
Mitteleuropa
Encyclopedia
Mitteleuropa is the German
term equal to Central Europe
. The word has political, geographic and cultural meaning. While it describes a geographical location, it also is the word denoting a political concept of a German
-dominated and exploited Central European union that was put into motion during First World War. The historian Jörg Brechtefeld describes 'Mitteleuropa' as the following:
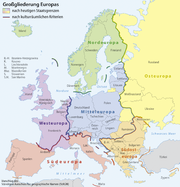 The German academic Ständiger Ausschuss für geographische Namen (Permanent Committee on Geographical Names) at the
The German academic Ständiger Ausschuss für geographische Namen (Permanent Committee on Geographical Names) at the
Federal Agency for Cartography and Geodesy refers to a territory roughly bounded by the river Rhine in the west, the Bug
in the east, the North Sea
and the Baltic
coast in the north, as well as the Alps
and the Adriatic Sea
in the south. The area is covered by the modern states of:
Baltic states
(Baltikum):
Mitteleuropa construed as a cultural area would further include:
process was stopped by the Black Death
in the mid 14th century, Germans had settled the "Wendish
" Central European areas of Germania Slavica
far beyond the Elbe
and Saale
rivers. They had moved along the Baltic coast from Holstein
to Farther Pomerania
, up the Oder
river to the Moravian Gate
, down the Danube
into the Kingdom of Hungary
and to the Slovene lands of Carniola
. From the mouth of the Vistula
river and the Prussian
region, the Teutonic Knights
by force continued the eastward migration up to Estonian Reval
(Tallinn), Germans also settled in the mountainous border regions of Bohemia
and Moravia
and formed a distinct social class of citizens in towns like Prague
, Havlíčkův Brod
(Deutsch-Brod), Olomouc
(Olmütz) and Brno
(Brünn). They had moved into the Polish Kraków Voivodeship, the Western Carpathians
and Transylvania
(Siebenbürgen), introducing the crop rotation
practice and German town law
.
In the course of the Black Death, widespread pogrom
s against Jews
from 1348 occurred in the German Rhineland
, causing an emigration in huge numbers to the Kingdom of Poland under Casimir the Great
and to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
under Vytautas granting them extensive privileges. The Ashkenazi
expellees and their High German Yiddish language
left a significant imprint on Eastern Central Europe, in towns like Lviv
(Lemberg), Lublin
, Minsk
and Chernivtsi
(Czernowitz), but also in the Bohemian
capital Prague
as well as in numerous shtetl
s. The rabbi
s at first received their religious education at German yeshivot
. During the Age of Enlightenment
, the Jewish Haskalah
movement pursueing emancipation
orientated itself by German protagonists like Moses Mendelssohn
as in the Prussian
lands under Frederick the Great, so-called Schutzjude
n were able to live under the circumstances of a limited religious tolerance
. With the increasing persecutions from the 1648 Khmelnytsky Uprising
onwards, especially the 19th century Anti-Jewish pogroms in the Russian Empire
, the approach to Germany was heightened. The Jewish Mitteleuropa culture was erased in The Holocaust
.
Upon the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire
in 1806 and the formation of the Concert of Europe
after the Napoleonic Wars
, the Romantic
writer Constantin Frantz during the Vormärz
era developed the concept of a Central European federation overcoming the German dualism between Austria
and Prussia
. Frantz opposed the idea of a nation state as it was raised by the German question
and advocated a commonwealth of the member states of the former Confederation of the Rhine
together with the Austrian multiethnic state and Prussia with its large Polish share of population. This Central European block should have been joined by Belgium
, the Netherlands
and Switzerland
as well as by Congress Poland
, seeking autonomy from the hegemony of the great power
s of France
and the British Empire
in the west as well as from the Pan-Slav
policies of the Russian Empire
in the east.
After the Revolutions of 1848
these ideas were adpoted by liberal
theorists like Friedrich List
and Heinrich von Gagern
, later by the German National Liberal Party
, then however with a distinct Pan-German
notion and accompanied by the concept of a renewed settler colonialism
under the firm leadership of the German Empire
and Austria-Hungary
. Upon the 1871 Unification of Germany
under Chancellor Otto von Bismarck
, the Ostforschung
concentrated on the achievements by Ethnic Germans in East-Central Europe
on the basis of Ethnocentrism
with significant anti-Slavic
, especially anti-Polish notions, as propagated by the Pan-German League
. Meanwhile Austria had to abandon her claim to leadership and thereafter referred Mitteleuropa to the lands of the Habsburg Monarchy
in the Danube basin.
over Central Europe
by the German Empire
and subsequent economic & financial exploitation
of this region combined with direct annexations, settlement of German colonists, expulsion of non-Germans from annexed areas, and eventual Germanization of puppet states created as a buffer between Germany and Russia
.
