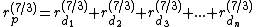Murray's law
Encyclopedia
Murray's law, or Murray's principle is a formula
for relating the radii
of daughter branches to the radii of the parent branch of a lumen
-based system. The branches classically refer to the branching of the circulatory system
or the respiratory system
, but have been shown to also hold true for the branchings of xylem
, the water transport system in plants.
Murray's original analysis was intended to determine the vessel radius that required minimum expenditure of energy by the organism. Larger vessels lower the energy expended in pumping blood because the pressure drop in the vessels reduces with increasing diameter according to the Hagen-Poiseuille equation
. However, larger vessels increase the overall volume of blood in the system; blood being a living fluid requires metabolic support. Murray's law is therefore an optimisation exercise to balance these factors.
For daughter branches arising from a common parent branch, the formula is:
daughter branches arising from a common parent branch, the formula is:
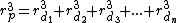
where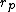 is the radius of the parent branch, and
is the radius of the parent branch, and 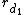 ,
, 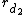 ,
,  ...
...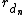 are the radii of the respective daughter branches.
are the radii of the respective daughter branches.
Murray's law is seeing increasing use as a biomimetic
design tool in engineering - for example it has recently been applied in the design of minimum mass vascular networks carrying a liquid healing agent to areas of damage in a Self-healing material
and the expression developed could readily be applied to minimum mass fluid systems in other engineering applications. The trade-off is directly analogous - larger diameter tubes are heavier because of both the tubing and the additional volume of enclosed fluid, but the pressure losses incurred are reduced and so the mass of the pumping system required is lower. The (inner) tube diameter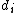 which minimizes the total mass (tube + fluid + pump), is given by the following equation in Laminar flow
which minimizes the total mass (tube + fluid + pump), is given by the following equation in Laminar flow
:
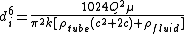
where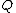 is the volume flow rate,
is the volume flow rate, 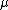 the fluid viscosity,
the fluid viscosity, 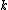 the power-to-weight ratio of the pump,
the power-to-weight ratio of the pump, 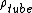 the density of the tubing material,
the density of the tubing material,  a constant of proportionality linking vessel wall thickness with internal diameter and
a constant of proportionality linking vessel wall thickness with internal diameter and 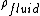 the density of the fluid.
the density of the fluid.
For Turbulent flow the equivalent relation (derived from the Darcy-Weisbach equation
) is :
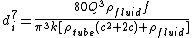
where f is the Darcy Friction Factor
. The junction relations above can therefore be applied in the following form in turbulent flow:
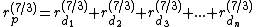
Formula
In mathematics, a formula is an entity constructed using the symbols and formation rules of a given logical language....
for relating the radii
Radius
In classical geometry, a radius of a circle or sphere is any line segment from its center to its perimeter. By extension, the radius of a circle or sphere is the length of any such segment, which is half the diameter. If the object does not have an obvious center, the term may refer to its...
of daughter branches to the radii of the parent branch of a lumen
Lumen (anatomy)
A lumen in biology is the inside space of a tubular structure, such as an artery or intestine...
-based system. The branches classically refer to the branching of the circulatory system
Circulatory system
The circulatory system is an organ system that passes nutrients , gases, hormones, blood cells, etc...
or the respiratory system
Respiratory system
The respiratory system is the anatomical system of an organism that introduces respiratory gases to the interior and performs gas exchange. In humans and other mammals, the anatomical features of the respiratory system include airways, lungs, and the respiratory muscles...
, but have been shown to also hold true for the branchings of xylem
Xylem
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue in vascular plants. . The word xylem is derived from the Classical Greek word ξυλον , meaning "wood"; the best-known xylem tissue is wood, though it is found throughout the plant...
, the water transport system in plants.
Murray's original analysis was intended to determine the vessel radius that required minimum expenditure of energy by the organism. Larger vessels lower the energy expended in pumping blood because the pressure drop in the vessels reduces with increasing diameter according to the Hagen-Poiseuille equation
Hagen-Poiseuille equation
In fluid dynamics, the Hagen–Poiseuille equation is a physical law that gives the pressure drop in a fluid flowing through a long cylindrical pipe. The assumptions of the equation are that the flow is laminar viscous and incompressible and the flow is through a constant circular cross-section that...
. However, larger vessels increase the overall volume of blood in the system; blood being a living fluid requires metabolic support. Murray's law is therefore an optimisation exercise to balance these factors.
For
 daughter branches arising from a common parent branch, the formula is:
daughter branches arising from a common parent branch, the formula is: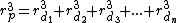
where
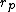 is the radius of the parent branch, and
is the radius of the parent branch, and 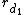 ,
, 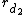 ,
,  ...
...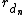 are the radii of the respective daughter branches.
are the radii of the respective daughter branches.Murray's law is seeing increasing use as a biomimetic
Biomimicry
Biomimicry or biomimetics is the examination of nature, its models, systems, processes, and elements to emulate or take inspiration from in order to solve human problems. The term biomimicry and biomimetics come from the Greek words bios, meaning life, and mimesis, meaning to imitate...
design tool in engineering - for example it has recently been applied in the design of minimum mass vascular networks carrying a liquid healing agent to areas of damage in a Self-healing material
Self-healing material
Self-healing materials are a class of smart materials that have the structurally incorporated ability to repair damage caused by mechanical usage over time. The inspiration comes from biological systems, which have the ability to heal after being wounded...
and the expression developed could readily be applied to minimum mass fluid systems in other engineering applications. The trade-off is directly analogous - larger diameter tubes are heavier because of both the tubing and the additional volume of enclosed fluid, but the pressure losses incurred are reduced and so the mass of the pumping system required is lower. The (inner) tube diameter
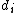 which minimizes the total mass (tube + fluid + pump), is given by the following equation in Laminar flow
which minimizes the total mass (tube + fluid + pump), is given by the following equation in Laminar flowLaminar flow
Laminar flow, sometimes known as streamline flow, occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers, with no disruption between the layers. At low velocities the fluid tends to flow without lateral mixing, and adjacent layers slide past one another like playing cards. There are no cross currents...
:
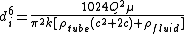
where
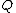 is the volume flow rate,
is the volume flow rate, 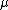 the fluid viscosity,
the fluid viscosity, 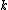 the power-to-weight ratio of the pump,
the power-to-weight ratio of the pump, 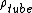 the density of the tubing material,
the density of the tubing material,  a constant of proportionality linking vessel wall thickness with internal diameter and
a constant of proportionality linking vessel wall thickness with internal diameter and 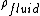 the density of the fluid.
the density of the fluid.For Turbulent flow the equivalent relation (derived from the Darcy-Weisbach equation
Darcy-Weisbach equation
In fluid dynamics, the Darcy–Weisbach equation is a phenomenological equation, which relates the head loss — or pressure loss — due to friction along a given length of pipe to the average velocity of the fluid flow. The equation is named after Henry Darcy and Julius Weisbach.The Darcy–Weisbach...
) is :
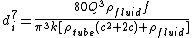
where f is the Darcy Friction Factor
Darcy friction factor formulae
In fluid dynamics, the Darcy friction factor formulae are equations — based on experimental data and theory — for the Darcy friction factor. The Darcy friction factor is a dimensionless quantity used in the Darcy–Weisbach equation, for the description of friction losses in pipe flow as well as open...
. The junction relations above can therefore be applied in the following form in turbulent flow: