
Metal ions in aqueous solution
Encyclopedia
A metal ion in aqueous solution is a cation, dissolved in water
, of chemical formula
[M(H2O)n]z+. The solvation number, n, determined by a variety of experimental methods is 4 for Li+ and Be2+ and 6 for elements in rows 3 and 4 of the periodic table
. Lanthanide and actinide aqua ions have solvation number of 8 and 9. The strength of the bonds between the metal ion and water molecules in the primary solvation shell increases with the electrical charge, z, on the metal ion and decreases as its radius, r, increases. Aqua ions are subject to hydrolysis. The logarithm of the first hydrolysis constant is proportional to z2/r for most aqua ions. The aqua ion is associated, through hydrogen bond
ing with other water molecules in a secondary solvation shell. Water molecules in the first hydration shell exchange with molecules in the second solvation shell and molecules in the bulk liquid. The residence time of a molecule in the first shell varies among the chemical element
s from about 100 ps
to more than 200 y
. Aqua ions are prominent in electrochemistry
.
Most chemical element
s are metal
lic and form simple aqua ions with the formula [M(H2O)n]z+ when the oxidation state
is 1, 2 or 3. With the higher oxidation states the simple aqua ions dissociate
losing hydrogen ion
s to yield complexes that contain both water molecules and hydroxide or oxide ions, such as the vanadium
(IV) species [VO(H2O)5]2+. In the highest oxidation state only oxyanion
s, such as the permanganate
(VII) ion, MnO4- are known.
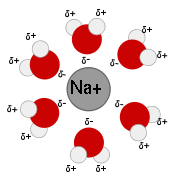 In aqueous solution the water molecules directly attached to the metal ion are said to belong to the first coordination sphere, also known as the first, or primary, solvation shell. The bond between a water molecule and the metal ion is a dative covalent bond, with the oxygen atom donating both electrons to the bond. Each coordinated water molecule may be attached by hydrogen bond
In aqueous solution the water molecules directly attached to the metal ion are said to belong to the first coordination sphere, also known as the first, or primary, solvation shell. The bond between a water molecule and the metal ion is a dative covalent bond, with the oxygen atom donating both electrons to the bond. Each coordinated water molecule may be attached by hydrogen bond
s to other water molecules. The latter are said to reside in the second coordination sphere. The second coordination sphere is not a well defined entity for ions with charge 1 or 2. In dilute solutions it merges into the water structure in which there is an irregular network of hydrogen bonds between water molecules. With tripositive ions the high charge on the cation polarizes the water molecules in the first solvation shell to such an extent that they form strong enough hydrogen bonds with molecules in the second shell to form a more stable entity.
The strength of the metal-oxygen bond can be estimated in various ways. The hydration enthalpy, though based indirectly on experimental measurements, is the most reliable measure. The scale of values is based on an arbitrarily chosen zero, but this does not affect differences between the values for two metals. Other measures include the M-O vibration frequency and the M-O bond length. The strength of the M-O bond tends to increase with the charge and decrease as the size of the metal ion increases. In fact there is a very good linear correlation between hydration enthalpy and the ratio of charge squared to ionic radius, z2/r. For ions in solution Shannon's "effective ionic radius" is the measure most often used.
Water molecules in the first and second solvation shells can exchange places. The rate of exchange varies enormously, depending on the metal and its oxidation state. Metal aqua ions are always accompanied in solution by solvated anions, but much less is known about anion solvation than about cation solvation.
Understanding of the nature of aqua ions is helped by having information on the nature of solvated cations in mixed solvents and non-aqueous solvent
s, such as liquid ammonia, methanol
, dimethyl formamide and dimethyl sulphoxide to mention a few.
.
Many other aqua ions are present in seawater in concentrations ranging from ppm
to ppt
. The concentrations of sodium, potassium, magnesium and calcium in blood
are similar to those of seawater. Blood also has lower concentrations of essential element
s such as iron and zinc. Sports drink
is designed to be isotonic
and also contains the minerals which are lost in perspiration.
Magnesium and calcium ions are common constituents of domestic water and are responsible for permanent and temporary hardness
, respectively. They are often found in mineral water
.
give separate peaks for molecules in the first solvation shell and for other water molecules. The solvation number is obtained as a ratio of peak areas. Here it refers to the number of water molecules in the first solvation shell. Molecules in the second solvation shell exchange rapidly with solvent molecules, giving rise to a small change in the chemical shift value of un-coordinated water molecules from that of water itself. The main disadvantage of this method is that it requires fairly concentrated solutions, with the associated risk of ion-pair formation with the anion.
from which the coordination number of the metal ion and metal-oxygen distance may be derived. With aqua ions of high charge some information is obtained about the second solvation shell.
This technique requires the use of relatively concentrated solutions. X-rays are scatted by electrons, so scattering power increases with atomic number. This makes hydrogen atoms all but invisible to X-ray scattering.
Large angle X-ray scattering has been used to characterize the second solvation shell with trivalent ions such as Cr3+ and Rh3+. The second hydration shell of Cr3+ was found to have 13 ± 1 molecules at an average distance of 402 ± 20 pm. This implies that every molecule in the first hydration shell is hydrogen bonded to two molecules in the second shell.
moles solute per kg of solvent. (b) angle between M-O and the H-m lines, m= mid point between H or D atoms. (c) Figures in brackets are standard deviation
s on the last sgnificant figure of the value.
Most of these data refer to concentrated solutions in which there are very few water molecules that are not in the primary hydration spheres of the cation or anion, which may account for some of the variation of solvation number with concentration even if there is no contact ion-pairing. The angle θ gives the angle of tilt of the water molecules relative to a plane in the aqua ion. This angle is affected by the hydrogen bonds formed between water molecules in the primary and secondary solvation shells.
The measured solvation number is a time-averaged value for the solution as a whole. When a measured primary solvation number is fractional there are two or more species with integral solvation numbers present in equilibrium with each other. This also applies to solvation numbers that are integral numbers, within experimental error. For example, the solvation number of 5.5 for a lithium chloride
solution could be interpreted as being due to presence of two different aqua ions with equal concentrations.
Another possibility is that there is interaction between a solvated cation and an anion, forming an ion-pair.This is particularly relevant when measurements are made on concentrated salt solutions. For example, a solvation number of 3 for a lithium chloride solution could be interpreted as being due to the equilibrium
lying wholly in favour of the ion-pair.
and Raman spectra
can be used to measure the M-O stretching frequency in metal aqua ions. Raman spectroscopy is particularly useful because the Raman spectrum of water is weak whereas the infrared spectrum of water is intense. Interpretation of the vibration frequencies is somewhat complicated by the presence, in octahedral and tetrahedral ions, of two vibrations, a symmetric one measured in the Raman spectrum and an anti-symmetric one, measured in the infrared spectrum.
Although the relationship between vibration frequency and force constant
is not simple, the general conclusion that can be taken from these data is that the strength of the M-O bond increases with increasing ionic charge and decreasing ionic size. The M-O stretching frequency of an aqua ion in solution may be compared with its counterpart in a crystal of known structure. If the frequencies are very similar it can be concluded that the coordination number of the metal ion is the same in solution as it is in a compound in the solid state.
, mobility
and diffusion
relate to the movement of ions through as solution. When an ion moves through a solution it tends to take both first and second solvation shells with it. Hence solvation numbers measured from dynamic properties tend to be much higher that those obtained from static properties.
[Be(H2O)4]2+ has a very well-defined primary solvation shell; The BeO4 part has tetrahedral symmetry
, Td. [Mg(H2O)6]2+ is also a well-characterized species, with an octahedral core. The situation for calcium is more complicated. Neutron diffraction data gave a solvation number for calcium chloride, CaCl2, which is strongly dependent on concentration: 10.0 ± 0.6 at 1 mol dm−3, decreasing to 6.4± 0.3 at 2.8 mol dm−3. The Shannon radius of the 6-coordinate calcium ion is 100 pm compared to 72 pm for magnesium, a 28% increase in size. This allows for higher aquation numbers and the lower charge density (z2/r) results in weaker M-O bonds, which makes ion-pairing easier. Various solid hydrates are known with 8-coordination in square antiprism
and dodecahedral geometry.
, with gallium
, indium
and thallium
. Nevertheless a comparison of aluminium and scandium
aqua ions illustrates a trend between the congener
s Na+/K+, Mg2+/Ca2+ and Al3+/Sc3+ which depends on the increase in size on going from row 3 to row 4 in the periodic table
. Shannon radii for 6-coordinate Al3+ and Sc3+ are 54 and 74.5 pm. Ga3+ has a Shannon radius of 62 pm, only about 13% larger than that of Al3+. This is due to the presence of the ten elements between scandium and gallium, which make an additional contribution to the general decrease in size across all rows of the periodic table. The aluminium aqua ion, [Al(H2O)6]3+ is very well characterized in solution and the solid state. The AlO6 core has octahedral symmetry, point group Oh.
There is now a substantial body of indirect evidence that seven molecules of water are present in the aqua ion of scandium
, Sc3+. Yttrium
(III) has approximately the same Shannon radius as holmium
(III) so Y3+ has very similar properties to those of Ho3+, so its aqua ion is probably 8-coordinate. The Lanthanum
aqua ion is probably 9-coordinate, as are those of the lighter lanthanides.
-3d-balls.png) The ions of these metals in the +2 and +3 oxidation state
The ions of these metals in the +2 and +3 oxidation state
s have a solvation number of 6. All have a regular octahedral structure except the aqua ions of chromium
(II) and copper
(II) which are subject to Jahn-Teller distortion. In the copper case the two axial Cu−O distances are 238 pm, whereas the four equatorial Cu−O distances are 195 pm. Silver
(I) is probably 4-coordinate, [Ag(H2O)4]+.
A solvation number of 6 with an octahedral structure is well established for zinc
(II) and cadmium
(II) in dilute solutions. In concentrated solutions the Zn2+ ion may adopt a 4-coordinate, tetrahedral, structure, but the evidence is not conclusive because of the possibility of ion-pairing and/or hydrolysis. The solvation number of mercury
(II)) is most likely to be 6.
The bis aqua structure of the mercury(I) ion,[(H2O)-Hg-Hg-(OH2]+, found in solid compounds, is also found in solution. Another aqua species in which there is a metal-metal bond is the molybdenum
(II) species formulated as [(H4O)-Mo-Mo-(OH4]4+ on the basis of theoretical considerations of the nature of the Mo-Mo bond. Each molybdenum is surrounded by four water molecules in a square-planar arrangement, in a structure similar to that of the known structure of the chloro complex [Mo2Cl8]4-. The presence of a fifth water molecule in the axial position is not ruled out, however.
There are a few divalent and trivalent aqua ions of transition metals in the second and third transition series. With oxidation state 4, however, only hydrolyzed species exist.
(III) and indium
(III) and thallium
(III)have a solvation number of 6. The aqua ion of thallium(I) is often assumed to be 6-coordinate, but this assumption is not based on strong experimental evidence. The Shannon radius of Tl+, at 150 pm, is not very different from that of K+, at 138 pm, so some similarity between Tl+ and K+ chemistry is both expected and observed.
The solvation number of the tin
(II) aqua ion, [Sn(H2O)n]2+ is not known with any certainty due to the presence of hydrolysis in the concentrated solutions needed for X-ray scattering measurements. The same is true for the lead
(II) aqua ion. With bismuth
(III) there is indirect evidence for a solvation number of 9. A nonahydrate is been characterized in the solid state, with a face-capped trigonal prism structure. The Shannon radius for 9-coordinate bismuth (115 pm) is comparable to that of neodymium (116.3 pm) for which a solvation number of 9 is well-established.
to lutetium, an effect known as the lanthanide contraction
. Nevertheless there is strong evidence that the hydration number changes from 9 to 8 at around gadolinium
. Structures of aqua ions in the solid state include the 9-coordinate tricapped trigonal prism structure with the lighter lanthanide ions and the 8-coordinate square antiprism
structure with the heavier lanthanide ions.There are no experimental data for the solvation state of cerium
(IV) or europium
(II).
Solvation numbers of 9 or more a believed to apply the actinide ions in the +3 and +4 oxidation states, but an experimental value is available only for thorium
(IV).
(VI) ions. They can be viewed as particularly stable hydrolysis products in a hypothetical reaction such as
The vanadium
has a distorted octahedral environment (point group C4v) of one oxide ion and 5 water molecules. Vanadium(V) is believed to exist as the dioxo-ion [VO2(H2O)4]+ at pH less than 2, but the evidence for this ion depends on the formation of complexes, such as oxalate
complexes which have been shown to have the VO2+ unit, with cis-VO bonds, in the solid state. The chromium
(IV) ion [CrO(H2O)5]2+ , similar to the vanadium ion has been proposed on the basis of indirect evidence.
The uranyl ion, UO22+, has a trans structure. The aqua ion UO22+(aq) has been assumed, on the basis of indirect evidence, to have 5 water molecules in the plane perpendicular to the O-U-O axis in a pentagonal bipyramid structure, point group D5h. However it is also possible that there are 6 water molecules in the equatorial plane, hexagonal bipyramid
, point group D6h, as many complexes with this structure are known. The solvation state of the plutonyl
ion, PuO22+, is not known.
and hydration entropy
. These quantities relate to the reaction
The enthalpy for this reaction is not directly measurable, because all measurements use salt solutions that contain both cation and anion. Most experimental measurements relate to the heat evolved when a salt dissolves in water, which gives the sum of cation and anion solvation enthalpies. Then, by considering the data for different anions with the same cation and different cations with the same anion, single ion values relative to an arbitrary zero, are derived.
