
Miletus
Encyclopedia
Miletus (Ancient Greek
: Μίλητος, Milētos; Latin: Miletus) was an ancient Greek
city on the western coast of Anatolia
(in what is now Aydin Province
, Turkey
), near the mouth of the Maeander River
in ancient Caria
. Before the Persian
invasion in the middle of the 6th century BC, Miletus was considered the greatest and wealthiest of Greek cities.
Evidence of first settlement at the site has been made inaccessible by the rise of sea level and deposition of sediments from the Maeander. The first available evidence is of the Neolithic
.
In the early and middle Bronze age
the settlement came under Minoan influence. Legend has it that an influx of Cretans occurred displacing the indigenous Leleges
. The site was renamed Miletus after a place in Crete
.
The Late Bronze Age, 13th century BCE, saw the arrival of Luwian language
speakers from south central Anatolia calling themselves the Carians
. Later in that century the first Greeks arrived. The city at that time rebelled against the Hittite Empire. After the fall of that empire the city was destroyed in the 12th century BCE and starting about 1000 BCE was resettled extensively by the Ionian Greeks
. Legend offers an Ionian foundation event sponsored by a founder named Neleus from the Peloponnesus.
The Greek Dark Ages
were a time of Ionian settlement and consolidation in an alliance called the Ionian League
. The Archaic Period
of Greece began with a sudden and brilliant flash of art and philosophy on the coast of Anatolia
. In the 6th century BC, Miletus was the site of origin of the Greek philosophical (and scientific) tradition, when Thales
, followed by Anaximander
and Anaximines (known collectively, to modern scholars, as the Milesian School
) began to speculate about the material constitution of the world, and to propose speculative naturalistic (as opposed to traditional, supernatural) explanations for various natural phenomena.
A thousand years after birthing Western philosophy and science, Miletus served as birthplace of Hagia Sophia
's legendary architect (and inventor of the flying buttress
) Isidore of Miletus
.
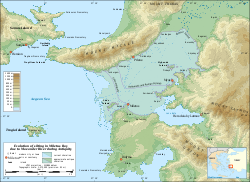 The ruins lies about 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) north of Akkoy
The ruins lies about 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) north of Akkoy
.
In antiquity the city possessed a harbor
at the southern entry of a large bay, on which two more of the traditional twelve Ionian cities stood: Priene
and Myus
. The harbor of Miletus was additionally protected by the nearby small island of Lade
. Over the centuries the gulf silted up with alluvium
carried by the Meander River. Priene and Myus had lost their harbors by the Roman era, and Miletus itself became an inland town in the early Christian era; all three were abandoned to ruin as their economies were strangled by the lack of access to the sea. There is a Great Harbour Monument where, according to the New Testament account, the apostle Paul stopped on his way back to Jerusalem by boat. He met the Ephesian Elders and then headed out to the beach to bid them farewell, recorded in the book of .
epoch the Miletus region was submerged in the Aegean Sea
. It subsequently emerged slowly, the sea reaching a low level of about 130 metres (426.5 ft) below present level at about 18,000 BP
. The site of Miletus was part of the mainland.
A gradual rise brought a level of about 1.75 metres (5.7 ft) below present at about 5500 BP, creating several karst
block islands of limestone, the location of the first settlements at Miletus. At about 1500 BCE the karst shifted due to small crustal movements and the islands consolidated into a peninsula. Since then the sea has risen 1.75 m but the peninsula has been surrounded by sediment from the Maeander river and is now land-locked. Sedimentation of the harbor began at about 1000 BCE, and by 300 CE Lake Bafa had been created.
population in the 2nd half of the 4th millennium BCE (3500–3000 BCE). Pollen in core samples from Lake Bafa in the Latmus region inland of Miletus suggests that a lightly grazed climax forest prevailed in the Maeander valley, otherwise untenanted. Sparse Neolithic settlements were made at springs, numerous and sometimes geothermal in this karst, rift valley topography. The islands offshore were settled perhaps for their strategic significance at the mouth of the Maeander, a route inland protected by escarpments. The grazers in the valley may have belonged to them, but the location looked to the sea.
acquired by trade arrived at Miletus. For some centuries the location received a strong impulse from that civilization, an archaeological fact that tends to support but not necessarily confirm the founding legend—that is, a population influx, from Crete
. According to Strabo
:
Annals of Mursili II
as Millawanda. In ca. 1320 BC, Millawanda supported the rebellion of Uhha-Ziti
of Arzawa
. Mursili ordered his generals Mala-Ziti and Gulla to raid Millawanda, and they proceeded to burn parts of it; damage from LHIIIA
found on-site has been associated with this raid. In addition the town was fortified according to a Hittite plan.
Millawanda is then mentioned in the "Tawagalawa letter
", part of a series including the Manapa-Tarhunta letter
and the Milawata letter
, all of which are less securely dated. The Tawagalawa letter notes that Milawata had a governor, Atpa, who was under the jurisdiction of "Ahhiyawa" (a growing state probably in LHIIIB
Mycenaean Greece
); and that the town of Atriya was under Milesian jurisdiction. The Manapa-Tarhunta letter also mentions Atpa. Together the two letters tell that the adventurer Piyama-Radu
had humiliated Manapa-Tarhunta before Atpa (in addition to other misadventures); a Hittite king then chased Piyama-Radu into Millawanda and, in the Tawagalawa letter, requested Piyama-Radu's extradition to Hatti.
The Milawata letter mentions a joint expedition by the Hittite king and a Luwiyan vassal (probably Kupanta-Kurunta
of Mira) against Milawata (apparently its new name), and notes that Milawata (and Atriya) were now under Hittite control.
Homer
records that during the time of the Trojan War
, it was a Carian city.
In the last stage of LHIIIB, the citadel of bronze age Pylos
counted among its female slaves a mi-ra-ti-ja, Mycenaean Greek for "women from Miletus", written in Linear B
syllabic script.
