
Multinational state
Encyclopedia
A multinational state is a sovereign state
which is viewed as comprising two or more nation
s. Such a state contrasts with a nation-state
where a single nation comprises the bulk of the population. The United Kingdom
, the Russian Federation
and Canada
are viewed as present-day examples of multinational states, while Austria-Hungary
, the USSR and Yugoslavia
are examples of historical multinational states which have since split into a number of sovereign states.
A multinational state need not also be multicultural
.
Generally, in the early modern era, multinational states proved to be less successful than nation-states.
Many attempts have been made to define what a multinational state is. One complicating factor is that it is possible for many of the people of what can be considered a 'nation' to consider they have two different nationalities simultaneously. As Ilan Peleg has noted,
has over a hundred and sixty different ethnic groups and indigenous peoples. The largest population is the ethnic Russians
, who are Slavs with Orthodox traditions, while the Tatars
and Bashkirs
have a Muslim
culture. Russia also has Buddhist populations, such as the nomad
ic Buryats
and Kalmyks, and the Shamanistic
peoples of Siberia
and the Extreme North
, as well as the Finno-Ugric peoples
of the Russian North West and the Volga Region
and the peoples of the Northern Caucasus, all contributing to the extreme cultural and national diversity of the country.
Out of a total of more than a hundred languages which are spoken in the Russian Federation, the country has twenty-seven official languages
. More than 3% of the whole population of the Federation speak Tatar
.
In parts of the Federal state conflicts of nationality and other factors have led to secessionism, most notably in Chechnya
, where the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria
and the Caucasus Emirate
have sought independence from Russia.
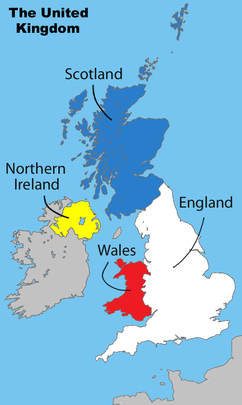 While the Office for National Statistics
While the Office for National Statistics
and others describe the United Kingdom
as a 'nation state', others, including a then Prime Minister, describe it as a 'multinational state', and the term Home Nations
is used to describe the four national teams that represent the four nations of the United Kingdom (England
, Northern Ireland
, Scotland
, Wales
).
The Kingdom of Great Britain
was created by the political union
of the Kingdom of England
and the Kingdom of Scotland
on 1 May 1707. This event was the result of the Treaty of Union
that was agreed on 22 July 1706, and then ratified by both the Parliament of England
and Parliament of Scotland
each passing an Act of Union
in 1707. The kingdoms of England and Scotland, together with the kingdom of Ireland, had already been in a personal union
as a result of the Union of the Crowns
in 1603, when James VI, King of Scots
inherited the Kingdoms of England and Ireland and moved his court from Edinburgh to London. However, until 1707, all three remained separate political entities and retained their separate political institutions. At the outset of this state, many of its inhabitants retained the sensation of having English, Scottish, Welsh, or indeed Cornish nationality. It is also notable that languages other than English were spoken, principally Scottish Gaelic, Scots
, Welsh
, Cornish
, and Norn
.
Almost a century later the Kingdom of Ireland
merged with the Kingdom of Great Britain to form the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
with the passing of the Act of Union 1800. In this way, the United Kingdom became the union of the kingdoms of England
, Ireland
and Scotland
. Disputes within Ireland
over the terms of Irish Home Rule led eventually to the partition of the island
in 1921, with Dominion status for the Irish Free State
in 1922 while Northern Ireland remained part of the UK. As a result, in 1927, the formal title of the UK was changed
to its current form, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
The end of the 20th century saw major changes to the governance of the UK with the establishment of devolved
national administrations for Northern Ireland, Scotland, and Wales following pre-legislative referendums
.
The Scottish National Party
, a major political force in Scotland, is committed to the goal of an independent Scotland
within the European Union
, but this is opposed by the other parties in Scotland. Plaid Cymru
has a similar ambition for Wales.
Austria-Hungary
, which succeeded the Austrian Empire
, is a historical instance of a multinational state. The centrifugal forces within it, together with the loss of the First World War, led to its breaking up in 1918, when its successor states included the First Austrian Republic
, the Kingdom of Hungary
, Czechoslovakia
, and the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs
which became part of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia
. Parts of Austria-Hungary were also incorporated into Poland
, Ukraine
, the Kingdom of Romania
and the Kingdom of Italy
.
The Empire's principal languages were German
, Hungarian
, Polish
Czech
and Croatian
, but there were many more besides, including Ukrainian
, Romanian
, Slovak
, Serbian
, Slovene, Rusyn
, Italian
, and Yiddish
.
of Soviet republics
(of which there were 15 after 1956) with the capital in Moscow
. It was founded in December 1922 when the Russian SFSR, which formed during the Russian Revolution of 1917
and emerged victorious in the ensuing Russian Civil War
, unified with the Transcaucasian, Ukrainian
and Belorussian SSRs. Addressing the Extraordinary Eighth Congress of Soviets of the U.S.S.R. on 25 November 1936, Stalin stated that "within the Soviet Union there are about sixty nations, national groups and nationalities. The Soviet state is a multi-national state."
In the late 1980s, some constituent republics of the Soviet Union started legal moves towards or even declaration of sovereignty
over their territories, citing Article 72 of the USSR Constitution, which stated that any constituent republic was free to secede. On 7 April 1990, a law was passed allowing a republic to secede if more than two-thirds of that republic's residents vote for secession on a referendum. Many held their first free elections in the Soviet era for their own national legislatures in 1990. Many of these legislatures proceeded to produce legislation contradicting the Union laws in what was known as the "War of Laws
".
In 1989, the Russian SFSR
, which was then the largest constituent republic (with about half of the population) convened a newly elected Congress of People's Deputies. Boris Yeltsin
was elected the chairman of the Congress. On 12 June 1990, the Congress declared Russia's sovereignty over its territory
and proceeded to pass laws that attempted to supersede some of the USSR's laws. The period of legal uncertainty continued throughout 1991 as constituent republics slowly became de facto
independent.