The issue of Central Europe was taken by German thinker Friedrich Naumann in 1915 in his work Mitteleuropa. According to his thought, this part of Europe was to become a politically and economically integrated block subjected to German rule. In his program, Naumann also supported programs of Germanization and Hungarization as well. Naumann in his book used imperialist rhetoric combined with praises to nature, and imperial condescension towards non-German people, while advising to show some "flexbility" towards non-German languages to achieve "harmony"Neuman wrote that it would stabilize the whole Central Europe region. See Some parts of the planning included designs on creating a German colony in Crimea
and colonization of the Baltic states
.
The ruling political elites of Germany accepted the Mitteleuropa plan during World War I while drawing out German war aims
and plans for the new order of Europe. Mitteleuropa was to be created by establishing a series of puppet states whose political, economic and military aspects would be under the control of the German Reich. The entire region was to serve as an economic backyard of Germany whose exploitation would enable it to compete with the British Empire
and any other competitors for the position of the world's dominant power. Political, military and economic organization was to be based on German domination, with commercial treaties imposed on countries like Poland and Ukraine. It was believed that the German working classes could be appeased by German politicians through the economic benefits of territorial annexation, settlement of Germans in Central and Eastern Europe
and exploitation
of conquered countries for the material benefit of Germany.
Partial realization of these plans was reflected in the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
, where guarantees of economic and military domination over Ukraine by Germany were laid out. Both Ottoman Empire and Austro-Hungary would become reliant on German support in post-war Europe,reducing them to the status of vassals
The Mitteleuropa plan was viewed as threat by the British Empire, which concluded it would destroy British continental trade, and as consequence the source of its military power
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
term equal to Central Europe
Central Europe
Central Europe or alternatively Middle Europe is a region of the European continent lying between the variously defined areas of Eastern and Western Europe...
. The word has political, geographic and cultural meaning. While it describes a geographical location, it also is the word denoting a political concept of a German
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
-dominated and exploited Central European union that was put into motion during First World War. The historian Jörg Brechtefeld describes 'Mitteleuropa' as the following:
Geography

Federal Agency for Cartography and Geodesy refers to a territory roughly bounded by the river Rhine in the west, the Bug
Bug River
The Bug River is a left tributary of the Narew river flows from central Ukraine to the west, passing along the Ukraine-Polish and Polish-Belarusian border and into Poland, where it empties into the Narew river near Serock. The part between the lake and the Vistula River is sometimes referred to as...
in the east, the North Sea
North Sea
In the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel connecting to the Atlantic Ocean. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively...
and the Baltic
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
coast in the north, as well as the Alps
Alps
The Alps is one of the great mountain range systems of Europe, stretching from Austria and Slovenia in the east through Italy, Switzerland, Liechtenstein and Germany to France in the west....
and the Adriatic Sea
Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan peninsula, and the system of the Apennine Mountains from that of the Dinaric Alps and adjacent ranges...
in the south. The area is covered by the modern states of:
Baltic states
Baltic states
The term Baltic states refers to the Baltic territories which gained independence from the Russian Empire in the wake of World War I: primarily the contiguous trio of Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania ; Finland also fell within the scope of the term after initially gaining independence in the 1920s.The...
(Baltikum):
Mitteleuropa construed as a cultural area would further include:
- AlsaceAlsaceAlsace is the fifth-smallest of the 27 regions of France in land area , and the smallest in metropolitan France. It is also the seventh-most densely populated region in France and third most densely populated region in metropolitan France, with ca. 220 inhabitants per km²...
and the MoselleMoselleMoselle is a department in the east of France named after the river Moselle.- History :Moselle is one of the original 83 departments created during the French Revolution on March 4, 1790...
département of northern LorraineLorraine (région)Lorraine is one of the 27 régions of France. The administrative region has two cities of equal importance, Metz and Nancy. Metz is considered to be the official capital since that is where the regional parliament is situated...
in Early Modern France, though usually referred to as a West EuropeanWestern EuropeWestern Europe is a loose term for the collection of countries in the western most region of the European continents, though this definition is context-dependent and carries cultural and political connotations. One definition describes Western Europe as a geographic entity—the region lying in the...
Early Modern France, though usually referred to as a West EuropeanWestern EuropeWestern Europe is a loose term for the collection of countries in the western most region of the European continents, though this definition is context-dependent and carries cultural and political connotations. One definition describes Western Europe as a geographic entity—the region lying in the...
country - the Kaliningrad OblastKaliningrad OblastKaliningrad Oblast is a federal subject of Russia situated on the Baltic coast. It has a population of The oblast forms the westernmost part of the Russian Federation, but it has no land connection to the rest of Russia. Since its creation it has been an exclave of the Russian SFSR and then the...
exclave of Russia
Russia - the eastern Vilnius RegionVilnius regionVilnius Region , refers to the territory in the present day Lithuania, that was originally inhabited by ethnic Baltic tribes and was a part of Lithuania proper, but came under East Slavic and Polish cultural influences over time,...
in Belarus
Belarus - territories of former Austria-HungaryAustria-HungaryAustria-Hungary , more formally known as the Kingdoms and Lands Represented in the Imperial Council and the Lands of the Holy Hungarian Crown of Saint Stephen, was a constitutional monarchic union between the crowns of the Austrian Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary in...
in-
 Italy Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol and the area of the former Austrian LittoralAustrian LittoralThe Austrian Littoral was established as a crown land of the Austrian Empire in 1849. In 1861 it was divided into the three crown lands of the Imperial Free City of Trieste and its suburbs, the Margraviate of Istria, and the Princely County of Gorizia and Gradisca, which each had separate...
