
Naked eye
Encyclopedia
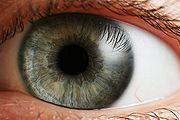
Figure of speech
A figure of speech is the use of a word or words diverging from its usual meaning. It can also be a special repetition, arrangement or omission of words with literal meaning, or a phrase with a specialized meaning not based on the literal meaning of the words in it, as in idiom, metaphor, simile,...
referring to human visual perception
Visual perception
Visual perception is the ability to interpret information and surroundings from the effects of visible light reaching the eye. The resulting perception is also known as eyesight, sight, or vision...
unaided by a magnifying or light-collecting optical device, such as a telescope
Telescope
A telescope is an instrument that aids in the observation of remote objects by collecting electromagnetic radiation . The first known practical telescopes were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 1600s , using glass lenses...
or microscope
Microscope
A microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small for the naked eye. The science of investigating small objects using such an instrument is called microscopy...
. Vision corrected to normal acuity using corrective lens
Corrective lens
A corrective lens is a lens worn in front of the eye, mainly used to treat myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and presbyopia. Glasses or "spectacles" are worn on the face a short distance in front of the eye. Contact lenses are worn directly on the surface of the eye...
es is considered "naked". The term is often used in astronomy
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
when referring to events that can be viewed without equipment, such as an astronomical conjunction, the passage of a comet
Comet
A comet is an icy small Solar System body that, when close enough to the Sun, displays a visible coma and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena are both due to the effects of solar radiation and the solar wind upon the nucleus of the comet...
, or a meteor shower
Meteor shower
A meteor shower is a celestial event in which a number of meteors are observed to radiate from one point in the night sky. These meteors are caused by streams of cosmic debris called meteoroids entering Earth's atmosphere at extremely high speeds on parallel trajectories. Most meteors are smaller...
. Sky lore and various tests demonstrate an impressive wealth of phenomena that can be seen with the unaided eye.
Basic accuracies
The basic accuracies of the human eye are:- Quick autofocusAutofocusAn autofocus optical system uses a sensor, a control system and a motor to focus fully automatic or on a manually selected point or area. An electronic rangefinder has a display instead of the motor; the adjustment of the optical system has to be done manually until indication...
from distances of 10 cm (young people) to 50 cm (most people 50 years and older) to infinity. - Angular resolutionAngular resolutionAngular resolution, or spatial resolution, describes the ability of any image-forming device such as an optical or radio telescope, a microscope, a camera, or an eye, to distinguish small details of an object...
: 1-2' (about 0.02°-0.03°), which corresponds to 30–60 cm at a 1 km distance. - Field of viewField of viewThe field of view is the extent of the observable world that is seen at any given moment....
(FOV): simultaneous visual perception in an area of about 160° × 175°. - Faint starStarA star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
s up to +6.5 magnitudeApparent magnitudeThe apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
under a modern dark sky. - Distance (factor of light intensity and light interference) the Andromeda GalaxyAndromeda GalaxyThe Andromeda Galaxy is a spiral galaxy approximately 2.5 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Andromeda. It is also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224, and is often referred to as the Great Andromeda Nebula in older texts. Andromeda is the nearest spiral galaxy to the...
is visible at 2.5 million light years or 10 million trillion km. - PhotometryPhotometry (optics)Photometry is the science of the measurement of light, in terms of its perceived brightness to the human eye. It is distinct from radiometry, which is the science of measurement of radiant energy in terms of absolute power; rather, in photometry, the radiant power at each wavelength is weighted by...
(brightness) to ±10% or 1% of intensity - in a range between night and day of 1:10,000,000,000. - SymmetriesSymmetrySymmetry generally conveys two primary meanings. The first is an imprecise sense of harmonious or aesthetically pleasing proportionality and balance; such that it reflects beauty or perfection...
of 10-20' (3-6 m per 1 km), see the measurements of Tycho BraheTycho BraheTycho Brahe , born Tyge Ottesen Brahe, was a Danish nobleman known for his accurate and comprehensive astronomical and planetary observations...
and the EgyptiansEgyptiansEgyptians are nation an ethnic group made up of Mediterranean North Africans, the indigenous people of Egypt.Egyptian identity is closely tied to geography. The population of Egypt is concentrated in the lower Nile Valley, the small strip of cultivable land stretching from the First Cataract to...