Other values include Zn2+ -2044.3, Cd2+ -1805.8 and Ag+ -475.3 kJ mol−1.
There is an excellent linear correlation between hydration enthalpy and the ratio of charge squared, z2, to M-O distance, reff.
Values for transition metals are affected by crystal field stabilization. The general trend is shown by the magenta line which passes through Ca2+, Mn2+ and Zn2+, for which there is no stabilization in an octahedral crystal field. Hydration energy increases as size decreases. Crystal field splitting confers extra stability on the aqua ion. The maximum crystal field stabilization energy occurs at Ni2+. The agreement of the hydration enthalpies with predictions provided one basis for the general acceptance of crystal field theory.
The hydration enthalpies of the trivalent lanthanide
ions show an increasingly negative values at atomic number increases, in line with the decrease in ionic radius known as the lanthanide contraction
.
Single ion hydration entropy can be derived. Values are shown in the following table. The more negative the value, the more there is ordering in forming the aqua ion. It is notable that the heavy alkali metals have rather small entropy values which suggests that both the first and second solvation shells are somewhat indistinct.
the activity of the hydrolysis product, omitting the water molecules, is given by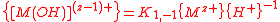
The alternative is to write the equilibrium as a complexation or substitution reaction
In which case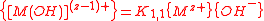
The concentration of hydrogen and hydroxide ions are related by the self-ionization of water
, Kw = {H+} {OH-} so the two equilibrium constants are related as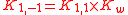
In practice the first definition is more useful because equilibrium constants are determined from measurements of hydrogen ion concentrations. In general,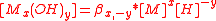
charges are omitted for the sake of generality and activities have been replaced by concentrations.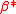 are cumulative hydrolysis constants.
are cumulative hydrolysis constants.
Modeling the hydrolysis reactions that occur in solution is usually based on the determination of equilibrium constants
from potentiometric (pH) titration data. The process is far from straightforward for a variety of reasons. Sometimes the species in solution can be precipitated as salts and their structure confirmed by X-ray crystallography. In other cases, precipitated salts bear no relation to what is postulated to be in solution, because a particular crystalline substances may have both low solubility and very low concentration in the solutions.
shows a linear relationship with the ratio of charge to M-O distance, z/d. Ions fall into four groups. The slope of the straight line is the same for all groups, but the intercept, A, is different.
The cations most resistant to hydrolysis for their size and charge are hard
pre-transition metal ions or lanthanide ions. The slightly less resistant group includes the transition metal ions. The third group contains mostly soft
ions ion of post-transition metals. The ions which show the strongest tendency to hydrolyze for their charge and size are Pd2+, Sn2+ and Hg2+.
The standard enthalpy change for the first hydrolysis step is generally not very different from that of the dissociation of pure water. Consequently, the standard enthalpy change for the substitution reaction
is close to zero. This is typical of reactions between a hard cation and a hard anion, such as the hydroxide ion. It means that the standard entropy charge is the major contributor to the standard free energy change and hence the equilibrium constant.
The change in ionic charge is responsible for the effect as the aqua ion has a greater ordering effect on the solution than the less highly charged hydroxo complex.
The hydrolysis product of aluminium
formulated as [Al13O4(OH)24(H2O)12]7+ is very well characterized and may be present in nature in water at pH ca. 5.4.
The overall reaction for the loss of two protons from an aqua ion can be written as
However, the equilibrium constant for the loss of two protons applies equally well to the equilibrium
because the concentration of water is assumed to be constant. This applies in general: any equilibrium constant is equally valid for a product with an oxide ion as for the product with two hydroxyl ions. The two possibilities can only be distinguished by determining the structure of a salt in the solid state. Oxo bridges tend to occur when the metal oxidation state is high. An example is provided by the molybdenum
(IV) complex [Mo3O4(H2O)9]4+ in which there is a triangle of molybdenum atoms joined by σ- bonds
with an oxide bridge on each edge of the triangle and a fourth oxide which bridges to all three Mo atoms.
is a dissociation reaction
.
The * symbol signifies that this is the transition state
in a chemical reaction. The rate of this reaction is proportional to the concentration of the aqua ion, [A].
The proportionality constant, k, is called a first-order rate constant at temperature T. The unit of the rate constant for water exchange is usually taken as mol dm−3s−1. The half-life
for this reaction is equal to loge2 / k. This measure is useful because it is independent of concentration. It has the dimension of time. The quantity 1/k, equal to the half life divided by 0.6932, is known as the residence time
or time constant
.
The residence time for water exchange varies from about 10−10 s
for Cs+ to about 10+10 s (more than 200 y
) for Ir3+. It depends on factors such as the size and charge on the ion and, in the case of transition metal ions, crystal field effects. Very fast and very slow reactions are difficult to study. The most information on the kinetics a water exchange comes from systems with a residence time between about 1 μs and 1 s. The enthalpy and entropy of activation, ΔH‡ and ΔS‡ can be obtained by observing the variation of rate constant with temperature.
The kinetic parameters for aqua ions of the transition metals are affected by crystal field stabilization energy (CFSE) on both the aqua ion and its dissociation product which has one less water molecule in the primary solvation shell. This explains the inertness (long residence time) of Cr3+, which has an octahedral structure and a d3 electronic configuration and Rh3+ and Ir3+ which are also octahedral and have a low-spin d6 configuration. Trivalent ions have longer residence time than divalent ions, except for the very large lanthanide ions. The values in the table show that this is due to both activation enthalpy and entropy factors.
Three possible mechanism arise.
This classification represents extreme cases; the actual mechanism may have something of an intermediate nature. The most useful parameter for distinguishing between possible mechanism is the activation volume change, ΔV‡, which is obtained from the pressure variation of the rate constant.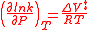
The activation volume increases for dissociative mechanisms and decreases for associative mechanisms.
In reality this is a substitution reaction in which one or more water molecules from the first hydration shell of the metal ion are replaced by ligands, L. The complex is described as an inner-sphere complex. A complex such as [ML](p-q)+ may be described as a contact ion pair.
