Migraine
Encyclopedia
Migraine is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by moderate to severe headache
s, and nausea
. It is about three times more common in women than in men.
The typical migraine headache is unilateral (affecting one half of the head) and pulsating in nature and lasting from four to 72 hours; symptoms include nausea
, vomiting
, photophobia
(increased sensitivity to light) and phonophobia
(increased sensitivity to sound); the symptoms are generally aggravated by routine activity. Approximately one-third of people who suffer from migraine headaches perceive an aura
—transient visual, sensory, language, or motor disturbances signaling the migraine will soon occur.
Initial treatment is with analgesics for the headache, an antiemetic
for the nausea, and the avoidance of triggers. The cause of migraine headache is unknown
; the most supported theory is that it is related to hyperexcitability of the cerebral cortex
and/or abnormal control of pain neurons in the trigeminal nucleus of the brainstem.
Studies of twins indicate a 60- to 65-percent genetic influence upon their propensity to develop migraine headaches. Moreover, fluctuating hormone levels indicate a migraine relation: 75 percent of adult patients are women, although migraine affects approximately equal numbers of prepubescent boys and girls. Propensity to migraine headache sometimes disappears during pregnancy, but in some women, migraines may become more frequent.
(IHS) offers guidelines for the classification and diagnosis of migraine headaches, in a document called "The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 2nd edition" (ICHD-2). These guidelines constitute arbitrary definitions, and are not supported by scientific data.
According to ICHD-2, there are seven subclasses of migraines (some of which include further subdivisions):
associated with autonomic
symptoms. An aura
only occurs in a small percentage of people. The severity of the pain, duration of the headache, and frequency of attacks is variable. A migraine lasting 72 hours is termed status migrainosus
and can be treated with intravenous prochlorperazine
.
The four possible phases to a migraine attack are listed below — not all the phases are necessarily experienced. Additionally, the phases experienced and the symptoms experienced during them can vary from one migraine attack to another in the same person:
or euphoria
, fatigue
, yawning, excessive sleepiness, craving for certain food (e.g. chocolate
), stiff muscles (especially in the neck), dizziness, hot ears, constipation or diarrhea, increased or decreased urination, and other visceral symptoms. These symptoms usually precede the headache phase of the migraine attack by several hours or days, and experience teaches the patient or observant family how to detect a migraine attack is near.
Visual aura
is the most common of the neurological events, and can occur without any headache. There is a disturbance of vision consisting often of unformed flashes of white and/or black or rarely of multicolored lights (photopsia
) or formations of dazzling zigzag lines (scintillating scotoma
, often arranged like the battlements of a castle, hence the alternative terms "fortification spectra" or "teichopsia"). Some patients complain of blurred or shimmering or cloudy vision, as though they were looking at an area above a heated surface, looking through thick or smoked glass
, or, in some cases, tunnel vision
and hemianopsia
.
The somatosensory aura of migraine may consist of digitolingual or cheiro-oral paresthesia
s, a feeling of pins-and-needles experienced in the hand and arm, as well as in the nose-mouth area on the same side. The paresthesia may migrate up the arm and then extend to involve the face, lips and tongue.
Other symptoms of the aura phase can include auditory, gustatory or olfactory hallucinations, temporary dysphasia, vertigo
, tingling or numbness of the face and extremities, and hypersensitivity to touch.
Oliver Sacks
's book Migraine describes "migrainous deliria" as a result of such intense migraine aura that it is indistinguishable from "free-wheeling states of hallucinosis, illusion, or dreaming."
The pain of migraine is invariably accompanied by other features. Nausea
occurs in almost 90 percent of patients, and vomiting occurs in about one third of patients. Many patients experience sensory hyperexcitability manifested by photophobia
, phonophobia, and osmophobia
and seek a dark and quiet room. Blurred vision, delirium, nasal stuffiness, diarrhea, tinnitus
, polyuria
, pallor
, or sweating may be noted during the headache phase. There may be localized edema
of the scalp or face, scalp tenderness, prominence of a vein or artery in the temple, or stiffness and tenderness of the neck. Impairment of concentration and mood are common. The extremities tend to feel cold and moist. Vertigo
may be experienced; a variation of the typical migraine, called vestibular migraine, has also been described. Lightheadedness, rather than true vertigo, and a feeling of faintness may occur.
."
(ptosis-drooping lid, miosis-smaller pupil) may occur during a migraine attack and disappear afterwards.
on migraine. A 2005 literature review
on dietary triggers found the available scientific studies, mostly relying on subjective assessments, were not rigorous enough to prove or disprove any particular triggers. This is in line with other reviews. A 2009 review of potential triggers in the indoor and outdoor environment concluded the overall evidence was of poor quality, but nevertheless suggested migraineurs take some preventative measures related to indoor air quality and lighting. While monosodium glutamate
(MSG) is frequently reported as a dietary trigger evidence does not consistently support this. Migraines are more likely to occur around menstruation
. Other hormonal influences, such as menarche
, oral contraceptive
use, pregnancy
, perimenopause, and menopause
, also play a role.
, which is associated with the aura of migraine, has been theorized as a possible cause of migraines. In cortical spreading depression
, neurological activity
is initially activated, then depressed over an area of the cerebral cortex
. This situation has been suggested to result in the release of inflammatory
mediators leading to irritation of cranial nerve roots, most particularly the trigeminal nerve
, which conveys the sensory information for the face and much of the head. This theory is, however, speculative, without any supporting evidence, and there are indeed cogent arguments against it. First, only about one third of migraineurs experience an aura, and those who do not experience aura do not have cortical spreading depression. Second, many migraineurs have a prodrome (see above), which occurs up to three days before the aura.
, in the back of the brain, as arteries spasm. The reduced flow of blood from the occipital lobe triggers the aura some individuals who have migraines experience, because the visual cortex is in the occipital area.
When the constriction of blood vessels in the brain stops and the aura subsides, the blood vessels of the scalp dilate. The walls of these blood vessels become permeable and some fluid leaks out. This leakage is recognized by pain receptors in the blood vessels of surrounding tissue. In response, the body supplies the area with chemicals which cause inflammation. With each heart beat, blood passes through this sensitive area, causing a throb of pain.
Although cerebral vasodilation can trigger migraine attacks, blood vessel diameters return to normal more than an hour before the migraine headaches occur.
is a type of neurotransmitter, or "communication chemical" which passes messages between nerve cells. It helps to control mood, pain sensation, sexual behaviour and sleep, as well as dilation and constriction of the blood vessels, among other things. Low serotonin
levels in the brain may lead to a process of constriction and dilation of the blood vessels which trigger a migraine. Serotonergic agonists, such as triptan
s, LSD
or psilocin
, activate serotonin receptors to stop a migraine attack.
-based receptor has been linked to the association between light sensitivity and migraine pain, but this is currently speculation.
become irritated, a migraine begins. In response to the irritation, the body releases chemicals which cause inflammation of the blood vessels. These chemicals cause further irritation of the nerves and blood vessels and results in pain. Substance P
is one of the substances released with first irritation. Pain then increases because substance P aids in sending pain signals to the brain.
, and in particular its superficial temporal and occipital branches. Dilatation of the arteries in the brain and dura mater previously was thought to be the origin of the vascular pain, but these vessels have been shown to not dilate during migraine. Because these arteries are relatively superficial, it is easy to diagnose whether they are the source of the pain. If they are, then they are also accessible to a form of migraine surgery
being promoted, largely to the efforts of Dr Elliot Shevel
, a South African surgeon, who has reported excellent success using the procedure.
Pericranial (jaw and neck) muscle tenderness is a common finding in migraine. Muscle tenderness has been shown to be present in 100% of migraine attacks, making muscle tenderness the single most common finding in migraine. Tender muscle trigger points can be at least part of the cause, and perpetuate most kinds of headaches.
, can be made according to the following criteria, the "5, 4, 3, 2, 1 criteria":
The mnemonic POUNDing (Pulsating, duration of 4–72 hOurs, Unilateral, Nausea, Disabling) can help diagnose migraine. If four of the five criteria are met, then the positive likelihood ratio
for diagnosing migraine is 24.
The presence of either disability, nausea or sensitivity can diagnose migraine with:
Migraine should be differentiated
from other causes of headaches, such as cluster headaches. These are extremely painful, unilateral headaches of a piercing quality. The duration of the common attack is 15 minutes to three hours. Onset of an attack is rapid, and most often without the preliminary signs characteristic of a migraine.
Medical imaging
of the head and neck may be used to rule out secondary causes of headaches.
The goals of preventive therapy are to reduce the frequency, painfulness, and/or duration of migraines, and to increase the effectiveness of abortive therapy. Another reason to pursue these goals is to avoid medication overuse headache (MOH), otherwise known as rebound headache
. This is a common problem among migraineurs, and can result in chronic daily headache.
Many of the preventive treatments are quite effective. Even with a placebo
, one-quarter of patients find their migraine frequency is reduced by half or more, and actual treatments often far exceed this figure.
Many medicines are available to prevent or reduce frequency, duration and severity of migraine attacks. They may also prevent complications of migraine. Beta blockers, such as Propranolol, atenolol, and metoprolol
; calcium channel blockers, such as amlodipine
, flunarizine
and verapamil
; the anticonvulsants sodium valproate
, divalproex, gabapentin
and topiramate
; and tricyclic antidepressants are some of the commonly used drugs.
Tricyclic antidepressants have been found to be more effective than SSRIs. Tricyclic antidepressants have been long established as efficacious prophylactic treatments. These drugs, however, may give rise to undesirable side effects, such as insomnia, sedation or sexual dysfunction. There is no consistent evidence that SSRI antidepressants are effective for migraine prophylaxis. While amitryptiline (Elavil) is the only tricyclic to have received FDA approval for migraine treatment, other tricyclic antidepressants are believed to act similarly and are widely prescribed, often to find one with a profile of side effects that is acceptable to the patient. In addition to tricyclics a, the antidepressant nefazodone
may also be beneficial in the prophylaxis of migraines due to its antagonistic effects on the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors It has a more favorable side effect profile than amitriptyline
, a tricyclic antidepressant commonly used for migraine prophylaxis. Antidepressants offer advantages for treating migraine patients with comorbid depression. SSRIs are not approved by the FDA for treatment of migraines, but have been found to be effective by some practitioners.
There is some evidence that low-dose asprin has benefit for reducing the occurrence of migraines in susceptible individuals.
is a field that shows a great deal of promise, particularly in those who suffer more frequent attacks, and in those who have not had an adequate response to prophylactic medications. Patients often still experience a poor quality of life despite an aggressive regimen of pharmacotherapy. For these reasons, surgical solutions to migraines have been developed, which have excellent results. A major advantage of migraine surgery is that, with the correct diagnostic techniques, a definite diagnosis can be made before the surgery is undertaken. Once a positive diagnosis has been made, the results of surgery are outstanding and provide permanent pain relief, as well as relief from the associated symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, light sensitivity, and sound sensitivity. Surgical cauterization of the superficial blood vessels of the scalp (the terminal branches of the external carotid artery) is only carried out if it has been established with certainty that these vessels are indeed the source of pain. It is a safe and relatively atraumatic procedure which can be performed in a day facility. The value of arterial sugery for migraine treatment is gaining recognition as a result of the efforts of a South African surgeon, Dr Elliot Shevel
, who has produced a number of papers on the subject.
The removal of muscles or nerves in areas known as "trigger sites" provides good results, but only in patients who respond well to Botox injections in specific areas.
There is also evidence that the correction of a congenital heart defect
, patent foramen ovale (PFO), reduces migraine frequency and severity. Recent studies have advised caution, though, in relation to PFO closure for migraines, as insufficient evidence exists to justify this dangerous procedure.
helps patient to be conscious of some physiologic parameters to control them and try to relax. This method is considered to be efficient for migraine and tension-type headache
treatment. A recent clinical trial has demonstrated that simple use of biofeedback as a relaxation technique has similar efficacy for migraine treatment to sophisticated sessions in clinics. Neurostimulation
used initially implantable neurostimulators similar to pacemakers for the treatment of intractable chronic migraines with encouraging good results. But the needed surgery with implantable neurostimulators is limiting the indication to sever cases. Recently, a new technique of external trigeminal (V1) or occipital nerve
(CII) neurostimulation (Cefaly
) could offer a larger use for migraine treatment or prevention.
A systematic review stated that chiropractic manipulation, physiotherapy, massage and relaxation might be as effective as propranolol or topiramate
in the prevention of migraine headaches; however, the research had some problems with methodology.
"The therapeutic potential of magnesium
, coenzyme Q(10), riboflavin
, and vitamin B(12)
can be cautiously inferred from some published open clinical trials." A review has concluded that "[c]urrent clinical data support the use of fever-few
, butterbur
, magnesium, and riboflavin
in migraine prophylaxis."
analgesics.
are effective for both pain and nausea in up to 75% of people. The different forms available include oral, injection, nasal spray
, and oral dissolving tablets. Most side effects are mild, such as flushing; however, rare cases of myocardial ischemia
have occurred. They are not addictive, but may cause medication overuse headaches if used more than 10 days per month.
are older medications still prescribed for migraines, the latter in nasal spray and injectable forms. They were the primary drugs available to abort a migraine prior to the triptans, and are much less expensive than triptans.
, when added to standard treatment of a migraine attack, is associated with a 26% decrease in headache recurrence in the following 72 hours.
s by mouth may help relieve symptoms of nausea and help prevent vomiting, which can diminish the effectiveness of orally taken analgesics. In addition, some antiemetics, such as metoclopramide
, are prokinetics and help gastric emptying, which is often impaired during episodes of migraine. In the UK, three combination antiemetic and analgesic preparations are available: MigraMax (aspirin
with metoclopramide), (paracetamol/codeine for analgesia, with buclizine
as the antiemetic) and paracetamol/metoclopramide
(Paramax in UK). The earlier these drugs are taken in the attack, the better their effect.
may be increased two- to three-fold in migraine sufferers. Young adult sufferers and women using hormonal contraception
appear to be at particular risk. The mechanism of any association is unclear, but chronic abnormalities of cerebral blood vessel
tone may be involved. Women who experience auras have been found to have twice the risk of strokes and heart attacks over nonaura migraine sufferers and women who do not have migraines. (Note: Women who experience auras and also take oral contraceptives have an even higher risk of stroke). Migraine sufferers seem to be at risk for both thrombotic and hemorrhagic stroke as well as transient ischemic attack
s. Death from cardiovascular causes was higher in people with migraine with aura in a Women's Health Initiative
study, but more research is needed to confirm this.
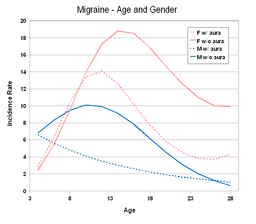 Worldwide, migraines affect more than 10% of people. In the United States, about 6% of men and 18% of women get a migraine in a given year, with a lifetime risk of about 18% and 43% respectively. In Europe, migraines affect 12–28% of people at some point in their lives. Based on the results of a number of studies, one-year prevalence of migraine ranges from 6–15% in adult men and from 14–35% in adult women. These figures vary substantially with age: approximately 4–5% of children aged under 12 suffer from migraine, with little apparent difference between boys and girls. A rapid growth in incidence amongst girls occurs after puberty, which continues throughout early adult life. By early middle age, around 25% of women experience a migraine at least once a year, compared with fewer than 10% of men. After menopause, attacks in women tend to decline dramatically, so that in the over 70s, approximately equal numbers of males and females are sufferers, with prevalence returning to around 5%.
Worldwide, migraines affect more than 10% of people. In the United States, about 6% of men and 18% of women get a migraine in a given year, with a lifetime risk of about 18% and 43% respectively. In Europe, migraines affect 12–28% of people at some point in their lives. Based on the results of a number of studies, one-year prevalence of migraine ranges from 6–15% in adult men and from 14–35% in adult women. These figures vary substantially with age: approximately 4–5% of children aged under 12 suffer from migraine, with little apparent difference between boys and girls. A rapid growth in incidence amongst girls occurs after puberty, which continues throughout early adult life. By early middle age, around 25% of women experience a migraine at least once a year, compared with fewer than 10% of men. After menopause, attacks in women tend to decline dramatically, so that in the over 70s, approximately equal numbers of males and females are sufferers, with prevalence returning to around 5%.
At all ages, migraine without aura is more common than migraine with aura, with a ratio of between 1.5 and 2.0:1. Incidence figures show the excess of migraine seen in women of reproductive age is mainly due to migraine without aura. Thus, in prepubertal and postmenopausal populations, migraine with aura is somewhat more common than amongst 15–50 year olds.
There is a strong relationship between age, sex and type of migraine.
Studies in Asia and South America suggest the rates there are relatively low, but they do not fall outside the range of values seen in European and North American studies.
The incidence of migraine is related to the incidence of epilepsy
in families, with migraine twice as prevalent in family members of epilepsy sufferers, and more common in epilepsy sufferers themselves.
 Trepanation
Trepanation
, the deliberate and (usually) nonfatal drilling of holes into a skull, was practiced 9,000 years ago and earlier. Some scholars have (controversially) speculated this drastic procedure might have been a migraine treatment, based on cave paintings and on the fact that trepanation was a historical migraine treatment in 17th-century Europe. An early written description consistent with migraines is contained in the Ebers papyrus
, written around 1200 BC in ancient Egypt.
In 400 BC, Hippocrates
described the visual aura that can precede the migraine headache, and the relief which can occur through vomiting. Aretaeus
of Cappadocia
is credited as the "discoverer" of migraines because of his second-century description of the symptoms of a unilateral headache associated with vomiting, with headache-free intervals in between attacks.
Galenus of Pergamon used the term "hemicrania" (half-head), from which the word "migraine" was derived. He thought there was a connection between the stomach
and the brain because of the nausea and vomiting that often accompany an attack. For relief of migraine, Andalusian-born physician Abulcasis, also known as Abu El Qasim, suggested application of a hot iron to the head or insertion of garlic into an incision made in the temple.
In the Middle Ages
. migraine was recognized as a discrete medical disorder. Followers of Galenus explained migraine as being caused by aggressive yellow bile.
Ebn Sina (Avicenna
) described migraine in his textbook "El Qanoon fel teb" as "... small movements, drinking and eating, and sounds provoke the pain... the patient cannot tolerate the sound of speaking and light. He would like to rest in darkness alone."
Abu Bakr Mohamed Ibn Zakariya Râzi noted the association of headache with different events in the lives of women, "...And such a headache may be observed after delivery and abortion
or during menopause
and dysmenorrhea
."
In Bibliotheca Anatomica, Medic, Chirurgica, published in London in 1712, five major types of headaches are described, including the "Megrim", recognizable as classic migraine. The term "classic migraine" is no longer used, and has been replaced by the term "migraine with aura" Graham and Wolff
(1938) published their paper advocating ergotamine tartrate for relieving migraine. Later in the 20th century, Harold Wolff (1950) developed the experimental approach to the study of headache and elaborated the vascular theory of migraine, which has come under attack as the pendulum again swings to the neurogenic theory. Recently, there has been renewed interest in Wolff's vascular theory of migraine led by Elliot Shevel
, a South African headache specialist, who has published a number of articles providing compelling evidence that Wolff was correct.