. - IntervalIntervalInterval may refer to:* Interval , a range of numbers * Interval measurements or interval variables in statistics is a level of measurement...
estimations (for example at a plan on paper) to 3-5%. - Unconscious recognizing of movementMotion (physics)In physics, motion is a change in position of an object with respect to time. Change in action is the result of an unbalanced force. Motion is typically described in terms of velocity, acceleration, displacement and time . An object's velocity cannot change unless it is acted upon by a force, as...
(that is "alarmAlarmAn alarm device or system of alarm devices gives an audible or visual alarm signal about a problem or condition.Alarm devices include:* burglar alarms, designed to warn of burglaries; this is often a silent alarm: the police or guards are warned without indication to the burglar, which increases...
system" and reflexes).
Visual perception allows a person to gain much information about his or her surroundings:
- the distances and 3-dimensional position of things and persons
- the vertical (plumb line) and the slope of plain objects
- luminosities and colors and their changes by time and direction
Naked eye in astronomy
The visibility of astronomical objects is strongly affected by light pollutionLight pollution
Light pollution, also known as photopollution or luminous pollution, is excessive or obtrusive artificial light.The International Dark-Sky Association defines light pollution as:...
. Even a few hundred kilometers away from a metropolitan area where the sky can appear to be very dark, it is still the residual light pollution that sets the limit on the visibility of faint objects. For most people, this is likely to be the best observing conditions within their reach. Under such "typical" dark sky conditions, the naked eye can see stars with an apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
up to +6m. Under perfect dark sky conditions where all light pollution is absent, stars as faint as +8m might be visible.
The angular resolution of the naked eye is about 1′; however, some people have sharper vision than that. There is anecdotal evidence that people had seen the Galilean moons of Jupiter
Jupiter's natural satellites
Jupiter has 64 confirmed moons, giving it the largest retinue of moons with "reasonably secure" orbits of any planet in the Solar System. The most massive of them, the four Galilean moons, were discovered in 1610 by Galileo Galilei and were the first objects found to orbit a body that was neither...
before telescopes were invented. Of similar magnitude, Uranus
Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It has the third-largest planetary radius and fourth-largest planetary mass in the Solar System. It is named after the ancient Greek deity of the sky Uranus , the father of Cronus and grandfather of Zeus...
and Vesta had most probably been seen but could not be recognized as planets because they appear so small even at maximum brightness that their motion could not be detected. Uranus, when discovered in 1781, was the first planet discovered using technology
Technology
Technology is the making, usage, and knowledge of tools, machines, techniques, crafts, systems or methods of organization in order to solve a problem or perform a specific function. It can also refer to the collection of such tools, machinery, and procedures. The word technology comes ;...
, a telescope
Telescope
A telescope is an instrument that aids in the observation of remote objects by collecting electromagnetic radiation . The first known practical telescopes were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 1600s , using glass lenses...
, rather than being spotted by the naked eye.
Theoretically, in a typical dark sky, the dark adapted
Adaptation (eye)
In ocular physiology, adaptation is the ability of the eye to adjust to various levels of darkness and light.-Efficacy:The human eye can function from very dark to very bright levels of light; its sensing capabilities reach across nine orders of magnitude. This means that the brightest and the...
human eye would see the about 5,600 stars brighter than +6m while in perfect dark sky conditions about 45,000 stars brighter than +8m might be visible. In practice, the atmospheric extinction
Extinction (astronomy)
Extinction is a term used in astronomy to describe the absorption and scattering of electromagnetic radiation by matter between an emitting astronomical object and the observer. Interstellar extinction—also called Galactic extinction, when it occurs in the Milky Way—was first...
and dust reduces this number somewhat. In the center of a city, where the naked-eye limiting magnitude due to extreme amounts of light pollution can be +4m or less, as few as 200 to 500 stars may be visible. Colors can be seen but this is limited by the fact that the eye uses rods instead of cones to view fainter stars.
The visibility of diffuse objects such as star cluster
Star cluster
Star clusters or star clouds are groups of stars. Two types of star clusters can be distinguished: globular clusters are tight groups of hundreds of thousands of very old stars which are gravitationally bound, while open clusters, more loosely clustered groups of stars, generally contain less than...
s and galaxies is much more strongly affected by light pollution than the visibility of planets and stars. Under typical dark conditions only a few such objects are visible. These include the Pleiades
Pleiades (star cluster)
In astronomy, the Pleiades, or Seven Sisters , is an open star cluster containing middle-aged hot B-type stars located in the constellation of Taurus. It is among the nearest star clusters to Earth and is the cluster most obvious to the naked eye in the night sky...
