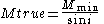Minimum mass
Encyclopedia
In astronomy
, minimum mass is the lower-bound calculated mass
of observed objects such as planet
s, star
s and binary system
s, nebula
e, and black hole
s. Minimum mass is a widely cited statistic for extrasolar planet
s. Because most extrasolar planets are currently detected by the radial velocity method, which reveals planets by measuring changes in the movement of stars in the line-of-sight
, the real orbital inclination
s and true mass
es of the planets are generally unknown.
If inclination can be determined, the true mass can be obtained from the calculated minimum mass using the following relationship:
For orbiting bodies in extrasolar stellar
and planetary system
s, an inclination of 0° or 180° corresponds to a face-on orbit, while an inclination of 90° corresponds to an edge-on orbit.
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
, minimum mass is the lower-bound calculated mass
Mass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
of observed objects such as planet
Planet
A planet is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science,...
s, star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
s and binary system
Binary system
Binary system may refer to:* Binary numeral system, the base-2 internal "machine language" of computers* Binary opposition, a bipolar distinction in philosophy, structuralism and critical theory...
s, nebula
Nebula
A nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen gas, helium gas and other ionized gases...
e, and black hole
Black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime from which nothing, not even light, can escape. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass will deform spacetime to form a black hole. Around a black hole there is a mathematically defined surface called an event horizon that...
s. Minimum mass is a widely cited statistic for extrasolar planet
Extrasolar planet
An extrasolar planet, or exoplanet, is a planet outside the Solar System. A total of such planets have been identified as of . It is now known that a substantial fraction of stars have planets, including perhaps half of all Sun-like stars...
s. Because most extrasolar planets are currently detected by the radial velocity method, which reveals planets by measuring changes in the movement of stars in the line-of-sight
Line-of-sight propagation
Line-of-sight propagation refers to electro-magnetic radiation or acoustic wave propagation. Electromagnetic transmission includes light emissions traveling in a straight line...
, the real orbital inclination
Inclination
Inclination in general is the angle between a reference plane and another plane or axis of direction.-Orbits:The inclination is one of the six orbital parameters describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit...
s and true mass
True mass
The term true mass is synonymous with the term mass, but is used in astronomy to differentiate the measured mass of a planet from the lower limit of mass usually obtained from radial velocity techniques...
es of the planets are generally unknown.
If inclination can be determined, the true mass can be obtained from the calculated minimum mass using the following relationship:
For orbiting bodies in extrasolar stellar
Star system
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars which orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. A large number of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a star cluster or galaxy, although, broadly speaking, they are also star systems.-Binary star systems:A stellar...
and planetary system
Planetary system
A planetary system consists of the various non-stellar objects orbiting a star such as planets, dwarf planets , asteroids, meteoroids, comets, and cosmic dust...
s, an inclination of 0° or 180° corresponds to a face-on orbit, while an inclination of 90° corresponds to an edge-on orbit.