A referendum for the preservation of the USSR
was held on 17 March 1991, with the majority of the population voting for preservation of the Union in nine out of 15 republics. The referendum gave Gorbachev a minor boost, and, in the summer of 1991, the New Union Treaty
was designed and agreed upon by eight republics which would have turned the Soviet Union into a much looser federation. The signing of the treaty, however, was interrupted by the August Coup—an attempted coup d'état
against Gorbachev by hardline Communist Party members of the government and the KGB, who sought to reverse Gorbachev's reforms and reassert the central government's control over the republics. After the coup collapsed, Yeltsin—who had publicly opposed it—came out as a hero while Gorbachev's power was effectively ended. The balance of power tipped significantly towards the republics. In August 1991, Latvia and Estonia immediately declared restoration of full independence (following Lithuania's 1990 example), while the other twelve republics continued discussing new, increasingly looser, models of the Union.
On 8 December 1991, the presidents of Russia, Ukraine
and Belarus
signed the Belavezha Accords
which declared the Soviet Union dissolved and established the Commonwealth of Independent States
(CIS) in its place. While doubts remained over the authority of the Belavezha Accords to dissolve the Union, on 21 December 1991, the representatives of all Soviet republics except Georgia, including those republics that had signed the Belavezha Accords, signed the Alma-Ata Protocol
, which confirmed the dismemberment and consequential extinction of the USSR and restated the establishment of the CIS. The summit of Alma-Ata also agreed on several other practical measures consequential to the extinction of the Union. On 25 December 1991, Gorbachev yielded to the inevitable and resigned as the president of the USSR, declaring the office extinct. He turned the powers that until then were vested in the presidency over to Boris Yeltsin
, president of Russia
.
The following day, the Supreme Soviet, the highest governmental body of the Soviet Union, recognized the bankruptcy and collapse of the Soviet Union and dissolved itself. This is generally recognized as the official, final dissolution of the Soviet Union as a functioning state. Many organizations such as the Soviet Army
and police forces continued to remain in place in the early months of 1992 but were slowly phased out and either withdrawn from or were absorbed by the newly independent states.
 The first country to be known by this name was the Kingdom of Yugoslavia
The first country to be known by this name was the Kingdom of Yugoslavia
, which before 3 October 1929 was known as the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. It was established on 1 December 1918 by the union of the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs
and the Kingdom of Serbia
(to which the Kingdom of Montenegro
was annexed on 13 November 1918, and the Conference of Ambassadors in Paris
gave international recognition to the union on 13 July 1922). The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was invaded by the Axis powers
in 1941, and because of the events that followed, was officially abolished in 1943 and 1945.
The second country with this name was the Democratic Federal Yugoslavia, proclaimed in 1943 by the Yugoslav Partisans resistance movement during World War II
. It was renamed to the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia in 1946, when a communist government was established. In 1963, it was renamed again to the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia
(SFRY). This was the largest Yugoslav state, as Istria
and Rijeka
were added to the new Yugoslavia after the end of World War II.
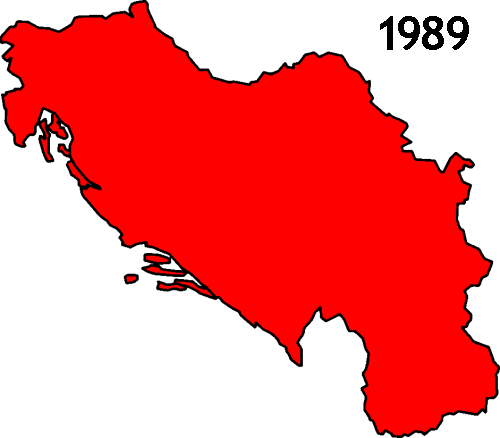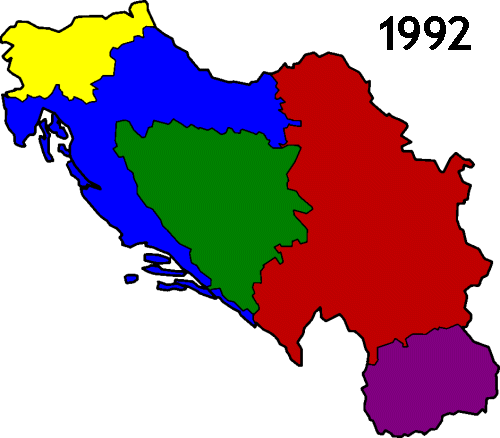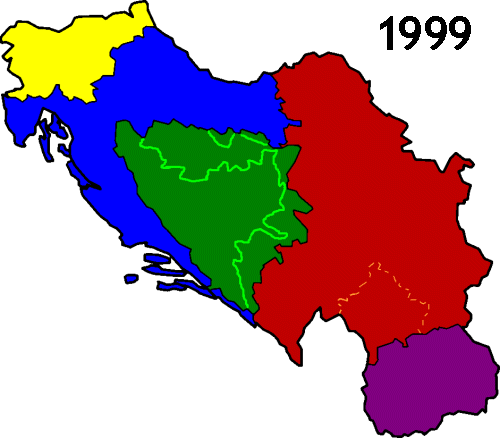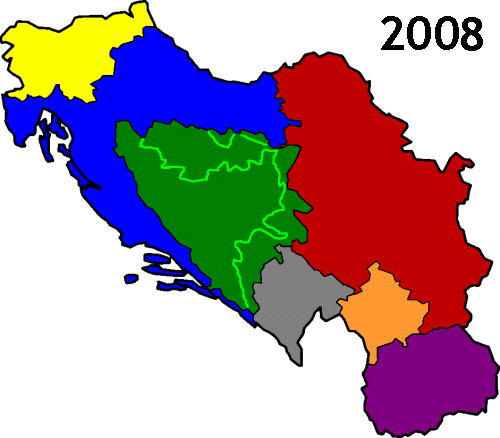
The constituent six Socialist Republics and two Socialist Autonomous Provinces that made up the country were: SR Bosnia and Herzegovina, SR Croatia, SR Macedonia, SR Montenegro, SR Slovenia and SR Serbia (including the autonomous
provinces of SAP Vojvodina and SAP Kosovo which after 1974 were largely equal to the other members of the federation).