, h/χ Persei
Double Cluster
The Double Cluster is the common name for the naked-eye open clusters NGC 884 and NGC 869 , which are close together in the constellation Perseus. NGC 884 and NGC 869 are at distances of 7600 and 6800 light-years away, respectively, so they are also close to one another in space...
, the Andromeda galaxy
Andromeda Galaxy
The Andromeda Galaxy is a spiral galaxy approximately 2.5 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Andromeda. It is also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224, and is often referred to as the Great Andromeda Nebula in older texts. Andromeda is the nearest spiral galaxy to the...
, the Carina Nebula, the Orion Nebula
Orion Nebula
The Orion Nebula is a diffuse nebula situated south of Orion's Belt. It is one of the brightest nebulae, and is visible to the naked eye in the night sky. M42 is located at a distance of and is the closest region of massive star formation to Earth. The M42 nebula is estimated to be 24 light...
, Omega Centauri
Omega Centauri
Omega Centauri or NGC 5139 is a globular clusterin the constellation of Centaurus, discovered by Edmond Halley in 1677 who listed it as a nebula. Omega Centauri had been listed in Ptolemy's catalog 2000 years ago as a star. Lacaille included it in his catalog as number I.5...
, 47 Tucanae
47 Tucanae
47 Tucanae or just 47 Tuc is a globular cluster located in the constellation Tucana. It is about 16,700 light years away from Earth, and 120 light years across. It can be seen with the naked eye, with a visual magnitude of 4.0...
and the globular cluster M13 in Hercules
Hercules (constellation)
Hercules is a constellation named after Hercules, the Roman mythological hero adapted from the Greek hero Heracles. Hercules was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today...
. The Triangulum Galaxy (M33)
Triangulum Galaxy
The Triangulum Galaxy is a spiral galaxy approximately 3 million light years from Earth in the constellation Triangulum. It is catalogued as Messier 33 or NGC 598, and is sometimes informally referred to as the Pinwheel Galaxy, a nickname it shares with Messier 101...
is a difficult averted vision
Averted vision
Averted vision is a technique for viewing faint objects which uses peripheral vision. It involves not looking directly at the object, but looking a little off to the side, while continuing to concentrate on the object. This subject is discussed in the popular astronomy literature but only a few...
object and only visible at all if it is higher than 50° in the sky. Under really dark sky conditions, however, M33 is easy to see, even in direct vision. Many other Messier objects are also visible under such conditions. The most distant objects that have been seen by the naked eye are nearby bright galaxies such as Centaurus A
Centaurus A
Centaurus A is a prominent galaxy in the constellation of Centaurus. There is considerable debate in the literature regarding the galaxy's fundamental properties such as its Hubble type and distance...
, Bode's Galaxy, Sculptor Galaxy
Sculptor Galaxy
The Sculptor Galaxy is an intermediate spiral galaxy in the constellation Sculptor...
, and Messier 83.
Five planets can be recognized as planets from earth with the naked eye: Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn. Under typical dark sky conditions Uranus
Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It has the third-largest planetary radius and fourth-largest planetary mass in the Solar System. It is named after the ancient Greek deity of the sky Uranus , the father of Cronus and grandfather of Zeus...
(magnitude +5.8) can be seen as well with averted vision. The Sun and the Moon—the remaining noticeable naked-eye objects of the solar system—are sometimes added to make seven "planets." During daylight only the Moon
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
and Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
are obvious naked eye objects, but in many cases Venus
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun, orbiting it every 224.7 Earth days. The planet is named after Venus, the Roman goddess of love and beauty. After the Moon, it is the brightest natural object in the night sky, reaching an apparent magnitude of −4.6, bright enough to cast shadows...
can be spotted in daylight and in rarer cases Jupiter
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet within the Solar System. It is a gas giant with mass one-thousandth that of the Sun but is two and a half times the mass of all the other planets in our Solar System combined. Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn,...
. Close to sunset and sunrise bright stars like Sirius
Sirius
Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky. With a visual apparent magnitude of −1.46, it is almost twice as bright as Canopus, the next brightest star. The name "Sirius" is derived from the Ancient Greek: Seirios . The star has the Bayer designation Alpha Canis Majoris...
or even Canopus
Canopus
Canopus |Alpha]] Carinae) is the brightest star in the southern constellation of Carina and Argo Navis, and the second brightest star in the night-time sky, after Sirius. Canopus's visual magnitude is −0.72, and it has an absolute magnitude of −5.53.Canopus is a supergiant of spectral...
can be spotted with the naked eye as long as one knows the exact position in which to look.
