Molecular sensor
Encyclopedia
A molecular sensor or chemosensor
is a molecule that interacts with an analyte to produce a detectable change. Molecular sensors combine molecular recognition
with some form of reporter so the presence of the guest can be observed. The term supramolecular analytical chemistry has recently been coined to describe the application of molecular sensors to analytical chemistry
.
Early examples of molecular sensors are crown ether
s with large affinity for sodium ions but not for potassium and forms of metal detection by so-called complexones which are traditional pH indicator
s retrofitted with molecular groups sensitive to metals. This receptor-spacer-reporter concept is a recurring theme often with the reporter displaying photoinduced electron transfer
. One example is a sensor sensitive to heparin
.
Other receptors are sensitive not to a specific molecule but to a molecular compound class. One example is the grouped analysis of several tannic acid
s that accumulate in ageing scotch whiskey in oak barrels. The grouped results demonstrated a correlation with the age but the individual components did not. A similar receptor can be used to analyze tartrates in wine.
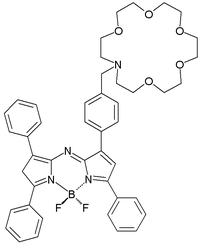
The compound saxitoxin
is a neurotoxin found in shellfish and a chemical weapon. An experimental sensor for this compound is again based on PET. Interaction of saxitoxin with the sensor's crown ether
moiety kills its PET process towards the fluorophore
and fluorescence
is switched from off to on . The unusual boron
moiety makes sure the fluorescence takes place in the visible light part of the electromagnetic spectrum
In another strategy called indicator-displacement assay (IDA) an analyte
such as citrate
or phosphate
ions displace a fluorescent indicator in an indicator-host complex. The so-called UT taste chip (University of Texas) is a prototype electronic tongue and combines supramolecular chemistry with charge-coupled device
s based on silicon wafers and immobilized receptor molecules.
Chemosensor
A chemoreceptor, also known as chemosensor, is a sensory receptor that transduces a chemical signal into an action potential. In more general terms, a chemosensor detects certain chemical stimuli in the environment.- Classes :...
is a molecule that interacts with an analyte to produce a detectable change. Molecular sensors combine molecular recognition
Molecular recognition
The term molecular recognition refers to the specific interaction between two or more molecules through noncovalent bonding such as hydrogen bonding, metal coordination, hydrophobic forces, van der Waals forces, π-π interactions, electrostatic and/or electromagnetic effects...
with some form of reporter so the presence of the guest can be observed. The term supramolecular analytical chemistry has recently been coined to describe the application of molecular sensors to analytical chemistry
Analytical chemistry
Analytical chemistry is the study of the separation, identification, and quantification of the chemical components of natural and artificial materials. Qualitative analysis gives an indication of the identity of the chemical species in the sample and quantitative analysis determines the amount of...
.
Early examples of molecular sensors are crown ether
Crown ether
Crown ethers are cyclic chemical compounds that consist of a ring containing several ether groups. The most common crown ethers are oligomers of ethylene oxide, the repeating unit being ethyleneoxy, i.e., -CH2CH2O-. Important members of this series are the tetramer , the pentamer , and the hexamer...
s with large affinity for sodium ions but not for potassium and forms of metal detection by so-called complexones which are traditional pH indicator
PH indicator
A pH indicator is a halochromic chemical compound that is added in small amounts to a solution so that the pH of the solution can be determined visually. Hence a pH indicator is a chemical detector for hydronium ions or hydrogen ions in the Arrhenius model. Normally, the indicator causes the...
s retrofitted with molecular groups sensitive to metals. This receptor-spacer-reporter concept is a recurring theme often with the reporter displaying photoinduced electron transfer
Photoinduced electron transfer
Photoinduced electron transfer is an electron transfer which occurs when certain photoactive materials interact with light. - Breadth :Such materials include semiconductors that can be photoactivated like many solar cells, biological systems such as those used in photosynthesis, and small...
. One example is a sensor sensitive to heparin
Heparin
Heparin , also known as unfractionated heparin, a highly sulfated glycosaminoglycan, is widely used as an injectable anticoagulant, and has the highest negative charge density of any known biological molecule...
.