Starting in 1991, the SFRY disintegrated in the Yugoslav Wars
which followed the secession
of most of the country's constituent entities. The next Yugoslavia, known as the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, existed until 2003, when it was renamed Serbia and Montenegro
, but in 2006 this state finally separated into Serbia
and Montenegro
.
Sovereign state
A sovereign state, or simply, state, is a state with a defined territory on which it exercises internal and external sovereignty, a permanent population, a government, and the capacity to enter into relations with other sovereign states. It is also normally understood to be a state which is neither...
which is viewed as comprising two or more nation
Nation
A nation may refer to a community of people who share a common language, culture, ethnicity, descent, and/or history. In this definition, a nation has no physical borders. However, it can also refer to people who share a common territory and government irrespective of their ethnic make-up...
s. Such a state contrasts with a nation-state
Nation-state
The nation state is a state that self-identifies as deriving its political legitimacy from serving as a sovereign entity for a nation as a sovereign territorial unit. The state is a political and geopolitical entity; the nation is a cultural and/or ethnic entity...
where a single nation comprises the bulk of the population. The United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, the Russian Federation
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
and Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
are viewed as present-day examples of multinational states, while Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary , more formally known as the Kingdoms and Lands Represented in the Imperial Council and the Lands of the Holy Hungarian Crown of Saint Stephen, was a constitutional monarchic union between the crowns of the Austrian Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary in...
, the USSR and Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia refers to three political entities that existed successively on the western part of the Balkans during most of the 20th century....
are examples of historical multinational states which have since split into a number of sovereign states.
A multinational state need not also be multicultural
Multiculturalism
Multiculturalism is the appreciation, acceptance or promotion of multiple cultures, applied to the demographic make-up of a specific place, usually at the organizational level, e.g...
.
Generally, in the early modern era, multinational states proved to be less successful than nation-states.
Many attempts have been made to define what a multinational state is. One complicating factor is that it is possible for many of the people of what can be considered a 'nation' to consider they have two different nationalities simultaneously. As Ilan Peleg has noted,
Russia
The present-day federal state of RussiaRussia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
has over a hundred and sixty different ethnic groups and indigenous peoples. The largest population is the ethnic Russians
Russians
The Russian people are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Russia, speaking the Russian language and primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries....
, who are Slavs with Orthodox traditions, while the Tatars
Tatars
Tatars are a Turkic speaking ethnic group , numbering roughly 7 million.The majority of Tatars live in the Russian Federation, with a population of around 5.5 million, about 2 million of which in the republic of Tatarstan.Significant minority populations are found in Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan,...
and Bashkirs
Bashkirs
The Bashkirs are a Turkic people indigenous to Bashkortostan extending on both parts of the Ural mountains, on the place where Europe meets Asia. Groups of Bashkirs also live in the republic of Tatarstan, Perm Krai, Chelyabinsk, Orenburg, Tyumen, Sverdlovsk, Kurgan, Samara and Saratov Oblasts of...
have a Muslim
Muslim
A Muslim, also spelled Moslem, is an adherent of Islam, a monotheistic, Abrahamic religion based on the Quran, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God as revealed to prophet Muhammad. "Muslim" is the Arabic term for "submitter" .Muslims believe that God is one and incomparable...
culture. Russia also has Buddhist populations, such as the nomad
Nomad
Nomadic people , commonly known as itinerants in modern-day contexts, are communities of people who move from one place to another, rather than settling permanently in one location. There are an estimated 30-40 million nomads in the world. Many cultures have traditionally been nomadic, but...
ic Buryats
Buryats
The Buryats or Buriyads , numbering approximately 436,000, are the largest ethnic minority group in Siberia and are mainly concentrated in their homeland, the Buryat Republic, a federal subject of Russia...
and Kalmyks, and the Shamanistic
Shamanism
Shamanism is an anthropological term referencing a range of beliefs and practices regarding communication with the spiritual world. To quote Eliade: "A first definition of this complex phenomenon, and perhaps the least hazardous, will be: shamanism = technique of ecstasy." Shamanism encompasses the...
peoples of Siberia
Siberia
Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th...
and the Extreme North
Extreme North (Russia)
The Extreme North or Far North is a large part of Russia located mainly north of the Arctic Circle and boasting enormous mineral and natural resources....
, as well as the Finno-Ugric peoples
Finno-Ugric peoples
The Finno-Ugric peoples are any of several peoples of Europe who speak languages of the proposed Finno-Ugric language family, such as the Finns, Estonians, Mordvins, and Hungarians...
of the Russian North West and the Volga Region
Volga Region
Volga Region is a historical region of Russia that encompasses the territories adjacent to the flow of Volga River. According to the flow of the river, it is usually classified into the Middle Volga Region and Lower Volga Region...
and the peoples of the Northern Caucasus, all contributing to the extreme cultural and national diversity of the country.
Out of a total of more than a hundred languages which are spoken in the Russian Federation, the country has twenty-seven official languages
Languages of Russia
Of all the languages of Russia, Russian is the only official language. 27 different languages are considered official languages in various regions of Russia, along with Russian. There are over 100 minority languages spoken in Russia today.-History:...
. More than 3% of the whole population of the Federation speak Tatar
Tatar language
The Tatar language , or more specifically Kazan Tatar, is a Turkic language spoken by the Tatars of historical Kazan Khanate, including modern Tatarstan and Bashkiria...
.
In parts of the Federal state conflicts of nationality and other factors have led to secessionism, most notably in Chechnya
Chechnya
The Chechen Republic , commonly referred to as Chechnya , also spelled Chechnia or Chechenia, sometimes referred to as Ichkeria , is a federal subject of Russia . It is located in the southeastern part of Europe in the Northern Caucasus mountains. The capital of the republic is the city of Grozny...