Historically, the zenith of naked-eye astronomy was the work of Tycho Brahe
Tycho Brahe
Tycho Brahe , born Tyge Ottesen Brahe, was a Danish nobleman known for his accurate and comprehensive astronomical and planetary observations...
(1546–1601). He built an extensive observatory to make precise measurements of the heavens without any instruments for magnification. In 1610, Galileo Galilei
Galileo Galilei
Galileo Galilei , was an Italian physicist, mathematician, astronomer, and philosopher who played a major role in the Scientific Revolution. His achievements include improvements to the telescope and consequent astronomical observations and support for Copernicanism...
pointed a telescope
Telescope
A telescope is an instrument that aids in the observation of remote objects by collecting electromagnetic radiation . The first known practical telescopes were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 1600s , using glass lenses...
towards the sky. He immediately discovered the moons of Jupiter
Galilean moons
The Galilean moons are the four moons of Jupiter discovered by Galileo Galilei in January 1610. They are the largest of the many moons of Jupiter and derive their names from the lovers of Zeus: Io, Europa, Ganymede and Callisto. Ganymede, Europa and Io participate in a 1:2:4 orbital resonance...
and the phases
Planetary phase
Planetary phase is the term used to describe the appearance of the illuminated section of a planet. Like lunar phases, the planetary phase depends on the relative position of the sun, the planet and the observer....
of Venus
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun, orbiting it every 224.7 Earth days. The planet is named after Venus, the Roman goddess of love and beauty. After the Moon, it is the brightest natural object in the night sky, reaching an apparent magnitude of −4.6, bright enough to cast shadows...
, among other things.
Meteor showers are better observed by naked eye than with binoculars. Such showers include the Perseids
Perseids
The Perseids are a prolific meteor shower associated with the comet Swift-Tuttle. The Perseids are so-called because the point from which they appear to come, called the radiant, lies in the constellation Perseus. The name derives in part from the word Perseides , a term found in Greek mythology...
(10–12 August) and the December Geminids
Geminids
The Geminids are a meteor shower caused by the object 3200 Phaethon, which is thought to be a Palladian asteroid. This would make the Geminids, together with the Quadrantids, the only major meteor showers not originating from a comet...
. Some 100 satellite
Satellite
In the context of spaceflight, a satellite is an object which has been placed into orbit by human endeavour. Such objects are sometimes called artificial satellites to distinguish them from natural satellites such as the Moon....
s per night, the International Space Station
International Space Station
The International Space Station is a habitable, artificial satellite in low Earth orbit. The ISS follows the Salyut, Almaz, Cosmos, Skylab, and Mir space stations, as the 11th space station launched, not including the Genesis I and II prototypes...
and the Milky Way
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
are other popular objects visible to the naked eye.
Space, geodesy and navigation
Many other things can be estimated without an instrument. If an arm is stretched the span of the hand corresponds to an angle of 18 to 20°. The distance of a person, just covered up by the outstretched thumbnail, is about 100 meters. The vertical can be estimated to about 2° and, in the northern hemisphere, observing the Pole StarPole star
The term "Pole Star" usually refers to Polaris, which is the current northern pole star, also known as the North Star.In general, however, a pole star is a visible star, especially a prominent one, that is approximately aligned with the Earth's axis of rotation; that is, a star whose apparent...
and using a protractor can give the observer's geographic latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
, up to 1 degree of accuracy.
The Babylonians, Mayans
Maya civilization
The Maya is a Mesoamerican civilization, noted for the only known fully developed written language of the pre-Columbian Americas, as well as for its art, architecture, and mathematical and astronomical systems. Initially established during the Pre-Classic period The Maya is a Mesoamerican...
, ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
ians, ancient Indians, and Chinese
Chinese astronomy
Astronomy in China has a very long history, with historians considering that "they [the Chinese] were the most persistent and accurate observers of celestial phenomena anywhere in the world before the Arabs."...
measured all the basics of their respective time and calendar systems by naked eye:
- the length of a year and a month to ±0.1 hour or to better than 1 minute (0.001%)
- the 24 hours of a day, and the equinoxEquinoxAn equinox occurs twice a year, when the tilt of the Earth's axis is inclined neither away from nor towards the Sun, the center of the Sun being in the same plane as the Earth's equator...
es - the periods of the PlanetPlanetA planet is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science,...
s was calculated by Mayan astronomers, to within 5 to 10 minutes accuracy in the case of Venus and Mars.
