health under David Lloyd George and Leader of the House of Lords under...
(later Lord Addison) chaired a government committee that proposed a 'National Park Authority' to choose areas for designation as national parks. A system of national reserves and nature sanctuaries was proposed:
- "(i) to safeguard areas of exceptional natural interest against (a) disorderly development and (b) spoliation; (ii) to improve the means of access for pedestrians to areas of natural beauty; and (iii) to promote measures for the protection of flora and fauna."
However, no further action was taken after the intervention of the 1931 General Election
United Kingdom general election, 1931
The United Kingdom general election on Tuesday 27 October 1931 was the last in the United Kingdom not held on a Thursday. It was also the last election, and the only one under universal suffrage, where one party received an absolute majority of the votes cast.The 1931 general election was the...
.
The voluntary Standing Committee on National Parks first met on 26 May 1936 to put the case to the government for national parks in the UK. After World War II, the Labour Party
Labour Party (UK)
The Labour Party is a centre-left democratic socialist party in the United Kingdom. It surpassed the Liberal Party in general elections during the early 1920s, forming minority governments under Ramsay MacDonald in 1924 and 1929-1931. The party was in a wartime coalition from 1940 to 1945, after...
proposed the establishment of national parks as part of the post-war reconstruction of the UK. A report by John Dower
John Dower
John Gordon Dower was a civil servant and architect, who, as secretary of the Standing Committee on National Parks, produced in 1945 the first post-war official report which set out what National Parks in England and Wales should be like:This report, and a subsequent one by Sir Arthur Hobhouse,...
, secretary of the Standing Committee on National Parks, to the Minister of Town and Country Planning in 1945 was followed in 1947 by a Government committee, this time chaired by Sir Arthur Hobhouse
Arthur Hobhouse
Sir Arthur Lawrence Hobhouse was a long-serving English local government Liberal politician, who is best remembered as the architect of the system of National parks of England and Wales....
, which prepared legislation for national parks, and proposed 12 national parks. Sir Arthur had this to say on the criteria for designating suitable areas:
National Parks and Access to the Countryside Act 1949
The National Parks and Access to the Countryside Act 1949National Parks and Access to the Countryside Act 1949
The National Parks and Access to the Countryside Act 1949 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which created the National Parks Commission which later became the Countryside Commission and then the Countryside Agency, which became Natural England when it merged with English Nature in...
was passed with all party support. The first 10 national parks were designated as such in the 1950s under the Act in mostly poor-quality agricultural upland. Much of the land was still owned by individual landowners, often private estates, but there was also property owned by public bodies such as the Crown
The Crown
The Crown is a corporation sole that in the Commonwealth realms and any provincial or state sub-divisions thereof represents the legal embodiment of governance, whether executive, legislative, or judicial...
, or charities which allow and encourage access such as the National Trust
National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty
The National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, usually known as the National Trust, is a conservation organisation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland...
. Accessibility from the cities was also considered important.
Other areas were also considered: for example, parts of the coast of Cornwall
Cornwall
Cornwall is a unitary authority and ceremonial county of England, within the United Kingdom. It is bordered to the north and west by the Celtic Sea, to the south by the English Channel, and to the east by the county of Devon, over the River Tamar. Cornwall has a population of , and covers an area of...
were considered as a possible national park in the 1950s but were thought to be too disparate to form a single coherent national park and were eventually designated as an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB) instead. The north Pennines
Pennines
The Pennines are a low-rising mountain range, separating the North West of England from Yorkshire and the North East.Often described as the "backbone of England", they form a more-or-less continuous range stretching from the Peak District in Derbyshire, around the northern and eastern edges of...
were also considered for designation as a national park in the 1970s but the proposal was thought to be administratively too difficult because the area was administered by 5 different county council
County council
A county council is the elected administrative body governing an area known as a county. This term has slightly different meanings in different countries.-United Kingdom:...
s.
Later additions
The BroadsThe Broads
The Broads are a network of mostly navigable rivers and lakes in the English counties of Norfolk and Suffolk. The Broads, and some surrounding land were constituted as a special area with a level of protection similar to a UK National Park by The Norfolk and Suffolk Broads Act of 1988...
in East Anglia
East Anglia
East Anglia is a traditional name for a region of eastern England, named after an ancient Anglo-Saxon kingdom, the Kingdom of the East Angles. The Angles took their name from their homeland Angeln, in northern Germany. East Anglia initially consisted of Norfolk and Suffolk, but upon the marriage of...
are not in the strictest sense a National Park, being run by a separately constituted Broads Authority set up by a special Act of Parliament
Act of Parliament
An Act of Parliament is a statute enacted as primary legislation by a national or sub-national parliament. In the Republic of Ireland the term Act of the Oireachtas is used, and in the United States the term Act of Congress is used.In Commonwealth countries, the term is used both in a narrow...
in 1988 and with a structure in which conservation is subordinate to navigational concerns (see Sandford Principle below), but it is generally regarded as being "equivalent to" a national park.