During the collapse of Bronze Age civilisation, Miletus was burnt again, presumably by the Sea Peoples
.
the last King of Athens
, had come to Miletus after the "Return of the Heraclids" (so, during the Greek Dark Ages
). The Ionians killed the men of Miletus and married their widows. This is the mythical commencement of the enduring alliance between Athens and Miletus, which played an important role in the subsequent Persian Wars.
 The city of Miletus became one of the twelve
The city of Miletus became one of the twelve
Ionia
n cities of Asia Minor
.
Miletus was one of the cities involved in the Lelantine War
of the 8th century BCE.
In the late 7th century BCE the tyrant Thrasybulus
preserved the independence of Miletus during a 12 year war fought against the Lydian Empire. Thrasybulus was an ally of the famous Corinthian
tyrant Periander
.
Miletus was an important center of philosophy and science, producing such men as Thales
, Anaximander
and Anaximenes
.
By the 6th century BCE, Miletus had earned a maritime empire with many colonies, but brushed up against powerful Lydia
at home, and the tyrant Polycrates
of its neighbour to the west, Samos
.
When Cyrus
of Persia defeated Croesus
of Lydia in the middle of the 6th century BCE, Miletus fell under Persian rule. In 499 BC, Miletus's tyrant
Aristagoras
became the leader of the Ionian Revolt
against the Persians. Persia quashed this rebellion and punished Miletus in such a fashion that the whole of Greece mourned it. A year afterward, Phrynicus produced the tragedy The Capture of Miletus in Athens. The Athenians fined him for reminding them of their loss.
 Its gridlike layout, planned by Hippodamos, became the basic layout for Roman
Its gridlike layout, planned by Hippodamos, became the basic layout for Roman
cities.
In 479 BC, the Greeks decisively defeated the Persians at the Greek mainland, and Miletus was freed of Persian rule. During this time several other cities were formed by Milesian
settlers, spanning across what is now Turkey and even as far as Crimea
.
The eponymous founder of the bawdy Miletian school of literature Aristides of Miletus taught here.
mentions Miletus as the site where the Apostle Paul
in 57 CE met with the elders of the church of Ephesus
near the close of his Third Missionary Journey, as recorded in Acts of the Apostles
(Acts 20:15–38). It is believed that Paul stopped by the Great Harbour Monument and sat on its steps. He may have met the Ephesian elders there and then bid them farewell on the nearby beach. Miletus is also the city where Paul left Trophimus
, one of his travelling companions, to recover from an illness (2 Timothy 4:20). Because this cannot be the same visit as Acts 20 (in which Trophimus accompanied Paul all the way to Jerusalem, according to Acts 21:29), Paul must have made at least one additional visit to Miletus, perhaps as late as 65 or 66 CE. Paul's previous successful three-year ministry in nearby Ephesus
resulted in the evangelization of the entire province of Asia (see Acts 19:10, 20; 1 Corinthians 16:9). It is safe to assume that at least by the time of the apostle's second visit to Miletus, a fledgling Christian community was established in Miletus.
age Miletus became a residence for archbishops. The small Byzantine castle called Castro Palation located on the hill beside the city, was built at this time. From Miletus came the famous merchant family of Mauros, one of their members became judge of the Hippodrome of Constantinople
. Miletus was headed by a curator
.
.
Finally, Ottomans utilized the city as a harbour during their rule in Anatolia
. As the harbour became silted up, the city was abandoned. Today the ruins of city lie some 10 kilometres from the sea.
.
between 1899 and 1931.
Excavations, however, were interrupted several times by wars and various other events.
Carl Weickart excavated for a short season in 1938 and again between
1955 and 1957.
He was followed by Gerhard Kleiner and then by Wolfgang Muller-Wiener.
Today, excavations are organized by the Ruhr University
of Bochum
, Germany
.
One remarkable artifact recovered from the city during the first excavations of the 19th century, the Market Gate of Miletus
, was transported piece by piece to Germany
and reassembled. It is currently exhibited at the Pergamon museum
in Berlin
. The main collection of artifacts resides in the Miletus Museum in Didim
, Aydın
, serving since 1973.
Pliny the Elder
mentions 90 colonies founded by Miletus in his Natural History (5.31), among them:
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek is the stage of the Greek language in the periods spanning the times c. 9th–6th centuries BC, , c. 5th–4th centuries BC , and the c. 3rd century BC – 6th century AD of ancient Greece and the ancient world; being predated in the 2nd millennium BC by Mycenaean Greek...
: Μίλητος, Milētos; Latin: Miletus) was an ancient Greek
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece is a civilization belonging to a period of Greek history that lasted from the Archaic period of the 8th to 6th centuries BC to the end of antiquity. Immediately following this period was the beginning of the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine era. Included in Ancient Greece is the...
city on the western coast of Anatolia
Anatolia
Anatolia is a geographic and historical term denoting the westernmost protrusion of Asia, comprising the majority of the Republic of Turkey...
(in what is now Aydin Province
Aydin Province
Aydın Province is a province of southwestern Turkey, located in the Aegean Region. The provincial capital is the city of Aydın which has a population of approx. 150,000 . Other towns in the province include the summer seaside resorts of Didim and Kuşadası.-History:Aydın was founded by the ancient...
, Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
), near the mouth of the Maeander River
Maeander River
The Büyük Menderes River ; , Ancient Greek: Μαίανδρος, Maíandros) is a river in southwestern Turkey. It rises in west central Turkey near Dinar before flowing west through the Büyük Menderes graben until reaching the Aegean Sea in the proximity of the ancient Ionian city Miletus...
in ancient Caria
Caria
Caria was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid-Ionia south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionian and Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joined the Carian population in forming Greek-dominated states there...
. Before the Persian
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire , sometimes known as First Persian Empire and/or Persian Empire, was founded in the 6th century BCE by Cyrus the Great who overthrew the Median confederation...
invasion in the middle of the 6th century BC, Miletus was considered the greatest and wealthiest of Greek cities.
