
NHMFL
Encyclopedia

Florida State University
The Florida State University is a space-grant and sea-grant public university located in Tallahassee, Florida, United States. It is a comprehensive doctoral research university with medical programs and significant research activity as determined by the Carnegie Foundation...
, with branches in University of Florida
University of Florida
The University of Florida is an American public land-grant, sea-grant, and space-grant research university located on a campus in Gainesville, Florida. The university traces its historical origins to 1853, and has operated continuously on its present Gainesville campus since September 1906...
and at Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory, managed and operated by Los Alamos National Security , located in Los Alamos, New Mexico...
. NHMFL develops and research at magnetic fields for research in physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, biology
Biology
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines...
, bioengineering, chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, geochemistry
Geochemistry
The field of geochemistry involves study of the chemical composition of the Earth and other planets, chemical processes and reactions that govern the composition of rocks, water, and soils, and the cycles of matter and energy that transport the Earth's chemical components in time and space, and...
, biochemistry
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
. The world's highest powered magnet laboratory, it is the only facility of its kind in the United States, among nine worldwide. The lab is supported by the National Science Foundation
National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation is a United States government agency that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National Institutes of Health...
and the state of Florida
Florida
Florida is a state in the southeastern United States, located on the nation's Atlantic and Gulf coasts. It is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the north by Alabama and Georgia and to the east by the Atlantic Ocean. With a population of 18,801,310 as measured by the 2010 census, it...
, and works in collaboration with private industry.
Proposal and award
In 1989 Florida State University (FSU), Los Alamos National Laboratory, and the University of Florida submitted a proposal to the National Science Foundation (NSF) for a new national laboratory supporting interdisciplinary research in high magnetic fields. The plan proposed a federalFederal government of the United States
The federal government of the United States is the national government of the constitutional republic of fifty states that is the United States of America. The federal government comprises three distinct branches of government: a legislative, an executive and a judiciary. These branches and...
-state
U.S. state
A U.S. state is any one of the 50 federated states of the United States of America that share sovereignty with the federal government. Because of this shared sovereignty, an American is a citizen both of the federal entity and of his or her state of domicile. Four states use the official title of...
partnership serving magnet-related research, science and technology education, and partnering industry. The goal was to maintain the competitive position of the United States in magnet-related research and development. Following a peer-review competition, the NSF approved the FSU-led consortium's proposal.
Competing proposal by MIT
In a competing proposal to the NSF, the Massachusetts Institute of TechnologyMassachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology is a private research university located in Cambridge, Massachusetts. MIT has five schools and one college, containing a total of 32 academic departments, with a strong emphasis on scientific and technological education and research.Founded in 1861 in...
(MIT), with the University of Iowa
University of Iowa
The University of Iowa is a public state-supported research university located in Iowa City, Iowa, United States. It is the oldest public university in the state. The university is organized into eleven colleges granting undergraduate, graduate, and professional degrees...
, the University of Wisconsin–Madison
University of Wisconsin–Madison
The University of Wisconsin–Madison is a public research university located in Madison, Wisconsin, United States. Founded in 1848, UW–Madison is the flagship campus of the University of Wisconsin System. It became a land-grant institution in 1866...
, Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory , is a United States national laboratory located in Upton, New York on Long Island, and was formally established in 1947 at the site of Camp Upton, a former U.S. Army base...
, and Argonne National Laboratory
Argonne National Laboratory
Argonne National Laboratory is the first science and engineering research national laboratory in the United States, receiving this designation on July 1, 1946. It is the largest national laboratory by size and scope in the Midwest...
, had suggested improving the existing world-class Francis Bitter Magnet Laboratory at MIT instead. On September 5, 1990, MIT researchers asked the 21 members of the National Science Board
National Science Board
The National Science Board of the United States is composed of 25 members appointed by the President and confirmed by the United States Senate, representing the broad U.S. science and engineering community. The Board establishes the policies of the National Science Foundation within the framework...
(NSB) to "review and reconsider" its decision. With $60 million at stake in the NSF grant, MIT stated it would phase out the Francis Bitter Lab if it lost its appeal, the first of its kind in NSF history. The request was turned down September 18, 1990.