The New Forest
New Forest
The New Forest is an area of southern England which includes the largest remaining tracts of unenclosed pasture land, heathland and forest in the heavily-populated south east of England. It covers south-west Hampshire and extends into south-east Wiltshire....
, which includes the largest remaining tracts of unenclosed pasture land, heathland
Heath (habitat)
A heath or heathland is a dwarf-shrub habitat found on mainly low quality acidic soils, characterised by open, low growing woody vegetation, often dominated by plants of the Ericaceae. There are some clear differences between heath and moorland...
and old-growth forest
Forest
A forest, also referred to as a wood or the woods, is an area with a high density of trees. As with cities, depending where you are in the world, what is considered a forest may vary significantly in size and have various classification according to how and what of the forest is composed...
in the heavily-populated south east
South East England
South East England is one of the nine official regions of England, designated in 1994 and adopted for statistical purposes in 1999. It consists of Berkshire, Buckinghamshire, East Sussex, Hampshire, Isle of Wight, Kent, Oxfordshire, Surrey and West Sussex...
of the country was designated as a National Park on March 1, 2005.
On 31 March 2009, Environment Secretary
Secretary of State for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs
The Secretary of State for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs is a UK cabinet-level position in charge of the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs, and the successor to the positions of Minister of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food and Secretary of State for the Environment, Transport...
Hilary Benn
Hilary Benn
Hilary James Wedgwood Benn is a British Labour Party politician who has been the Member of Parliament for Leeds Central since 1999. He served in the Cabinet as Secretary of State for International Development from 2003 to 2007 and as the Secretary of State for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs...
announced that the South Downs
South Downs
The South Downs is a range of chalk hills that extends for about across the south-eastern coastal counties of England from the Itchen Valley of Hampshire in the west to Beachy Head, near Eastbourne, East Sussex, in the east. It is bounded on its northern side by a steep escarpment, from whose...
would be designated a National Park. The South Downs National Park
South Downs National Park
The South Downs National Park is England's newest National Park, having become fully operational on 1 April 2011. The park, covering an area of in southern England, stretches for from Winchester in the west to Eastbourne in the east through the counties of Hampshire, West Sussex and East Sussex...
came into effect on 31 March 2010.
Organisation
Following the Environment Act 1995Environment Act 1995
The Environment Act 1995 is a United Kingdom Act of Parliament which created a number of new agencies and set new standards for environmental management...
, each national park has been managed by its own national park authority since April 1997. Previously, all but the Peak District
Peak District
The Peak District is an upland area in central and northern England, lying mainly in northern Derbyshire, but also covering parts of Cheshire, Greater Manchester, Staffordshire, and South and West Yorkshire....
and the Lake District
Lake District
The Lake District, also commonly known as The Lakes or Lakeland, is a mountainous region in North West England. A popular holiday destination, it is famous not only for its lakes and its mountains but also for its associations with the early 19th century poetry and writings of William Wordsworth...
were governed by the local county council
County council
A county council is the elected administrative body governing an area known as a county. This term has slightly different meanings in different countries.-United Kingdom:...
s. The Peak District
Peak District
The Peak District is an upland area in central and northern England, lying mainly in northern Derbyshire, but also covering parts of Cheshire, Greater Manchester, Staffordshire, and South and West Yorkshire....
and the Lake District
Lake District
The Lake District, also commonly known as The Lakes or Lakeland, is a mountainous region in North West England. A popular holiday destination, it is famous not only for its lakes and its mountains but also for its associations with the early 19th century poetry and writings of William Wordsworth...
, the first two national parks to be designated, were under the control of Planning Boards that were independent of the local county councils.
Each Authority is required to carry out two "statutory purposes":
- to conserve and enhance the natural beauty, wildlife and cultural heritage of the area; and
- to promote opportunities for the understanding and enjoyment of the parks' special qualities by the public.
