
Michael Praetorius
Encyclopedia
Michael Praetorius was a German composer
, organist
, and music theorist. He was one of the most versatile composers of his age, being particularly significant in the development of musical forms based on Protestant
hymn
s, many of which reflect an effort to make better the relationship between Protestants and Catholic
s.
, Thuringia
. After attending school in Torgau
and Zerbst
, he studied divinity
and philosophy
at the University of Frankfurt (Oder). After receiving his musical education, from 1587 he served as organist at the Marienkirche in Frankfurt. From 1592/3 he served at the court in Wolfenbüttel
, under the employ of Henry Julius, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg
. He served in the duke's State Orchestra Brunswick
first as organist
and later (from 1604) as Kapellmeister
.
His first compositions appeared around 1602/3. Praetorius had begun writing some of them when Regensburg
was the parliamentary seat of the Holy Roman Empire
. Their publication primarily reflects the care for music at the court of Gröningen
. The motet
s of this collection were the first in Germany to make use of the new Italian performance practices; as a result, they established him as a proficient composer.
These "modern" pieces mark the end of his middle creative period. The nine parts of his Musae Sioniae (1605–10) and the 1611 published collections of liturgical music (mass
es, hymn
s, magnificat
s) follow the German Protestant chorale
style. With these, at the behest of a circle of orthodox Lutherans, he followed the Duchess Elizabeth, who ruled the duchy in the duke's absence. In place of popular music, one now expected religious music from Praetorius.
When the duke died in 1613 and was succeeded by Frederick Ulrich
, Praetorius retained his employment. From 1613 he also worked at the court of John George I, Elector of Saxony
at Dresden
, where he was responsible for festive music. He was exposed to the latest Italian music, including the polychoral
works of the Venetian School. His subsequent development of the form of the chorale concerto
, particularly the polychoral variety, resulted directly from his familiarity with the music of such Venetians as Giovanni Gabrieli
. The solo-voice, polychoral, and instrumental compositions Praetorius prepared for these events mark the high period of his artistic creativity. Until his death, Praetorius stayed at the court in Dresden, where he was declared Kapellmeister von Haus aus and worked with Heinrich Schütz
.
Michael Praetorius died on his birthday, in Wolfenbüttel
, Germany and is entombed in a vault beneath the organ of St. Mary's Church in Wolfenbüttel.
was the conventional Latinized form of this family name.
 Praetorius was a prolific composer; his compositions show the influence of Italian composers and his younger contemporary Heinrich Schütz
Praetorius was a prolific composer; his compositions show the influence of Italian composers and his younger contemporary Heinrich Schütz
. His works include the nine volume Musae Sioniae (1605–10), a collection of more than one thousand (~1244) chorale
and song
arrangements; many other works for the Lutheran church; and Terpsichore
(1612), a compendium of more than 300 instrumental dances, which is both his most widely known work, and his sole surviving secular work.
, Christoph Bernhard
or Joachim Burmeister
, he compiled an encyclopedic record of contemporary musical practices. While Praetorius made some refinements to figured-bass practice and to tuning practice, his importance to scholars of the 17th century derives from his discussions of the normal use of instruments and voices in ensembles, the standard pitch of the time, and the state of modal, metrical, and fugal theory. His meticulous documentation of 17th-century practice was of inestimable value to the early-music revival of the 20th century.
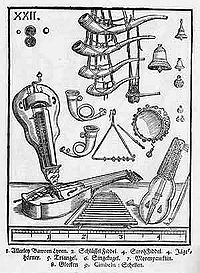
His expansive but incomplete treatise, Syntagma Musicum, appeared in three volumes (with appendix) between 1614 and 1620. The first volume (1614), titled Musicae Artis Analecta, was written mostly in Latin, and regarded the music of the ancients and of the church. The second (De Organographia, 1618) regarded the musical instruments of the day, especially the organ; it was one of the first theoretical treatises written in the vernacular. The third (Termini Musicali, 1618), also in German, regarded the genres of composition and the technical essentials for professional musicians. An appendix to the second volume (Theatrum Instrumentorum seu Sciagraphia, 1620) consisted of 42 beautifully drawn woodcuts, depicting instruments of the early 17th century, all grouped in families and shown to scale. A fourth volume on composition was planned, with the help of Baryphonus, but was left incomplete at his death.