Italy Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol and the area of the former Austrian LittoralAustrian LittoralThe Austrian Littoral was established as a crown land of the Austrian Empire in 1849. In 1861 it was divided into the three crown lands of the Imperial Free City of Trieste and its suburbs, the Margraviate of Istria, and the Princely County of Gorizia and Gradisca, which each had separate...
in eastern FriuliFriuliFriuli is an area of northeastern Italy with its own particular cultural and historical identity. It comprises the major part of the autonomous region Friuli-Venezia Giulia, i.e. the province of Udine, Pordenone, Gorizia, excluding Trieste...
and TriesteTriesteTrieste is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is situated towards the end of a narrow strip of land lying between the Adriatic Sea and Italy's border with Slovenia, which lies almost immediately south and east of the city... -
 SerbiaVojvodinaVojvodinaVojvodina, officially called Autonomous Province of Vojvodina is an autonomous province of Serbia. Its capital and largest city is Novi Sad...
SerbiaVojvodinaVojvodinaVojvodina, officially called Autonomous Province of Vojvodina is an autonomous province of Serbia. Its capital and largest city is Novi Sad...
, BelgradeBelgradeBelgrade is the capital and largest city of Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers, where the Pannonian Plain meets the Balkans. According to official results of Census 2011, the city has a population of 1,639,121. It is one of the 15 largest cities in Europe...
, MačvaMacvaMačva is a geographical region in Serbia, mostly situated in the northwest of Central Serbia. It is located in a fertile plain between the Sava and Drina rivers. The chief town of this region is Šabac. The modern Mačva District of Serbia is named after the region, although the region of Mačva...
regions -
 Kingdom of RomaniaTransylvaniaTransylvaniaTransylvania is a historical region in the central part of Romania. Bounded on the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains; however, the term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also the historical...
Kingdom of RomaniaTransylvaniaTransylvaniaTransylvania is a historical region in the central part of Romania. Bounded on the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains; however, the term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also the historical...
(Siebenbürgen) and southern BukovinaBukovinaBukovina is a historical region on the northern slopes of the northeastern Carpathian Mountains and the adjoining plains.-Name:The name Bukovina came into official use in 1775 with the region's annexation from the Principality of Moldavia to the possessions of the Habsburg Monarchy, which became... -
 Ukraineeastern Galicia, Carpathian RutheniaCarpathian RutheniaCarpathian Ruthenia is a region in Eastern Europe, mostly located in western Ukraine's Zakarpattia Oblast , with smaller parts in easternmost Slovakia , Poland's Lemkovyna and Romanian Maramureş.It is...
Ukraineeastern Galicia, Carpathian RutheniaCarpathian RutheniaCarpathian Ruthenia is a region in Eastern Europe, mostly located in western Ukraine's Zakarpattia Oblast , with smaller parts in easternmost Slovakia , Poland's Lemkovyna and Romanian Maramureş.It is...
and northern BukovinaBukovinaBukovina is a historical region on the northern slopes of the northeastern Carpathian Mountains and the adjoining plains.-Name:The name Bukovina came into official use in 1775 with the region's annexation from the Principality of Moldavia to the possessions of the Habsburg Monarchy, which became...
-
Conceptual history
At the time when the 500 years long OstsiedlungOstsiedlung
Ostsiedlung , also called German eastward expansion, was the medieval eastward migration and settlement of Germans from modern day western and central Germany into less-populated regions and countries of eastern Central Europe and Eastern Europe. The affected area roughly stretched from Slovenia...
process was stopped by the Black Death
Black Death
The Black Death was one of the most devastating pandemics in human history, peaking in Europe between 1348 and 1350. Of several competing theories, the dominant explanation for the Black Death is the plague theory, which attributes the outbreak to the bacterium Yersinia pestis. Thought to have...
in the mid 14th century, Germans had settled the "Wendish
Wends
Wends is a historic name for West Slavs living near Germanic settlement areas. It does not refer to a homogeneous people, but to various peoples, tribes or groups depending on where and when it is used...
" Central European areas of Germania Slavica
Germania Slavica
Germania Slavica is a historiographic term used since the 1950s to denote the medieval contact zone between Germans and Slavs in East Central Europe...
far beyond the Elbe
Elbe
The Elbe is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Krkonoše Mountains of the northwestern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia , then Germany and flowing into the North Sea at Cuxhaven, 110 km northwest of Hamburg...
and Saale
Saale
The Saale, also known as the Saxon Saale and Thuringian Saale , is a river in Germany and a left-bank tributary of the Elbe. It is not to be confused with the smaller Franconian Saale, a right-bank tributary of the Main, or the Saale in Lower Saxony, a tributary of the Leine.-Course:The Saale...
rivers. They had moved along the Baltic coast from Holstein
Holstein
Holstein is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider. It is part of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost state of Germany....
to Farther Pomerania
Farther Pomerania
Farther Pomerania, Further Pomerania, Transpomerania or Eastern Pomerania , which before the German-Polish border shift of 1945 comprised the eastern part of the Duchy, later Province of Pomerania, roughly stretching from the Oder River in the West to Pomerelia in the East...