In a similar manner star occultation
Occultation
An occultation is an event that occurs when one object is hidden by another object that passes between it and the observer. The word is used in astronomy . It can also refer to any situation wherein an object in the foreground blocks from view an object in the background...
s by the moon can be observed. By using a digital clock
Clock
A clock is an instrument used to indicate, keep, and co-ordinate time. The word clock is derived ultimately from the Celtic words clagan and clocca meaning "bell". A silent instrument missing such a mechanism has traditionally been known as a timepiece...
an accuracy of 0.2 second is possible. This represents only 200 meters at the moon's distance of 385,000 km.
Small objects and maps
Observing a nearby small object without a magnifying glassMagnifying glass
A magnifying glass is a convex lens that is used to produce a magnified image of an object. The lens is usually mounted in a frame with a handle ....
or a microscope
Microscope
A microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small for the naked eye. The science of investigating small objects using such an instrument is called microscopy...
, the optimal distance is 20–25 cm. At this close range, 0.05 mm can be seen clearly. The accuracy of a measurement ranges from 0.1 to 0.3 mm and depends on the experience of the observer. The latter figure is the usual positional accuracy of faint details in maps and technical plans.
Environmental pollution
A clean atmosphereEarth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention , and reducing temperature extremes between day and night...
is indicated by the fact that the Milky Way is visible. Comparing the zenith with the horizon
Horizon
The horizon is the apparent line that separates earth from sky, the line that divides all visible directions into two categories: those that intersect the Earth's surface, and those that do not. At many locations, the true horizon is obscured by trees, buildings, mountains, etc., and the resulting...
, shows how the "blue quality" is degraded depending on the amount of air pollution and dust. The twinkling of a star is an indication of the turbulence
Turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is a flow regime characterized by chaotic and stochastic property changes. This includes low momentum diffusion, high momentum convection, and rapid variation of pressure and velocity in space and time...
of the air. This is of importance in meteorology
Meteorology
Meteorology is the interdisciplinary scientific study of the atmosphere. Studies in the field stretch back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not occur until the 18th century. The 19th century saw breakthroughs occur after observing networks developed across several countries...
and for the "seeing
Astronomical seeing
Astronomical seeing refers to the blurring and twinkling of astronomical objects such as stars caused by turbulent mixing in the Earth's atmosphere varying the optical refractive index...
" of astronomy.
Light pollution
Light pollution
Light pollution, also known as photopollution or luminous pollution, is excessive or obtrusive artificial light.The International Dark-Sky Association defines light pollution as:...
is a significant problem for amateur astronomers but becomes less late at night when many lights are shut off. Air dust can be seen even far away from a city by its "light dome".
Literature
- Adobe Comp.: "Photoshop", program handbook, versions 5/6, Adobe 2002.
- Davidson, N.: Sky Phenomena: A Guide to Naked Eye Observation of the Heavens. FlorisBooks (208p), ISBN 0-86315-168-X, Edinburgh 1993.
- Gerstbach G.: Auge und Sehen — der lange Weg zu digitalem Erkennen. Astro Journal SternenboteSternenboteThe Sternenbote is a monthly astronomy journal, edited by the Austrian astronomical Society in Vienna. The journal was first published in 1958, and contents include ephemerides of comets and other solar system objects, and observation reports....
, 20p., Vol.2000/8, Vienna 2000. - Kahmen H. (Ed.): Geodesy for Geotechnical and Structural Engineering. Proceedings, Eisenstadt 1999.
External links
- Naked Eye Observing in Astronomy
- Naked-Eye Stargazing: Learning the SkySkyThe sky is the part of the atmosphere or outer space visible from the surface of any astronomical object. It is difficult to define precisely for several reasons. During daylight, the sky of Earth has the appearance of a pale blue surface because the air scatters the sunlight. The sky is sometimes...
and its constellations - Naked Eye Navigation, PolynesiaPolynesiaPolynesia is a subregion of Oceania, made up of over 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are termed Polynesians and they share many similar traits including language, culture and beliefs...
Voyages - Detection of weak optical signals by the human visual system: Perspectives in Neuroscience and in Quantum Physics
- The Naked-eye Planets in the Night Sky (and how to identify them)