 |
 |
 |
||
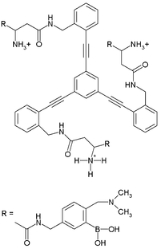
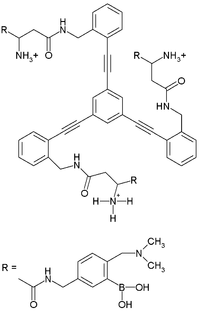
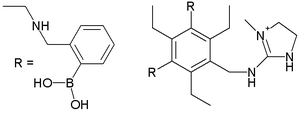
| Heparin Heparin Heparin , also known as unfractionated heparin, a highly sulfated glycosaminoglycan, is widely used as an injectable anticoagulant, and has the highest negative charge density of any known biological molecule... binding |
Tannic acid Tannic acid Tannic acid is a specific commercial form of tannin, a type of polyphenol. Its weak acidity is due to the numerous phenol groups in the structure... binding |
Saxitoxin Saxitoxin Saxitoxin is a neurotoxin naturally produced by certain species of marine dinoflagellates and cyanobacteria Saxitoxin (STX) is a neurotoxin naturally produced by certain species of marine dinoflagellates (Alexandrium sp., Gymnodinium sp., Pyrodinium sp.) and cyanobacteria Saxitoxin (STX) is a... binding |
||
Other receptors are sensitive not to a specific molecule but to a molecular compound class. One example is the grouped analysis of several tannic acid
Tannic acid
Tannic acid is a specific commercial form of tannin, a type of polyphenol. Its weak acidity is due to the numerous phenol groups in the structure...
s that accumulate in ageing scotch whiskey in oak barrels. The grouped results demonstrated a correlation with the age but the individual components did not. A similar receptor can be used to analyze tartrates in wine.
The compound saxitoxin
Saxitoxin
Saxitoxin is a neurotoxin naturally produced by certain species of marine dinoflagellates and cyanobacteria Saxitoxin (STX) is a neurotoxin naturally produced by certain species of marine dinoflagellates (Alexandrium sp., Gymnodinium sp., Pyrodinium sp.) and cyanobacteria Saxitoxin (STX) is a...
is a neurotoxin found in shellfish and a chemical weapon. An experimental sensor for this compound is again based on PET. Interaction of saxitoxin with the sensor's crown ether
Crown ether
Crown ethers are cyclic chemical compounds that consist of a ring containing several ether groups. The most common crown ethers are oligomers of ethylene oxide, the repeating unit being ethyleneoxy, i.e., -CH2CH2O-. Important members of this series are the tetramer , the pentamer , and the hexamer...
moiety kills its PET process towards the fluorophore
Fluorophore
A fluorophore, in analogy to a chromophore, is a component of a molecule which causes a molecule to be fluorescent. It is a functional group in a molecule which will absorb energy of a specific wavelength and re-emit energy at a different wavelength...
and fluorescence
Fluorescence
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation of a different wavelength. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore lower energy, than the absorbed radiation...
is switched from off to on . The unusual boron
Boron
Boron is the chemical element with atomic number 5 and the chemical symbol B. Boron is a metalloid. Because boron is not produced by stellar nucleosynthesis, it is a low-abundance element in both the solar system and the Earth's crust. However, boron is concentrated on Earth by the...
moiety makes sure the fluorescence takes place in the visible light part of the electromagnetic spectrum
Electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. The "electromagnetic spectrum" of an object is the characteristic distribution of electromagnetic radiation emitted or absorbed by that particular object....
In another strategy called indicator-displacement assay (IDA) an analyte
Analyte
An analyte, or component , is a substance or chemical constituent that is of interest in an analytical procedure. Grammatically, it is important to note that experiments always seek to measure properties of analytes—and that analytes themselves can never be measured. For instance, one cannot...
such as citrate
Citrate
A citrate can refer either to the conjugate base of citric acid, , or to the esters of citric acid. An example of the former, a salt is trisodium citrate; an ester is triethyl citrate.-Other citric acid ions:...
or phosphate
Phosphate
A phosphate, an inorganic chemical, is a salt of phosphoric acid. In organic chemistry, a phosphate, or organophosphate, is an ester of phosphoric acid. Organic phosphates are important in biochemistry and biogeochemistry or ecology. Inorganic phosphates are mined to obtain phosphorus for use in...
ions displace a fluorescent indicator in an indicator-host complex. The so-called UT taste chip (University of Texas) is a prototype electronic tongue and combines supramolecular chemistry with charge-coupled device
Charge-coupled device
A charge-coupled device is a device for the movement of electrical charge, usually from within the device to an area where the charge can be manipulated, for example conversion into a digital value. This is achieved by "shifting" the signals between stages within the device one at a time...
s based on silicon wafers and immobilized receptor molecules.
See also
- Molecular recognitionMolecular recognitionThe term molecular recognition refers to the specific interaction between two or more molecules through noncovalent bonding such as hydrogen bonding, metal coordination, hydrophobic forces, van der Waals forces, π-π interactions, electrostatic and/or electromagnetic effects...
- Boronic acids in supramolecular chemistry: Saccharide recognition
- Host-guest chemistryHost-guest chemistryIn supramolecular chemistry, host-guest chemistry describes complexes that are composed of two or more molecules or ions that are held together in unique structural relationships by forces other than those of full covalent bonds. Host-guest chemistry encompasses the idea of molecular recognition...
- Molecular machineMolecular machineA molecular machine, or nanomachine, is any discrete number of molecular components that produce quasi-mechanical movements in response to specific stimuli . The expression is often more generally applied to molecules that simply mimic functions that occur at the macroscopic level...