, up the Oder
Oder
The Oder is a river in Central Europe. It rises in the Czech Republic and flows through western Poland, later forming of the border between Poland and Germany, part of the Oder-Neisse line...
river to the Moravian Gate
Moravian Gate
The Moravian Gate is a geomorphological feature in the Moravian region of the Czech Republic. It is formed by the depression between the Carpathian Mountains in the east and the Sudetes in the west...
, down the Danube
Danube
The Danube is a river in the Central Europe and the Europe's second longest river after the Volga. It is classified as an international waterway....
into the Kingdom of Hungary
Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary comprised present-day Hungary, Slovakia and Croatia , Transylvania , Carpatho Ruthenia , Vojvodina , Burgenland , and other smaller territories surrounding present-day Hungary's borders...
and to the Slovene lands of Carniola
Carniola
Carniola was a historical region that comprised parts of what is now Slovenia. As part of Austria-Hungary, the region was a crown land officially known as the Duchy of Carniola until 1918. In 1849, the region was subdivided into Upper Carniola, Lower Carniola, and Inner Carniola...
. From the mouth of the Vistula
Vistula
The Vistula is the longest and the most important river in Poland, at 1,047 km in length. The watershed area of the Vistula is , of which lies within Poland ....
river and the Prussian
Prussia (region)
Prussia is a historical region in Central Europe extending from the south-eastern coast of the Baltic Sea to the Masurian Lake District. It is now divided between Poland, Russia, and Lithuania...
region, the Teutonic Knights
Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem , commonly the Teutonic Order , is a German medieval military order, in modern times a purely religious Catholic order...
by force continued the eastward migration up to Estonian Reval
Tallinn
Tallinn is the capital and largest city of Estonia. It occupies an area of with a population of 414,940. It is situated on the northern coast of the country, on the banks of the Gulf of Finland, south of Helsinki, east of Stockholm and west of Saint Petersburg. Tallinn's Old Town is in the list...
(Tallinn), Germans also settled in the mountainous border regions of Bohemia
Bohemia
Bohemia is a historical region in central Europe, occupying the western two-thirds of the traditional Czech Lands. It is located in the contemporary Czech Republic with its capital in Prague...
and Moravia
Moravia
Moravia is a historical region in Central Europe in the east of the Czech Republic, and one of the former Czech lands, together with Bohemia and Silesia. It takes its name from the Morava River which rises in the northwest of the region...
and formed a distinct social class of citizens in towns like Prague
Prague
Prague is the capital and largest city of the Czech Republic. Situated in the north-west of the country on the Vltava river, the city is home to about 1.3 million people, while its metropolitan area is estimated to have a population of over 2.3 million...
, Havlíčkův Brod
Havlíckuv Brod
Havlíčkův Brod , Německý Brod until 1945 is a town in the Vysočina Region of the Czech Republic. It is also the capital of the Havlíčkův Brod district. It is located on the Sázava River in the Bohemian-Moravian Highlands and has a population of 24,321 as of 2003...
(Deutsch-Brod), Olomouc
Olomouc
Olomouc is a city in Moravia, in the east of the Czech Republic. The city is located on the Morava river and is the ecclesiastical metropolis and historical capital city of Moravia. Nowadays, it is an administrative centre of the Olomouc Region and sixth largest city in the Czech Republic...
(Olmütz) and Brno
Brno
Brno by population and area is the second largest city in the Czech Republic, the largest Moravian city, and the historical capital city of the Margraviate of Moravia. Brno is the administrative centre of the South Moravian Region where it forms a separate district Brno-City District...
(Brünn). They had moved into the Polish Kraków Voivodeship, the Western Carpathians
Western Carpathians
The Western Carpathians are a mountain range and geomorphological province that forms the western part of the Carpathian Mountains.The mountain belt stretches from the Low Beskids range of the Eastern Carpathians along the border of Poland with Slovakia toward the Moravian region of the Czech...
and Transylvania
Transylvania
Transylvania is a historical region in the central part of Romania. Bounded on the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains; however, the term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also the historical...
(Siebenbürgen), introducing the crop rotation
Crop rotation
Crop rotation is the practice of growing a series of dissimilar types of crops in the same area in sequential seasons.Crop rotation confers various benefits to the soil. A traditional element of crop rotation is the replenishment of nitrogen through the use of green manure in sequence with cereals...
practice and German town law
German town law
German town law or German municipal concerns concerns town privileges used by many cities, towns, and villages throughout Central and Eastern Europe during the Middle Ages.- Town law in Germany :...