Evidence of first settlement at the site has been made inaccessible by the rise of sea level and deposition of sediments from the Maeander. The first available evidence is of the Neolithic
Neolithic
The Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
.
In the early and middle Bronze age
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a period characterized by the use of copper and its alloy bronze as the chief hard materials in the manufacture of some implements and weapons. Chronologically, it stands between the Stone Age and Iron Age...
the settlement came under Minoan influence. Legend has it that an influx of Cretans occurred displacing the indigenous Leleges
Leleges
The Leleges were one of the aboriginal peoples of southwest Anatolia , who were already there when the Indo-European Hellenes emerged. The distinction between the Leleges and the Carians is unclear. According to Homer the Leleges were a distinct Anatolian tribe Homer...
. The site was renamed Miletus after a place in Crete
Crete
Crete is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, and one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. It forms a significant part of the economy and cultural heritage of Greece while retaining its own local cultural traits...
.
The Late Bronze Age, 13th century BCE, saw the arrival of Luwian language
Luwian language
Luwian is an extinct language of the Anatolian branch of the Indo-European language family. Luwian is closely related to Hittite, and was among the languages spoken during the second and first millennia BC by population groups in central and western Anatolia and northern Syria...
speakers from south central Anatolia calling themselves the Carians
Carians
The Carians were the ancient inhabitants of Caria in southwest Anatolia.-Historical accounts:It is not clear when the Carians enter into history. The definition is dependent on corresponding Caria and the Carians to the "Karkiya" or "Karkisa" mentioned in the Hittite records...
. Later in that century the first Greeks arrived. The city at that time rebelled against the Hittite Empire. After the fall of that empire the city was destroyed in the 12th century BCE and starting about 1000 BCE was resettled extensively by the Ionian Greeks
Ionians
The Ionians were one of the four major tribes into which the Classical Greeks considered the population of Hellenes to have been divided...
. Legend offers an Ionian foundation event sponsored by a founder named Neleus from the Peloponnesus.
The Greek Dark Ages
Greek Dark Ages
The Greek Dark Age or Ages also known as Geometric or Homeric Age are terms which have regularly been used to refer to the period of Greek history from the presumed Dorian invasion and end of the Mycenaean Palatial civilization around 1200 BC, to the first signs of the Greek city-states in the 9th...
were a time of Ionian settlement and consolidation in an alliance called the Ionian League
Ionian League
The Ionian League , also called the Panionic League, was a confederation formed at the end of the Meliac War in the mid-7th century BC comprising twelve Ionian cities .These were listed by Herodotus as*Miletus, Myus, and...
. The Archaic Period
Archaic period in Greece
The Archaic period in Greece was a period of ancient Greek history that followed the Greek Dark Ages. This period saw the rise of the polis and the founding of colonies, as well as the first inklings of classical philosophy, theatre in the form of tragedies performed during Dionysia, and written...
of Greece began with a sudden and brilliant flash of art and philosophy on the coast of Anatolia
Anatolia
Anatolia is a geographic and historical term denoting the westernmost protrusion of Asia, comprising the majority of the Republic of Turkey...
. In the 6th century BC, Miletus was the site of origin of the Greek philosophical (and scientific) tradition, when Thales
Thales
Thales of Miletus was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher from Miletus in Asia Minor, and one of the Seven Sages of Greece. Many, most notably Aristotle, regard him as the first philosopher in the Greek tradition...
, followed by Anaximander
Anaximander
Anaximander was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher who lived in Miletus, a city of Ionia; Milet in modern Turkey. He belonged to the Milesian school and learned the teachings of his master Thales...
and Anaximines (known collectively, to modern scholars, as the Milesian School
Milesian school
The Milesian school was a school of thought founded in the 6th century BC. The ideas associated with it are exemplified by three philosophers from the Ionian town of Miletus, on the Aegean coast of Anatolia: Thales, Anaximander, and Anaximenes...
) began to speculate about the material constitution of the world, and to propose speculative naturalistic (as opposed to traditional, supernatural) explanations for various natural phenomena.
A thousand years after birthing Western philosophy and science, Miletus served as birthplace of Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia is a former Orthodox patriarchal basilica, later a mosque, and now a museum in Istanbul, Turkey...
's legendary architect (and inventor of the flying buttress
Flying buttress
A flying buttress is a specific form of buttressing most strongly associated with Gothic church architecture. The purpose of any buttress is to resist the lateral forces pushing a wall outwards by redirecting them to the ground...
) Isidore of Miletus
Isidore of Miletus
Isidore of Miletus was one of the two main Byzantine architects that Emperor Justinian I commissioned to design the church of Hagia Sophia in Constantinople from 532-537A.D.-Summary:...
.
Geography

Akkoy
Akkoy is a village in Aydın Province, Turkey, situated near the western coast south of İzmir. It is named after its white stone houses .The village of Akkoy is close to the ruins of the ancient city of Miletus....
.
In antiquity the city possessed a harbor
Harbor
A harbor or harbour , or haven, is a place where ships, boats, and barges can seek shelter from stormy weather, or else are stored for future use. Harbors can be natural or artificial...
at the southern entry of a large bay, on which two more of the traditional twelve Ionian cities stood: Priene
Priene
Priene was an ancient Greek city of Ionia at the base of an escarpment of Mycale, about north of the then course of the Maeander River, from today's Aydin, from today's Söke and from ancient Miletus...
and Myus
Myus
Myus, Caria was an ancient city-state and was one of twelve major settlements formed in the Ionian Confederation, called the Ionian League. The city was said to have been founded by Cyaretus , a son of Codrus. Myus was a small peninsula, it is now however surrounded by land...
. The harbor of Miletus was additionally protected by the nearby small island of Lade
Lade
Lade may refer to:People* Brendon Lade , Australian rules footballer* Sir John Lade , baronet and Regency horse-breeder* Heinrich Eduard von Lade , German banker and amateur astronomer...