, where the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria
Chechen Republic of Ichkeria
The Chechen Republic of Ichkeria is the unrecognized secessionist government of Chechnya. The republic was proclaimed in late 1991 by Dzokhar Dudayev, and fought two devastating wars between separatists and the Russian Federation which denounced secession...
and the Caucasus Emirate
Caucasus Emirate
The Caucasus Emirate also known as the Caucasian Emirate is a self-proclaimed virtual state entity, partially successor to the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria and was officially announced on October 31, 2007 by former President of Ichkeria Dokka Umarov, who became the first Emir...
have sought independence from Russia.
United Kingdom

Office for National Statistics
The Office for National Statistics is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department which reports directly to the Parliament of the United Kingdom.- Overview :...
and others describe the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
as a 'nation state', others, including a then Prime Minister, describe it as a 'multinational state', and the term Home Nations
Home Nations
Home Nations is a collective term with one of two meanings depending on the context. Politically, it means the nations of the constituent countries of the United Kingdom...
is used to describe the four national teams that represent the four nations of the United Kingdom (England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
, Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland is one of the four countries of the United Kingdom. Situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, it shares a border with the Republic of Ireland to the south and west...
, Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
, Wales
Wales
Wales is a country that is part of the United Kingdom and the island of Great Britain, bordered by England to its east and the Atlantic Ocean and Irish Sea to its west. It has a population of three million, and a total area of 20,779 km²...
).
The Kingdom of Great Britain
Kingdom of Great Britain
The former Kingdom of Great Britain, sometimes described as the 'United Kingdom of Great Britain', That the Two Kingdoms of Scotland and England, shall upon the 1st May next ensuing the date hereof, and forever after, be United into One Kingdom by the Name of GREAT BRITAIN. was a sovereign...
was created by the political union
Political union
A political union is a type of state which is composed of or created out of smaller states. Unlike a personal union, the individual states share a common government and the union is recognized internationally as a single political entity...
of the Kingdom of England
Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was, from 927 to 1707, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe. At its height, the Kingdom of England spanned the southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain and several smaller outlying islands; what today comprises the legal jurisdiction of England...
and the Kingdom of Scotland
Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland was a Sovereign state in North-West Europe that existed from 843 until 1707. It occupied the northern third of the island of Great Britain and shared a land border to the south with the Kingdom of England...
on 1 May 1707. This event was the result of the Treaty of Union
Treaty of Union
The Treaty of Union is the name given to the agreement that led to the creation of the united kingdom of Great Britain, the political union of the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of Scotland, which took effect on 1 May 1707...
that was agreed on 22 July 1706, and then ratified by both the Parliament of England
Parliament of England
The Parliament of England was the legislature of the Kingdom of England. In 1066, William of Normandy introduced a feudal system, by which he sought the advice of a council of tenants-in-chief and ecclesiastics before making laws...
and Parliament of Scotland
Parliament of Scotland
The Parliament of Scotland, officially the Estates of Parliament, was the legislature of the Kingdom of Scotland. The unicameral parliament of Scotland is first found on record during the early 13th century, with the first meeting for which a primary source survives at...
each passing an Act of Union
Acts of Union 1707
The Acts of Union were two Parliamentary Acts - the Union with Scotland Act passed in 1706 by the Parliament of England, and the Union with England Act passed in 1707 by the Parliament of Scotland - which put into effect the terms of the Treaty of Union that had been agreed on 22 July 1706,...
in 1707. The kingdoms of England and Scotland, together with the kingdom of Ireland, had already been in a personal union
Personal union
A personal union is the combination by which two or more different states have the same monarch while their boundaries, their laws and their interests remain distinct. It should not be confused with a federation which is internationally considered a single state...
as a result of the Union of the Crowns
Union of the Crowns
The Union of the Crowns was the accession of James VI, King of Scots, to the throne of England, and the consequential unification of Scotland and England under one monarch. The Union of Crowns followed the death of James' unmarried and childless first cousin twice removed, Queen Elizabeth I of...
in 1603, when James VI, King of Scots
James I of England
James VI and I was King of Scots as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the English and Scottish crowns on 24 March 1603...
inherited the Kingdoms of England and Ireland and moved his court from Edinburgh to London. However, until 1707, all three remained separate political entities and retained their separate political institutions. At the outset of this state, many of its inhabitants retained the sensation of having English, Scottish, Welsh, or indeed Cornish nationality. It is also notable that languages other than English were spoken, principally Scottish Gaelic, Scots
Scots language
Scots is the Germanic language variety spoken in Lowland Scotland and parts of Ulster . It is sometimes called Lowland Scots to distinguish it from Scottish Gaelic, the Celtic language variety spoken in most of the western Highlands and in the Hebrides.Since there are no universally accepted...
, Welsh
Welsh language
Welsh is a member of the Brythonic branch of the Celtic languages spoken natively in Wales, by some along the Welsh border in England, and in Y Wladfa...
, Cornish
Cornish language
Cornish is a Brythonic Celtic language and a recognised minority language of the United Kingdom. Along with Welsh and Breton, it is directly descended from the ancient British language spoken throughout much of Britain before the English language came to dominate...
, and Norn
Norn language
Norn is an extinct North Germanic language that was spoken in Shetland and Orkney, off the north coast of mainland Scotland, and in Caithness. After the islands were pledged to Scotland by Norway in the 15th century, it was gradually replaced by Scots and on the mainland by Scottish...
.
Almost a century later the Kingdom of Ireland
Kingdom of Ireland
The Kingdom of Ireland refers to the country of Ireland in the period between the proclamation of Henry VIII as King of Ireland by the Crown of Ireland Act 1542 and the Act of Union in 1800. It replaced the Lordship of Ireland, which had been created in 1171...
merged with the Kingdom of Great Britain to form the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was the formal name of the United Kingdom during the period when what is now the Republic of Ireland formed a part of it....
with the passing of the Act of Union 1800. In this way, the United Kingdom became the union of the kingdoms of England
Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was, from 927 to 1707, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe. At its height, the Kingdom of England spanned the southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain and several smaller outlying islands; what today comprises the legal jurisdiction of England...