It has been estimated to be the most costly neurological disorder in the European Community, costing more than €27 billion per year.
new drug, Telcagepant, intended to relieve pain without causing vasoconstriction
(narrowing of blood vessels) as current medications such as triptans do, was pulled from the market after clinical trials showed liver function abnormalities in some study subjects. ^ Merck & Co.: Memo to all US study locations involved in protocol MK0974-049
Recently, calcitonin gene related peptides (CGRPs) have been found to play a role in the pathogenesis of the pain associated with migraine, as triptans also decrease its release and action. CGRP receptor antagonists, such as olcegepant and telcagepant
, are being investigated both in vitro and in clinical studies for the treatment of migraine.
In 2010, scientists identified a genetic defect linked to migraines which could provide a target for new drug treatments.
Headache
A headache or cephalalgia is pain anywhere in the region of the head or neck. It can be a symptom of a number of different conditions of the head and neck. The brain tissue itself is not sensitive to pain because it lacks pain receptors. Rather, the pain is caused by disturbance of the...
s, and nausea
Nausea
Nausea , is a sensation of unease and discomfort in the upper stomach with an involuntary urge to vomit. It often, but not always, precedes vomiting...
. It is about three times more common in women than in men.
The typical migraine headache is unilateral (affecting one half of the head) and pulsating in nature and lasting from four to 72 hours; symptoms include nausea
Nausea
Nausea , is a sensation of unease and discomfort in the upper stomach with an involuntary urge to vomit. It often, but not always, precedes vomiting...
, vomiting
Vomiting
Vomiting is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose...
, photophobia
Photophobia
Photophobia is a symptom of abnormal intolerance to visual perception of light. As a medical symptom photophobia is not a morbid fear or phobia, but an experience of discomfort or pain to the eyes due to light exposure or by presence of actual physical photosensitivity of the eyes, though the term...
(increased sensitivity to light) and phonophobia
Hyperacusis
Hyperacusis is a health condition characterized by an over-sensitivity to certain frequency ranges of sound...
(increased sensitivity to sound); the symptoms are generally aggravated by routine activity. Approximately one-third of people who suffer from migraine headaches perceive an aura
Aura (symptom)
An aura is a perceptual disturbance experienced by some migraine sufferers before a migraine headache, and the telltale sensation experienced by some people with epilepsy before a seizure. It often manifests as the perception of a strange light, an unpleasant smell or confusing thoughts or...
—transient visual, sensory, language, or motor disturbances signaling the migraine will soon occur.
Initial treatment is with analgesics for the headache, an antiemetic
Antiemetic
An antiemetic is a drug that is effective against vomiting and nausea. Antiemetics are typically used to treat motion sickness and the side effects of opioid analgesics, general anaesthetics, and chemotherapy directed against cancer....
for the nausea, and the avoidance of triggers. The cause of migraine headache is unknown
Idiopathic
Idiopathic is an adjective used primarily in medicine meaning arising spontaneously or from an obscure or unknown cause. From Greek ἴδιος, idios + πάθος, pathos , it means approximately "a disease of its own kind". It is technically a term from nosology, the classification of disease...
; the most supported theory is that it is related to hyperexcitability of the cerebral cortex
Cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex is a sheet of neural tissue that is outermost to the cerebrum of the mammalian brain. It plays a key role in memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language, and consciousness. It is constituted of up to six horizontal layers, each of which has a different...
and/or abnormal control of pain neurons in the trigeminal nucleus of the brainstem.
Studies of twins indicate a 60- to 65-percent genetic influence upon their propensity to develop migraine headaches. Moreover, fluctuating hormone levels indicate a migraine relation: 75 percent of adult patients are women, although migraine affects approximately equal numbers of prepubescent boys and girls. Propensity to migraine headache sometimes disappears during pregnancy, but in some women, migraines may become more frequent.
Classification
The International Headache SocietyInternational Headache Society
The International Headache Society is a charity organization founded in 1981 for people from all professions that are working to treat headache disorders....
(IHS) offers guidelines for the classification and diagnosis of migraine headaches, in a document called "The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 2nd edition" (ICHD-2). These guidelines constitute arbitrary definitions, and are not supported by scientific data.
According to ICHD-2, there are seven subclasses of migraines (some of which include further subdivisions):
- Migraine without aura, or common migraine, involves migraine headaches that are not accompanied by an aura (visual disturbance, see below).
- Migraine with aura usually involves migraine headaches accompanied by an aura. Less commonly, an aura can occur without a headache, or with a nonmigraine headache. Two other varieties are familial hemiplegic migraineFamilial hemiplegic migraineFamilial hemiplegic migraine is an autosomal dominant classical migraine subtype that typically includes hemiparesis during the aura phase. It can be accompanied by other symptoms, such as ataxia, coma and epileptic seizures...
and sporadic hemiplegic migraine, in which a patient has migraines with aura and with accompanying motor weakness. If a close relative has had the same condition, it is called "familial", otherwise it is called "sporadic". Another variety is basilar-type migraine, where a headache and aura are accompanied by difficulty speakingDysarthriaDysarthria is a motor speech disorder resulting from neurological injury of the motor component of the motor-speech system and is characterized by poor articulation of phonemes...
, vertigoVertigo (medical)Vertigo is a type of dizziness, where there is a feeling of motion when one is stationary. The symptoms are due to a dysfunction of the vestibular system in the inner ear...
, ringing in earsTinnitusTinnitus |ringing]]") is the perception of sound within the human ear in the absence of corresponding external sound.Tinnitus is not a disease, but a symptom that can result from a wide range of underlying causes: abnormally loud sounds in the ear canal for even the briefest period , ear...
, or a number of other brainstem-related symptoms, but not motor weakness. - Childhood periodic syndromes that are commonly precursors of migraine include cyclical vomiting (occasional intense periods of vomiting), abdominal migraine (abdominal pain, usually accompanied by nausea), and benign paroxysmal vertigo of childhood (occasional attacks of vertigo).
- Retinal migraineRetinal migraineRetinal migraine is a retinal disease often accompanied by migraine headache and typically affects only one eye...
involves migraine headaches accompanied by visual disturbances or even temporary blindness in one eye. - Complications of migraine describe migraine headaches and/or auras that are unusually long or unusually frequent, or associated with a seizure or brain lesion.
- Probable migraine describes conditions that have some characteristics of migraines, but where there is not enough evidence to diagnose it as a migraine with certainty (in the presence of concurrent medication overuse).
- Chronic migraine, according to the American Headache Society and the international headache society, is a "complication of migraine"s and is a headache fulfilling the diagnostic criteria for "migraine headache", which occurs for a greater time interval. Specifically, greater or equal to 15 days/month for greater than 3 months.
Signs and symptoms
Migraines typically present with recurrent severe headacheHeadache
A headache or cephalalgia is pain anywhere in the region of the head or neck. It can be a symptom of a number of different conditions of the head and neck. The brain tissue itself is not sensitive to pain because it lacks pain receptors. Rather, the pain is caused by disturbance of the...
associated with autonomic
Autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils,...
symptoms. An aura
Aura (symptom)
An aura is a perceptual disturbance experienced by some migraine sufferers before a migraine headache, and the telltale sensation experienced by some people with epilepsy before a seizure. It often manifests as the perception of a strange light, an unpleasant smell or confusing thoughts or...
only occurs in a small percentage of people. The severity of the pain, duration of the headache, and frequency of attacks is variable. A migraine lasting 72 hours is termed status migrainosus
Status migrainosus
Status migrainosus is a debilitating migraine headache lasting for more than 72 hours....
and can be treated with intravenous prochlorperazine
Prochlorperazine
Prochlorperazine is a dopamine receptor antagonist that belongs to the phenothiazine class of antipsychotic agents that are used for the antiemetic treatment of nausea and vertigo. It is also a highly-potent typical antipsychotic, 10-20x more potent than chlorpromazine...
.
The four possible phases to a migraine attack are listed below — not all the phases are necessarily experienced. Additionally, the phases experienced and the symptoms experienced during them can vary from one migraine attack to another in the same person:
- The prodromeProdromeIn medicine, a prodrome is an early symptom that might indicate the start of a disease before specific symptoms occur. It is derived from the Greek word prodromos or precursor...
, which occurs hours or days before the headache - The aura, which immediately precedes the headache
- The painPainPain is an unpleasant sensation often caused by intense or damaging stimuli such as stubbing a toe, burning a finger, putting iodine on a cut, and bumping the "funny bone."...
phase, also known as headache phase - The postdrome
Prodrome
Prodromal symptoms occur in 40–60% of those with migraines. This phase may consist of altered mood, irritability, depressionClinical depression
Major depressive disorder is a mental disorder characterized by an all-encompassing low mood accompanied by low self-esteem, and by loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities...
or euphoria
Euphoria (emotion)
Euphoria is medically recognized as a mental and emotional condition in which a person experiences intense feelings of well-being, elation, happiness, ecstasy, excitement and joy...
, fatigue
Fatigue (physical)
Fatigue is a state of awareness describing a range of afflictions, usually associated with physical and/or mental weakness, though varying from a general state of lethargy to a specific work-induced burning sensation within one's muscles...
, yawning, excessive sleepiness, craving for certain food (e.g. chocolate
Chocolate
Chocolate is a raw or processed food produced from the seed of the tropical Theobroma cacao tree. Cacao has been cultivated for at least three millennia in Mexico, Central and South America. Its earliest documented use is around 1100 BC...
), stiff muscles (especially in the neck), dizziness, hot ears, constipation or diarrhea, increased or decreased urination, and other visceral symptoms. These symptoms usually precede the headache phase of the migraine attack by several hours or days, and experience teaches the patient or observant family how to detect a migraine attack is near.