. Over the centuries the gulf silted up with alluvium
Alluvium
Alluvium is loose, unconsolidated soil or sediments, eroded, deposited, and reshaped by water in some form in a non-marine setting. Alluvium is typically made up of a variety of materials, including fine particles of silt and clay and larger particles of sand and gravel...
carried by the Meander River. Priene and Myus had lost their harbors by the Roman era, and Miletus itself became an inland town in the early Christian era; all three were abandoned to ruin as their economies were strangled by the lack of access to the sea. There is a Great Harbour Monument where, according to the New Testament account, the apostle Paul stopped on his way back to Jerusalem by boat. He met the Ephesian Elders and then headed out to the beach to bid them farewell, recorded in the book of .
Geology
During the PleistocenePleistocene
The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and ....
epoch the Miletus region was submerged in the Aegean Sea
Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea[p] is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea located between the southern Balkan and Anatolian peninsulas, i.e., between the mainlands of Greece and Turkey. In the north, it is connected to the Marmara Sea and Black Sea by the Dardanelles and Bosporus...
. It subsequently emerged slowly, the sea reaching a low level of about 130 metres (426.5 ft) below present level at about 18,000 BP
Before Present
Before Present years is a time scale used in archaeology, geology, and other scientific disciplines to specify when events in the past occurred. Because the "present" time changes, standard practice is to use AD 1950 as the origin of the age scale, reflecting the fact that radiocarbon...
. The site of Miletus was part of the mainland.
A gradual rise brought a level of about 1.75 metres (5.7 ft) below present at about 5500 BP, creating several karst
KARST
Kilometer-square Area Radio Synthesis Telescope is a Chinese telescope project to which FAST is a forerunner. KARST is a set of large spherical reflectors on karst landforms, which are bowlshaped limestone sinkholes named after the Kras region in Slovenia and Northern Italy. It will consist of...
block islands of limestone, the location of the first settlements at Miletus. At about 1500 BCE the karst shifted due to small crustal movements and the islands consolidated into a peninsula. Since then the sea has risen 1.75 m but the peninsula has been surrounded by sediment from the Maeander river and is now land-locked. Sedimentation of the harbor began at about 1000 BCE, and by 300 CE Lake Bafa had been created.
Neolithic
The earliest available archaeological evidence indicates that the islands on which Miletus was originally placed were inhabited by a NeolithicNeolithic
The Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
population in the 2nd half of the 4th millennium BCE (3500–3000 BCE). Pollen in core samples from Lake Bafa in the Latmus region inland of Miletus suggests that a lightly grazed climax forest prevailed in the Maeander valley, otherwise untenanted. Sparse Neolithic settlements were made at springs, numerous and sometimes geothermal in this karst, rift valley topography. The islands offshore were settled perhaps for their strategic significance at the mouth of the Maeander, a route inland protected by escarpments. The grazers in the valley may have belonged to them, but the location looked to the sea.
Bronze Age
Recorded history at Miletus begins with the records of the Hittite Empire in the Late Bronze Age. The prehistoric archaeology of the Early and Middle Bronze Age portrays a city heavily influenced by society and events elsewhere in the Aegean, rather than inland.Cretan period
Beginning at about 1900 BCE artifacts of the Minoan civilizationMinoan civilization
The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age civilization that arose on the island of Crete and flourished from approximately the 27th century BC to the 15th century BC. It was rediscovered at the beginning of the 20th century through the work of the British archaeologist Arthur Evans...
acquired by trade arrived at Miletus. For some centuries the location received a strong impulse from that civilization, an archaeological fact that tends to support but not necessarily confirm the founding legend—that is, a population influx, from Crete
Crete
Crete is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, and one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. It forms a significant part of the economy and cultural heritage of Greece while retaining its own local cultural traits...
. According to Strabo
Strabo
Strabo, also written Strabon was a Greek historian, geographer and philosopher.-Life:Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus , a city which he said was situated the approximate equivalent of 75 km from the Black Sea...
:
Ephorus says: Miletus was first founded and fortified above the sea by Cretans, where the Miletus of olden times is now situated, being settled by Sarpedon, who brought colonists from the Cretan Miletus and named the city after that Miletus, the place formerly being in possession of the LelegesThe legends recounted as history by the ancient historians and geographers are perhaps the strongest; the late mythographers have nothing historically significant to relate.LelegesThe Leleges were one of the aboriginal peoples of southwest Anatolia , who were already there when the Indo-European Hellenes emerged. The distinction between the Leleges and the Carians is unclear. According to Homer the Leleges were a distinct Anatolian tribe Homer...
.
Luwian and Greek period
Miletus is first mentioned in the HittiteHittites
The Hittites were a Bronze Age people of Anatolia.They established a kingdom centered at Hattusa in north-central Anatolia c. the 18th century BC. The Hittite empire reached its height c...
Annals of Mursili II
Mursili II
Mursili II was a king of the Hittite Empire ca. 1321–1295 BC .-Family:Mursili II was the younger son of Suppiluliuma I, one of the most powerful rulers of the Hittite Empire...
as Millawanda. In ca. 1320 BC, Millawanda supported the rebellion of Uhha-Ziti
Uhha-Ziti
Uhha-Ziti was the last independent king of Arzawa, a Bronze Age kingdom of western Anatolia.Uhha-Ziti had two recorded children, Piyama-Kurunta and Tapalazunauli, who were of fighting age as of 1322 BC....
of Arzawa
Arzawa
Arzawa in the second half of the second millennium BC was the name of a region and a political entity in Western Anatolia, the core area of which was centered on the Hermos and Maeander river valleys, corresponding with the Late Bronze Age kingdoms of the...
. Mursili ordered his generals Mala-Ziti and Gulla to raid Millawanda, and they proceeded to burn parts of it; damage from LHIIIA
Helladic period
Helladic is a modern archaeological term meant to identify a sequence of periods characterizing the culture of mainland ancient Greece during the Bronze Age. The term is commonly used in archaeology and art history...
found on-site has been associated with this raid. In addition the town was fortified according to a Hittite plan.
