
Motif (widget toolkit)
Encyclopedia
Graphical user interface
In computing, a graphical user interface is a type of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices with images rather than text commands. GUIs can be used in computers, hand-held devices such as MP3 players, portable media players or gaming devices, household appliances and...
(GUI) specification and the widget toolkit
Widget toolkit
In computing, a widget toolkit, widget library, or GUI toolkit is a set of widgets for use in designing applications with graphical user interfaces...
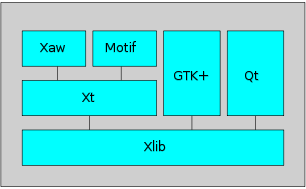
for building applications that follow that specification under the X Window System
X Window System
The X window system is a computer software system and network protocol that provides a basis for graphical user interfaces and rich input device capability for networked computers...
on Unix
Unix
Unix is a multitasking, multi-user computer operating system originally developed in 1969 by a group of AT&T employees at Bell Labs, including Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, Brian Kernighan, Douglas McIlroy, and Joe Ossanna...
and other POSIX
POSIX
POSIX , an acronym for "Portable Operating System Interface", is a family of standards specified by the IEEE for maintaining compatibility between operating systems...
-compliant systems. It emerged in the 1980s as Unix workstation
Workstation
A workstation is a high-end microcomputer designed for technical or scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by one person at a time, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating systems...
s were on the rise, as a competitor to the OPEN LOOK
OPEN LOOK
OPEN LOOK is a graphical user interface specification for UNIX workstations. It was originally defined in the late 1980s by Sun Microsystems and AT&T.-History:...
GUI. It is now the basic building block of the Common Desktop Environment
Common Desktop Environment
The Common Desktop Environment is a desktop environment for Unix and OpenVMS, based on the Motif widget toolkit.- Corporate history :...
.
The IEEE 1295 standard
Standardization
Standardization is the process of developing and implementing technical standards.The goals of standardization can be to help with independence of single suppliers , compatibility, interoperability, safety, repeatability, or quality....
defines the Motif API
Application programming interface
An application programming interface is a source code based specification intended to be used as an interface by software components to communicate with each other...
. As of version 2.1 Motif supports Unicode
Unicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
, which has made it widely used in several multilingual environments.
The Motif look and feel is distinguished by its use of square, chiseled, three-dimensional effects for its various user interface elements — menus, buttons, sliders, text boxes, and the like. Motif's operation was designed to correspond closely with the then-familiar Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
and OS/2's Presentation Manager
Presentation Manager
Presentation Manager is the graphical user interface that IBM and Microsoft introduced in version 1.1 of their operating system OS/2 in late 1988.-History:...
interfaces, and Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American public multinational corporation headquartered in Redmond, Washington, USA that develops, manufactures, licenses, and supports a wide range of products and services predominantly related to computing through its various product divisions...
played a key role in designing the original style guide.
Motif was created by the Open Software Foundation
Open Software Foundation
The Open Software Foundation was a not-for-profit organization founded in 1988 under the U.S. National Cooperative Research Act of 1984 to create an open standard for an implementation of the UNIX operating system.-History:...
(and was sometimes even called OSF/Motif), which has now been subsumed by The Open Group
The Open Group
The Open Group is a vendor and technology-neutral industry consortium, currently with over three hundred member organizations. It was formed in 1996 when X/Open merged with the Open Software Foundation...
.
There are a few implementation
Implementation
Implementation is the realization of an application, or execution of a plan, idea, model, design, specification, standard, algorithm, or policy.-Computer Science:...
s of the Motif API. Motif the toolkit is the first. There is also Open Motif
Open Motif
Open Motif is a source code release of the Motif computer programming toolkit by The Open Group, the current owners of Motif....
which is a release of the "original" Motif under more liberal licensing terms. Finally, the LessTif
LessTif
LessTif is a free software reimplementation or clone of the Motif computer programming toolkit, developed by the Hungry Programmers.As opposed to Motif, which is distributed under a proprietary license that can require the payment of royalties, LessTif is distributed under the GNU Lesser General...
project aims to implement the API under the LGPL license.
See also
- Motif Window ManagerMotif Window ManagerIn computing, the Motif Window Manager is an X window manager based on the Motif toolkit.MWM is a lightweight and, by today's standards, extremely minimalist window manager. MWM lacks support for desktop icons or virtual desktops. A plain text file is used to generate a root menu that the user can...
- MoOLITMoOLITMoOLIT is a graphical user interface library and application programming interface created by Unix System Laboratories in an attempt to create a bridge between the two competing look-and-feels for Unix workstations at the time: OPEN LOOK and OSF Motif.The library provided common GUI features such...
- FLTKFLTKFLTK is a cross-platform GUI library developed by Bill Spitzak and others. Made with 3D graphics programming in mind, it has an interface to OpenGL, but it is also suitable for general GUI programming....
and EDEEDEEDE or Equinox Desktop Environment is a small desktop environment that is meant to be simple and fast. Previous 1.x versions were based on a modified version of FLTK called eFLTK, while later versions are based on FLTK.-EDE 2:... - GTK+GTK+GTK+ is a cross-platform widget toolkit for creating graphical user interfaces. It is licensed under the terms of the GNU LGPL, allowing both free and proprietary software to use it. It is one of the most popular toolkits for the X Window System, along with Qt.The name GTK+ originates from GTK;...
and GNOMEGNOMEGNOME is a desktop environment and graphical user interface that runs on top of a computer operating system. It is composed entirely of free and open source software... - QtQt (toolkit)Qt is a cross-platform application framework that is widely used for developing application software with a graphical user interface , and also used for developing non-GUI programs such as command-line tools and consoles for servers...
and KDEKDEKDE is an international free software community producing an integrated set of cross-platform applications designed to run on Linux, FreeBSD, Microsoft Windows, Solaris and Mac OS X systems... - 4Dwm4Dwm4Dwm is a window manager normally used on Silicon Graphics workstations running IRIX. 4Dwm is derived from the older mwm window manager and uses the Motif widget toolkit on top of the X Window System found on most Unix systems....
- IBM Common User Access
External links
- Motif homepage at Open Group
- Open Motif project page
- The Motif FAQ (Kenton Lee)
- Motif: Volumes 6A and 6B (O'Reilly and Associates, free PDFPortable Document FormatPortable Document Format is an open standard for document exchange. This file format, created by Adobe Systems in 1993, is used for representing documents in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems....
downloads)] - Motif for OpenVMS