Aura
For the 20–30% of migraine sufferers who experience migraine with aura, this aura comprises focal neurological phenomena that precede or accompany the attack. They appear gradually over five to 20 minutes and generally last fewer than 60 minutes. The headache phase of the migraine attack usually begins within 60 minutes of the end of the aura phase, but it is sometimes delayed up to several hours, and it can be missing entirely (see silent migraine). The pain may also begin before the aura has completely subsided. Symptoms of migraine aura can be sensory or motor in nature.Visual aura
Aura (symptom)
An aura is a perceptual disturbance experienced by some migraine sufferers before a migraine headache, and the telltale sensation experienced by some people with epilepsy before a seizure. It often manifests as the perception of a strange light, an unpleasant smell or confusing thoughts or...
is the most common of the neurological events, and can occur without any headache. There is a disturbance of vision consisting often of unformed flashes of white and/or black or rarely of multicolored lights (photopsia
Photopsia
Photopsia is the presence of perceived flashes of light. It is most commonly associated with posterior vitreous detachment, migraine with aura, migraine aura without headache, retinal break or detachment, occipital lobe infarction and sensory deprivation...
) or formations of dazzling zigzag lines (scintillating scotoma
Scintillating scotoma
Scintillating scotoma is the most common visual aura preceding migraine and was first described by 19th century physician Hubert Airy . It is often confused with ocular migraine which originates in the eyeball or socket.-Presentation:...
, often arranged like the battlements of a castle, hence the alternative terms "fortification spectra" or "teichopsia"). Some patients complain of blurred or shimmering or cloudy vision, as though they were looking at an area above a heated surface, looking through thick or smoked glass
Smoked glass
The term smoked glass refers to two different types of glass. It can be either of the following: Smoked glass is a flat sheet of glass held in the smoke of a candle flame such that one surface of the sheet of glass is covered in a layer of smoke residue...
, or, in some cases, tunnel vision
Tunnel vision
Tunnel vision is the loss of peripheral vision with retention of central vision, resulting in a constricted circular tunnel-like field of vision.- Medical / biological causes :Tunnel vision can be caused by:...
and hemianopsia
Hemianopsia
Hemianopia, or hemianopsia, is a type of anopsia where the decreased vision or blindness takes place in half the visual field of one or both eyes. In most cases, the visual field loss respects the vertical midline...
.
The somatosensory aura of migraine may consist of digitolingual or cheiro-oral paresthesia
Paresthesia
Paresthesia , spelled "paraesthesia" in British English, is a sensation of tingling, burning, pricking, or numbness of a person's skin with no apparent long-term physical effect. It is more generally known as the feeling of "pins and needles" or of a limb "falling asleep"...
s, a feeling of pins-and-needles experienced in the hand and arm, as well as in the nose-mouth area on the same side. The paresthesia may migrate up the arm and then extend to involve the face, lips and tongue.
Other symptoms of the aura phase can include auditory, gustatory or olfactory hallucinations, temporary dysphasia, vertigo
Vertigo (medical)
Vertigo is a type of dizziness, where there is a feeling of motion when one is stationary. The symptoms are due to a dysfunction of the vestibular system in the inner ear...
, tingling or numbness of the face and extremities, and hypersensitivity to touch.
Oliver Sacks
Oliver Sacks
Oliver Wolf Sacks, CBE , is a British neurologist and psychologist residing in New York City. He is a professor of neurology and psychiatry at Columbia University, where he also holds the position of Columbia Artist...
's book Migraine describes "migrainous deliria" as a result of such intense migraine aura that it is indistinguishable from "free-wheeling states of hallucinosis, illusion, or dreaming."
Pain
The typical migraine headache is unilateral, throbbing, and moderate to severe, and can be aggravated by physical activity. Not all these features are necessary. The pain may be bilateral at the onset or start on one side and become generalized, and may occur primarily on one side or alternate sides from one attack to the next. The onset is usually gradual. The pain peaks and then subsides and usually lasts four to 72 hours in adults and one to 48 hours in children. The frequency of attacks is extremely variable, from a few in a lifetime to several a week, and the average sufferer experiences one to three headaches a month. The head pain varies greatly in intensity, and can be very severe.The pain of migraine is invariably accompanied by other features. Nausea
Nausea
Nausea , is a sensation of unease and discomfort in the upper stomach with an involuntary urge to vomit. It often, but not always, precedes vomiting...
occurs in almost 90 percent of patients, and vomiting occurs in about one third of patients. Many patients experience sensory hyperexcitability manifested by photophobia
Photophobia
Photophobia is a symptom of abnormal intolerance to visual perception of light. As a medical symptom photophobia is not a morbid fear or phobia, but an experience of discomfort or pain to the eyes due to light exposure or by presence of actual physical photosensitivity of the eyes, though the term...
, phonophobia, and osmophobia
Osmophobia
Osmophobia or olfactophobia refers to a fear, aversion, or psychological hypersensitivity to smells or odors. The phobia generally occurs in chronic migraine sufferers who may have odor triggered migraines. Such migraines are most frequently triggered by foul odors, but the hypersensitivity may...
and seek a dark and quiet room. Blurred vision, delirium, nasal stuffiness, diarrhea, tinnitus
Tinnitus
Tinnitus |ringing]]") is the perception of sound within the human ear in the absence of corresponding external sound.Tinnitus is not a disease, but a symptom that can result from a wide range of underlying causes: abnormally loud sounds in the ear canal for even the briefest period , ear...
, polyuria
Polyuria
Polyuria is a condition usually defined as excessive or abnormally large production or passage of urine . Frequent urination is sometimes included by definition, but is nonetheless usually an accompanying symptom...
, pallor
Pallor
Pallor is a reduced amount of oxyhaemoglobin in skin or mucous membrane, a pale color which can be caused by illness, emotional shock or stress, stimulant use, lack of exposure to sunlight, anaemia or genetics....
, or sweating may be noted during the headache phase. There may be localized edema
Edema
Edema or oedema ; both words from the Greek , oídēma "swelling"), formerly known as dropsy or hydropsy, is an abnormal accumulation of fluid beneath the skin or in one or more cavities of the body that produces swelling...
of the scalp or face, scalp tenderness, prominence of a vein or artery in the temple, or stiffness and tenderness of the neck. Impairment of concentration and mood are common. The extremities tend to feel cold and moist. Vertigo
Vertigo (medical)
Vertigo is a type of dizziness, where there is a feeling of motion when one is stationary. The symptoms are due to a dysfunction of the vestibular system in the inner ear...
may be experienced; a variation of the typical migraine, called vestibular migraine, has also been described. Lightheadedness, rather than true vertigo, and a feeling of faintness may occur.
Postdrome
The effects of migraine may persist for some days after the main headache has ended. Many sufferers report a sore feeling in the area where the migraine was, and some report impaired thinking for a few days after the headache has passed. The patient may feel tired or "hungover" and have head pain, cognitive difficulties, gastrointestinal symptoms, mood changes, and weakness. According to one summary, "Some people feel unusually refreshed or euphoric after an attack, whereas others note depression and malaiseMalaise
Malaise is a feeling of general discomfort or uneasiness, of being "out of sorts", often the first indication of an infection or other disease. Malaise is often defined in medicinal research as a "general feeling of being unwell"...
."
Objective signs
A temporary Horner's syndromeHorner's syndrome
Horner's syndrome is the combination of drooping of the eyelid and constriction of the pupil , sometimes accompanied by decreased sweating of the face on the same side; redness of the conjunctiva of the eye is often also present...
(ptosis-drooping lid, miosis-smaller pupil) may occur during a migraine attack and disappear afterwards.
Cause
The underlying cause of migraines is unknown. There are, however, many biological events that have been clinically associated with migraine.Triggers
Migraines may be induced by triggers, with some reporting it as an influence in a minority of cases and others the majority. Many things have been labeled as triggers, however the strength and significance of these relationships are uncertain. Common triggers quoted are stress, hunger, and fatigue (these equally contribute to tension headaches). A 2003 review concluded there was no scientific evidence for an effect of tyramineTyramine
Tyramine is a naturally occurring monoamine compound and trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Tyramine acts as a catecholamine releasing agent...
on migraine. A 2005 literature review
Literature review
A literature review is a body of text that aims to review the critical points of current knowledge including substantive findings as well as theoretical and methodological contributions to a particular topic...
on dietary triggers found the available scientific studies, mostly relying on subjective assessments, were not rigorous enough to prove or disprove any particular triggers. This is in line with other reviews. A 2009 review of potential triggers in the indoor and outdoor environment concluded the overall evidence was of poor quality, but nevertheless suggested migraineurs take some preventative measures related to indoor air quality and lighting. While monosodium glutamate
Monosodium glutamate
Monosodium glutamate, also known as sodium glutamate or MSG, is the sodium salt of glutamic acid, one of the most abundant naturally occurring non-essential amino acids....
(MSG) is frequently reported as a dietary trigger evidence does not consistently support this. Migraines are more likely to occur around menstruation
Menstruation
Menstruation is the shedding of the uterine lining . It occurs on a regular basis in sexually reproductive-age females of certain mammal species. This article focuses on human menstruation.-Overview:...
. Other hormonal influences, such as menarche
Menarche
Menarche is the first menstrual cycle, or first menstrual bleeding, in female human beings. From both social and medical perspectives it is often considered the central event of female puberty, as it signals the possibility of fertility....
, oral contraceptive
Oral contraceptive
The combined oral contraceptive pill , often referred to as the birth-control pill or colloquially as "the Pill", is a birth control method that includes a combination of an estrogen and a progestin . When taken by mouth every day, these pills inhibit female fertility...
use, pregnancy
Pregnancy
Pregnancy refers to the fertilization and development of one or more offspring, known as a fetus or embryo, in a woman's uterus. In a pregnancy, there can be multiple gestations, as in the case of twins or triplets...