.
In the course of the Black Death, widespread pogrom
Pogrom
A pogrom is a form of violent riot, a mob attack directed against a minority group, and characterized by killings and destruction of their homes and properties, businesses, and religious centres...
s against Jews
History of the Jews in Germany
The presence of Jews in Germany has been established since the early 4th century. The community prospered under Charlemagne, but suffered during the Crusades...
from 1348 occurred in the German Rhineland
Rhineland
Historically, the Rhinelands refers to a loosely-defined region embracing the land on either bank of the River Rhine in central Europe....
, causing an emigration in huge numbers to the Kingdom of Poland under Casimir the Great
Casimir III of Poland
Casimir III the Great , last King of Poland from the Piast dynasty , was the son of King Władysław I the Elbow-high and Hedwig of Kalisz.-Biography:...
and to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state from the 12th /13th century until 1569 and then as a constituent part of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1791 when Constitution of May 3, 1791 abolished it in favor of unitary state. It was founded by the Lithuanians, one of the polytheistic...
under Vytautas granting them extensive privileges. The Ashkenazi
Ashkenazi Jews
Ashkenazi Jews, also known as Ashkenazic Jews or Ashkenazim , are the Jews descended from the medieval Jewish communities along the Rhine in Germany from Alsace in the south to the Rhineland in the north. Ashkenaz is the medieval Hebrew name for this region and thus for Germany...
expellees and their High German Yiddish language
Yiddish language
Yiddish is a High German language of Ashkenazi Jewish origin, spoken throughout the world. It developed as a fusion of German dialects with Hebrew, Aramaic, Slavic languages and traces of Romance languages...
left a significant imprint on Eastern Central Europe, in towns like Lviv
Lviv
Lviv is a city in western Ukraine. The city is regarded as one of the main cultural centres of today's Ukraine and historically has also been a major Polish and Jewish cultural center, as Poles and Jews were the two main ethnicities of the city until the outbreak of World War II and the following...
(Lemberg), Lublin
Lublin
Lublin is the ninth largest city in Poland. It is the capital of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 350,392 . Lublin is also the largest Polish city east of the Vistula river...
, Minsk
Minsk
- Ecological situation :The ecological situation is monitored by Republican Center of Radioactive and Environmental Control .During 2003–2008 the overall weight of contaminants increased from 186,000 to 247,400 tons. The change of gas as industrial fuel to mazut for financial reasons has worsened...
and Chernivtsi
Chernivtsi
Chernivtsi is the administrative center of Chernivtsi Oblast in southwestern Ukraine. The city is situated on the upper course of the River Prut, a tributary of the Danube, in the northern part of the historic region of Bukovina, which is currently divided between Romania and Ukraine...
(Czernowitz), but also in the Bohemian
Kingdom of Bohemia
The Kingdom of Bohemia was a country located in the region of Bohemia in Central Europe, most of whose territory is currently located in the modern-day Czech Republic. The King was Elector of Holy Roman Empire until its dissolution in 1806, whereupon it became part of the Austrian Empire, and...
capital Prague
Prague
Prague is the capital and largest city of the Czech Republic. Situated in the north-west of the country on the Vltava river, the city is home to about 1.3 million people, while its metropolitan area is estimated to have a population of over 2.3 million...
as well as in numerous shtetl
Shtetl
A shtetl was typically a small town with a large Jewish population in Central and Eastern Europe until The Holocaust. Shtetls were mainly found in the areas which constituted the 19th century Pale of Settlement in the Russian Empire, the Congress Kingdom of Poland, Galicia and Romania...
s. The rabbi
Rabbi
In Judaism, a rabbi is a teacher of Torah. This title derives from the Hebrew word רבי , meaning "My Master" , which is the way a student would address a master of Torah...
s at first received their religious education at German yeshivot
Yeshiva
Yeshiva is a Jewish educational institution that focuses on the study of traditional religious texts, primarily the Talmud and Torah study. Study is usually done through daily shiurim and in study pairs called chavrutas...
. During the Age of Enlightenment
Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment was an elite cultural movement of intellectuals in 18th century Europe that sought to mobilize the power of reason in order to reform society and advance knowledge. It promoted intellectual interchange and opposed intolerance and abuses in church and state...