Praetorius wrote in a florid style, replete with long asides, polemics, and word-puzzles – all typical of 17th-century scholarly prose. As a lifelong committed Christian
, he often regretted not taking holy orders but did write several theological tracts, which are now lost. As a Lutheran from a militantly Protestant family, he contributed greatly to the development of the vernacular liturgy, but also favored Italian compositional methods, performance practice and figured-bass notation.
Praetorius' most recognizable piece from Terpsichore, La Bouree, became part of current popular culture in several ways, including as part of the song, "Ding-Dong! The Witch is Dead" by The Fifth Estate
, first appearing on their album "The Rub-a-Dub," released in 1967 by Jubilee Records
. "La Bouree" was also played as the 7 AM time signal every weekday morning throughout the 1980s on WCPN
, Cleveland's NPR radio station.
Composer
A composer is a person who creates music, either by musical notation or oral tradition, for interpretation and performance, or through direct manipulation of sonic material through electronic media...
, organist
Organ (music)
The organ , is a keyboard instrument of one or more divisions, each played with its own keyboard operated either with the hands or with the feet. The organ is a relatively old musical instrument in the Western musical tradition, dating from the time of Ctesibius of Alexandria who is credited with...
, and music theorist. He was one of the most versatile composers of his age, being particularly significant in the development of musical forms based on Protestant
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
hymn
Hymn
A hymn is a type of song, usually religious, specifically written for the purpose of praise, adoration or prayer, and typically addressed to a deity or deities, or to a prominent figure or personification...
s, many of which reflect an effort to make better the relationship between Protestants and Catholic
Catholic
The word catholic comes from the Greek phrase , meaning "on the whole," "according to the whole" or "in general", and is a combination of the Greek words meaning "about" and meaning "whole"...
s.
Life
He was born Michael Schultze, the youngest son of a Lutheran pastor, in CreuzburgCreuzburg
Creuzburg is a town on the Werra river in the Wartburgkreis in Thuringia, Germany.-Geography:Creuzburg is in the area known as the Muschelkalk...
, Thuringia
Thuringia
The Free State of Thuringia is a state of Germany, located in the central part of the country.It has an area of and 2.29 million inhabitants, making it the sixth smallest by area and the fifth smallest by population of Germany's sixteen states....
. After attending school in Torgau
Torgau
Torgau is a town on the banks of the Elbe in northwestern Saxony, Germany. It is the capital of the district Nordsachsen.Outside Germany, the town is most well known as the place where during the Second World War, United States Army forces coming from the west met with forces of the Soviet Union...
and Zerbst
Zerbst
Zerbst is a town in the district of Anhalt-Bitterfeld, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Until the administrative reform of 2007, Zerbst was the capital of the Anhalt-Zerbst district. Since the 1 January 2010 local government reform, Zerbst has about 24,000 inhabitants.It is not clear when was it founded;...
, he studied divinity
Divinity
Divinity and divine are broadly applied but loosely defined terms, used variously within different faiths and belief systems — and even by different individuals within a given faith — to refer to some transcendent or transcendental power or deity, or its attributes or manifestations in...
and philosophy
Philosophy
Philosophy is the study of general and fundamental problems, such as those connected with existence, knowledge, values, reason, mind, and language. Philosophy is distinguished from other ways of addressing such problems by its critical, generally systematic approach and its reliance on rational...
at the University of Frankfurt (Oder). After receiving his musical education, from 1587 he served as organist at the Marienkirche in Frankfurt. From 1592/3 he served at the court in Wolfenbüttel
Wolfenbüttel
Wolfenbüttel is a town in Lower Saxony, Germany, located on the Oker river about 13 kilometres south of Brunswick. It is the seat of the District of Wolfenbüttel and of the bishop of the Protestant Lutheran State Church of Brunswick...
, under the employ of Henry Julius, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg
Henry Julius, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg
Henry Julius was duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg and prince of Wolfenbüttel from 1589 until his death. In 1576 he had become the first rector of the Protestant University of Helmstedt.- Life :...