, Ireland
Kingdom of Ireland
The Kingdom of Ireland refers to the country of Ireland in the period between the proclamation of Henry VIII as King of Ireland by the Crown of Ireland Act 1542 and the Act of Union in 1800. It replaced the Lordship of Ireland, which had been created in 1171...
and Scotland
Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland was a Sovereign state in North-West Europe that existed from 843 until 1707. It occupied the northern third of the island of Great Britain and shared a land border to the south with the Kingdom of England...
. Disputes within Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
over the terms of Irish Home Rule led eventually to the partition of the island
Partition of Ireland
The partition of Ireland was the division of the island of Ireland into two distinct territories, now Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland . Partition occurred when the British Parliament passed the Government of Ireland Act 1920...
in 1921, with Dominion status for the Irish Free State
Irish Free State
The Irish Free State was the state established as a Dominion on 6 December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty, signed by the British government and Irish representatives exactly twelve months beforehand...
in 1922 while Northern Ireland remained part of the UK. As a result, in 1927, the formal title of the UK was changed
Royal and Parliamentary Titles Act 1927
The Royal and Parliamentary Titles Act 1927 [17 & 18 Geo. 5 c. 4] was an Act of Parliament of the United Kingdom that authorised the alteration of the British monarch's royal style and titles, and altered the formal name of the British Parliament, in recognition of much of Ireland separating from...
to its current form, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
The end of the 20th century saw major changes to the governance of the UK with the establishment of devolved
Devolution
Devolution is the statutory granting of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to government at a subnational level, such as a regional, local, or state level. Devolution can be mainly financial, e.g. giving areas a budget which was formerly administered by central government...
national administrations for Northern Ireland, Scotland, and Wales following pre-legislative referendums
Referendums in the United Kingdom
Referendums are only occasionally held by the government of the United Kingdom. Eleven referendums have been held so far , the first in 1973; only two of these covered the whole UK...
.
The Scottish National Party
Scottish National Party
The Scottish National Party is a social-democratic political party in Scotland which campaigns for Scottish independence from the United Kingdom....
, a major political force in Scotland, is committed to the goal of an independent Scotland
Scottish independence
Scottish independence is a political ambition of political parties, advocacy groups and individuals for Scotland to secede from the United Kingdom and become an independent sovereign state, separate from England, Wales and Northern Ireland....
within the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
, but this is opposed by the other parties in Scotland. Plaid Cymru
Plaid Cymru
' is a political party in Wales. It advocates the establishment of an independent Welsh state within the European Union. was formed in 1925 and won its first seat in 1966...
has a similar ambition for Wales.
Austria-Hungary
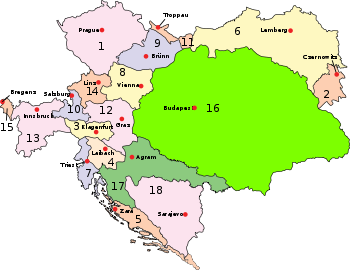 Kingdom of Bohemia The Kingdom of Bohemia was a country located in the region of Bohemia in Central Europe, most of whose territory is currently located in the modern-day Czech Republic. The King was Elector of Holy Roman Empire until its dissolution in 1806, whereupon it became part of the Austrian Empire, and... , 2. Bukovina Bukovina Bukovina is a historical region on the northern slopes of the northeastern Carpathian Mountains and the adjoining plains.-Name:The name Bukovina came into official use in 1775 with the region's annexation from the Principality of Moldavia to the possessions of the Habsburg Monarchy, which became... , 3. Carinthia Duchy of Carinthia The Duchy of Carinthia was a duchy located in southern Austria and parts of northern Slovenia. It was separated from the Duchy of Bavaria in 976, then the first newly created Imperial State beside the original German stem duchies.... , 4. Carniola Carniola Carniola was a historical region that comprised parts of what is now Slovenia. As part of Austria-Hungary, the region was a crown land officially known as the Duchy of Carniola until 1918. In 1849, the region was subdivided into Upper Carniola, Lower Carniola, and Inner Carniola... , 5. Dalmatia Kingdom of Dalmatia The Kingdom of Dalmatia was an administrative division of the Habsburg Monarchy from 1815 to 1918. Its capital was Zadar.-History:... , 6. Galicia Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria The Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria was a crownland of the Habsburg Monarchy, the Austrian Empire, and Austria–Hungary from 1772 to 1918 .This historical region in eastern Central Europe is currently divided between Poland and Ukraine... , 7. Küstenland Austrian Littoral The Austrian Littoral was established as a crown land of the Austrian Empire in 1849. In 1861 it was divided into the three crown lands of the Imperial Free City of Trieste and its suburbs, the Margraviate of Istria, and the Princely County of Gorizia and Gradisca, which each had separate... , 8. Lower Austria Lower Austria Lower Austria is the northeasternmost state of the nine states in Austria. The capital of Lower Austria since 1986 is Sankt Pölten, the most recently designated capital town in Austria. The capital of Lower Austria had formerly been Vienna, even though Vienna is not officially part of Lower Austria... , 9. Moravia Moravia Moravia is a historical region in Central Europe in the east of the Czech Republic, and one of the former Czech lands, together with Bohemia and Silesia. It takes its name from the Morava River which rises in the northwest of the region... , 10. Salzburg Duchy of Salzburg The Duchy of Salzburg was a Cisleithanian Kronland of the Austrian Empire and Austria-Hungary from 1849–1918. Its capital was Salzburg, while other towns in the duchy included Zell am See and Gastein.... , 11. Silesia Austrian Silesia Austrian Silesia , officially the Duchy of Upper and Lower Silesia was an autonomous region of the Kingdom of Bohemia and the Austrian Empire, from 1867 a Cisleithanian crown land of Austria-Hungary... , 12. Styria Duchy of Styria The history of Styria concerns the region roughly corresponding to the modern Austrian state of Styria and the Slovene region of Styria from its settlement by Germans and Slavs in the Dark Ages until the present... , 13. Tirol Tyrol (state) Tyrol is a state or Bundesland, located in the west of Austria. It comprises the Austrian part of the historical region of Tyrol.The state is split into two parts–called North Tyrol and East Tyrol–by a -wide strip of land where the state of Salzburg borders directly on the Italian province of... , 14. Upper Austria Upper Austria Upper Austria is one of the nine states or Bundesländer of Austria. Its capital is Linz. Upper Austria borders on Germany and the Czech Republic, as well as on the other Austrian states of Lower Austria, Styria, and Salzburg... , 15. Vorarlberg Vorarlberg Vorarlberg is the westernmost federal-state of Austria. Although it is the second smallest in terms of area and population , it borders three countries: Germany , Switzerland and Liechtenstein... ; 16. Hungary Administrative divisions of the Kingdom of Hungary The following lists show the administrative divisions of the lands belonging to the Hungarian crown at selected points of time. The names are given in the main official language used in the Kingdom at the times in question.... 17. Croatia-Slavonia; 18. Bosnia Bosnia and Herzegovina (Austro-Hungarian condominium) The Austro-Hungarian condominium of Bosnia and Herzegovina was a condominium established after the annexation of Bosnia and Herzegovina by Austria-Hungary in 1908, following its occupation in 1878 under the terms of the Treaty of Berlin.-History:... |
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary , more formally known as the Kingdoms and Lands Represented in the Imperial Council and the Lands of the Holy Hungarian Crown of Saint Stephen, was a constitutional monarchic union between the crowns of the Austrian Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary in...
