
Multiple (mathematics)
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, a multiple is the product
of any quantity and an integer
. In other words, for the quantities a and b, we say that b is a multiple of a if b = na for some integer n , which is called the multiplier
or coefficient
. If a is not zero, this is equivalent to saying that b/a is an integer with no remainder
. If a and b are both integers, and b is a multiple of a, then a is called a divisor
of b.
kb
The product of two integers is sometimes called an integer multiple.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, a multiple is the product
Multiplication
Multiplication is the mathematical operation of scaling one number by another. It is one of the four basic operations in elementary arithmetic ....
of any quantity and an integer
Integer
The integers are formed by the natural numbers together with the negatives of the non-zero natural numbers .They are known as Positive and Negative Integers respectively...
. In other words, for the quantities a and b, we say that b is a multiple of a if b = na for some integer n , which is called the multiplier
Multiplier
The term multiplier may refer to:In electrical engineering:* Binary multiplier, a digital circuit to perform rapid multiplication of two numbers in binary representation* Analog multiplier, a device that multiplies two analog signals...
or coefficient
Coefficient
In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor in some term of an expression ; it is usually a number, but in any case does not involve any variables of the expression...
. If a is not zero, this is equivalent to saying that b/a is an integer with no remainder
Remainder
In arithmetic, the remainder is the amount "left over" after the division of two integers which cannot be expressed with an integer quotient....
. If a and b are both integers, and b is a multiple of a, then a is called a divisor
Divisor
In mathematics, a divisor of an integer n, also called a factor of n, is an integer which divides n without leaving a remainder.-Explanation:...
of b.
kb
The product of two integers is sometimes called an integer multiple.
Examples
14, 49, -21 and 0 are multiples of 7 where as 3 and -6 are not. This is because there are integers that 7 may be multiplied by to reach the values of 14, 49, 0 and -21, while there are no such integers for 3 and -6. Each of the products listed below, and in particular, the products for 3 and -6, is the only way that the relevant number can be written as a product of 7 and another real number:-
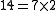
-
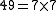
-

-

-
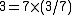 , and
, and 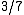 is a rational number, not an integer
is a rational number, not an integer -
 , and
, and 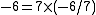 is a rational number, not an integer.
is a rational number, not an integer.
Properties
- 0 is a multiple of everything (
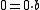 ).
). - The product of any integer
 and any integer is a multiple of
and any integer is a multiple of  . In particular,
. In particular,  , which is equal to
, which is equal to 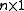 , is a multiple of
, is a multiple of  (every integer is a multiple of itself), since 1 is an integer.
(every integer is a multiple of itself), since 1 is an integer. - If
 and
and 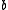 are multiples of
are multiples of  then
then  and
and 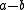 are also multiples of
are also multiples of  .
.
See also
- Ideal (ring theory)Ideal (ring theory)In ring theory, a branch of abstract algebra, an ideal is a special subset of a ring. The ideal concept allows the generalization in an appropriate way of some important properties of integers like "even number" or "multiple of 3"....
- DecimalDecimalThe decimal numeral system has ten as its base. It is the numerical base most widely used by modern civilizations....
and SI prefixSI prefixThe International System of Units specifies a set of unit prefixes known as SI prefixes or metric prefixes. An SI prefix is a name that precedes a basic unit of measure to indicate a decadic multiple or fraction of the unit. Each prefix has a unique symbol that is prepended to the unit symbol...