When the water molecule(s) of the second hydration shell are replaced by ligands, the complex is said to be an outer-sphere complex, or solvent-shared ion pair. The formation of solvent-shared or contact ion pairs is particularly relevant to the determination of solvation numbers of aqua ions by methods that require the use of concentrated solutions of salts, as ion-pairing is concentration dependent. Consider, for example, the formation of the complex [MgCl]+ in solutions of MgCl2. The formation constant, K, of the complex is about 1 but varies with ionic strength. The concentration of the rather weak complex increases from about 0.1% for a 10mM solution to about 70% for a 1M solution (1M = 1 mol dm−3).
for the half-cell equilibrium Mz+ + z M(s) has been measured for all metals except for the heaviest trans-uranium elements.
As the standard electrode potential is more negative the aqua ion is more difficult to reduce. For example, comparing the potentials for zinc (-0.75 V) with those of iron (Fe(II) -0.47 V, Fe(III) -0.06 V) it is seen that iron ions are more easily reduced than zinc ions. This is the basis for using zinc to provide anodic protection
for large structures made of iron or to protect small structures by galvanization
.
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
, of chemical formula
Chemical formula
A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound....
[M(H2O)n]z+. The solvation number, n, determined by a variety of experimental methods is 4 for Li+ and Be2+ and 6 for elements in rows 3 and 4 of the periodic table
Periodic table
The periodic table of the chemical elements is a tabular display of the 118 known chemical elements organized by selected properties of their atomic structures. Elements are presented by increasing atomic number, the number of protons in an atom's atomic nucleus...
. Lanthanide and actinide aqua ions have solvation number of 8 and 9. The strength of the bonds between the metal ion and water molecules in the primary solvation shell increases with the electrical charge, z, on the metal ion and decreases as its radius, r, increases. Aqua ions are subject to hydrolysis. The logarithm of the first hydrolysis constant is proportional to z2/r for most aqua ions. The aqua ion is associated, through hydrogen bond
Hydrogen bond
A hydrogen bond is the attractive interaction of a hydrogen atom with an electronegative atom, such as nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine, that comes from another molecule or chemical group. The hydrogen must be covalently bonded to another electronegative atom to create the bond...
ing with other water molecules in a secondary solvation shell. Water molecules in the first hydration shell exchange with molecules in the second solvation shell and molecules in the bulk liquid. The residence time of a molecule in the first shell varies among the chemical element
Chemical element
A chemical element is a pure chemical substance consisting of one type of atom distinguished by its atomic number, which is the number of protons in its nucleus. Familiar examples of elements include carbon, oxygen, aluminum, iron, copper, gold, mercury, and lead.As of November 2011, 118 elements...
s from about 100 ps
Picosecond
A picosecond is 10−12 of a second. That is one trillionth, or one millionth of one millionth of a second, or 0.000 000 000 001 seconds. A picosecond is to one second as one second is to 31,700 years....
to more than 200 y
Year
A year is the orbital period of the Earth moving around the Sun. For an observer on Earth, this corresponds to the period it takes the Sun to complete one course throughout the zodiac along the ecliptic....
. Aqua ions are prominent in electrochemistry
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is a branch of chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place in a solution at the interface of an electron conductor and an ionic conductor , and which involve electron transfer between the electrode and the electrolyte or species in solution.If a chemical reaction is...
.
Introduction to metal aqua ions
| Li Lithium Lithium is a soft, silver-white metal that belongs to the alkali metal group of chemical elements. It is represented by the symbol Li, and it has the atomic number 3. Under standard conditions it is the lightest metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly... |
Be Beryllium Beryllium is the chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a divalent element which occurs naturally only in combination with other elements in minerals. Notable gemstones which contain beryllium include beryl and chrysoberyl... |
|||||||||||||||
| Na Sodium Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal and is a member of the alkali metals; its only stable isotope is 23Na. It is an abundant element that exists in numerous minerals, most commonly as sodium chloride... |
Mg Magnesium Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole... |
Al Aluminium Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances.... |
||||||||||||||
| K Potassium Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K and atomic number 19. Elemental potassium is a soft silvery-white alkali metal that oxidizes rapidly in air and is very reactive with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite the hydrogen emitted in the reaction.Potassium and sodium are... |
Ca Calcium Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust... |
Sc Scandium Scandium is a chemical element with symbol Sc and atomic number 21. A silvery-white metallic transition metal, it has historically been sometimes classified as a rare earth element, together with yttrium and the lanthanoids... |
Ti Titanium Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. It has a low density and is a strong, lustrous, corrosion-resistant transition metal with a silver color.... |
V Vanadium Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery gray, ductile and malleable transition metal. The formation of an oxide layer stabilizes the metal against oxidation. The element is found only in chemically combined form in nature... |
Cr Chromium Chromium is a chemical element which has the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6. It is a steely-gray, lustrous, hard metal that takes a high polish and has a high melting point. It is also odorless, tasteless, and malleable... |
Mn Manganese Manganese is a chemical element, designated by the symbol Mn. It has the atomic number 25. It is found as a free element in nature , and in many minerals... |
Fe Iron Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust... |
Co Cobalt Cobalt is a chemical element with symbol Co and atomic number 27. It is found naturally only in chemically combined form. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal.... |
Ni Nickel Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile... |
Cu Copper Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish... |
Zn Zinc Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2... |
Ga Gallium Gallium is a chemical element that has the symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Elemental gallium does not occur in nature, but as the gallium salt in trace amounts in bauxite and zinc ores. A soft silvery metallic poor metal, elemental gallium is a brittle solid at low temperatures. As it liquefies... |
||||
| Rb Rubidium Rubidium is a chemical element with the symbol Rb and atomic number 37. Rubidium is a soft, silvery-white metallic element of the alkali metal group. Its atomic mass is 85.4678. Elemental rubidium is highly reactive, with properties similar to those of other elements in group 1, such as very rapid... |
Sr Strontium Strontium is a chemical element with the symbol Sr and the atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white or yellowish metallic element that is highly reactive chemically. The metal turns yellow when exposed to air. It occurs naturally in the minerals celestine and... |
Y Yttrium Yttrium is a chemical element with symbol Y and atomic number 39. It is a silvery-metallic transition metal chemically similar to the lanthanides and it has often been classified as a "rare earth element". Yttrium is almost always found combined with the lanthanides in rare earth minerals and is... |
Zr Zirconium Zirconium is a chemical element with the symbol Zr and atomic number 40. The name of zirconium is taken from the mineral zircon. Its atomic mass is 91.224. It is a lustrous, grey-white, strong transition metal that resembles titanium... |
Nb Niobium Niobium or columbium , is a chemical element with the symbol Nb and atomic number 41. It's a soft, grey, ductile transition metal, which is often found in the pyrochlore mineral, the main commercial source for niobium, and columbite... |