, the Jewish Haskalah
Haskalah
Haskalah , the Jewish Enlightenment, was a movement among European Jews in the 18th–19th centuries that advocated adopting enlightenment values, pressing for better integration into European society, and increasing education in secular studies, Hebrew language, and Jewish history...
movement pursueing emancipation
Jewish Emancipation
Jewish emancipation was the external and internal process of freeing the Jewish people of Europe, including recognition of their rights as equal citizens, and the formal granting of citizenship as individuals; it occurred gradually between the late 18th century and the early 20th century...
orientated itself by German protagonists like Moses Mendelssohn
Moses Mendelssohn
Moses Mendelssohn was a German Jewish philosopher to whose ideas the renaissance of European Jews, Haskalah is indebted...
as in the Prussian
Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia was a German kingdom from 1701 to 1918. Until the defeat of Germany in World War I, it comprised almost two-thirds of the area of the German Empire...
lands under Frederick the Great, so-called Schutzjude
Schutzjude
Schutzjude was a status for German Jews granted by the imperial, princely or royal courts.Within the Holy Roman Empire, except of some eastern territories gained to the Empire in the 11th and 12th c. , Jews usually had the status as Servi camerae regis...
n were able to live under the circumstances of a limited religious tolerance
Toleration
Toleration is "the practice of deliberately allowing or permitting a thing of which one disapproves. One can meaningfully speak of tolerating, ie of allowing or permitting, only if one is in a position to disallow”. It has also been defined as "to bear or endure" or "to nourish, sustain or preserve"...
. With the increasing persecutions from the 1648 Khmelnytsky Uprising
Khmelnytsky Uprising
The Khmelnytsky Uprising, was a Cossack rebellion in the Ukraine between the years 1648–1657 which turned into a Ukrainian war of liberation from Poland...
onwards, especially the 19th century Anti-Jewish pogroms in the Russian Empire
Anti-Jewish pogroms in the Russian Empire
The term pogrom as a reference to large-scale, targeted, and repeated antisemitic rioting saw its first use in the 19th century.The first pogrom is often considered to be the 1821 Odessa pogroms after the death of the Greek Orthodox patriarch Gregory V in Constantinople, in which 14 Jews were killed...
, the approach to Germany was heightened. The Jewish Mitteleuropa culture was erased in The Holocaust
The Holocaust
The Holocaust , also known as the Shoah , was the genocide of approximately six million European Jews and millions of others during World War II, a programme of systematic state-sponsored murder by Nazi...
.
Upon the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
in 1806 and the formation of the Concert of Europe
Concert of Europe
The Concert of Europe , also known as the Congress System after the Congress of Vienna, was the balance of power that existed in Europe from the end of the Napoleonic Wars to the outbreak of World War I , albeit with major alterations after the revolutions of 1848...
after the Napoleonic Wars
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars were a series of wars declared against Napoleon's French Empire by opposing coalitions that ran from 1803 to 1815. As a continuation of the wars sparked by the French Revolution of 1789, they revolutionised European armies and played out on an unprecedented scale, mainly due to...
, the Romantic
German Romanticism
For the general context, see Romanticism.In the philosophy, art, and culture of German-speaking countries, German Romanticism was the dominant movement of the late 18th and early 19th centuries. German Romanticism developed relatively late compared to its English counterpart, coinciding in its...
writer Constantin Frantz during the Vormärz
Vormärz
' is the time period leading up to the failed March 1848 revolution in the German Confederation. Also known as the Age of Metternich, it was a period of Austrian and Prussian police states and vast censorship in response to calls for liberalism...
era developed the concept of a Central European federation overcoming the German dualism between Austria
Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire was a modern era successor empire, which was centered on what is today's Austria and which officially lasted from 1804 to 1867. It was followed by the Empire of Austria-Hungary, whose proclamation was a diplomatic move that elevated Hungary's status within the Austrian Empire...
and Prussia
Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia was a German kingdom from 1701 to 1918. Until the defeat of Germany in World War I, it comprised almost two-thirds of the area of the German Empire...
. Frantz opposed the idea of a nation state as it was raised by the German question
German question
The German question was a debate in the 19th century, especially during the Revolutions of 1848, over the best way to achieve the Unification of Germany. From 1815–1871, a number of 37 independent German-speaking states existed within the German Confederation...
and advocated a commonwealth of the member states of the former Confederation of the Rhine
Confederation of the Rhine
The Confederation of the Rhine was a confederation of client states of the First French Empire. It was formed initially from 16 German states by Napoleon after he defeated Austria's Francis II and Russia's Alexander I in the Battle of Austerlitz. The Treaty of Pressburg, in effect, led to the...
together with the Austrian multiethnic state and Prussia with its large Polish share of population. This Central European block should have been joined by Belgium
Belgium
Belgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
, the Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
and Switzerland
Switzerland
Switzerland name of one of the Swiss cantons. ; ; ; or ), in its full name the Swiss Confederation , is a federal republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities. The country is situated in Western Europe,Or Central Europe depending on the definition....
as well as by Congress Poland
Congress Poland
The Kingdom of Poland , informally known as Congress Poland , created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna, was a personal union of the Russian parcel of Poland with the Russian Empire...
, seeking autonomy from the hegemony of the great power
Great power
A great power is a nation or state that has the ability to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength and diplomatic and cultural influence which may cause small powers to consider the opinions of great powers before taking actions...
s of France
Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France was one of the most powerful states to exist in Europe during the second millennium.It originated from the Western portion of the Frankish empire, and consolidated significant power and influence over the next thousand years. Louis XIV, also known as the Sun King, developed a...
and the British Empire
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom. It originated with the overseas colonies and trading posts established by England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. At its height, it was the...
in the west as well as from the Pan-Slav
Pan-Slavism
Pan-Slavism was a movement in the mid-19th century aimed at unity of all the Slavic peoples. The main focus was in the Balkans where the South Slavs had been ruled for centuries by other empires, Byzantine Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Venice...
policies of the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
in the east.