These purposes can conflict: in such cases, under the "Sandford Principle
Sandford Principle
The Sandford Principle is a concept in the management of protected landscapes in the United Kingdom. It is called the Sandford Principle after Lord Sandford who chaired the National Parks Policy...
", conservation comes first. This principle was given statutory
Statute
A statute is a formal written enactment of a legislative authority that governs a state, city, or county. Typically, statutes command or prohibit something, or declare policy. The word is often used to distinguish law made by legislative bodies from case law, decided by courts, and regulations...
force by section 62 of the Environment Act 1995, although there are no explicit provisions as to how wildlife is to be preserved. In pursuing these purposes, National Park Authorities also have a duty to foster the social and economic well-being of their local communities.
Slightly over half the members of each national park authority are appointees from the principal local authorities covered by the park; the remainder are appointed by the Secretary of State for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs
Secretary of State for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs
The Secretary of State for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs is a UK cabinet-level position in charge of the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs, and the successor to the positions of Minister of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food and Secretary of State for the Environment, Transport...
, some to represent local parish councils
Civil parish
In England, a civil parish is a territorial designation and, where they are found, the lowest tier of local government below districts and counties...
, others selected to represent the "national interest". The Broads Authority also has members appointed by Natural England
Natural England
Natural England is the non-departmental public body of the UK government responsible for ensuring that England's natural environment, including its land, flora and fauna, freshwater and marine environments, geology and soils, are protected and improved...
, Great Yarmouth
Great Yarmouth
Great Yarmouth, often known to locals as Yarmouth, is a coastal town in Norfolk, England. It is at the mouth of the River Yare, east of Norwich.It has been a seaside resort since 1760, and is the gateway from the Norfolk Broads to the sea...
Port Authority and the Environment Agency
Environment Agency
The Environment Agency is a British non-departmental public body of the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs and an Assembly Government Sponsored Body of the Welsh Assembly Government that serves England and Wales.-Purpose:...
. The National Park and Broad Authorities are covered by similar regulatory controls to those applied to local councils.
Funding for national parks is complex, but the full cost of each Park Authority is funded from central government funds. In the past this was partly paid for by local authorities, and refunded to them from the government to varying degrees. In 2003/2004, the Park Authorities received around £35.5 million of central government funding.
Natural England
Natural England
Natural England is the non-departmental public body of the UK government responsible for ensuring that England's natural environment, including its land, flora and fauna, freshwater and marine environments, geology and soils, are protected and improved...
and the Countryside Council for Wales
Countryside Council for Wales
The Countryside Council for Wales is an Assembly Government Sponsored Body. It is the Welsh Assembly Government's wildlife conservation authority for Wales...
are the statutory bodies responsible for designating new national parks, subject to approval by the Secretary of State. The Association of National Park Authorities
Association of National Park Authorities
The Association of National Park Authorities is a body that exists to provide the National Park Authorities of England, Wales and Scotland with a single voice when dealing with government and its agencies...
exists to provide the Park Authorities with a single voice when dealing with government and its agencies. The Campaign for National Parks (formerly Council for National Parks) is a charity that works to protect and enhance the national parks of England and Wales.
Planning in national parks
National park authorities are strategic and local planning authorities for their areas. They are responsible for maintaining the Local Development Framework — the spatial planningSpatial planning
Spatial planning refers to the methods used by the public sector to influence the distribution of people and activities in spaces of various scales. Discrete professional disciplines which involve spatial planning include land use planning, urban planning, regional planning, transport planning and...
guide for their area. They also grant planning consent for development, within the constraints of the Framework. This gives them very considerable direct control over residential and industrial development, and the design of buildings and other structures; as well as strategic matters such as mineral extraction.
The national park authorities' planning powers vary only slightly from other authorities, but the policies and their interpretation are stricter than elsewhere. This is supported and encouraged by the Government who regard:
- "National Park designation as conferring the highest status of protection as far as landscape and scenic beauty are concerned." The Countryside — Environmental Quality and Economic and Social Development (1997)
Contribution to the local economy
Tourism is an important part of the economy of the regions which contain national parks. Through attractions, shops and accommodation, visitors provide an income and a livelihood to local employers and farmers. This income provides jobs for the park. For example, within the Peak District National Park the estimate in 2004 for visitor spending is £185 million, which supports over 3,400 jobs, representing 27% of total employment in the National Park.Conflicts in national parks
The national park authorities have two roles: to conserve and enhance the park, and to promote its use by visitors. These two objectives cause frequent conflicts between the needs of different groups of people. It is estimated that the national parks of England and Wales receive 110 million visitors each year. Although recreation and tourism brings many benefits to an area, it also brings a number of problems. The national funding offered to national park authorities is partly in recognition of the extra difficulties created in dealing with these conflicts.Congestion of villages and beauty spots : Some of the most popular "honeypot
Honeypot (geography)
In geography, a honeypot is a particularly popular visitor attraction which attracts tourists in large numbers. The term 'honeypot' originates from bees buzzing around a hive.-Tourism planning:...