Mo Molybdenum Molybdenum , is a Group 6 chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42. The name is from Neo-Latin Molybdaenum, from Ancient Greek , meaning lead, itself proposed as a loanword from Anatolian Luvian and Lydian languages, since its ores were confused with lead ores... |
Tc Technetium Technetium is the chemical element with atomic number 43 and symbol Tc. It is the lowest atomic number element without any stable isotopes; every form of it is radioactive. Nearly all technetium is produced synthetically and only minute amounts are found in nature... |
Ru Ruthenium Ruthenium is a chemical element with symbol Ru and atomic number 44. It is a rare transition metal belonging to the platinum group of the periodic table. Like the other metals of the platinum group, ruthenium is inert to most chemicals. The Russian scientist Karl Ernst Claus discovered the element... |
Rh Rhodium Rhodium is a chemical element that is a rare, silvery-white, hard and chemically inert transition metal and a member of the platinum group. It has the chemical symbol Rh and atomic number 45. It is composed of only one isotope, 103Rh. Naturally occurring rhodium is found as the free metal, alloyed... |
Pd Palladium Palladium is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pd and an atomic number of 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas, which was itself named after the epithet of the Greek goddess Athena, acquired... |
Ag Silver Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal... |
Cd Cadmium Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, bluish-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Similar to zinc, it prefers oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds and similar to mercury it shows a low... |
In Indium Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. This rare, very soft, malleable and easily fusible post-transition metal is chemically similar to gallium and thallium, and shows the intermediate properties between these two... |
Sn Tin Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn and atomic number 50. It is a main group metal in group 14 of the periodic table. Tin shows chemical similarity to both neighboring group 14 elements, germanium and lead and has two possible oxidation states, +2 and the slightly more stable +4... |
|||
| Cs | Ba Barium Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in Group 2, a soft silvery metallic alkaline earth metal. Barium is never found in nature in its pure form due to its reactivity with air. Its oxide is historically known as baryta but it reacts with... |
La Lanthanum Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57.Lanthanum is a silvery white metallic element that belongs to group 3 of the periodic table and is the first element of the lanthanide series. It is found in some rare-earth minerals, usually in combination with cerium and... † |
Hf Hafnium Hafnium is a chemical element with the symbol Hf and atomic number 72. A lustrous, silvery gray, tetravalent transition metal, hafnium chemically resembles zirconium and is found in zirconium minerals. Its existence was predicted by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. Hafnium was the penultimate stable... |
Ta Tantalum Tantalum is a chemical element with the symbol Ta and atomic number 73. Previously known as tantalium, the name comes from Tantalus, a character in Greek mythology. Tantalum is a rare, hard, blue-gray, lustrous transition metal that is highly corrosion resistant. It is part of the refractory... |
W Tungsten Tungsten , also known as wolfram , is a chemical element with the chemical symbol W and atomic number 74.A hard, rare metal under standard conditions when uncombined, tungsten is found naturally on Earth only in chemical compounds. It was identified as a new element in 1781, and first isolated as... |
Re Rhenium Rhenium is a chemical element with the symbol Re and atomic number 75. It is a silvery-white, heavy, third-row transition metal in group 7 of the periodic table. With an average concentration of 1 part per billion , rhenium is one of the rarest elements in the Earth's crust. The free element has... |
Os Osmium Osmium is a chemical element with the symbol Os and atomic number 76. Osmium is a hard, brittle, blue-gray or blue-blacktransition metal in the platinum family, and is the densest natural element. Osmium is twice as dense as lead. The density of osmium is , slightly greater than that of iridium,... |
Ir Iridium Iridium is the chemical element with atomic number 77, and is represented by the symbol Ir. A very hard, brittle, silvery-white transition metal of the platinum family, iridium is the second-densest element and is the most corrosion-resistant metal, even at temperatures as high as 2000 °C... |
Pt Platinum Platinum is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pt and an atomic number of 78. Its name is derived from the Spanish term platina del Pinto, which is literally translated into "little silver of the Pinto River." It is a dense, malleable, ductile, precious, gray-white transition metal... |
Au Gold Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a... |
Hg Mercury (element) Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum... |
Tl Thallium Thallium is a chemical element with the symbol Tl and atomic number 81. This soft gray poor metal resembles tin but discolors when exposed to air. The two chemists William Crookes and Claude-Auguste Lamy discovered thallium independently in 1861 by the newly developed method of flame spectroscopy... |
Pb Lead Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed... |
Bi Bismuth Bismuth is a chemical element with symbol Bi and atomic number 83. Bismuth, a trivalent poor metal, chemically resembles arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth may occur naturally uncombined, although its sulfide and oxide form important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead... |
Po Polonium Polonium is a chemical element with the symbol Po and atomic number 84, discovered in 1898 by Marie Skłodowska-Curie and Pierre Curie. A rare and highly radioactive element, polonium is chemically similar to bismuth and tellurium, and it occurs in uranium ores. Polonium has been studied for... |
|
| Fr Francium Francium is a chemical element with symbol Fr and atomic number 87. It was formerly known as eka-caesium and actinium K.Actually the least unstable isotope, francium-223 It has the lowest electronegativity of all known elements, and is the second rarest naturally occurring element... |
Ra Radium Radium is a chemical element with atomic number 88, represented by the symbol Ra. Radium is an almost pure-white alkaline earth metal, but it readily oxidizes on exposure to air, becoming black in color. All isotopes of radium are highly radioactive, with the most stable isotope being radium-226,... |
Ac Actinium Actinium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Ac and atomic number 89, which was discovered in 1899. It was the first non-primordial radioactive element to be isolated. Polonium, radium and radon were observed before actinium, but they were not isolated until 1902... ‡ |
||||||||||||||
| (La)† | Ce Cerium Cerium is a chemical element with the symbol Ce and atomic number 58. It is a soft, silvery, ductile metal which easily oxidizes in air. Cerium was named after the dwarf planet . Cerium is the most abundant of the rare earth elements, making up about 0.0046% of the Earth's crust by weight... |
Pr Praseodymium Praseodymium is a chemical element that has the symbol Pr and atomic number 59. Praseodymium is a soft, silvery, malleable and ductile metal in the lanthanide group. It is too reactive to be found in native form, and when artificially prepared, it slowly develops a green oxide coating.The element... |
Nd Neodymium Neodymium is a chemical element with the symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is a soft silvery metal that tarnishes in air. Neodymium was discovered in 1885 by the Austrian chemist Carl Auer von Welsbach. It is present in significant quantities in the ore minerals monazite and bastnäsite... |
Pm Promethium Promethium is a chemical element with the symbol Pm and atomic number 61. It is notable for being the only exclusively radioactive element besides technetium that is followed by chemical elements with stable isotopes.- Prediction :... |
Sm Samarium Samarium is a chemical element with the symbol Sm, atomic number 62 and atomic weight 150.36. It is a moderately hard silvery metal which readily oxidizes in air. Being a typical member of the lanthanide series, samarium usually assumes the oxidation state +3... |