, perimenopause, and menopause
Menopause
Menopause is a term used to describe the permanent cessation of the primary functions of the human ovaries: the ripening and release of ova and the release of hormones that cause both the creation of the uterine lining and the subsequent shedding of the uterine lining...
, also play a role.
Depolarization
The phenomenon known as cortical spreading depressionCortical spreading depression
Cortical spreading depression is a wave of electrophysiological hyperactivity followed by a wave of inhibition, usually in the visual cortex.The term is used by neuroscientists to represent at least one of the following cortical processes:...
, which is associated with the aura of migraine, has been theorized as a possible cause of migraines. In cortical spreading depression
Cortical spreading depression
Cortical spreading depression is a wave of electrophysiological hyperactivity followed by a wave of inhibition, usually in the visual cortex.The term is used by neuroscientists to represent at least one of the following cortical processes:...
, neurological activity
Neuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
is initially activated, then depressed over an area of the cerebral cortex
Cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex is a sheet of neural tissue that is outermost to the cerebrum of the mammalian brain. It plays a key role in memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language, and consciousness. It is constituted of up to six horizontal layers, each of which has a different...
. This situation has been suggested to result in the release of inflammatory
Inflammation
Inflammation is part of the complex biological response of vascular tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. Inflammation is a protective attempt by the organism to remove the injurious stimuli and to initiate the healing process...
mediators leading to irritation of cranial nerve roots, most particularly the trigeminal nerve
Trigeminal nerve
The trigeminal nerve contains both sensory and motor fibres. It is responsible for sensation in the face and certain motor functions such as biting, chewing, and swallowing. Sensory information from the face and body is processed by parallel pathways in the central nervous system...
, which conveys the sensory information for the face and much of the head. This theory is, however, speculative, without any supporting evidence, and there are indeed cogent arguments against it. First, only about one third of migraineurs experience an aura, and those who do not experience aura do not have cortical spreading depression. Second, many migraineurs have a prodrome (see above), which occurs up to three days before the aura.
Vascular
Studies have shown the aura coincides with constriction of blood vessels in the brain. This may start in the occipital lobeOccipital lobe
The occipital lobe is the visual processing center of the mammalian brain containing most of the anatomical region of the visual cortex. The primary visual cortex is Brodmann area 17, commonly called V1...
, in the back of the brain, as arteries spasm. The reduced flow of blood from the occipital lobe triggers the aura some individuals who have migraines experience, because the visual cortex is in the occipital area.
When the constriction of blood vessels in the brain stops and the aura subsides, the blood vessels of the scalp dilate. The walls of these blood vessels become permeable and some fluid leaks out. This leakage is recognized by pain receptors in the blood vessels of surrounding tissue. In response, the body supplies the area with chemicals which cause inflammation. With each heart beat, blood passes through this sensitive area, causing a throb of pain.
Although cerebral vasodilation can trigger migraine attacks, blood vessel diameters return to normal more than an hour before the migraine headaches occur.
Serotonin
SerotoninSerotonin
Serotonin or 5-hydroxytryptamine is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Biochemically derived from tryptophan, serotonin is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract, platelets, and in the central nervous system of animals including humans...
is a type of neurotransmitter, or "communication chemical" which passes messages between nerve cells. It helps to control mood, pain sensation, sexual behaviour and sleep, as well as dilation and constriction of the blood vessels, among other things. Low serotonin
Serotonin
Serotonin or 5-hydroxytryptamine is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Biochemically derived from tryptophan, serotonin is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract, platelets, and in the central nervous system of animals including humans...
levels in the brain may lead to a process of constriction and dilation of the blood vessels which trigger a migraine. Serotonergic agonists, such as triptan
Triptan
Triptans are a family of tryptamine-based drugs used as abortive medication in the treatment of migraines and cluster headaches. They were first introduced in the 1990s...
s, LSD
LSD
Lysergic acid diethylamide, abbreviated LSD or LSD-25, also known as lysergide and colloquially as acid, is a semisynthetic psychedelic drug of the ergoline family, well known for its psychological effects which can include altered thinking processes, closed and open eye visuals, synaesthesia, an...
or psilocin
Psilocin
Psilocin , an aromatic compound, sometimes also spelled psilocine, psilocyn, or psilotsin, is a psychedelic mushroom alkaloid. It is found in most psychedelic mushrooms together with its phosphorylated counterpart psilocybin...
, activate serotonin receptors to stop a migraine attack.
Melanopsin receptor
A melanopsinMelanopsin
Melanopsin is a photopigment found in specialized photosensitive ganglion cells of the retina that are involved in the regulation of circadian rhythms, pupillary light reflex, and other non-visual responses to light. In structure, melanopsin is an opsin, a retinylidene protein variety of...
-based receptor has been linked to the association between light sensitivity and migraine pain, but this is currently speculation.
Neural
When certain nerves or an area in the brain stemBrain stem
In vertebrate anatomy the brainstem is the posterior part of the brain, adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. The brain stem provides the main motor and sensory innervation to the face and neck via the cranial nerves...
become irritated, a migraine begins. In response to the irritation, the body releases chemicals which cause inflammation of the blood vessels. These chemicals cause further irritation of the nerves and blood vessels and results in pain. Substance P
Substance P
In the field of neuroscience, substance P is a neuropeptide: an undecapeptide that functions as a neurotransmitter and as a neuromodulator. It belongs to the tachykinin neuropeptide family. Substance P and its closely related neuropeptide neurokinin A are produced from a polyprotein precursor...
is one of the substances released with first irritation. Pain then increases because substance P aids in sending pain signals to the brain.
Unifying theory
Both vascular and neural influences cause migraines.- stressStress (biology)Stress is a term in psychology and biology, borrowed from physics and engineering and first used in the biological context in the 1930s, which has in more recent decades become commonly used in popular parlance...
triggers changes in the brain - these changes cause serotoninSerotoninSerotonin or 5-hydroxytryptamine is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Biochemically derived from tryptophan, serotonin is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract, platelets, and in the central nervous system of animals including humans...
and/or histamineHistamineHistamine is an organic nitrogen compound involved in local immune responses as well as regulating physiological function in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter. Histamine triggers the inflammatory response. As part of an immune response to foreign pathogens, histamine is produced by...
to be released - blood vessels constrict and dilate
- chemicals, including substance PSubstance PIn the field of neuroscience, substance P is a neuropeptide: an undecapeptide that functions as a neurotransmitter and as a neuromodulator. It belongs to the tachykinin neuropeptide family. Substance P and its closely related neuropeptide neurokinin A are produced from a polyprotein precursor...
, irritate nerves and blood vessels, causing neurogenic inflammationNeurogenic inflammationNeurogenic inflammation is inflammation arising from the local release from afferent neurons of inflammatory mediators such as Substance P and Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide ....
and painPainPain is an unpleasant sensation often caused by intense or damaging stimuli such as stubbing a toe, burning a finger, putting iodine on a cut, and bumping the "funny bone."...
.
Pathophysiology
Migraine is a neurovascular disorder. Although migraine is thought by some to be a neurological disease, in the absence of scientific evidence, this remains a hypothesis.Initiation
Migraines were once thought to be initiated exclusively by problems with blood vessels, but the vascular changes of migraines are now considered by some to be secondary to brain dysfunction, although this concept has not been supported by the evidence. This was eloquently summed up by Dodick, who wrote, "There is no disputing the role of the central nervous system in the susceptibility, modulation and expression of migraine headache and the associated affective, cognitive, sensory, and neurological symptoms and signs. However, to presume that migraine is always generated from within the central nervous system, based on the available evidence, is naïve at best and unscientific at worst.The emerging evidence would suggest that just as alterations in neuronal activity can lead to downstream effects on the cerebral blood vessel, so too can changes within endothelial cells or vascular smooth muscle lead to downstream alterations in neuronal activity. Therefore, there are likely patients, and/or at least attacks in certain patients, where primarily vascular mechanisms predominate." Some have even attempted to show that vascular changes are of no importance in migraine, but this claim is unsubstantiated and has not been supported by scientific evidence. 'If we swing between vascular and neurogenic views of migraine, it is probably because both vascular and neurogenic mechanisms for migraine exist and are important'- J EdmeadsPain
Although the initiating factor of migraine remains unknown, copious, irrefutable evidence shows the pain of migraine (the third phase) is, in some patients, related to painful dilatation of the terminal branches of the external carotid arteryExternal carotid artery
In human anatomy, the external carotid artery is a major artery of the head and neck. It arises from the common carotid artery when it bifurcates into the external and internal carotid artery.-Course:...
, and in particular its superficial temporal and occipital branches. Dilatation of the arteries in the brain and dura mater previously was thought to be the origin of the vascular pain, but these vessels have been shown to not dilate during migraine. Because these arteries are relatively superficial, it is easy to diagnose whether they are the source of the pain. If they are, then they are also accessible to a form of migraine surgery
Migraine surgery
Migraine surgery is any surgical operation undertaken with the goal of reducing or preventing migraines. Innovative surgical techniques have been developed to help patients with migraine headaches. Migraines affect an estimated 10% of the worldwide population annually and cause significant loss of...
being promoted, largely to the efforts of Dr Elliot Shevel
Elliot Shevel
Elliot Shevel BDS, DipMFOS, MBBCh is a South African Maxillo-Facial and Oral Surgeon, best known for his contribution to understanding of the underlying processes involved in the pain of migraine. He is, inter alia, a tireless campaigner to have the work of Harold Wolff, which many migraine...