" areas attract large numbers of visitors, resulting in overcrowded car parks, blocked roads, and overstretched local facilities, particularly on Sundays in the summer and on bank holiday
Bank Holiday
A bank holiday is a public holiday in the United Kingdom or a colloquialism for public holiday in Ireland. There is no automatic right to time off on these days, although the majority of the population is granted time off work or extra pay for working on these days, depending on their contract...
s. Examples include the areas near Keswick
Keswick, Cumbria
Keswick is a market town and civil parish within the Borough of Allerdale in Cumbria, England. It had a population of 4,984, according to the 2001 census, and is situated just north of Derwent Water, and a short distance from Bassenthwaite Lake, both in the Lake District National Park...
in the Lake District and Buxton
Buxton
Buxton is a spa town in Derbyshire, England. It has the highest elevation of any market town in England. Located close to the county boundary with Cheshire to the west and Staffordshire to the south, Buxton is described as "the gateway to the Peak District National Park"...
and Bakewell
Bakewell
Bakewell is a small market town in the Derbyshire Dales district of Derbyshire, England, deriving its name from 'Beadeca's Well'. It is the only town included in the Peak District National Park, and is well known for the local confection Bakewell Pudding...
in the Peak District.
Erosion : Hill-walking and use of other public rights-of-way is an extremely popular use of all the national parks. Heavy use of the most popular paths leads to considerable erosion, but strengthening of paths can be unsightly. Particularly heavy wear is caused by sponsored walks, walks promoted by national books and magazines, by horse riding
Trail riding
Trail riding sometimes called horse or pony trekking is riding outdoors on natural trails and roads as opposed to riding in an enclosed area such as a riding arena. The term may encompass those who travel on horses, on mountain bikes, or on motorcycles and other motorized all-terrain vehicles...
on unsurfaced bridleways, mountain biking
Mountain biking
Mountain biking is a sport which consists of riding bicycles off-road, often over rough terrain, using specially adapted mountain bikes. Mountain bikes share similarities with other bikes, but incorporate features designed to enhance durability and performance in rough terrain.Mountain biking can...
and use of off-road vehicle
Off-road vehicle
An off-road vehicle is considered to be any type of vehicle which is capable of driving on and off paved or gravel surface. It is generally characterized by having large tires with deep, open treads, a flexible suspension, or even caterpillar tracks...
s on green lanes. Examples include Dovedale
Dovedale
Dovedale is a popular dale in the Peak District, England. It is owned by the National Trust, and annually attracts a million visitors. The valley is cut by the River Dove and runs for just over between Milldale in the north and a wooded ravine near Thorpe Cloud and Bunster Hill in the south...
in the Peak District. Over-grazing, for example, by sheep on hill and moorland areas, can also reduce vegetation, leading to increased erosion.
Damage and disturbance to wildlife : Wildlife
Wildlife
Wildlife includes all non-domesticated plants, animals and other organisms. Domesticating wild plant and animal species for human benefit has occurred many times all over the planet, and has a major impact on the environment, both positive and negative....
may be disturbed by the level of use on some of the areas of the parks that are open to the public. Moorland
Moorland
Moorland or moor is a type of habitat, in the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome, found in upland areas, characterised by low-growing vegetation on acidic soils and heavy fog...
and chalk downland is easily damaged by regular use, and takes many years to recover. Moorland birds in particular nest and roost on the ground and are therefore especially sensitive. Orienteering
Orienteering
Orienteering is a family of sports that requires navigational skills using a map and compass to navigate from point to point in diverse and usually unfamiliar terrain, and normally moving at speed. Participants are given a topographical map, usually a specially prepared orienteering map, which they...
, mountain biking
Mountain biking
Mountain biking is a sport which consists of riding bicycles off-road, often over rough terrain, using specially adapted mountain bikes. Mountain bikes share similarities with other bikes, but incorporate features designed to enhance durability and performance in rough terrain.Mountain biking can...
and hang gliding
Hang gliding
Hang gliding is an air sport in which a pilot flies a light and unmotorized foot-launchable aircraft called a hang glider ....
are typical activities which are likely to cause disturbance to nesting birds.