Eu Europium Europium is a chemical element with the symbol Eu and atomic number 63. It is named after the continent of Europe. It is a moderately hard silvery metal which readily oxidizes in air and water... |
Gd Gadolinium Gadolinium is a chemical element with the symbol Gd and atomic number 64. It is a silvery-white, malleable and ductile rare-earth metal. It is found in nature only in combined form. Gadolinium was first detected spectroscopically in 1880 by de Marignac who separated its oxide and is credited with... |
Tb Terbium Terbium is a chemical element with the symbol Tb and atomic number 65. It is a silvery-white rare earth metal that is malleable, ductile and soft enough to be cut with a knife... |
Dy Dysprosium Dysprosium is a chemical element with the symbol Dy and atomic number 66. It is a rare earth element with a metallic silver luster. Dysprosium is never found in nature as a free element, though it is found in various minerals, such as xenotime... |
Ho Holmium Holmium is a chemical element with the symbol Ho and atomic number 67. Part of the lanthanide series, holmium is a rare earth element. Its oxide was first isolated from rare earth ores in 1878 and the element was named after the city of Stockholm.... |
Er Erbium Erbium is a chemical element in the lanthanide series, with the symbol Er and atomic number 68. A silvery-white solid metal when artificially isolated, natural erbium is always found in chemical combination with other elements on Earth... |
Tb Thulium Thulium is a chemical element that has the symbol Tm and atomic number 69. Thulium is the second least abundant of the lanthanides . It is an easily workable metal with a bright silvery-gray luster... |
Yb Ytterbium Ytterbium is a chemical element with the symbol Yb and atomic number 70. A soft silvery metallic element, ytterbium is a rare earth element of the lanthanide series and is found in the minerals gadolinite, monazite, and xenotime. The element is sometimes associated with yttrium or other related... |
Lu | ||
| (Ac)‡ | Th Thorium Thorium is a natural radioactive chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. It was discovered in 1828 and named after Thor, the Norse god of thunder.... |
Pa | U Uranium Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons... |
Np Neptunium Neptunium is a chemical element with the symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element and belongs to the actinide series. Its most stable isotope, 237Np, is a by-product of nuclear reactors and plutonium production and it can be used as a... |
Pu Plutonium Plutonium is a transuranic radioactive chemical element with the chemical symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, forming a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation... |
Am Americium Americium is a synthetic element that has the symbol Am and atomic number 95. This transuranic element of the actinide series is located in the periodic table below the lanthanide element europium, and thus by analogy was named after another continent, America.Americium was first produced in 1944... |
Cm Curium Curium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This radioactive transuranic element of the actinide series was named after Marie Skłodowska-Curie and her husband Pierre Curie. Curium was first intentionally produced and identified in summer 1944 by the group of... |
Bk Berkelium Berkelium , is a synthetic element with the symbol Bk and atomic number 97, a member of the actinide and transuranium element series. It is named after the city of Berkeley, California, the location of the University of California Radiation Laboratory where it was discovered in December 1949... |
Cf Californium Californium is a radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Cf and atomic number 98. The element was first made in the laboratory in 1950 by bombarding curium with alpha particles at the University of California, Berkeley. It is the ninth member of the actinide series and was the... |
Es Einsteinium Einsteinium is a synthetic element with the symbol Es and atomic number 99. It is the seventh transuranic element, and an actinide.Einsteinium was discovered in the debris of the first hydrogen bomb explosion in 1952, and named after Albert Einstein... |
Fm Fermium Fermium is a synthetic element with the symbol Fm. It is the 100th element in the periodic table and a member of the actinide series. It is the heaviest element that can be formed by neutron bombardment of lighter elements, and hence the last element that can be prepared in macroscopic quantities,... |
Md Mendelevium Mendelevium is a synthetic element with the symbol Md and the atomic number 101. A metallic radioactive transuranic element in the actinide series, mendelevium is usually synthesized by bombarding einsteinium with alpha particles. It was named after Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev, who created the... |
No Nobelium Nobelium is a synthetic element with the symbol No and atomic number 102. It was first correctly identified in 1966 by scientists at the Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions in Dubna, Soviet Union... |
Lr Lawrencium Lawrencium is a radioactive synthetic chemical element with the symbol Lr and atomic number 103. In the periodic table of the elements, it is a period 7 d-block element and the last element of actinide series... |
||
Most chemical element
Chemical element
A chemical element is a pure chemical substance consisting of one type of atom distinguished by its atomic number, which is the number of protons in its nucleus. Familiar examples of elements include carbon, oxygen, aluminum, iron, copper, gold, mercury, and lead.As of November 2011, 118 elements...
s are metal
Metal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
lic and form simple aqua ions with the formula [M(H2O)n]z+ when the oxidation state
Oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state is an indicator of the degree of oxidation of an atom in a chemical compound. The formal oxidation state is the hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all bonds to atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Oxidation states are typically represented by...
is 1, 2 or 3. With the higher oxidation states the simple aqua ions dissociate
Dissociation (chemistry)
Dissociation in chemistry and biochemistry is a general process in which ionic compounds separate or split into smaller particles, ions, or radicals, usually in a reversible manner...
losing hydrogen ion
Hydrogen ion
Hydrogen ion is recommended by IUPAC as a general term for all ions of hydrogen and its isotopes.Depending on the charge of the ion, two different classes can be distinguished: positively charged ions and negatively charged ions....
s to yield complexes that contain both water molecules and hydroxide or oxide ions, such as the vanadium
Vanadium
Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery gray, ductile and malleable transition metal. The formation of an oxide layer stabilizes the metal against oxidation. The element is found only in chemically combined form in nature...
(IV) species [VO(H2O)5]2+. In the highest oxidation state only oxyanion
Oxyanion
An oxyanion or oxoanion is a chemical compound with the generic formula AxOyz− . Oxoanions are formed by a large majority of the chemical elements. The formulae of simple oxoanions are determined by the octet rule...
s, such as the permanganate
Permanganate
A permanganate is the general name for a chemical compound containing the manganate ion, . Because manganese is in the +7 oxidation state, the permanganate ion is a strong oxidizing agent. The ion has tetrahedral geometry...
(VII) ion, MnO4- are known.

Hydrogen bond
A hydrogen bond is the attractive interaction of a hydrogen atom with an electronegative atom, such as nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine, that comes from another molecule or chemical group. The hydrogen must be covalently bonded to another electronegative atom to create the bond...
s to other water molecules. The latter are said to reside in the second coordination sphere. The second coordination sphere is not a well defined entity for ions with charge 1 or 2. In dilute solutions it merges into the water structure in which there is an irregular network of hydrogen bonds between water molecules. With tripositive ions the high charge on the cation polarizes the water molecules in the first solvation shell to such an extent that they form strong enough hydrogen bonds with molecules in the second shell to form a more stable entity.