, a South African surgeon, who has reported excellent success using the procedure.
Pericranial (jaw and neck) muscle tenderness is a common finding in migraine. Muscle tenderness has been shown to be present in 100% of migraine attacks, making muscle tenderness the single most common finding in migraine. Tender muscle trigger points can be at least part of the cause, and perpetuate most kinds of headaches.
Diagnosis
Migraines are underdiagnosed, and often are misdiagnosed. The diagnosis of migraine without aura, according to the International Headache SocietyInternational Headache Society
The International Headache Society is a charity organization founded in 1981 for people from all professions that are working to treat headache disorders....
, can be made according to the following criteria, the "5, 4, 3, 2, 1 criteria":
- 5 or more attacks - for migraine with aura, two attacks are sufficient for diagnosis.
- 4 hours to 3 days in duration
- 2 or more of the following:
- Unilateral (affecting half the head);
- Pulsating;
- "Moderate or severe pain intensity";
- "Aggravation by or causing avoidance of routine physical activity"
- 1 or more of the following:
- "Nausea and/or vomiting";
- Sensitivity to both light (photophobiaPhotophobiaPhotophobia is a symptom of abnormal intolerance to visual perception of light. As a medical symptom photophobia is not a morbid fear or phobia, but an experience of discomfort or pain to the eyes due to light exposure or by presence of actual physical photosensitivity of the eyes, though the term...
) and sound (phonophobia)
The mnemonic POUNDing (Pulsating, duration of 4–72 hOurs, Unilateral, Nausea, Disabling) can help diagnose migraine. If four of the five criteria are met, then the positive likelihood ratio
Likelihood-ratio test
In statistics, a likelihood ratio test is a statistical test used to compare the fit of two models, one of which is a special case of the other . The test is based on the likelihood ratio, which expresses how many times more likely the data are under one model than the other...
for diagnosing migraine is 24.
The presence of either disability, nausea or sensitivity can diagnose migraine with:
- sensitivity of 81%
- specificity of 75%
Migraine should be differentiated
Differential diagnosis
A differential diagnosis is a systematic diagnostic method used to identify the presence of an entity where multiple alternatives are possible , and may also refer to any of the included candidate alternatives A differential diagnosis (sometimes abbreviated DDx, ddx, DD, D/Dx, or ΔΔ) is a...
from other causes of headaches, such as cluster headaches. These are extremely painful, unilateral headaches of a piercing quality. The duration of the common attack is 15 minutes to three hours. Onset of an attack is rapid, and most often without the preliminary signs characteristic of a migraine.
Medical imaging
Medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process used to create images of the human body for clinical purposes or medical science...
of the head and neck may be used to rule out secondary causes of headaches.
Prevention
Preventive (also called prophylactic) treatment of migraines can be an important component of migraine management. Such treatments can take many forms, including taking preventive drugs, migraine surgery, taking nutritional supplements, lifestyle alterations, such as increased exercise, and avoidance of migraine triggers.The goals of preventive therapy are to reduce the frequency, painfulness, and/or duration of migraines, and to increase the effectiveness of abortive therapy. Another reason to pursue these goals is to avoid medication overuse headache (MOH), otherwise known as rebound headache
Rebound headache
Medication overuse headaches , also known as rebound headaches usually occur when analgesics are taken frequently to relieve headaches. Rebound headaches frequently occur daily and can be very painful and are a common cause of chronic daily headache...
. This is a common problem among migraineurs, and can result in chronic daily headache.
Many of the preventive treatments are quite effective. Even with a placebo
Placebo
A placebo is a simulated or otherwise medically ineffectual treatment for a disease or other medical condition intended to deceive the recipient...
, one-quarter of patients find their migraine frequency is reduced by half or more, and actual treatments often far exceed this figure.
Medication
Preventive migraine drugs are considered effective if they reduce the frequency or severity of migraine attacks by at least 50%. The major problem with migraine preventive drugs, apart from their relative inefficacy, is that unpleasant side effects are common. So, preventive medication is limited to patients with frequent or severe headaches.Many medicines are available to prevent or reduce frequency, duration and severity of migraine attacks. They may also prevent complications of migraine. Beta blockers, such as Propranolol, atenolol, and metoprolol
Metoprolol
Metoprolol is a selective β1 receptor blocker used in treatment of several diseases of the cardiovascular system, especially hypertension. The active substance metoprolol is employed either as metoprolol succinate or metoprolol tartrate...
; calcium channel blockers, such as amlodipine
Amlodipine
Amlodipine is a long-acting calcium channel blocker used as an anti-hypertensive and in the treatment of angina...
, flunarizine
Flunarizine
Flunarizine is a drug classified as a calcium channel blocker. Flunarizine is a non-selective calcium entry blocker with calmodulin binding properties and histamine H1 blocking activity. It is effective in the prophylaxis of migraine, occlusive peripheral vascular disease, vertigo of central and...
and verapamil
Verapamil
Verapamil is an L-type calcium channel blocker of the phenylalkylamine class. It has been used in the treatment of hypertension, angina pectoris, cardiac arrhythmia, and most recently, cluster headaches. It is also an effective preventive medication for migraine...
; the anticonvulsants sodium valproate
Sodium valproate
Sodium valproate or valproate sodium is the sodium salt of valproic acid and is an anticonvulsant used in the treatment of epilepsy, anorexia nervosa, panic attack, anxiety disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder, migraine and bipolar disorder, as well as other psychiatric conditions requiring...
, divalproex, gabapentin
Gabapentin
Gabapentin is a pharmaceutical drug, specifically a GABA analogue. It was originally developed for the treatment of epilepsy, and currently is also used to relieve neuropathic pain...
and topiramate
Topiramate
Topiramate is an anticonvulsant drug. It was originally produced by Ortho-McNeil Neurologics and Noramco, Inc., both divisions of the Johnson & Johnson Corporation. This medication was discovered in 1979 by Bruce E. Maryanoff and Joseph F. Gardocki during their research work at McNeil...
; and tricyclic antidepressants are some of the commonly used drugs.
Tricyclic antidepressants have been found to be more effective than SSRIs. Tricyclic antidepressants have been long established as efficacious prophylactic treatments. These drugs, however, may give rise to undesirable side effects, such as insomnia, sedation or sexual dysfunction. There is no consistent evidence that SSRI antidepressants are effective for migraine prophylaxis. While amitryptiline (Elavil) is the only tricyclic to have received FDA approval for migraine treatment, other tricyclic antidepressants are believed to act similarly and are widely prescribed, often to find one with a profile of side effects that is acceptable to the patient. In addition to tricyclics a, the antidepressant nefazodone
Nefazodone
Nefazodone is an antidepressant marketed by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Its sale was discontinued in 2003 in some countries due to the rare incidence of hepatotoxicity , which could lead to the need for a liver transplant, or even death. The incidence of severe liver damage is approximately 1 in every...
may also be beneficial in the prophylaxis of migraines due to its antagonistic effects on the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors It has a more favorable side effect profile than amitriptyline
Amitriptyline
Amitriptyline is a tricyclic antidepressant . It is the most widely used TCA and has at least equal efficacy against depression as the newer class of SSRIs...
, a tricyclic antidepressant commonly used for migraine prophylaxis. Antidepressants offer advantages for treating migraine patients with comorbid depression. SSRIs are not approved by the FDA for treatment of migraines, but have been found to be effective by some practitioners.
There is some evidence that low-dose asprin has benefit for reducing the occurrence of migraines in susceptible individuals.
Surgery
Migraine surgeryMigraine surgery
Migraine surgery is any surgical operation undertaken with the goal of reducing or preventing migraines. Innovative surgical techniques have been developed to help patients with migraine headaches. Migraines affect an estimated 10% of the worldwide population annually and cause significant loss of...
is a field that shows a great deal of promise, particularly in those who suffer more frequent attacks, and in those who have not had an adequate response to prophylactic medications. Patients often still experience a poor quality of life despite an aggressive regimen of pharmacotherapy. For these reasons, surgical solutions to migraines have been developed, which have excellent results. A major advantage of migraine surgery is that, with the correct diagnostic techniques, a definite diagnosis can be made before the surgery is undertaken. Once a positive diagnosis has been made, the results of surgery are outstanding and provide permanent pain relief, as well as relief from the associated symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, light sensitivity, and sound sensitivity. Surgical cauterization of the superficial blood vessels of the scalp (the terminal branches of the external carotid artery) is only carried out if it has been established with certainty that these vessels are indeed the source of pain. It is a safe and relatively atraumatic procedure which can be performed in a day facility. The value of arterial sugery for migraine treatment is gaining recognition as a result of the efforts of a South African surgeon, Dr Elliot Shevel
Elliot Shevel
Elliot Shevel BDS, DipMFOS, MBBCh is a South African Maxillo-Facial and Oral Surgeon, best known for his contribution to understanding of the underlying processes involved in the pain of migraine. He is, inter alia, a tireless campaigner to have the work of Harold Wolff, which many migraine...
, who has produced a number of papers on the subject.
The removal of muscles or nerves in areas known as "trigger sites" provides good results, but only in patients who respond well to Botox injections in specific areas.
There is also evidence that the correction of a congenital heart defect
Congenital heart defect
A congenital heart defect is a defect in the structure of the heart and great vessels which is present at birth. Many types of heart defects exist, most of which either obstruct blood flow in the heart or vessels near it, or cause blood to flow through the heart in an abnormal pattern. Other...
, patent foramen ovale (PFO), reduces migraine frequency and severity. Recent studies have advised caution, though, in relation to PFO closure for migraines, as insufficient evidence exists to justify this dangerous procedure.