After the Revolutions of 1848
Revolutions of 1848
The European Revolutions of 1848, known in some countries as the Spring of Nations, Springtime of the Peoples or the Year of Revolution, were a series of political upheavals throughout Europe in 1848. It was the first Europe-wide collapse of traditional authority, but within a year reactionary...
these ideas were adpoted by liberal
Liberalism
Liberalism is the belief in the importance of liberty and equal rights. Liberals espouse a wide array of views depending on their understanding of these principles, but generally, liberals support ideas such as constitutionalism, liberal democracy, free and fair elections, human rights,...
theorists like Friedrich List
Friedrich List
Georg Friedrich List was a leading 19th century German economist who developed the "National System" or what some would call today the National System of Innovation...
and Heinrich von Gagern
Heinrich von Gagern
Heinrich Wilhelm August Freiherr von Gagern was a statesman who argued for the unification of Germany.The third son of Hans Christoph Ernst, Baron von Gagern, a liberal statesman from Hesse, Heinrich von Gagern was born at Bayreuth, educated at the military academy at Munich, and, as an officer in...
, later by the German National Liberal Party
National Liberal Party (Germany)
The National Liberal Party was a German political party which flourished between 1867 and 1918. It was formed by Prussian liberals who put aside their differences with Bismarck over domestic policy due to their support for his highly successful foreign policy, which resulted in the unification of...
, then however with a distinct Pan-German
Pan-Germanism
Pan-Germanism is a pan-nationalist political idea. Pan-Germanists originally sought to unify the German-speaking populations of Europe in a single nation-state known as Großdeutschland , where "German-speaking" was taken to include the Low German, Frisian and Dutch-speaking populations of the Low...
notion and accompanied by the concept of a renewed settler colonialism
Settler colonialism
Settler colonialism is a specific colonial formation whereby foreign family units move into a region and reproduce. Land is thus the key resource in settler colonies, whereas natural and human resources are the main motivation behind other forms of colonialism...
under the firm leadership of the German Empire
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
and Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary , more formally known as the Kingdoms and Lands Represented in the Imperial Council and the Lands of the Holy Hungarian Crown of Saint Stephen, was a constitutional monarchic union between the crowns of the Austrian Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary in...
. Upon the 1871 Unification of Germany
Unification of Germany
The formal unification of Germany into a politically and administratively integrated nation state officially occurred on 18 January 1871 at the Versailles Palace's Hall of Mirrors in France. Princes of the German states gathered there to proclaim Wilhelm of Prussia as Emperor Wilhelm of the German...
under Chancellor Otto von Bismarck
Otto von Bismarck
Otto Eduard Leopold, Prince of Bismarck, Duke of Lauenburg , simply known as Otto von Bismarck, was a Prussian-German statesman whose actions unified Germany, made it a major player in world affairs, and created a balance of power that kept Europe at peace after 1871.As Minister President of...
, the Ostforschung
Ostforschung
Ostforschung in general describes since the 18th century any German research of areas to the East of Germany. Since the 1990s, the Ostforschung itself is a subject of historic research, while the names of institutes etc. were changed to more specific ones. For example, the journal „Zeitschrift für...
concentrated on the achievements by Ethnic Germans in East-Central Europe
East-Central Europe
East-Central Europe – a term defining the countries located between German-speaking countries and Russia. Those lands are described as situated “between two”: between two worlds, between two stages, between two futures...
on the basis of Ethnocentrism
Ethnocentrism
Ethnocentrism is the tendency to believe that one's ethnic or cultural group is centrally important, and that all other groups are measured in relation to one's own. The ethnocentric individual will judge other groups relative to his or her own particular ethnic group or culture, especially with...
with significant anti-Slavic
Anti-Slavism
Anti-Slavism, also known as Slavophobia, a form of racism or xenophobia, refers to various negative attitudes towards Slavic peoples, most common manifestation being claims of inferiority of Slavic nations with respect to other ethnic groups...
, especially anti-Polish notions, as propagated by the Pan-German League
Pan-German League
The Pan-German League was an extremist, ultra-nationalist political interest organization which was officially founded in 1891, a year after the Zanzibar Treaty was signed. It was concerned with a host of issues, concentrating on imperialism, anti-semitism, the so called Polish Question, and...
. Meanwhile Austria had to abandon her claim to leadership and thereafter referred Mitteleuropa to the lands of the Habsburg Monarchy
Habsburg Monarchy
The Habsburg Monarchy covered the territories ruled by the junior Austrian branch of the House of Habsburg , and then by the successor House of Habsburg-Lorraine , between 1526 and 1867/1918. The Imperial capital was Vienna, except from 1583 to 1611, when it was moved to Prague...
in the Danube basin.
