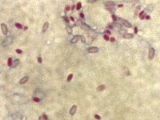
Mycobacterium smegmatis
Encyclopedia
Mycobacterium smegmatis is 3.0 to 5.0 µm long with a bacillus shape, an acid-fast
bacterial species in the phylum
Actinobacteria
. It can be stained by Ziehl-Neelsen method and the auramine-rhodamine fluorescent method. It was first reported in November 1884 by Lustgarten, who found a bacillus
with the staining appearance of tubercle bacilli in syphilitic chancres
. Subsequent to this, Alvarez and Tavel found organisms similar to that described by Lustgarten as well as in normal genital secretions (smegma
). This organism was later named M. smegmatis.
M. smegmatis is generally considered a non-pathogenic microorganism; however, in some very rare cases, it may cause disease, likely requiring an immunocompromised animal. M. smegmatis is useful for the research analysis of other Mycobacteria species in laboratory experiments. M. smegmatis is commonly used in work on the mycobacterium species due to its being a "fast grower" and non-pathogenic. M. smegmatis is a simple model that is easy to work with, i.e., with a fast doubling time and BSL-1 security level. The time and heavy infrastructure needed to work with pathogenic species prompted researchers to use M. smegmatis as a model for mycobacterial species. This species shares more than 2000 homologs with M. tuberculosis and shares the same unusual cell wall structure of M. tuberculosis and other mycobacterial species. The discovery of plasmids, phages, and mobile elements has enabled the construction of dedicated gene-inactivation and gene reporter systems. The M. smegmatis mc2155 strain is hypertransformable, and is now the work-horse of mycobacterial genetics. Furthermore, it is readily cultivatable in most synthetic or complex laboratory media, where it can form visible colonies in 3–5 days. These properties make it a very attractive model organism for M. tuberculosis and other mycobacterial pathogens. The complete genome of M. smegmatis has been sequenced by TIGR, and microarrays have been produced by PFGRC program (http://pfgrc.tigr.org/descriptionPages.shtml), adding further to its use as a model system to study mycobacteria.
Acid-fast
Acid-fastness is a physical property of certain bacteria, specifically their resistance to decolorization by acids during staining procedures.Acid-fast organisms are difficult to characterize using standard microbiological techniques Acid-fastness is a physical property of certain bacteria,...
bacterial species in the phylum
Phylum
In biology, a phylum The term was coined by Georges Cuvier from Greek φῦλον phylon, "race, stock," related to φυλή phyle, "tribe, clan." is a taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. "Phylum" is equivalent to the botanical term division....
Actinobacteria
Actinobacteria
Actinobacteria are a group of Gram-positive bacteria with high guanine and cytosine content. They can be terrestrial or aquatic. Actinobacteria is one of the dominant phyla of the bacteria....
. It can be stained by Ziehl-Neelsen method and the auramine-rhodamine fluorescent method. It was first reported in November 1884 by Lustgarten, who found a bacillus
Bacillus
Bacillus is a genus of Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria and a member of the division Firmicutes. Bacillus species can be obligate aerobes or facultative anaerobes, and test positive for the enzyme catalase. Ubiquitous in nature, Bacillus includes both free-living and pathogenic species...
with the staining appearance of tubercle bacilli in syphilitic chancres
Syphilis
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the spirochete bacterium Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum. The primary route of transmission is through sexual contact; however, it may also be transmitted from mother to fetus during pregnancy or at birth, resulting in congenital syphilis...
. Subsequent to this, Alvarez and Tavel found organisms similar to that described by Lustgarten as well as in normal genital secretions (smegma
Smegma
Smegma is a combination of exfoliated epithelial cells, transudated skin oils, and moisture. It occurs in both female and male mammalian genitalia.-Human smegma:Both females and males produce smegma...
). This organism was later named M. smegmatis.
M. smegmatis is generally considered a non-pathogenic microorganism; however, in some very rare cases, it may cause disease, likely requiring an immunocompromised animal. M. smegmatis is useful for the research analysis of other Mycobacteria species in laboratory experiments. M. smegmatis is commonly used in work on the mycobacterium species due to its being a "fast grower" and non-pathogenic. M. smegmatis is a simple model that is easy to work with, i.e., with a fast doubling time and BSL-1 security level. The time and heavy infrastructure needed to work with pathogenic species prompted researchers to use M. smegmatis as a model for mycobacterial species. This species shares more than 2000 homologs with M. tuberculosis and shares the same unusual cell wall structure of M. tuberculosis and other mycobacterial species. The discovery of plasmids, phages, and mobile elements has enabled the construction of dedicated gene-inactivation and gene reporter systems. The M. smegmatis mc2155 strain is hypertransformable, and is now the work-horse of mycobacterial genetics. Furthermore, it is readily cultivatable in most synthetic or complex laboratory media, where it can form visible colonies in 3–5 days. These properties make it a very attractive model organism for M. tuberculosis and other mycobacterial pathogens. The complete genome of M. smegmatis has been sequenced by TIGR, and microarrays have been produced by PFGRC program (http://pfgrc.tigr.org/descriptionPages.shtml), adding further to its use as a model system to study mycobacteria.