Other therapies
Medical devices, such as biofeedback and neurostimulators, have some advantages in the migraine treatment, mainly when common antimigraine medication is contraindicated or in case of medication over use. BiofeedbackBiofeedback
Biofeedback is the process of becoming aware of various physiological functions using instruments that provide information on the activity of those same systems, with a goal of being able to manipulate them at will...
helps patient to be conscious of some physiologic parameters to control them and try to relax. This method is considered to be efficient for migraine and tension-type headache
Tension headache
A tension headache is the most common type of primary headache. The pain can radiate from the neck, back, eyes, or other muscle groups in the body. Tension-type headaches account for nearly 90% of all headaches...
treatment. A recent clinical trial has demonstrated that simple use of biofeedback as a relaxation technique has similar efficacy for migraine treatment to sophisticated sessions in clinics. Neurostimulation
Neurostimulation
Neurostimulation involves modulation of the nervous system and electrically activate neurons in the body. The activation of neural elements in a part of the nervous system can be effectively facilitated by stimulation. Micro-electrodes are utilized to interface with excitable tissue in order to...
used initially implantable neurostimulators similar to pacemakers for the treatment of intractable chronic migraines with encouraging good results. But the needed surgery with implantable neurostimulators is limiting the indication to sever cases. Recently, a new technique of external trigeminal (V1) or occipital nerve
Greater occipital nerve
The greater occipital nerve is a spinal nerve, specifically the medial branch of the dorsal primary ramus of cervical spinal nerve 2. This nerve arises from between the first and second cervical vertebrae, along with the lesser occipital nerve. It ascends after emerging from the suboccipital...
(CII) neurostimulation (Cefaly
Cefaly
Cefaly is an external cranial neurostimulation device for the treatment and prevention of migraine and headache.This is an electronic device that generates electrical pulses....
) could offer a larger use for migraine treatment or prevention.
A systematic review stated that chiropractic manipulation, physiotherapy, massage and relaxation might be as effective as propranolol or topiramate
Topiramate
Topiramate is an anticonvulsant drug. It was originally produced by Ortho-McNeil Neurologics and Noramco, Inc., both divisions of the Johnson & Johnson Corporation. This medication was discovered in 1979 by Bruce E. Maryanoff and Joseph F. Gardocki during their research work at McNeil...
in the prevention of migraine headaches; however, the research had some problems with methodology.
"The therapeutic potential of magnesium
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole...
, coenzyme Q(10), riboflavin
Riboflavin
Riboflavin, also known as vitamin B2 or additive E101, is an easily absorbed micronutrient with a key role in maintaining health in humans and animals. It is the central component of the cofactors FAD and FMN, and is therefore required by all flavoproteins. As such, vitamin B2 is required for a...
, and vitamin B(12)
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, vitamin B12 or vitamin B-12, also called cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin with a key role in the normal functioning of the brain and nervous system, and for the formation of blood. It is one of the eight B vitamins...
can be cautiously inferred from some published open clinical trials." A review has concluded that "[c]urrent clinical data support the use of fever-few
Feverfew
Feverfew is a traditional medicinal herb which is found in many old gardens, and is also occasionally grown for ornament. The plant grows into a small bush up to around high, with citrus-scented leaves and is covered by flowers reminiscent of daisies...
, butterbur
Butterbur
The plants commonly referred to as Butterbur are found in the daisy family Asteraceae in the genus Petasites. They are mostly quite robust plants with thick, creeping underground rhizomes and large Rhubarb-like leaves during the growing season...
, magnesium, and riboflavin
Riboflavin
Riboflavin, also known as vitamin B2 or additive E101, is an easily absorbed micronutrient with a key role in maintaining health in humans and animals. It is the central component of the cofactors FAD and FMN, and is therefore required by all flavoproteins. As such, vitamin B2 is required for a...
in migraine prophylaxis."
Migraine diary
A migraine diary allows the assessment of headache characteristics, to differentiate between migraine and tension-type headache and to record the use and efficacy of acute medication. A diary also helps to analyse the relationship between migraine and menstruation. Finally, the diary can help to identify trigger factors. A trigger may occur up to 24 hours prior to the onset of symptoms; the majority of migraines, though, are not caused by identifiable triggers.Management
There are three main aspects of treatment: trigger avoidance, acute symptomatic control, and pharmacological prevention. Medications are more effective if used earlier in an attack. The frequent use of medications may, however, result in medication overuse headache, in which the headaches become more severe and more frequent. These may occur with triptans, ergotamines, and analgesics, especially narcoticNarcotic
The term narcotic originally referred medically to any psychoactive compound with any sleep-inducing properties. In the United States of America it has since become associated with opioids, commonly morphine and heroin and their derivatives, such as hydrocodone. The term is, today, imprecisely...
analgesics.
Analgesics
A number of analgesics are effective for treating migraines including:- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugNon-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugNonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, usually abbreviated to NSAIDs or NAIDs, but also referred to as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents/analgesics or nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory medicines , are drugs with analgesic and antipyretic effects and which have, in higher doses, anti-inflammatory...
s (NSAIDs): Ibuprofen provides effective pain relief in about half of people. NaproxenNaproxenNaproxen sodium is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug commonly used for the reduction of pain, fever, inflammation and stiffness caused by conditions such as:...
can abort about one third of migraine attacks, which was 5% less than the benefit of sumatriptanSumatriptanSumatriptan is a triptan sulfa drug containing a sulfonamide group. It is used for the treatment of migraine headaches. Sumatriptan is produced and marketed by various drug manufacturers with many different trade names such as Sumatriptan, Imitrex, Imigran, Imigran recovery.-Approval and...
. A 1000 mg dose of aspirinAspirinAspirin , also known as acetylsalicylic acid , is a salicylate drug, often used as an analgesic to relieve minor aches and pains, as an antipyretic to reduce fever, and as an anti-inflammatory medication. It was discovered by Arthur Eichengrun, a chemist with the German company Bayer...
could relieve moderate to severe migraine pain, with similar effectiveness to sumatriptan. - ParacetamolParacetamolParacetamol INN , or acetaminophen USAN , is a widely used over-the-counter analgesic and antipyretic . It is commonly used for the relief of headaches and other minor aches and pains and is a major ingredient in numerous cold and flu remedies...
/acetaminophen, either alone or in combination with metaclopramide, is effective for migraines. - Simple analgesics combined with caffeineCaffeineCaffeine is a bitter, white crystalline xanthine alkaloid that acts as a stimulant drug. Caffeine is found in varying quantities in the seeds, leaves, and fruit of some plants, where it acts as a natural pesticide that paralyzes and kills certain insects feeding on the plants...
may help. Even by itself, caffeine can be useful during an attack, despite the fact that migraine sufferers are generally advised to limit their caffeine intake.
Triptans
Triptans such as sumatriptanSumatriptan
Sumatriptan is a triptan sulfa drug containing a sulfonamide group. It is used for the treatment of migraine headaches. Sumatriptan is produced and marketed by various drug manufacturers with many different trade names such as Sumatriptan, Imitrex, Imigran, Imigran recovery.-Approval and...
are effective for both pain and nausea in up to 75% of people. The different forms available include oral, injection, nasal spray
Nasal spray
Nasal sprays come in a variety of forms. Medicated such as Astelin, Afrin and Nasonex and natural such as Sinusoothe and Sterimar. Although delivery methods vary, most nasal sprays function by instilling a fine mist into the nostril by action of a hand-operated pump mechanism.-Antihistamine nasal...
, and oral dissolving tablets. Most side effects are mild, such as flushing; however, rare cases of myocardial ischemia
Myocardial ischemia
Myocardial ischemia is an imbalance between myocardial oxygen supply and demand. Left untreated, it results in angina pectoris, myocardial stunning, myocardial hibernation, ischemic preconditioning, postconditioning, or under the most severe instances, acute coronary syndrome and myocardial...
have occurred. They are not addictive, but may cause medication overuse headaches if used more than 10 days per month.
Ergotamines
Ergotamine and dihydroergotamineDihydroergotamine
Dihydroergotamine is an ergot alkaloid used to treat migraines. It is a derivative of ergotamine. It is administered as a nasal spray or injection and has an efficacy similar to that of sumatriptan...
are older medications still prescribed for migraines, the latter in nasal spray and injectable forms. They were the primary drugs available to abort a migraine prior to the triptans, and are much less expensive than triptans.
Corticosteroids
A single dose of intravenous dexamethasoneDexamethasone
Dexamethasone is a potent synthetic member of the glucocorticoid class of steroid drugs. It acts as an anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressant...
, when added to standard treatment of a migraine attack, is associated with a 26% decrease in headache recurrence in the following 72 hours.
Other
AntiemeticAntiemetic
An antiemetic is a drug that is effective against vomiting and nausea. Antiemetics are typically used to treat motion sickness and the side effects of opioid analgesics, general anaesthetics, and chemotherapy directed against cancer....
s by mouth may help relieve symptoms of nausea and help prevent vomiting, which can diminish the effectiveness of orally taken analgesics. In addition, some antiemetics, such as metoclopramide
Metoclopramide
Metoclopramide is an antiemetic and gastroprokinetic agent. It is commonly used to treat nausea and vomiting, to facilitate gastric emptying in people with gastroparesis, and as a treatment for the gastric stasis often associated with migraine headaches.-Medical uses:Metoclopramide is commonly...