Early years
The laboratory's early years were spent establishing infrastructure, building the facility, and recruiting faculty. The Tallahassee complex was dedicated on October 1, 1994, to a large crowd, with keynote speaker Vice President Al GoreAl Gore
Albert Arnold "Al" Gore, Jr. served as the 45th Vice President of the United States , under President Bill Clinton. He was the Democratic Party's nominee for President in the 2000 U.S. presidential election....
.
Mission
The lab's mission, as set forth by the NSF, is: "To provide the highest magnetic fields and necessary services for scientific research conducted by users from a wide range of disciplines, including physics, chemistry, materials science, engineering, biology and geology."The lab focuses on four objectives:
- Develop user facilities and services for magnet-related research, open to all qualified scientists and engineers
- Advance magnet technology in cooperation with industry
- Promote a multidisciplinary research environment and administer in-house research program that uses and advances the facilities
- Develop an educational outreach program
Education and Public Outreach
The Magnet Lab promotes science educationScience education
Science education is the field concerned with sharing science content and process with individuals not traditionally considered part of the scientific community. The target individuals may be children, college students, or adults within the general public. The field of science education comprises...
and supports science, engineering, and science teachers. Programs include mentor
Mentor
In Greek mythology, Mentor was the son of Alcimus or Anchialus. In his old age Mentor was a friend of Odysseus who placed Mentor and Odysseus' foster-brother Eumaeus in charge of his son Telemachus, and of Odysseus' palace, when Odysseus left for the Trojan War.When Athena visited Telemachus she...
ships in an interdisciplinary learning environment. Through Mag Lab U, the lab's web site provides educational content on electricity and magnetism in general, and the work done at the Magnet Lab in particular.
Florida State University Programs

Tallahassee, Florida
Tallahassee is the capital of the U.S. state of Florida. It is the county seat and only incorporated municipality in Leon County, and is the 128th largest city in the United States. Tallahassee became the capital of Florida, then the Florida Territory, in 1824. In 2010, the population recorded by...
laboratory at Florida State University is a 34,374 square meter (370,000 sq ft.) complex and has approximately 300 faculty, staff, graduate, and postdoctoral students. Its director is physicist Gregory Scott Boebinger.
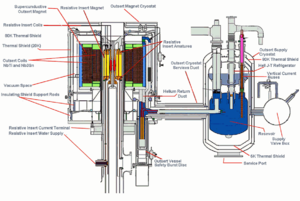
.jpg)
DC Field Program
The purpose of the DC (continuous field) field program is to provide to the user community with the strongest, quietest, steady and slowly varying magnetic fields in the world, coupled with state-of-the-art instrumentation and experimental expertise.The facility contains 14 resistive magnet cells connected to a newly upgraded 48 megawatt DC power supply and 15000 square feet (1,393.5 m²) of cooling equipment to remove the heat generated by the magnets. The research is supported by magnet plant and cryogenic system operators. Technicians design, build and repair instruments for user research. Scholar-scientists — world-class researchers with their own vibrant research interests — work directly with users to get the best measurements and data.
The facility houses several world-record magnets, including the 45 tesla hybrid magnet, which combines resistive and superconducting magnets to create the strongest steady magnetic field available anywhere. The lab's 35 tesla resistive magnet is the strongest resistive magnet in the world, and the 25 tesla Keck magnet boasts the highest homogeneity of any resistive magnet.
Future plans are in place to build a second hybrid magnet that can reach a magnitude of 55 to 60 teslas, using a similar system of resistive and superconducting magnets. It is hoped that due to current research into superconductivity and other advances that this goal may soon be reached, but there is no official word on a construction time table. To see a video of the current 45 tesla hybrid magnet, click here.
NMR Spectroscopy and Imaging Program
This program serves a broad user base in solution and solid state NMR spectroscopySpectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and radiated energy. Historically, spectroscopy originated through the study of visible light dispersed according to its wavelength, e.g., by a prism. Later the concept was expanded greatly to comprise any interaction with radiative...
and MRI and diffusion measurements at the highest possible magnetic field strengths. The lab develops technology, methodology, and applications at high magnetic fields through both in-house and external user activities. It has experienced research faculty, engineers, and technicians spanning these disciplines who are available to facilitate user activities on a wide range of unique equipment and to develop novel experiments and new instrumentation.