Millawanda is then mentioned in the "Tawagalawa letter
Tawagalawa letter
The Tawagalawa letter was written by a Hittite king to a king of Ahhiyawa around 1250 BC. This letter, of which only the third tablet has been preserved, concerns the activities of an adventurer Piyama-Radu against the Hittites, and requests his extradition to Hatti under assurances of safe conduct...
", part of a series including the Manapa-Tarhunta letter
Manapa-Tarhunta letter
The Manapa-Tarhunta letter is a Hittite letter discovered in the 1980s. It was written by a client king called Manapa-Tarhunta to an unnamed Hittite king around 1295 BCE....
and the Milawata letter
Milawata letter
The Milawata letter is a diplomatic correspondence from a Hittite king at Hattusa to a client king in western Anatolia around 1240 BCE...
, all of which are less securely dated. The Tawagalawa letter notes that Milawata had a governor, Atpa, who was under the jurisdiction of "Ahhiyawa" (a growing state probably in LHIIIB
Helladic period
Helladic is a modern archaeological term meant to identify a sequence of periods characterizing the culture of mainland ancient Greece during the Bronze Age. The term is commonly used in archaeology and art history...
Mycenaean Greece
Mycenaean Greece
Mycenaean Greece was a cultural period of Bronze Age Greece taking its name from the archaeological site of Mycenae in northeastern Argolis, in the Peloponnese of southern Greece. Athens, Pylos, Thebes, and Tiryns are also important Mycenaean sites...
); and that the town of Atriya was under Milesian jurisdiction. The Manapa-Tarhunta letter also mentions Atpa. Together the two letters tell that the adventurer Piyama-Radu
Piyama-Radu
Piyamaradu was a warlike aristocratic personage whose name figures prominently in the Hittite archives of the middle and late 13th century BC in western Anatolia. His history is of particular interest because it appears to intertwine with that of the Trojan War...
had humiliated Manapa-Tarhunta before Atpa (in addition to other misadventures); a Hittite king then chased Piyama-Radu into Millawanda and, in the Tawagalawa letter, requested Piyama-Radu's extradition to Hatti.
The Milawata letter mentions a joint expedition by the Hittite king and a Luwiyan vassal (probably Kupanta-Kurunta
Kupanta-Kurunta
Kupanta-Kurunta was the first recorded king of Arzawa, in the late 15th century BC. He was defeated by an earlier Tudhaliya and his son, the future Arnuwanda I. He then attacked Arnuwanda's restive vassal Madduwatta at Zippasla...
of Mira) against Milawata (apparently its new name), and notes that Milawata (and Atriya) were now under Hittite control.
Homer
Homer
In the Western classical tradition Homer , is the author of the Iliad and the Odyssey, and is revered as the greatest ancient Greek epic poet. These epics lie at the beginning of the Western canon of literature, and have had an enormous influence on the history of literature.When he lived is...
records that during the time of the Trojan War
Trojan War
In Greek mythology, the Trojan War was waged against the city of Troy by the Achaeans after Paris of Troy took Helen from her husband Menelaus, the king of Sparta. The war is among the most important events in Greek mythology and was narrated in many works of Greek literature, including the Iliad...
, it was a Carian city.
In the last stage of LHIIIB, the citadel of bronze age Pylos
Pylos
Pylos , historically known under its Italian name Navarino, is a town and a former municipality in Messenia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Pylos-Nestoras, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. It was the capital of the former...
counted among its female slaves a mi-ra-ti-ja, Mycenaean Greek for "women from Miletus", written in Linear B
Linear B
Linear B is a syllabic script that was used for writing Mycenaean Greek, an early form of Greek. It pre-dated the Greek alphabet by several centuries and seems to have died out with the fall of Mycenaean civilization...
syllabic script.
During the collapse of Bronze Age civilisation, Miletus was burnt again, presumably by the Sea Peoples
Sea Peoples
The Sea Peoples were a confederacy of seafaring raiders of the second millennium BC who sailed into the eastern Mediterranean, caused political unrest, and attempted to enter or control Egyptian territory during the late 19th dynasty and especially during year 8 of Ramesses III of the 20th Dynasty...
.
Dark Age
Mythographers told that Neleus, a son of CodrusCodrus
Codrus was the last of the semi-mythical Kings of Athens . He was an ancient exemplar of patriotism and self-sacrifice. He was succeeded by his son Medon, who ruled not as king but as the first Archon of Athens....
the last King of Athens
King of Athens
Before the Athenian democracy, the tyrants, and the Archons, the city-state of Athens was ruled by kings. Most of these are probably mythical or only semi-historical...
, had come to Miletus after the "Return of the Heraclids" (so, during the Greek Dark Ages
Greek Dark Ages
The Greek Dark Age or Ages also known as Geometric or Homeric Age are terms which have regularly been used to refer to the period of Greek history from the presumed Dorian invasion and end of the Mycenaean Palatial civilization around 1200 BC, to the first signs of the Greek city-states in the 9th...
). The Ionians killed the men of Miletus and married their widows. This is the mythical commencement of the enduring alliance between Athens and Miletus, which played an important role in the subsequent Persian Wars.
Archaic period

Ionian League
The Ionian League , also called the Panionic League, was a confederation formed at the end of the Meliac War in the mid-7th century BC comprising twelve Ionian cities .These were listed by Herodotus as*Miletus, Myus, and...
Ionia
Ionia
Ionia is an ancient region of central coastal Anatolia in present-day Turkey, the region nearest İzmir, which was historically Smyrna. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements...
n cities of Asia Minor
Asia Minor
Asia Minor is a geographical location at the westernmost protrusion of Asia, also called Anatolia, and corresponds to the western two thirds of the Asian part of Turkey...
.