, which succeeded the Austrian Empire
Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire was a modern era successor empire, which was centered on what is today's Austria and which officially lasted from 1804 to 1867. It was followed by the Empire of Austria-Hungary, whose proclamation was a diplomatic move that elevated Hungary's status within the Austrian Empire...
, is a historical instance of a multinational state. The centrifugal forces within it, together with the loss of the First World War, led to its breaking up in 1918, when its successor states included the First Austrian Republic
First Austrian Republic
The Republic of Austria encompasses the period of Austrian history following the signing of the Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye of September 1919, the settlement after the end of World War I which put an end to the Republic of German Austria, continuing up to World War II...
, the Kingdom of Hungary
Kingdom of Hungary (1920–1946)
The Kingdom of Hungary also known as the Regency, existed from 1920 to 1946 and was a de facto country under Regent Miklós Horthy. Horthy officially represented the abdicated Hungarian monarchy of Charles IV, Apostolic King of Hungary...
, Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia or Czecho-Slovakia was a sovereign state in Central Europe which existed from October 1918, when it declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, until 1992...
, and the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs
State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs
The State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs was a short-lived state formed from the southernmost parts of the Austro-Hungarian monarchy after its dissolution at the end of the World War I by the resident population of Slovenes, Croats, and Serbs...
which became part of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia
Kingdom of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was a state stretching from the Western Balkans to Central Europe which existed during the often-tumultuous interwar era of 1918–1941...
. Parts of Austria-Hungary were also incorporated into Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
, Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
, the Kingdom of Romania
Kingdom of Romania
The Kingdom of Romania was the Romanian state based on a form of parliamentary monarchy between 13 March 1881 and 30 December 1947, specified by the first three Constitutions of Romania...
and the Kingdom of Italy
Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946)
The Kingdom of Italy was a state forged in 1861 by the unification of Italy under the influence of the Kingdom of Sardinia, which was its legal predecessor state...
.
The Empire's principal languages were German
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
, Hungarian
Hungarian language
Hungarian is a Uralic language, part of the Ugric group. With some 14 million speakers, it is one of the most widely spoken non-Indo-European languages in Europe....
, Polish
Polish language
Polish is a language of the Lechitic subgroup of West Slavic languages, used throughout Poland and by Polish minorities in other countries...
Czech
Czech language
Czech is a West Slavic language with about 12 million native speakers; it is the majority language in the Czech Republic and spoken by Czechs worldwide. The language was known as Bohemian in English until the late 19th century...
and Croatian
Croatian language
Croatian is the collective name for the standard language and dialects spoken by Croats, principally in Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Serbian province of Vojvodina and other neighbouring countries...
, but there were many more besides, including Ukrainian
Ukrainian language
Ukrainian is a language of the East Slavic subgroup of the Slavic languages. It is the official state language of Ukraine. Written Ukrainian uses a variant of the Cyrillic alphabet....
, Romanian
Romanian language
Romanian Romanian Romanian (or Daco-Romanian; obsolete spellings Rumanian, Roumanian; self-designation: română, limba română ("the Romanian language") or românește (lit. "in Romanian") is a Romance language spoken by around 24 to 28 million people, primarily in Romania and Moldova...
, Slovak
Slovak language
Slovak , is an Indo-European language that belongs to the West Slavic languages .Slovak is the official language of Slovakia, where it is spoken by 5 million people...
, Serbian
Serbian language
Serbian is a form of Serbo-Croatian, a South Slavic language, spoken by Serbs in Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Croatia and neighbouring countries....
, Slovene, Rusyn
Rusyn language
Rusyn , also known in English as Ruthenian, is an East Slavic language variety spoken by the Rusyns of Central Europe. Some linguists treat it as a distinct language and it has its own ISO 639-3 code; others treat it as a dialect of Ukrainian...
, Italian
Italian language
Italian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia...
, and Yiddish
Yiddish language
Yiddish is a High German language of Ashkenazi Jewish origin, spoken throughout the world. It developed as a fusion of German dialects with Hebrew, Aramaic, Slavic languages and traces of Romance languages...
.
USSR
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics was a unionPolitical union
A political union is a type of state which is composed of or created out of smaller states. Unlike a personal union, the individual states share a common government and the union is recognized internationally as a single political entity...
of Soviet republics
Republics of the Soviet Union
The Republics of the Soviet Union or the Union Republics of the Soviet Union were ethnically-based administrative units that were subordinated directly to the Government of the Soviet Union...
(of which there were 15 after 1956) with the capital in Moscow
Moscow
Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent...