Mitteleuropa Plan
The Mitteleuropa plan was to achieve an economic and cultural hegemonyHegemony
Hegemony is an indirect form of imperial dominance in which the hegemon rules sub-ordinate states by the implied means of power rather than direct military force. In Ancient Greece , hegemony denoted the politico–military dominance of a city-state over other city-states...
over Central Europe
Central Europe
Central Europe or alternatively Middle Europe is a region of the European continent lying between the variously defined areas of Eastern and Western Europe...
by the German Empire
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
and subsequent economic & financial exploitation
Exploitation
This article discusses the term exploitation in the meaning of using something in an unjust or cruel manner.- As unjust benefit :In political economy, economics, and sociology, exploitation involves a persistent social relationship in which certain persons are being mistreated or unfairly used for...
of this region combined with direct annexations, settlement of German colonists, expulsion of non-Germans from annexed areas, and eventual Germanization of puppet states created as a buffer between Germany and Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
.
The issue of Central Europe was taken by German thinker Friedrich Naumann in 1915 in his work Mitteleuropa. According to his thought, this part of Europe was to become a politically and economically integrated block subjected to German rule. In his program, Naumann also supported programs of Germanization and Hungarization as well. Naumann in his book used imperialist rhetoric combined with praises to nature, and imperial condescension towards non-German people, while advising to show some "flexbility" towards non-German languages to achieve "harmony"Neuman wrote that it would stabilize the whole Central Europe region. See Some parts of the planning included designs on creating a German colony in Crimea
Crimea
Crimea , or the Autonomous Republic of Crimea , is a sub-national unit, an autonomous republic, of Ukraine. It is located on the northern coast of the Black Sea, occupying a peninsula of the same name...
and colonization of the Baltic states
Baltic states
The term Baltic states refers to the Baltic territories which gained independence from the Russian Empire in the wake of World War I: primarily the contiguous trio of Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania ; Finland also fell within the scope of the term after initially gaining independence in the 1920s.The...
.
The ruling political elites of Germany accepted the Mitteleuropa plan during World War I while drawing out German war aims
Septemberprogramm
The Septemberprogramm was a plan drafted by the German leadership in the early weeks of the First World War. It detailed Germany's ambitious gains should it win the war, as it expected...
and plans for the new order of Europe. Mitteleuropa was to be created by establishing a series of puppet states whose political, economic and military aspects would be under the control of the German Reich. The entire region was to serve as an economic backyard of Germany whose exploitation would enable it to compete with the British Empire
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom. It originated with the overseas colonies and trading posts established by England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. At its height, it was the...
and any other competitors for the position of the world's dominant power. Political, military and economic organization was to be based on German domination, with commercial treaties imposed on countries like Poland and Ukraine. It was believed that the German working classes could be appeased by German politicians through the economic benefits of territorial annexation, settlement of Germans in Central and Eastern Europe
Central and Eastern Europe
Central and Eastern Europe is a term describing former communist states in Europe, after the collapse of the Iron Curtain in 1989/90. In scholarly literature the abbreviations CEE or CEEC are often used for this concept...
and exploitation
Exploitation
This article discusses the term exploitation in the meaning of using something in an unjust or cruel manner.- As unjust benefit :In political economy, economics, and sociology, exploitation involves a persistent social relationship in which certain persons are being mistreated or unfairly used for...
of conquered countries for the material benefit of Germany.
Partial realization of these plans was reflected in the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was a peace treaty signed on March 3, 1918, mediated by South African Andrik Fuller, at Brest-Litovsk between Russia and the Central Powers, headed by Germany, marking Russia's exit from World War I.While the treaty was practically obsolete before the end of the year,...
, where guarantees of economic and military domination over Ukraine by Germany were laid out. Both Ottoman Empire and Austro-Hungary would become reliant on German support in post-war Europe,reducing them to the status of vassals
The Mitteleuropa plan was viewed as threat by the British Empire, which concluded it would destroy British continental trade, and as consequence the source of its military power
See also
- Central EuropeCentral EuropeCentral Europe or alternatively Middle Europe is a region of the European continent lying between the variously defined areas of Eastern and Western Europe...
- LebensraumLebensraumwas one of the major political ideas of Adolf Hitler, and an important component of Nazi ideology. It served as the motivation for the expansionist policies of Nazi Germany, aiming to provide extra space for the growth of the German population, for a Greater Germany...
- Drang nach OstenDrang nach OstenDrang nach Osten was a term coined in the 19th century to designate German expansion into Slavic lands. The term became a motto of the German nationalist movement in the late nineteenth century...
- Geographical centre of EuropeGeographical centre of EuropeThe location of the geographical centre of Europe depends on the definition of the borders of Europe, mainly whether remote islands are included to define the extreme points of Europe, and on the method of calculating the final result...
- League of East European StatesLeague of East European StatesThe League of East European States was a political idea conceived during World War I for the establishment of a buffer state within the Jewish Pale of Settlement of Russia, composed of the former Polish provinces annexed by Russia, which would be a de facto protectorate of the German Empire in...