. He served in the duke's State Orchestra Brunswick
Staatsorchester Braunschweig
The Staatsorchester Braunschweig is a German orchestra. It was founded in 1587 by Julius, Duke of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel as his court orchestra. It worked with Franz Liszt and Richard Strauss. It lost its independence as a court orchestra in 1918 and became the orchestra of the Braunschweiger...
first as organist
Organist
An organist is a musician who plays any type of organ. An organist may play solo organ works, play with an ensemble or orchestra, or accompany one or more singers or instrumental soloists...
and later (from 1604) as Kapellmeister
Kapellmeister
Kapellmeister is a German word designating a person in charge of music-making. The word is a compound, consisting of the roots Kapelle and Meister . The words Kapelle and Meister derive from the Latin: capella and magister...
.
His first compositions appeared around 1602/3. Praetorius had begun writing some of them when Regensburg
Regensburg
Regensburg is a city in Bavaria, Germany, located at the confluence of the Danube and Regen rivers, at the northernmost bend in the Danube. To the east lies the Bavarian Forest. Regensburg is the capital of the Bavarian administrative region Upper Palatinate...
was the parliamentary seat of the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
. Their publication primarily reflects the care for music at the court of Gröningen
Gröningen
Gröningen is a town in the Börde district in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It lies approx. 40 km south-west of Magdeburg, and 10 km east of Halberstadt. It has 4,180 inhabitants . Gröningen is part of the Verbandsgemeinde Westliche Börde....
. The motet
Motet
In classical music, motet is a word that is applied to a number of highly varied choral musical compositions.-Etymology:The name comes either from the Latin movere, or a Latinized version of Old French mot, "word" or "verbal utterance." The Medieval Latin for "motet" is motectum, and the Italian...
s of this collection were the first in Germany to make use of the new Italian performance practices; as a result, they established him as a proficient composer.
These "modern" pieces mark the end of his middle creative period. The nine parts of his Musae Sioniae (1605–10) and the 1611 published collections of liturgical music (mass
Mass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
es, hymn
Hymn
A hymn is a type of song, usually religious, specifically written for the purpose of praise, adoration or prayer, and typically addressed to a deity or deities, or to a prominent figure or personification...
s, magnificat
Magnificat
The Magnificat — also known as the Song of Mary or the Canticle of Mary — is a canticle frequently sung liturgically in Christian church services. It is one of the eight most ancient Christian hymns and perhaps the earliest Marian hymn...
s) follow the German Protestant chorale
Chorale
A chorale was originally a hymn sung by a Christian congregation. In certain modern usage, this term may also include classical settings of such hymns and works of a similar character....
style. With these, at the behest of a circle of orthodox Lutherans, he followed the Duchess Elizabeth, who ruled the duchy in the duke's absence. In place of popular music, one now expected religious music from Praetorius.
When the duke died in 1613 and was succeeded by Frederick Ulrich
Frederick Ulrich, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg
Frederick Ulrich , Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg, was prince of Wolfenbüttel from 1613 until his death....
, Praetorius retained his employment. From 1613 he also worked at the court of John George I, Elector of Saxony
John George I, Elector of Saxony
John George I was Elector of Saxony from 1611 to 1656.-Biography:Born in Dresden, he was the second son of the Elector Christian I and Sophie of Brandenburg....
at Dresden
Dresden
Dresden is the capital city of the Free State of Saxony in Germany. It is situated in a valley on the River Elbe, near the Czech border. The Dresden conurbation is part of the Saxon Triangle metropolitan area....
, where he was responsible for festive music. He was exposed to the latest Italian music, including the polychoral
Venetian polychoral style
The Venetian polychoral style was a type of music of the late Renaissance and early Baroque eras which involved spatially separate choirs singing in alternation...
works of the Venetian School. His subsequent development of the form of the chorale concerto
Chorale concerto
In music, a chorale concerto is a short sacred composition for one or more voices and instruments, principally from the very early German Baroque era...
, particularly the polychoral variety, resulted directly from his familiarity with the music of such Venetians as Giovanni Gabrieli
Giovanni Gabrieli
Giovanni Gabrieli was an Italian composer and organist. He was one of the most influential musicians of his time, and represents the culmination of the style of the Venetian School, at the time of the shift from Renaissance to Baroque idioms.-Biography:Gabrieli was born in Venice...