. It was founded in December 1922 when the Russian SFSR, which formed during the Russian Revolution of 1917
Russian Revolution of 1917
The Russian Revolution is the collective term for a series of revolutions in Russia in 1917, which destroyed the Tsarist autocracy and led to the creation of the Soviet Union. The Tsar was deposed and replaced by a provisional government in the first revolution of February 1917...
and emerged victorious in the ensuing Russian Civil War
Russian Civil War
The Russian Civil War was a multi-party war that occurred within the former Russian Empire after the Russian provisional government collapsed to the Soviets, under the domination of the Bolshevik party. Soviet forces first assumed power in Petrograd The Russian Civil War (1917–1923) was a...
, unified with the Transcaucasian, Ukrainian
Ukrainian SSR
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic or in short, the Ukrainian SSR was a sovereign Soviet Socialist state and one of the fifteen constituent republics of the Soviet Union lasting from its inception in 1922 to the breakup in 1991...
and Belorussian SSRs. Addressing the Extraordinary Eighth Congress of Soviets of the U.S.S.R. on 25 November 1936, Stalin stated that "within the Soviet Union there are about sixty nations, national groups and nationalities. The Soviet state is a multi-national state."
In the late 1980s, some constituent republics of the Soviet Union started legal moves towards or even declaration of sovereignty
Sovereignty
Sovereignty is the quality of having supreme, independent authority over a geographic area, such as a territory. It can be found in a power to rule and make law that rests on a political fact for which no purely legal explanation can be provided...
over their territories, citing Article 72 of the USSR Constitution, which stated that any constituent republic was free to secede. On 7 April 1990, a law was passed allowing a republic to secede if more than two-thirds of that republic's residents vote for secession on a referendum. Many held their first free elections in the Soviet era for their own national legislatures in 1990. Many of these legislatures proceeded to produce legislation contradicting the Union laws in what was known as the "War of Laws
War of Laws
The War of Laws was the series of conflicts between the Federal Government of the Soviet Union, and the governments of the Russian Federation and other constituent republics during the last years of the USSR, which eventually led to the dissolution of the union...
".
In 1989, the Russian SFSR
Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic , commonly referred to as Soviet Russia, Bolshevik Russia, or simply Russia, was the largest, most populous and economically developed republic in the former Soviet Union....
, which was then the largest constituent republic (with about half of the population) convened a newly elected Congress of People's Deputies. Boris Yeltsin
Boris Yeltsin
Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin was the first President of the Russian Federation, serving from 1991 to 1999.Originally a supporter of Mikhail Gorbachev, Yeltsin emerged under the perestroika reforms as one of Gorbachev's most powerful political opponents. On 29 May 1990 he was elected the chairman of...
was elected the chairman of the Congress. On 12 June 1990, the Congress declared Russia's sovereignty over its territory
Declaration of State Sovereignty of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
The Declaration on State Sovereignty of the RSFSR was a political act of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, then part of the Soviet Union, which marked the beginning of constitutional reform in Russia...
and proceeded to pass laws that attempted to supersede some of the USSR's laws. The period of legal uncertainty continued throughout 1991 as constituent republics slowly became de facto
De facto
De facto is a Latin expression that means "concerning fact." In law, it often means "in practice but not necessarily ordained by law" or "in practice or actuality, but not officially established." It is commonly used in contrast to de jure when referring to matters of law, governance, or...
independent.
A referendum for the preservation of the USSR
Soviet Union referendum, 1991
A referendum on the future of the Soviet Union was held on 17 March 1991. The question put to voters wasDo you consider necessary the preservation of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics as a renewed federation of equal sovereign republics in which the rights and freedom of an individual of any...
was held on 17 March 1991, with the majority of the population voting for preservation of the Union in nine out of 15 republics. The referendum gave Gorbachev a minor boost, and, in the summer of 1991, the New Union Treaty
New Union Treaty
Union of Sovereign States was the proposed name of a reorganization of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics into a new confederation body. Proposed by Mikhail Gorbachev, the proposal was an attempt to avert the collapse of the Soviet Union. The proposal was never implemented in the wake of the...
was designed and agreed upon by eight republics which would have turned the Soviet Union into a much looser federation. The signing of the treaty, however, was interrupted by the August Coup—an attempted coup d'état
Coup d'état
A coup d'état state, literally: strike/blow of state)—also known as a coup, putsch, and overthrow—is the sudden, extrajudicial deposition of a government, usually by a small group of the existing state establishment—typically the military—to replace the deposed government with another body; either...
against Gorbachev by hardline Communist Party members of the government and the KGB, who sought to reverse Gorbachev's reforms and reassert the central government's control over the republics. After the coup collapsed, Yeltsin—who had publicly opposed it—came out as a hero while Gorbachev's power was effectively ended. The balance of power tipped significantly towards the republics. In August 1991, Latvia and Estonia immediately declared restoration of full independence (following Lithuania's 1990 example), while the other twelve republics continued discussing new, increasingly looser, models of the Union.
On 8 December 1991, the presidents of Russia, Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
and Belarus
Belarus
Belarus , officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, bordered clockwise by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Its capital is Minsk; other major cities include Brest, Grodno , Gomel ,...
signed the Belavezha Accords
Belavezha Accords
The Belavezha Accords is the agreement which declared the Soviet Union effectively dissolved and established the Commonwealth of Independent States in its place...
which declared the Soviet Union dissolved and established the Commonwealth of Independent States
Commonwealth of Independent States
The Commonwealth of Independent States is a regional organization whose participating countries are former Soviet Republics, formed during the breakup of the Soviet Union....
(CIS) in its place. While doubts remained over the authority of the Belavezha Accords to dissolve the Union, on 21 December 1991, the representatives of all Soviet republics except Georgia, including those republics that had signed the Belavezha Accords, signed the Alma-Ata Protocol
Alma-Ata Protocol
The Alma-Ata Protocols are the founding declarations and principles of the Commonwealth of Independent States. It was signed soon after the Belavezha Accords on 21 December 1991, between the states of Moldova, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgizstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and...