Litter : Litter of all kinds is both unsightly and can cause pollution and damage to livestock and wild animals. Broken glass is a danger to people and, by focus
Focus (optics)
In geometrical optics, a focus, also called an image point, is the point where light rays originating from a point on the object converge. Although the focus is conceptually a point, physically the focus has a spatial extent, called the blur circle. This non-ideal focusing may be caused by...
ing the rays of the sun, a possible cause of fire, particularly in areas of moorland such as Exmoor
Exmoor
Exmoor is an area of hilly open moorland in west Somerset and north Devon in South West England, named after the main river that flows out of the district, the River Exe. The moor has given its name to a National Park, which includes the Brendon Hills, the East Lyn Valley, the Vale of Porlock and ...
, parts of the Peak District
Peak District
The Peak District is an upland area in central and northern England, lying mainly in northern Derbyshire, but also covering parts of Cheshire, Greater Manchester, Staffordshire, and South and West Yorkshire....
and the North York Moors
North York Moors
The North York Moors is a national park in North Yorkshire, England. The moors are one of the largest expanses of heather moorland in the United Kingdom. It covers an area of , and it has a population of about 25,000...
.
Damage to farmland : Trampling of grass meadow
Meadow
A meadow is a field vegetated primarily by grass and other non-woody plants . The term is from Old English mædwe. In agriculture a meadow is grassland which is not grazed by domestic livestock but rather allowed to grow unchecked in order to make hay...
s reduces the amount of winter feed for farm animals. Walkers who stray from footpaths may climb over fences or dry stone walls rather than looking out for the stile
Stile
A stile is a structure which provides people a passage through or over a fence or boundary via steps, ladders, or narrow gaps. Stiles are often built in rural areas or along footpaths to allow access to an adjacent field or area separated by a fence, wall or hedge...
s that mark the course of footpaths across farmland. Sheep can be injured or even killed by dogs not under proper control, especially at lambing time.
Local community displacement : Gift shops and café
Café
A café , also spelled cafe, in most countries refers to an establishment which focuses on serving coffee, like an American coffeehouse. In the United States, it may refer to an informal restaurant, offering a range of hot meals and made-to-order sandwiches...
s which cater for the needs of tourists are often more profitable than shops selling everyday goods for local people (such as butchers or bakers). In some villages where tourist shops are in the majority and there are few shops catering for the local people, the local community may feel pushed out by the tourists. Houses are often very expensive in tourist villages as there is demand for them as second home
Second home
Second home may refer to:* Vacation property* Pied-à-terre* Second Home , an album by Marié Digby...
s or holiday homes by holiday cottage
Holiday cottage
A holiday cottage is a cottage used for accommodation, which has become common in the United Kingdom and Canada. They are typically small homes that vacationers can rent and run as if it were their own home for the duration of their stay. This gives them the freedom to eat in, eat out, stay in bed...
firms or well-off people who live elsewhere, or who move to a local home from which they commute to work, making them unaffordable for local people. This is a particular problem in areas within easy commuting distance of large cities, such as the Peak District
Peak District
The Peak District is an upland area in central and northern England, lying mainly in northern Derbyshire, but also covering parts of Cheshire, Greater Manchester, Staffordshire, and South and West Yorkshire....
, the Lake District
Lake District
The Lake District, also commonly known as The Lakes or Lakeland, is a mountainous region in North West England. A popular holiday destination, it is famous not only for its lakes and its mountains but also for its associations with the early 19th century poetry and writings of William Wordsworth...
, the Yorkshire Dales
Yorkshire Dales
The Yorkshire Dales is the name given to an upland area in Northern England.The area lies within the historic county boundaries of Yorkshire, though it spans the ceremonial counties of North Yorkshire, West Yorkshire and Cumbria...
, and the New Forest
New Forest
The New Forest is an area of southern England which includes the largest remaining tracts of unenclosed pasture land, heathland and forest in the heavily-populated south east of England. It covers south-west Hampshire and extends into south-east Wiltshire....
and South Downs
South Downs
The South Downs is a range of chalk hills that extends for about across the south-eastern coastal counties of England from the Itchen Valley of Hampshire in the west to Beachy Head, near Eastbourne, East Sussex, in the east. It is bounded on its northern side by a steep escarpment, from whose...