. The solo-voice, polychoral, and instrumental compositions Praetorius prepared for these events mark the high period of his artistic creativity. Until his death, Praetorius stayed at the court in Dresden, where he was declared Kapellmeister von Haus aus and worked with Heinrich Schütz
Heinrich Schütz
Heinrich Schütz was a German composer and organist, generally regarded as the most important German composer before Johann Sebastian Bach and often considered to be one of the most important composers of the 17th century along with Claudio Monteverdi...
.
Michael Praetorius died on his birthday, in Wolfenbüttel
Wolfenbüttel
Wolfenbüttel is a town in Lower Saxony, Germany, located on the Oker river about 13 kilometres south of Brunswick. It is the seat of the District of Wolfenbüttel and of the bishop of the Protestant Lutheran State Church of Brunswick...
, Germany and is entombed in a vault beneath the organ of St. Mary's Church in Wolfenbüttel.
Name
His family name in German appears in various forms including Schultze, Schulte, Schultheiss, Schulz and Schulteis. PraetoriusPraetorius
Praetorius, Prätorius, Prætorius was the name of several musicians and scholars in Germany.In Germany of the 16th and 17th centuries it became a fashion that educated people named "Schulze" or "Schultheiß" or "Richter", which means "judge", put their name into the Latin language as "Praetorius",...
was the conventional Latinized form of this family name.
Works

Heinrich Schütz
Heinrich Schütz was a German composer and organist, generally regarded as the most important German composer before Johann Sebastian Bach and often considered to be one of the most important composers of the 17th century along with Claudio Monteverdi...
. His works include the nine volume Musae Sioniae (1605–10), a collection of more than one thousand (~1244) chorale
Chorale
A chorale was originally a hymn sung by a Christian congregation. In certain modern usage, this term may also include classical settings of such hymns and works of a similar character....
and song
Song
In music, a song is a composition for voice or voices, performed by singing.A song may be accompanied by musical instruments, or it may be unaccompanied, as in the case of a cappella songs...
arrangements; many other works for the Lutheran church; and Terpsichore
Terpsichore
In Greek mythology, Terpsichore "delight of dancing" was one of the nine Muses, ruling over dance and the dramatic chorus. She lends her name to the word "terpsichorean" which means "of or relating to dance". She is usually depicted sitting down, holding a lyre, accompanying the dancers' choirs...
(1612), a compendium of more than 300 instrumental dances, which is both his most widely known work, and his sole surviving secular work.
Musical writings
Praetorius was the greatest musical academic of his day and the Germanic writer of music best known to other 17th-century musicians. Although his original theoretical contributions were relatively few, with nowhere near the long-range impact of other 17th-century German writers, like Johannes LippiusJohannes Lippius
Johannes Lippius was a German Protestant theologian, philosopher, composer and music theorist.- Life :...
, Christoph Bernhard
Christoph Bernhard
Christoph Bernhard was born in Kolberg, Pomerania, and died in Dresden. He studied with former Sweelinck-pupil Paul Siefert in Danzig and in Warsaw By the age of 20 he was singing at the electoral court in Dresden under Heinrich Schütz...
or Joachim Burmeister
Joachim Burmeister
Joachim Burmeister was a north German poet, composer and music theorist.He was the oldest of five children born to a beadworker and townsman of Lüneburg. His brother Anton became the cantor of St...
, he compiled an encyclopedic record of contemporary musical practices. While Praetorius made some refinements to figured-bass practice and to tuning practice, his importance to scholars of the 17th century derives from his discussions of the normal use of instruments and voices in ensembles, the standard pitch of the time, and the state of modal, metrical, and fugal theory. His meticulous documentation of 17th-century practice was of inestimable value to the early-music revival of the 20th century.