, which confirmed the dismemberment and consequential extinction of the USSR and restated the establishment of the CIS. The summit of Alma-Ata also agreed on several other practical measures consequential to the extinction of the Union. On 25 December 1991, Gorbachev yielded to the inevitable and resigned as the president of the USSR, declaring the office extinct. He turned the powers that until then were vested in the presidency over to Boris Yeltsin
Boris Yeltsin
Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin was the first President of the Russian Federation, serving from 1991 to 1999.Originally a supporter of Mikhail Gorbachev, Yeltsin emerged under the perestroika reforms as one of Gorbachev's most powerful political opponents. On 29 May 1990 he was elected the chairman of...
, president of Russia
President of the Russian Federation
The President of the Russian Federation is the head of state, supreme commander-in-chief and holder of the highest office within the Russian Federation...
.
The following day, the Supreme Soviet, the highest governmental body of the Soviet Union, recognized the bankruptcy and collapse of the Soviet Union and dissolved itself. This is generally recognized as the official, final dissolution of the Soviet Union as a functioning state. Many organizations such as the Soviet Army
Soviet Army
The Soviet Army is the name given to the main part of the Armed Forces of the Soviet Union between 1946 and 1992. Previously, it had been known as the Red Army. Informally, Армия referred to all the MOD armed forces, except, in some cases, the Soviet Navy.This article covers the Soviet Ground...
and police forces continued to remain in place in the early months of 1992 but were slowly phased out and either withdrawn from or were absorbed by the newly independent states.
Yugoslavia

Kingdom of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was a state stretching from the Western Balkans to Central Europe which existed during the often-tumultuous interwar era of 1918–1941...
, which before 3 October 1929 was known as the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. It was established on 1 December 1918 by the union of the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs
State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs
The State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs was a short-lived state formed from the southernmost parts of the Austro-Hungarian monarchy after its dissolution at the end of the World War I by the resident population of Slovenes, Croats, and Serbs...
and the Kingdom of Serbia
Kingdom of Serbia
The Kingdom of Serbia was created when Prince Milan Obrenović, ruler of the Principality of Serbia, was crowned King in 1882. The Principality of Serbia was ruled by the Karađorđevic dynasty from 1817 onwards . The Principality, suzerain to the Porte, had expelled all Ottoman troops by 1867, de...
(to which the Kingdom of Montenegro
Kingdom of Montenegro
The Kingdom of Montenegro was a monarchy in southeastern Europe during the tumultuous years on the Balkan Peninsula leading up to and during World War I. Legally it was a constitutional monarchy, but absolutist in practice...
was annexed on 13 November 1918, and the Conference of Ambassadors in Paris
Paris
Paris is the capital and largest city in France, situated on the river Seine, in northern France, at the heart of the Île-de-France region...
gave international recognition to the union on 13 July 1922). The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was invaded by the Axis powers
Axis Powers
The Axis powers , also known as the Axis alliance, Axis nations, Axis countries, or just the Axis, was an alignment of great powers during the mid-20th century that fought World War II against the Allies. It began in 1936 with treaties of friendship between Germany and Italy and between Germany and...
in 1941, and because of the events that followed, was officially abolished in 1943 and 1945.
The second country with this name was the Democratic Federal Yugoslavia, proclaimed in 1943 by the Yugoslav Partisans resistance movement during World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
. It was renamed to the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia in 1946, when a communist government was established. In 1963, it was renamed again to the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia
Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was the Yugoslav state that existed from the abolition of the Yugoslav monarchy until it was dissolved in 1992 amid the Yugoslav Wars. It was a socialist state and a federation made up of six socialist republics: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia,...
(SFRY). This was the largest Yugoslav state, as Istria
Istria
Istria , formerly Histria , is the largest peninsula in the Adriatic Sea. The peninsula is located at the head of the Adriatic between the Gulf of Trieste and the Bay of Kvarner...
and Rijeka
Rijeka
Rijeka is the principal seaport and the third largest city in Croatia . It is located on Kvarner Bay, an inlet of the Adriatic Sea and has a population of 128,735 inhabitants...
were added to the new Yugoslavia after the end of World War II.
The constituent six Socialist Republics and two Socialist Autonomous Provinces that made up the country were: SR Bosnia and Herzegovina, SR Croatia, SR Macedonia, SR Montenegro, SR Slovenia and SR Serbia (including the autonomous
Autonomy
Autonomy is a concept found in moral, political and bioethical philosophy. Within these contexts, it is the capacity of a rational individual to make an informed, un-coerced decision...
provinces of SAP Vojvodina and SAP Kosovo which after 1974 were largely equal to the other members of the federation).
Starting in 1991, the SFRY disintegrated in the Yugoslav Wars
Yugoslav wars
The Yugoslav Wars were a series of wars, fought throughout the former Yugoslavia between 1991 and 1995. The wars were complex: characterized by bitter ethnic conflicts among the peoples of the former Yugoslavia, mostly between Serbs on the one side and Croats and Bosniaks on the other; but also...
which followed the secession
Secession
Secession is the act of withdrawing from an organization, union, or especially a political entity. Threats of secession also can be a strategy for achieving more limited goals.-Secession theory:...
of most of the country's constituent entities. The next Yugoslavia, known as the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, existed until 2003, when it was renamed Serbia and Montenegro
Serbia and Montenegro
Serbia and Montenegro was a country in southeastern Europe, formed from two former republics of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia : Serbia and Montenegro. Following the breakup of Yugoslavia, it was established in 1992 as a federation called the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia...
, but in 2006 this state finally separated into Serbia
Serbia
Serbia , officially the Republic of Serbia , is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe, covering the southern part of the Carpathian basin and the central part of the Balkans...
and Montenegro
Montenegro
Montenegro Montenegrin: Crna Gora Црна Гора , meaning "Black Mountain") is a country located in Southeastern Europe. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea to the south-west and is bordered by Croatia to the west, Bosnia and Herzegovina to the northwest, Serbia to the northeast and Albania to the...
.