.
Conflict between recreational users : Some forms of use of national parks interfere with other uses. For example, use of high-speed boat
Boat
A boat is a watercraft of any size designed to float or plane, to provide passage across water. Usually this water will be inland or in protected coastal areas. However, boats such as the whaleboat were designed to be operated from a ship in an offshore environment. In naval terms, a boat is a...
s causes noise pollution
Noise pollution
Noise pollution is excessive, displeasing human, animal or machine-created environmental noise that disrupts the activity or balance of human or animal life...
, and conflicts with other uses such as boat trips, yachting, canoeing, and swimming. A controversial bylaw
Bylaw
By-law can refer to a law of local or limited application passed under the authority of a higher law specifying what things may be regulated by the by-law...
imposing a 10 knot speed limit came into force on Windermere
Windermere (lake)
Windermere is the largest natural lake in England. It is a ribbon lake formed in a glacial trough after the retreat of ice at the start of the current interglacial. It has been one of the country’s most popular places for holidays and summer homes since the arrival of the Kendal and Windermere...
on 29 March 2005. The new speed limit for Windermere effectively prohibits speedboats
Motorboat
A motorboat is a boat which is powered by an engine. Some motorboats are fitted with inboard engines, others have an outboard motor installed on the rear, containing the internal combustion engine, the gearbox and the propeller in one portable unit.An inboard/outboard contains a hybrid of a...
and water skiing
Water skiing
thumb|right|A slalom skier making a turn on a slalom waterski.Waterskiing is a sport where an individual is pulled behind a boat or a cable ski installation on a body of water, skimming the surface.-History:...
in the Lake District (of the 16 larger lakes in the Lake District
Lake District
The Lake District, also commonly known as The Lakes or Lakeland, is a mountainous region in North West England. A popular holiday destination, it is famous not only for its lakes and its mountains but also for its associations with the early 19th century poetry and writings of William Wordsworth...
, only Windermere, Coniston Water
Coniston Water
Coniston Water in Cumbria, England is the third largest lake in the English Lake District. It is five miles long, half a mile wide, has a maximum depth of 184 feet , and covers an area of . The lake has an elevation of 143 feet above sea level...
, Derwent Water
Derwent Water
Derwentwater is one of the principal bodies of water in the Lake District National Park in north west England. It lies wholly within the Borough of Allerdale, in the county of Cumbria....
and Ullswater
Ullswater
Ullswater is the second largest lake in the English Lake District, being approximately nine miles long and 0.75 miles wide with a maximum depth of slightly more than ....
have a public right of navigation
Navigation
Navigation is the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another. It is also the term of art used for the specialized knowledge used by navigators to perform navigation tasks...
; speed limits were imposed on the three lakes other than Windermere in the 1970s and 1980s).
List of national parks
|
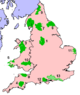 |
|||
At the beginning of 2005, some 9.3% of the area of England and Wales lay within national parks; the addition of South Downs and the New Forest would increase this proportion to 10.7%. The three Welsh national parks cover around 20% of the land area of Wales.
See also
- Area of Outstanding Natural BeautyArea of Outstanding Natural BeautyAn Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty is an area of countryside considered to have significant landscape value in England, Wales or Northern Ireland, that has been specially designated by the Countryside Agency on behalf of the United Kingdom government; the Countryside Council for Wales on...
- Conservation in the United KingdomConservation in the United KingdomThis page gives an overview of the complex structure of environmental and cultural conservation in the United Kingdom.With the advent of devolved government for Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland and of evolving regional government for England, the responsibilities for environment and...
- National parks of Northern IrelandNational parks of Northern IrelandThere are, at present, no national parks in Northern Ireland and moves to establish a national park in the Mourne Mountains have proved to be controversial. If established, it would stretch from Carlingford Lough to Newcastle and Slieve Croob, creating a tourism boom and up to 2,000 jobs...
- National parks of ScotlandNational parks of ScotlandNational parks of Scotland are managed areas of outstanding landscape where habitation and commercial activities are restricted. At present, Scotland has two national parks: Loch Lomond and The Trossachs National Park, created in 2002, and the Cairngorms National Park, created in 2003...
External links
- National Parks Portal
- Association of National Park Authorities
- Campaign for National Parks
- Natural England
- The Countryside Council for Wales
- Landscape Protection - National Parks from the Department for the Environment, Food and Rural Affairs