His expansive but incomplete treatise, Syntagma Musicum, appeared in three volumes (with appendix) between 1614 and 1620. The first volume (1614), titled Musicae Artis Analecta, was written mostly in Latin, and regarded the music of the ancients and of the church. The second (De Organographia, 1618) regarded the musical instruments of the day, especially the organ; it was one of the first theoretical treatises written in the vernacular. The third (Termini Musicali, 1618), also in German, regarded the genres of composition and the technical essentials for professional musicians. An appendix to the second volume (Theatrum Instrumentorum seu Sciagraphia, 1620) consisted of 42 beautifully drawn woodcuts, depicting instruments of the early 17th century, all grouped in families and shown to scale. A fourth volume on composition was planned, with the help of Baryphonus, but was left incomplete at his death.
Praetorius wrote in a florid style, replete with long asides, polemics, and word-puzzles – all typical of 17th-century scholarly prose. As a lifelong committed Christian
Christian
A Christian is a person who adheres to Christianity, an Abrahamic, monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth as recorded in the Canonical gospels and the letters of the New Testament...
, he often regretted not taking holy orders but did write several theological tracts, which are now lost. As a Lutheran from a militantly Protestant family, he contributed greatly to the development of the vernacular liturgy, but also favored Italian compositional methods, performance practice and figured-bass notation.
Praetorius' most recognizable piece from Terpsichore, La Bouree, became part of current popular culture in several ways, including as part of the song, "Ding-Dong! The Witch is Dead" by The Fifth Estate
The fifth estate
the fifth estate is a Canadian television newsmagazine, which airs on the English language CBC Television network. The name is a play on the fact that the media are sometimes referred to as the Fourth Estate, and was chosen to highlight the program's determination to go beyond everyday news into...
, first appearing on their album "The Rub-a-Dub," released in 1967 by Jubilee Records
Jubilee Records
Jubilee Records was a record label specializing in rhythm and blues along with novelty records. It was founded in New York City in 1946 by Herb Abramson. Jerry Blaine became Abramson's partner. Blaine bought out Abramson's half of the company in 1947. The company name was Jay-Gee Recording...
. "La Bouree" was also played as the 7 AM time signal every weekday morning throughout the 1980s on WCPN
WCPN
WCPN — branded 90.3 WCPN — is a public radio station licensed to Cleveland, Ohio, and serving the serving Greater Cleveland area....
, Cleveland's NPR radio station.
See also
- CornettCornettThe cornett, cornetto or zink is an early wind instrument, dating from the Medieval, Renaissance and Baroque periods. It was used in what are now called alta capellas or wind ensembles. It is not to be confused with the trumpet-like instrument cornet.-Construction:There are three basic types of...
- CrumhornCrumhornThe crumhorn is a musical instrument of the woodwind family, most commonly used during the Renaissance period. In modern times, there has been a revival of interest in Early Music, and crumhorns are being played again....
- RecorderRecorderThe recorder is a woodwind musical instrument of the family known as fipple flutes or internal duct flutes—whistle-like instruments which include the tin whistle. The recorder is end-blown and the mouth of the instrument is constricted by a wooden plug, known as a block or fipple...
- SackbutSackbutThe sackbut is a trombone from the Renaissance and Baroque eras, i.e., a musical instrument in the brass family similar to the trumpet except characterised by a telescopic slide with which the player varies the length of the tube to change pitches, thus allowing them to obtain chromaticism, as...
- ShawmShawmThe shawm was a medieval and Renaissance musical instrument of the woodwind family made in Europe from the 12th century until the 17th century. It was developed from the oriental zurna and is the predecessor of the modern oboe. The body of the shawm was usually turned from a single piece of wood,...
- Tenor cornettTenor cornettThe tenor cornett or lizard was a common musical instrument in the Renaissance and Baroque periods. This instrument was normally built in C and the pedal note of the majority of tenor cornetts was the C below middle C. A number of surviving instruments feature a key to secure the lowest note...
- TromboneTromboneThe trombone is a musical instrument in the brass family. Like all brass instruments, sound is produced when the player’s vibrating lips cause the air column inside the instrument to vibrate...
External links
- Michael Praetorius, biography on Goldberg, the Early Music Portal.
- Michael Pratorius - facsimiles in The Royal Library, Copenhagen
- Listen to free Vocal Evangelical Church Music by Michael Praetorius at "Early Vocal Music Map" from Umeå Akademiska Kör.
- More free scores