The strength of the metal-oxygen bond can be estimated in various ways. The hydration enthalpy, though based indirectly on experimental measurements, is the most reliable measure. The scale of values is based on an arbitrarily chosen zero, but this does not affect differences between the values for two metals. Other measures include the M-O vibration frequency and the M-O bond length. The strength of the M-O bond tends to increase with the charge and decrease as the size of the metal ion increases. In fact there is a very good linear correlation between hydration enthalpy and the ratio of charge squared to ionic radius, z2/r. For ions in solution Shannon's "effective ionic radius" is the measure most often used.
Water molecules in the first and second solvation shells can exchange places. The rate of exchange varies enormously, depending on the metal and its oxidation state. Metal aqua ions are always accompanied in solution by solvated anions, but much less is known about anion solvation than about cation solvation.
Understanding of the nature of aqua ions is helped by having information on the nature of solvated cations in mixed solvents and non-aqueous solvent
Solvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
s, such as liquid ammonia, methanol
Methanol
Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol, wood alcohol, wood naphtha or wood spirits, is a chemical with the formula CH3OH . It is the simplest alcohol, and is a light, volatile, colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive odor very similar to, but slightly sweeter than, ethanol...
, dimethyl formamide and dimethyl sulphoxide to mention a few.
Occurrence in nature
Aqua ions are present in most natural waters. Na+, K+, Mg2+ and Ca2+ are major constiuents of seawaterSeawater
Seawater is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% . This means that every kilogram of seawater has approximately of dissolved salts . The average density of seawater at the ocean surface is 1.025 g/ml...
.
Many other aqua ions are present in seawater in concentrations ranging from ppm
Parts-per notation
In science and engineering, the parts-per notation is a set of pseudo units to describe small values of miscellaneous dimensionless quantities, e.g. mole fraction or mass fraction. Since these fractions are quantity-per-quantity measures, they are pure numbers with no associated units of measurement...
to ppt
Parts-per notation
In science and engineering, the parts-per notation is a set of pseudo units to describe small values of miscellaneous dimensionless quantities, e.g. mole fraction or mass fraction. Since these fractions are quantity-per-quantity measures, they are pure numbers with no associated units of measurement...
. The concentrations of sodium, potassium, magnesium and calcium in blood
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
are similar to those of seawater. Blood also has lower concentrations of essential element
Dietary mineral
Dietary minerals are the chemical elements required by living organisms, other than the four elements carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen present in common organic molecules. Examples of mineral elements include calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, zinc, and iodine...
s such as iron and zinc. Sports drink
Sports drink
A sports drink beverage is designed to help athletes rehydrate when fluids are depleted after training or competition. Electrolyte replacement promotes proper rehydration, which is important in delaying the onset of fatigue during exercise...
is designed to be isotonic
Isotonic
The term isotonic may refer to;*Isotonic for the term associated with muscle contraction*An isotone in nuclear physics*Sports drinks are sometimes designed in an isotonic way to assist athletes rehydrate while balancing electrolytes...
and also contains the minerals which are lost in perspiration.
Magnesium and calcium ions are common constituents of domestic water and are responsible for permanent and temporary hardness
Hard water
Hard water is water that has high mineral content . Hard water has high concentrations of Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions. Hard water is generally not harmful to one's health but can pose serious problems in industrial settings, where water hardness is monitored to avoid costly breakdowns in boilers, cooling...
, respectively. They are often found in mineral water
Mineral water
Mineral water is water containing minerals or other dissolved substances that alter its taste or give it therapeutic value, generally obtained from a naturally occurring mineral spring or source. Dissolved substances in the water may include various salts and sulfur compounds...
.
Experimental methods
Information obtained on the nature of ions in solution varies with the nature of the experimental method used. Some methods reveal properties of the cation directly, others reveal properties that depend on both cation and anion. Some methods supply information of a static nature, a kind of snapshot of average properties, others give information about the dynamics of the solution.Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
Ions for which the water-exchange rate is slow on the NMR time-scaleRelaxation (NMR)
In nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and magnetic resonance imaging the term relaxation describes several processes by which nuclear magnetization prepared in a non-equilibrium state return to the equilibrium distribution. In other words, relaxation describes how fast spins "forget" the...
give separate peaks for molecules in the first solvation shell and for other water molecules. The solvation number is obtained as a ratio of peak areas. Here it refers to the number of water molecules in the first solvation shell. Molecules in the second solvation shell exchange rapidly with solvent molecules, giving rise to a small change in the chemical shift value of un-coordinated water molecules from that of water itself. The main disadvantage of this method is that it requires fairly concentrated solutions, with the associated risk of ion-pair formation with the anion.
| ion | number | nucleus |
|---|---|---|
| Be Beryllium Beryllium is the chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a divalent element which occurs naturally only in combination with other elements in minerals. Notable gemstones which contain beryllium include beryl and chrysoberyl... 2+ |
4 | 1H 17O |
| Mg Magnesium Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole... 2+ |
6 | 1H |
| Zn Zinc Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2... 2+ |
6 | 1H |
| Al Aluminium Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances.... 3+ |
6 | 1H 17O |
| Ga Gallium Gallium is a chemical element that has the symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Elemental gallium does not occur in nature, but as the gallium salt in trace amounts in bauxite and zinc ores. A soft silvery metallic poor metal, elemental gallium is a brittle solid at low temperatures. As it liquefies... 3+ |
6 | 1H 17O |
| In Indium Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. This rare, very soft, malleable and easily fusible post-transition metal is chemically similar to gallium and thallium, and shows the intermediate properties between these two... 3+ |
6 | 1H |
| Fe Iron Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust... 2+ |
6 | 17O |
| Co Cobalt Cobalt is a chemical element with symbol Co and atomic number 27. It is found naturally only in chemically combined form. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal.... 2+ |
6 | 1H |
| Ni Nickel Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile... 2+ |
6 | 1H 17O |
| Th Thorium Thorium is a natural radioactive chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. It was discovered in 1828 and named after Thor, the Norse god of thunder.... 4+ |
9 | 1H |
X-ray diffraction (XRD)
A solution containing an aqua ion does not have the long-range order that would be present in a crystal containing the same ion, but there is short-range order. X-ray diffraction on solutions yields a radial distribution functionRadial distribution function
In statistical mechanics, a radial distribution function , g, describes how the atomic density varies as a function of the distance from one particular atom....
from which the coordination number of the metal ion and metal-oxygen distance may be derived. With aqua ions of high charge some information is obtained about the second solvation shell.