Miletus was one of the cities involved in the Lelantine War
Lelantine War
The Lelantine War was a long-remembered military conflict between the two ancient Greek city states Chalkis and Eretria in Euboea which took place in the early Archaic period, at some time between ca 710 and 650 BC. The reason for war was, according to tradition, the struggle for the fertile...
of the 8th century BCE.
In the late 7th century BCE the tyrant Thrasybulus
Thrasybulus (tyrant)
Thrasybulus was the tyrant of Miletus in the 7th century BC. Under his rule, Miletus fought a lengthy war against Lydia. This war ended without a decisive victor . Following the war, Miletus and Lydia concluded an alliance.Thrasybulus was an ally of Periander, the tyrant of Corinth...
preserved the independence of Miletus during a 12 year war fought against the Lydian Empire. Thrasybulus was an ally of the famous Corinthian
Corinth
Corinth is a city and former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Corinth, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit...
tyrant Periander
Periander
Periander was the second tyrant of Corinth, Greece in the 7th century BC. He was the son of the first tyrant, Cypselus. Periander succeeded his father in 627 BC. He died in 585 BC....
.
Miletus was an important center of philosophy and science, producing such men as Thales
Thales
Thales of Miletus was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher from Miletus in Asia Minor, and one of the Seven Sages of Greece. Many, most notably Aristotle, regard him as the first philosopher in the Greek tradition...
, Anaximander
Anaximander
Anaximander was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher who lived in Miletus, a city of Ionia; Milet in modern Turkey. He belonged to the Milesian school and learned the teachings of his master Thales...
and Anaximenes
Anaximenes of Miletus
Anaximenes of Miletus was an Archaic Greek Pre-Socratic philosopher active in the latter half of the 6th century BC. One of the three Milesian philosophers, he is identified as a younger friend or student of Anaximander. Anaximenes, like others in his school of thought, practiced material monism...
.
By the 6th century BCE, Miletus had earned a maritime empire with many colonies, but brushed up against powerful Lydia
Lydia
Lydia was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern Turkish provinces of Manisa and inland İzmir. Its population spoke an Anatolian language known as Lydian....
at home, and the tyrant Polycrates
Polycrates
Polycrates , son of Aeaces, was the tyrant of Samos from c. 538 BC to 522 BC.He took power during a festival of Hera with his brothers Pantagnotus and Syloson, but soon had Pantagnotus killed and exiled Syloson to take full control for himself. He then allied with Amasis II, pharaoh of Egypt, as...
of its neighbour to the west, Samos
Samoš
Samoš is a village in Serbia. It is situated in the Kovačica municipality, in the South Banat District, Vojvodina province. The village has a Serb ethnic majority and its population numbering 1,247 people .-See also:...
.
When Cyrus
Cyrus the Great
Cyrus II of Persia , commonly known as Cyrus the Great, also known as Cyrus the Elder, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire. Under his rule, the empire embraced all the previous civilized states of the ancient Near East, expanded vastly and eventually conquered most of Southwest Asia and much...
of Persia defeated Croesus
Croesus
Croesus was the king of Lydia from 560 to 547 BC until his defeat by the Persians. The fall of Croesus made a profound impact on the Hellenes, providing a fixed point in their calendar. "By the fifth century at least," J.A.S...
of Lydia in the middle of the 6th century BCE, Miletus fell under Persian rule. In 499 BC, Miletus's tyrant
Tyrant
A tyrant was originally one who illegally seized and controlled a governmental power in a polis. Tyrants were a group of individuals who took over many Greek poleis during the uprising of the middle classes in the sixth and seventh centuries BC, ousting the aristocratic governments.Plato and...
Aristagoras
Aristagoras
Aristagoras was the leader of Miletus in the late 6th century BC and early 5th century BC.- Background :Aristagoras served as deputy governor of Miletus, a polis on the western coast of Anatolia around 500 BC. He was the son of Molpagoras, and son-in-law of Histiaeus, whom the Persians had set up...
became the leader of the Ionian Revolt
Ionian Revolt
The Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several regions of Asia Minor against Persian rule, lasting from 499 BC to 493 BC...
against the Persians. Persia quashed this rebellion and punished Miletus in such a fashion that the whole of Greece mourned it. A year afterward, Phrynicus produced the tragedy The Capture of Miletus in Athens. The Athenians fined him for reminding them of their loss.
Classical period

Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
cities.
In 479 BC, the Greeks decisively defeated the Persians at the Greek mainland, and Miletus was freed of Persian rule. During this time several other cities were formed by Milesian
Milesians (Greek)
The Milesians of Hellenic civilization were the inhabitants of Miletus, a city in the Anatolia province of modern-day Turkey, near the coast of the Mediterranean Sea and at the mouth of the Meander River. Settlers from Crete moved to Miletus sometime in 16th century BC...
settlers, spanning across what is now Turkey and even as far as Crimea
Crimea
Crimea , or the Autonomous Republic of Crimea , is a sub-national unit, an autonomous republic, of Ukraine. It is located on the northern coast of the Black Sea, occupying a peninsula of the same name...
.
The eponymous founder of the bawdy Miletian school of literature Aristides of Miletus taught here.
Alexandrian period
In 334 BC, the city was liberated from Persian rule by Alexander the Great.Roman period
The New TestamentNew Testament
The New Testament is the second major division of the Christian biblical canon, the first such division being the much longer Old Testament....
mentions Miletus as the site where the Apostle Paul
Paul of Tarsus
Paul the Apostle , also known as Saul of Tarsus, is described in the Christian New Testament as one of the most influential early Christian missionaries, with the writings ascribed to him by the church forming a considerable portion of the New Testament...
in 57 CE met with the elders of the church of Ephesus
Ephesus
Ephesus was an ancient Greek city, and later a major Roman city, on the west coast of Asia Minor, near present-day Selçuk, Izmir Province, Turkey. It was one of the twelve cities of the Ionian League during the Classical Greek era...
near the close of his Third Missionary Journey, as recorded in Acts of the Apostles
Acts of the Apostles
The Acts of the Apostles , usually referred to simply as Acts, is the fifth book of the New Testament; Acts outlines the history of the Apostolic Age...