The program's flagship magnet is the Mag Lab-made 900 MHz (21.1 tesla) NMR magnet. With an ultra-wide bore measuring 105 mm (about 4 inches) in diameter, this superconducting magnet offers the highest field for an MRI study of a living animal in the world.
Ion Cyclotron Resonance Program
This program is charged with developing and exploiting the unique capabilities of FT-ICR (Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron ResonanceFourier transform ion cyclotron resonance
Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry, also known as Fourier transform mass spectrometry, is a type of mass analyzer for determining the mass-to-charge ratio of ions based on the cyclotron frequency of the ions in a fixed magnetic field...
) mass spectrometry. The ICR program leads the world in instrument and technique development as well as pursuing novel applications of FT-ICR mass spectrometry. Under the leadership of director Alan G. Marshall
Alan G. Marshall
Alan G. Marshall is an American analytical chemist who has devoted his scientific career to developing a scientific technique known as Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry, which he co-invented. He was born in Bluffton, Ohio, in 1944, and earned his Bachelor's in Chemistry...
, the program continuously develops techniques and instruments and pursues novel applications of FT-ICR mass spectrometry. The program features several instruments, including the 14.5 tesla, 104 mm bore system, the highest-field superconducting ICR magnet in the world.
Electron Magnetic Resonance Program
The most common form of EMR is electron paramagnetic/spin resonance (EPR/ESR). In EPR experiments, transitions are observed between the mS sublevels of an electronic spin state S that are split by the applied magnetic field as well as by the fine structure interactions and the electron-nuclear hyperfine interactions. This technique has extensive applications in chemistry, biochemistry, biology, physics and materials research.Magnet Science and Technology
The Magnet Science and Technology division is charged with developing the technology and expertise for cutting-edge magnet systems. These magnet projects include building advanced magnet systems for the Tallahassee and Los Alamos sites, working with industry to develop the technology to improve high-field magnet manufacturing capabilities, and pushing the state of the art beyond what is currently available in high field magnet systems through research and development.Also at the lab's FSU headquarters, the Applied Superconductivity Center advances the science and technology of superconductivity by understanding and pushing the limits of both the low temperature niobium-based and the high temperature cuprate or MgB2-based materials. Focusing heavily on understanding and exploiting the interface between the “R” and the “D” in R&D, the ASC pursues the superconductors needed for everything from magnets for fusion, high energy physics, MRI, to electric power transmission lines and transformers.
In-House Research
An in-house research program flourishes at the Magnet Lab. The program utilizes Magnet Lab facilities to pursue high field research at the forefront of science and engineering, while advancing the lab’s user programs through development of new techniques and equipments.Condensed Matter Group
The Condensed Matter Group scientists concentrate on various aspects of condensed matter physics
Condensed matter physics
Condensed matter physics deals with the physical properties of condensed phases of matter. These properties appear when a number of atoms at the supramolecular and macromolecular scale interact strongly and adhere to each other or are otherwise highly concentrated in a system. The most familiar...
, including studies and experiments involving magnetism, the quantum hall effect, quantum oscillations, high temperature superconductivity, and heavy fermion systems.
Geochemistry Program
The geochemistry research program is centered around the use of trace elements and isotopes to understand the Earth processes and environment. The research interests range from the chemical evolution of Earth and solar system
Solar System
The Solar System consists of the Sun and the astronomical objects gravitationally bound in orbit around it, all of which formed from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud approximately 4.6 billion years ago. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun...
through time to local scale problems on the sources and transport of environmentally significant substances. The studies conducted by the geochemistry division concern terrestrial
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
and extraterrestrial
Extraterrestrial life
Extraterrestrial life is defined as life that does not originate from Earth...
questions and involve land-based and sea-going expeditions and spacecraft missions. Together with FSU's Chemistry and Oceanography departments, Geochemistry has started a program in Biogeochemical Dynamics.
Other Programs
The lab’s long-range planning includes enhancements to user programs, both for high field research and related fields. Various affiliated programs complement and help extend the capabilities of existing programs. These include cryogenics, optical microscopy, quantum materials and resonant ultrasound spectroscopy.