, are prokinetics and help gastric emptying, which is often impaired during episodes of migraine. In the UK, three combination antiemetic and analgesic preparations are available: MigraMax (aspirin
Aspirin
Aspirin , also known as acetylsalicylic acid , is a salicylate drug, often used as an analgesic to relieve minor aches and pains, as an antipyretic to reduce fever, and as an anti-inflammatory medication. It was discovered by Arthur Eichengrun, a chemist with the German company Bayer...
with metoclopramide), (paracetamol/codeine for analgesia, with buclizine
Buclizine
Buclizine is an antihistamine and anticholinergic of the piperazine derivative family. It is considered to be an antiemetic, similar to meclozine....
as the antiemetic) and paracetamol/metoclopramide
Paracetamol/metoclopramide
Paracetamol/metoclopramide hydrochloride is an oral fixed dose combination prescription medication containing the analgesic paracetamol and the anti-emetic metoclopramide hydrochloride...
(Paramax in UK). The earlier these drugs are taken in the attack, the better their effect.
Prognosis
The risk of strokeStroke
A stroke, previously known medically as a cerebrovascular accident , is the rapidly developing loss of brain function due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. This can be due to ischemia caused by blockage , or a hemorrhage...
may be increased two- to three-fold in migraine sufferers. Young adult sufferers and women using hormonal contraception
Hormonal contraception
Hormonal contraception refers to birth control methods that act on the endocrine system. Almost all methods are composed of steroid hormones, although in India one selective estrogen receptor modulator is marketed as a contraceptive. The original hormonal method—the combined oral contraceptive...
appear to be at particular risk. The mechanism of any association is unclear, but chronic abnormalities of cerebral blood vessel
Blood vessel
The blood vessels are the part of the circulatory system that transports blood throughout the body. There are three major types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the capillaries, which enable the actual exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and...
tone may be involved. Women who experience auras have been found to have twice the risk of strokes and heart attacks over nonaura migraine sufferers and women who do not have migraines. (Note: Women who experience auras and also take oral contraceptives have an even higher risk of stroke). Migraine sufferers seem to be at risk for both thrombotic and hemorrhagic stroke as well as transient ischemic attack
Transient ischemic attack
A transient ischemic attack is a transient episode of neurologic dysfunction caused by ischemia – either focal brain, spinal cord or retinal – without acute infarction...
s. Death from cardiovascular causes was higher in people with migraine with aura in a Women's Health Initiative
Women's Health Initiative
The Women's Health Initiative was initiated by the U.S. National Institutes of Health in 1991. The objective of this women's health research initiative was to conduct medical research into some of the major health problems of older women...
study, but more research is needed to confirm this.
Epidemiology

At all ages, migraine without aura is more common than migraine with aura, with a ratio of between 1.5 and 2.0:1. Incidence figures show the excess of migraine seen in women of reproductive age is mainly due to migraine without aura. Thus, in prepubertal and postmenopausal populations, migraine with aura is somewhat more common than amongst 15–50 year olds.
There is a strong relationship between age, sex and type of migraine.
Studies in Asia and South America suggest the rates there are relatively low, but they do not fall outside the range of values seen in European and North American studies.
The incidence of migraine is related to the incidence of epilepsy
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a common chronic neurological disorder characterized by seizures. These seizures are transient signs and/or symptoms of abnormal, excessive or hypersynchronous neuronal activity in the brain.About 50 million people worldwide have epilepsy, and nearly two out of every three new cases...
in families, with migraine twice as prevalent in family members of epilepsy sufferers, and more common in epilepsy sufferers themselves.
History

Trepanation
Trepanning, also known as trephination, trephining or making a burr hole, is a surgical intervention in which a hole is drilled or scraped into the human skull, exposing the dura mater in order to treat health problems related to intracranial diseases. It may also refer to any "burr" hole created...
, the deliberate and (usually) nonfatal drilling of holes into a skull, was practiced 9,000 years ago and earlier. Some scholars have (controversially) speculated this drastic procedure might have been a migraine treatment, based on cave paintings and on the fact that trepanation was a historical migraine treatment in 17th-century Europe. An early written description consistent with migraines is contained in the Ebers papyrus
Ebers papyrus
The Ebers Papyrus, also known as Papyrus Ebers, is an Egyptian medical papyrus dating to circa 1550 BC. Among the oldest and most important medical papyri of ancient Egypt, it was purchased at Luxor, in the winter of 1873–74 by Georg Ebers...
, written around 1200 BC in ancient Egypt.
In 400 BC, Hippocrates
Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Cos or Hippokrates of Kos was an ancient Greek physician of the Age of Pericles , and is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine...
described the visual aura that can precede the migraine headache, and the relief which can occur through vomiting. Aretaeus
Aretaeus of Cappadocia
Aretaeus , is one of the most celebrated of the ancient Greek physicians, of whose life, however, few particulars are known. There is some uncertainty regarding both his age and country, but it seems probable that he practised in the 1st century CE, during the reign of Nero or Vespasian...
of Cappadocia
Cappadocia
Cappadocia is a historical region in Central Anatolia, largely in Nevşehir Province.In the time of Herodotus, the Cappadocians were reported as occupying the whole region from Mount Taurus to the vicinity of the Euxine...
is credited as the "discoverer" of migraines because of his second-century description of the symptoms of a unilateral headache associated with vomiting, with headache-free intervals in between attacks.
Galenus of Pergamon used the term "hemicrania" (half-head), from which the word "migraine" was derived. He thought there was a connection between the stomach
Stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow, dilated part of the alimentary canal which functions as an important organ of the digestive tract in some animals, including vertebrates, echinoderms, insects , and molluscs. It is involved in the second phase of digestion, following mastication .The stomach is...
and the brain because of the nausea and vomiting that often accompany an attack. For relief of migraine, Andalusian-born physician Abulcasis, also known as Abu El Qasim, suggested application of a hot iron to the head or insertion of garlic into an incision made in the temple.
In the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
. migraine was recognized as a discrete medical disorder. Followers of Galenus explained migraine as being caused by aggressive yellow bile.
Ebn Sina (Avicenna
Avicenna
Abū ʿAlī al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn Sīnā , commonly known as Ibn Sīnā or by his Latinized name Avicenna, was a Persian polymath, who wrote almost 450 treatises on a wide range of subjects, of which around 240 have survived...
) described migraine in his textbook "El Qanoon fel teb" as "... small movements, drinking and eating, and sounds provoke the pain... the patient cannot tolerate the sound of speaking and light. He would like to rest in darkness alone."
Abu Bakr Mohamed Ibn Zakariya Râzi noted the association of headache with different events in the lives of women, "...And such a headache may be observed after delivery and abortion
Abortion
Abortion is defined as the termination of pregnancy by the removal or expulsion from the uterus of a fetus or embryo prior to viability. An abortion can occur spontaneously, in which case it is usually called a miscarriage, or it can be purposely induced...
or during menopause
Menopause
Menopause is a term used to describe the permanent cessation of the primary functions of the human ovaries: the ripening and release of ova and the release of hormones that cause both the creation of the uterine lining and the subsequent shedding of the uterine lining...
and dysmenorrhea
Dysmenorrhea
Dysmenorrhea is a gynecological medical condition of pain during menstruation that interferes with daily activities, as defined by ACOG and others. Still, dysmenorrhea is often defined simply as menstrual pain, or at least menstrual pain that is excessive...
."
In Bibliotheca Anatomica, Medic, Chirurgica, published in London in 1712, five major types of headaches are described, including the "Megrim", recognizable as classic migraine. The term "classic migraine" is no longer used, and has been replaced by the term "migraine with aura" Graham and Wolff
Wolff
Wolff is the surname of:*Albert Wolff , Dutch conductor and pianist*Albert Wolff , German sculptor*Albert Moritz Wolff , German sculptor*Albert Wolff *Alexander Wolff, American writer...
(1938) published their paper advocating ergotamine tartrate for relieving migraine. Later in the 20th century, Harold Wolff (1950) developed the experimental approach to the study of headache and elaborated the vascular theory of migraine, which has come under attack as the pendulum again swings to the neurogenic theory. Recently, there has been renewed interest in Wolff's vascular theory of migraine led by Elliot Shevel
Elliot Shevel
Elliot Shevel BDS, DipMFOS, MBBCh is a South African Maxillo-Facial and Oral Surgeon, best known for his contribution to understanding of the underlying processes involved in the pain of migraine. He is, inter alia, a tireless campaigner to have the work of Harold Wolff, which many migraine...
, a South African headache specialist, who has published a number of articles providing compelling evidence that Wolff was correct.
Economic impact
Chronic migraine attacks are a significant source of both medical costs and lost productivity.It has been estimated to be the most costly neurological disorder in the European Community, costing more than €27 billion per year.
Research
Merck CorpMerck & Co.
Merck & Co., Inc. , also known as Merck Sharp & Dohme or MSD outside the United States and Canada, is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world. The Merck headquarters is located in Whitehouse Station, New Jersey, an unincorporated area in Readington Township...
new drug, Telcagepant, intended to relieve pain without causing vasoconstriction
Vasoconstriction
Vasoconstriction is the narrowing of the blood vessels resulting from contraction of the muscular wall of the vessels, particularly the large arteries, small arterioles and veins. The process is the opposite of vasodilation, the widening of blood vessels. The process is particularly important in...
(narrowing of blood vessels) as current medications such as triptans do, was pulled from the market after clinical trials showed liver function abnormalities in some study subjects. ^ Merck & Co.: Memo to all US study locations involved in protocol MK0974-049
Recently, calcitonin gene related peptides (CGRPs) have been found to play a role in the pathogenesis of the pain associated with migraine, as triptans also decrease its release and action. CGRP receptor antagonists, such as olcegepant and telcagepant
Telcagepant
Telcagepant was an investigational drug for the acute treatment and prevention of migraine, developed by Merck & Co. In the acute treatment of migraine, it was found to have equal potency to rizatriptan and zolmitriptan in two Phase III clinical trials...
, are being investigated both in vitro and in clinical studies for the treatment of migraine.
In 2010, scientists identified a genetic defect linked to migraines which could provide a target for new drug treatments.