(Acts 20:15–38). It is believed that Paul stopped by the Great Harbour Monument and sat on its steps. He may have met the Ephesian elders there and then bid them farewell on the nearby beach. Miletus is also the city where Paul left Trophimus
Trophimus
Trophimus, meaning a foster-child, was an Ephesian who accompanied Paul during a part of his third missionary journey . He was with Paul in Jerusalem, and the Jews, supposing that the apostle had brought him with him into the temple, raised a tumult which resulted in Paul’s imprisonment....
, one of his travelling companions, to recover from an illness (2 Timothy 4:20). Because this cannot be the same visit as Acts 20 (in which Trophimus accompanied Paul all the way to Jerusalem, according to Acts 21:29), Paul must have made at least one additional visit to Miletus, perhaps as late as 65 or 66 CE. Paul's previous successful three-year ministry in nearby Ephesus
Ephesus
Ephesus was an ancient Greek city, and later a major Roman city, on the west coast of Asia Minor, near present-day Selçuk, Izmir Province, Turkey. It was one of the twelve cities of the Ionian League during the Classical Greek era...
resulted in the evangelization of the entire province of Asia (see Acts 19:10, 20; 1 Corinthians 16:9). It is safe to assume that at least by the time of the apostle's second visit to Miletus, a fledgling Christian community was established in Miletus.
Byzantine period
During the ByzantineByzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
age Miletus became a residence for archbishops. The small Byzantine castle called Castro Palation located on the hill beside the city, was built at this time. From Miletus came the famous merchant family of Mauros, one of their members became judge of the Hippodrome of Constantinople
Hippodrome of Constantinople
The Hippodrome of Constantinople was a circus that was the sporting and social centre of Constantinople, capital of the Byzantine Empire. Today it is a square named Sultanahmet Meydanı in the Turkish city of Istanbul, with only a few fragments of the original structure surviving...
. Miletus was headed by a curator
Curator bonis
A Curator bonis is a person appointed by a court to manage the finances, property, or estate of another person unable to do so because of mental or physical incapacity....
.
Turkish rule
Seljuk Turks conquered the city in the 14th century AD and used Miletus as a port to trade with VeniceVenice
Venice is a city in northern Italy which is renowned for the beauty of its setting, its architecture and its artworks. It is the capital of the Veneto region...
.
Finally, Ottomans utilized the city as a harbour during their rule in Anatolia
Anatolia
Anatolia is a geographic and historical term denoting the westernmost protrusion of Asia, comprising the majority of the Republic of Turkey...
. As the harbour became silted up, the city was abandoned. Today the ruins of city lie some 10 kilometres from the sea.
Archaeological excavations
The first excavations in Miletus were conducted by the French archaeologist Olivier Rayet in 1873, followed by the German archaeologist Theodor WiegandTheodor Wiegand
Theodor Wiegand was one of the most famous German archaeologists.Wiegand was born in Bendorf, Rhenish Prussia. He studied at Munich, Berlin, and Freiburg. In 1894 he worked under Wilhelm Dörpfeld at the excavation of the Athenian Acropolis...
.
between 1899 and 1931.
Excavations, however, were interrupted several times by wars and various other events.
Carl Weickart excavated for a short season in 1938 and again between
1955 and 1957.
He was followed by Gerhard Kleiner and then by Wolfgang Muller-Wiener.
Today, excavations are organized by the Ruhr University
Ruhr University
Ruhr University Bochum , located on the southern hills of central Ruhr area Bochum, was founded in 1962 as the first new public university in Germany since World War II...
of Bochum
Bochum
Bochum is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, western Germany. It is located in the Ruhr area and is surrounded by the cities of Essen, Gelsenkirchen, Herne, Castrop-Rauxel, Dortmund, Witten and Hattingen.-History:...
, Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
.
One remarkable artifact recovered from the city during the first excavations of the 19th century, the Market Gate of Miletus
Market Gate of Miletus
The Market Gate of Miletus dates from about 120 AD. It is almost 17m high and 29m wide. The well preserved elements of the gate, which were destroyed by an earthquake around the year 1100, were dug up by Theodor Wiegand during the museum's excavations . It is currently located in the Pergamon...
, was transported piece by piece to Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
and reassembled. It is currently exhibited at the Pergamon museum
Pergamon Museum
The Pergamon Museum is situated on the Museum Island in Berlin. The site was designed by Alfred Messel and Ludwig Hoffmann and was constructed in twenty years, from 1910 to 1930. The Pergamon houses original-sized, reconstructed monumental buildings such as the Pergamon Altar and the Market Gate...
in Berlin
Berlin
Berlin is the capital city of Germany and is one of the 16 states of Germany. With a population of 3.45 million people, Berlin is Germany's largest city. It is the second most populous city proper and the seventh most populous urban area in the European Union...
. The main collection of artifacts resides in the Miletus Museum in Didim
Didim
Didim, home of the antique city of Didyma with its ruined Temple of Apollo, is a small town, popular seaside holiday resort and district of Aydın Province on the Aegean coast of western Turkey, from the city of Aydın.-Geography:...
, Aydın
Aydin
Aydın is a city in and the seat of Aydın Province in Turkey's Aegean Region. The city is located at the heart of the lower valley of Büyük Menderes River at a commanding position for the region extending from the uplands of the valley down to the seacoast...
, serving since 1973.
Colonies of Miletus
Miletus became known for the great number of colonies she founded. She was considered the greater Greek metropolis and she has founded more colonies than any other Greek city.Pliny the Elder
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus , better known as Pliny the Elder, was a Roman author, naturalist, and natural philosopher, as well as naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and personal friend of the emperor Vespasian...
mentions 90 colonies founded by Miletus in his Natural History (5.31), among them:
- Amisos
- ApoloniaSozopolSozopol is an ancient seaside town located 35 km south of Burgas on the southern Bulgarian Black Sea Coast. Today it is one of the major seaside resorts in the country, known for the Apollonia art and film festival that is named after one of the town's ancient names.The busiest times of the year...