Los Alamos National Laboratory - The Pulsed Field Facility
Los Alamos National LaboratoryLos Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory, managed and operated by Los Alamos National Security , located in Los Alamos, New Mexico...
in New Mexico
New Mexico
New Mexico is a state located in the southwest and western regions of the United States. New Mexico is also usually considered one of the Mountain States. With a population density of 16 per square mile, New Mexico is the sixth-most sparsely inhabited U.S...
hosts the Pulsed Field Facility, which provides researchers with experimental capabilities for a wide range of measurements in non-destructive pulsed fields to 60 teslas. Pulsed field magnets create very high magnetic fields, but only for fractions of a second. A 100 tesla multi-shot magnet is being jointly constructed by the Department of Energy
United States Department of Energy
The United States Department of Energy is a Cabinet-level department of the United States government concerned with the United States' policies regarding energy and safety in handling nuclear material...
and the National Science Foundation. The laboratory is located at the center of Los Alamos. In 1999-2000, the facility was relocated into a new specially designed Experimental Hall to better accommodate user operations and support. The program is an integral component of the Magnet Lab and continues to be the first and only high pulsed field user facility in the United States. The laboratory is dedicated to driving pulsed magnetic field technology and instrumentation and to make research using pulsed magnetic fields available to scientists from the United States and around the world.
The facility provides a wide variety of experimental capabilities to 60 teslas, using short and long pulse magnets. Power comes from a pulsed power infrastructure which includes a 1.43 gigawatt motor generator and five 64-megawatt power supplies. The 1200-ton motor generator sits on a 4800-short ton (4350 t) inertia block which rests on 60 springs to minimize earth tremors is the centerpiece of the Pulsed Field Laboratory.
The facility's magnets include a 60 tesla long-pulse magnet that is the most powerful controlled-pulse magnet in the world.
University of Florida Programs
The University of Florida is home to user facilities in magnetic resonance imaging or (MRI) with an ultra-low temperature, ultra-quiet environment for experimental studies in the High B/T (high magnetic field/low temperature) Facility. Facilities are also available for the fabricationMicrofabrication
Microfabrication is the term that describes processes of fabrication of miniature structures, of micrometre sizes and smaller. Historically the earliest microfabrication processes were used for integrated circuit fabrication, also known as "semiconductor manufacturing" or "semiconductor device...
and characterization of nanostructure
Nanostructure
A nanostructure is an object of intermediate size between molecular and microscopic structures.In describing nanostructures it is necessary to differentiate between the number of dimensions on the nanoscale. Nanotextured surfaces have one dimension on the nanoscale, i.e., only the thickness of the...
s at a new Nanoscale Research Facility being operated in conjunction with the university's Major Analytical and Instrumentation Center.
High B/T Facility
The High B/T Facility is operated as part of the Microkelvin Laboratory of the Physics Department. The facility is designed to meet the needs of Magnet Lab users who wish to conduct experiments in high magnetic fields up to 15.2 teslas and at temperatures as low as 0.4 mK simultaneously. Faculty members in the facility work with users in the design of experiments where needed. Instrumentation is available for studies of magnetization, thermodynamic quantities, transport measurements, magnetic resonance, viscosity, diffusion, and pressure.The facility holds world records for high B/T in Bay 1 for short term low field capabilities and world records for high field long time (> 1 week) experiments. The research group leads the world in collective studies of quantum fluids and solids in terms of breadth and low temperature techniques (thermometry, NMR, ultrasound, heat capacity, sample cooling.)
Advanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectroscopy
The Advanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectroscopy program (AMRIS) contains facilities for the Mag Lab's NMR Program that complement the facilities at the lab's headquarters in Tallahassee. AMRIS is located at the University of Florida's McKnight Brain Institute. Their instruments include the 600 MHz NMR Magnet with 1 mm Triple-Resonance, High-Temperature Superconducting Probe, which delivers the highest mass sensitivity of any probe at any frequency in the world.External links
- National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, Florida State University
- Pulsed Field Facility, Los Alamos National Laboratory
- High B/T Facility, University of Florida
- Advanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectroscopy Facility, (AMRIS), University of Florida