- Dioscurias
- HistriaHistria (Sinoe)Ancient Histria or Istros , was a Greek colony or polis on the Black Sea coast, established by Milesian settlers to trade with the native Getae. It became the first Greek town on the present day Romanian territory. Scymnus of Chios , the Greek geographer and poet, dated it to 630 BC...
- OdessosVarnaVarna is the largest city and seaside resort on the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast and third-largest in Bulgaria after Sofia and Plovdiv, with a population of 334,870 inhabitants according to Census 2011...
- OlbiaOlbia, UkrainePontic Olbia or Olvia is the site of a colony founded by the Milesians on the shores of the Southern Bug estuary , opposite Berezan Island...
- PanticapaeumPanticapaeumPanticapaeum , present-day Kerch: an important city and port in Taurica , situated on a hill Panticapaeum (Greek: Παντικάπαιον, Pantikápaion), present-day Kerch: an important city and port in Taurica (Tauric Chersonese), situated on a hill Panticapaeum (Greek: Παντικάπαιον, Pantikápaion),...
- Phanagoria
- PhasisPhasis (town)Phasis was an ancient and early medieval city on the eastern Black Sea coast, founded in the 7th/6th century BC as a colony of the Milesian Greeks at the mouth of the eponymous river in Colchis, near the modern-day port city of Poti, Georgia.-Etymology:...
- Pityus
- SinopeSinop, TurkeySinop is a city with a population of 36,734 on İnce Burun , by its Cape Sinop which is situated on the most northern edge of the Turkish side of Black Sea coast, in the ancient region of Paphlagonia, in modern-day northern Turkey, historically known as Sinope...
- TanaisTanaisTanais is the ancient name for the River Don in Russia. Strabo regarded it as the boundary between Europe and Asia.In antiquity, Tanais was also the name of a city in the Don river delta that reaches into the northeasternmost part of the Sea of Azov, which the Greeks called Lake Maeotis...
- Theodosia
- Tomis
- TyrasTyrasTyras , was an ancient Greek city founded as colony of Miletus, probably about 600 BC, situated some 10 m from the mouth of the Tyras River...
- Trapezunt
Notable people
- ThalesThalesThales of Miletus was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher from Miletus in Asia Minor, and one of the Seven Sages of Greece. Many, most notably Aristotle, regard him as the first philosopher in the Greek tradition...
(c. 624 BC–c. 546 BC) Pre-SocraticPre-Socratic philosophyPre-Socratic philosophy is Greek philosophy before Socrates . In Classical antiquity, the Presocratic philosophers were called physiologoi...
philosopher - AnaximanderAnaximanderAnaximander was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher who lived in Miletus, a city of Ionia; Milet in modern Turkey. He belonged to the Milesian school and learned the teachings of his master Thales...
(c. 610 BC–c. 546 BC) Pre-Socratic philosopher - AnaximenesAnaximenes of MiletusAnaximenes of Miletus was an Archaic Greek Pre-Socratic philosopher active in the latter half of the 6th century BC. One of the three Milesian philosophers, he is identified as a younger friend or student of Anaximander. Anaximenes, like others in his school of thought, practiced material monism...
(c. 585 BC–c. 525 BC) Pre-Socratic philosopher - Hippodamus of MiletusHippodamus of MiletusHippodamus of Miletos was an ancient Greek architect, urban planner, physician, mathematician, meteorologist and philosopher and is considered to be the “father” of urban planning, the namesake of Hippodamian plan of city layouts...
(c. 498—408 BC) urban planner - AspasiaAspasiaAspasia was a Milesian woman who was famous for her involvement with the Athenian statesman Pericles. Very little is known about the details of her life. She spent most of her adult life in Athens, and she may have influenced Pericles and Athenian politics...
(c. 470–400 BC) courtesan , and mistress of PericlesPericlesPericles was a prominent and influential statesman, orator, and general of Athens during the city's Golden Age—specifically, the time between the Persian and Peloponnesian wars...
, was born here - Aristides of Miletus, writer
- Hecataeus of Miletus, historian
- HesychiusHesychius of MiletusHesychius of Miletus, Greek chronicler and biographer, surnamed Illustrius, son of an advocate, flourished at Constantinople in the 6th century AD during the reign of Justinian.According to Photius he was the author of three important works:...
(6th century) Greek chronicler and biographer - IsidoreIsidore of MiletusIsidore of Miletus was one of the two main Byzantine architects that Emperor Justinian I commissioned to design the church of Hagia Sophia in Constantinople from 532-537A.D.-Summary:...
(4th–5th century) Greek architect - AristagorasAristagorasAristagoras was the leader of Miletus in the late 6th century BC and early 5th century BC.- Background :Aristagoras served as deputy governor of Miletus, a polis on the western coast of Anatolia around 500 BC. He was the son of Molpagoras, and son-in-law of Histiaeus, whom the Persians had set up...
(5th–6th century) Tyrant of Miletus - LeucippusLeucippusLeucippus or Leukippos was one of the earliest Greeks to develop the theory of atomism — the idea that everything is composed entirely of various imperishable, indivisible elements called atoms — which was elaborated in greater detail by his pupil and successor, Democritus...
(first half of 5th century BC) Philosopher and originator of Atomism (his association with Miletus is traditional, but disputed)
External links
- Miletus Pictures
- Ausgrabungen in Milet official site of the excavations in Miletus by Ruhr-Universität Bochum
- Ancient Coins of Miletus
- Livius Picture Archive: Miletus
- A Small Desription About Miletus
- MA in Black Sea Cultural Studies. International Hellenic University-School of Humanities.
- The Theatre at Miletus, The Ancient Theatre Archive, Theatre specifications and virtual reality tour of theatre
- Virtual Tour at Ancient Miletus