This technique requires the use of relatively concentrated solutions. X-rays are scatted by electrons, so scattering power increases with atomic number. This makes hydrogen atoms all but invisible to X-ray scattering.
Large angle X-ray scattering has been used to characterize the second solvation shell with trivalent ions such as Cr3+ and Rh3+. The second hydration shell of Cr3+ was found to have 13 ± 1 molecules at an average distance of 402 ± 20 pm. This implies that every molecule in the first hydration shell is hydrogen bonded to two molecules in the second shell.
Neutron diffraction
Diffraction by neutrons also give a radial distribution function. In contrast to X-ray diffraction, neutrons are scatted by nuclei and there is no relationship with atomic number. Indeed, use can be made of the fact that different isotopes of the same element can have widely different scattering powers. In a classic experiment, measurements were made on four nickel chloride solutions using the combinations of 58Ni, 60Ni, 35Cl and 37Cl isotopes to yield a very detailed picture of cation and anion solvation. Data for a number of metal salts show some dependence on the salt concentration.| Cation | Anion!!Molality /mol kg-1 (a)!!Hydration number!!θ /deg (b) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li Lithium Lithium is a soft, silver-white metal that belongs to the alkali metal group of chemical elements. It is represented by the symbol Li, and it has the atomic number 3. Under standard conditions it is the lightest metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly... + |
Cl- | 27.77 | 2.3 (2)(c) | 75 (5) |
| 9.95 | 3.0 (5) | 52 (5) | ||
| 3.57 | 5.5 (3) | 40 (5) | ||
| Ca Calcium Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust... 2+ |
Cl- | 4.49 | 6.4 (3) | 34 (9) |
| 2.80 | 7.2 (2) | 34 (9) | ||
| 1.0 | 10.0 (6) | 38 (9) | ||
| Ni Nickel Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile... 2+ |
Cl- | 3.05 | 5.8 (2) | 42 (8) |
| 0.85 | 6.6 (5) | 27 (10) | ||
| 0.46 | 6.8 (8) | 17 (10) | ||
| 0.086 | 6.8 (8) | 0 (20) | ||
| Ni Nickel Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile... 2+ |
ClO4- | 3.80 | 5.8 (2) | 42 (8) |
| Cu Copper Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish... 2+ |
ClO4- | 2.00 | 4.9 (3) | 38 (6) |
| Fe Iron Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust... 3+ |
NO3- | 2.0 | 5.0 (2) | 22 (4) |
| Nd Neodymium Neodymium is a chemical element with the symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is a soft silvery metal that tarnishes in air. Neodymium was discovered in 1885 by the Austrian chemist Carl Auer von Welsbach. It is present in significant quantities in the ore minerals monazite and bastnäsite... 3+ |
Cl- | 2.85 | 8.5 (2) | 24 (4) |
| Dy Dysprosium Dysprosium is a chemical element with the symbol Dy and atomic number 66. It is a rare earth element with a metallic silver luster. Dysprosium is never found in nature as a free element, though it is found in various minerals, such as xenotime... 3+ |
Cl- | 2.38 | 7.4 (5) | 17 (3) |
Standard deviation
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
s on the last sgnificant figure of the value.
Most of these data refer to concentrated solutions in which there are very few water molecules that are not in the primary hydration spheres of the cation or anion, which may account for some of the variation of solvation number with concentration even if there is no contact ion-pairing. The angle θ gives the angle of tilt of the water molecules relative to a plane in the aqua ion. This angle is affected by the hydrogen bonds formed between water molecules in the primary and secondary solvation shells.
The measured solvation number is a time-averaged value for the solution as a whole. When a measured primary solvation number is fractional there are two or more species with integral solvation numbers present in equilibrium with each other. This also applies to solvation numbers that are integral numbers, within experimental error. For example, the solvation number of 5.5 for a lithium chloride
Lithium chloride
Lithium chloride is a chemical compound with the formula LiCl. The salt is a typical ionic compound, although the small size of the Li+ ion gives rise to properties not seen for other alkali metal chlorides, such as extraordinary solubility in polar solvents and its hygroscopic...
solution could be interpreted as being due to presence of two different aqua ions with equal concentrations.
- [Li(H2O)6]+ [Li(H2O)5]+ + H2O
Another possibility is that there is interaction between a solvated cation and an anion, forming an ion-pair.This is particularly relevant when measurements are made on concentrated salt solutions. For example, a solvation number of 3 for a lithium chloride solution could be interpreted as being due to the equilibrium
- [Li(H2O)4]+ + Cl- [Li(H2O)3Cl] + H2O
lying wholly in favour of the ion-pair.
Vibrational spectra
Infrared spectraInfrared spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy is the spectroscopy that deals with the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum, that is light with a longer wavelength and lower frequency than visible light. It covers a range of techniques, mostly based on absorption spectroscopy. As with all spectroscopic...
and Raman spectra
Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique used to study vibrational, rotational, and other low-frequency modes in a system.It relies on inelastic scattering, or Raman scattering, of monochromatic light, usually from a laser in the visible, near infrared, or near ultraviolet range...
can be used to measure the M-O stretching frequency in metal aqua ions. Raman spectroscopy is particularly useful because the Raman spectrum of water is weak whereas the infrared spectrum of water is intense. Interpretation of the vibration frequencies is somewhat complicated by the presence, in octahedral and tetrahedral ions, of two vibrations, a symmetric one measured in the Raman spectrum and an anti-symmetric one, measured in the infrared spectrum.
| metal ion | wavenumber /cm−1 |
|---|---|
| Be Beryllium Beryllium is the chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a divalent element which occurs naturally only in combination with other elements in minerals. Notable gemstones which contain beryllium include beryl and chrysoberyl... 2+ |
530-543 |
| Mg Magnesium Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole... 2+ |
360-365 |
| Mn Manganese Manganese is a chemical element, designated by the symbol Mn. It has the atomic number 25. It is found as a free element in nature , and in many minerals... 2+ |
395 |
| Fe Iron Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust... 2+ |
389 |
| Ni Nickel Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile... 2+ |
405 |
| Cu Copper Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish... 2+ |
440 |
| Zn Zinc Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2... 2+ |
385-400 |
| Hg Mercury (element) Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum... 2+ |
380 |
| Al Aluminium Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances.... 3+ |
520-526 |
| Ga Gallium Gallium is a chemical element that has the symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Elemental gallium does not occur in nature, but as the gallium salt in trace amounts in bauxite and zinc ores. A soft silvery metallic poor metal, elemental gallium is a brittle solid at low temperatures. As it liquefies... 3+ |
475 |
| In Indium Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. This rare, very soft, malleable and easily fusible post-transition metal is chemically similar to gallium and thallium, and shows the intermediate properties between these two... 3+ |
400 |
Although the relationship between vibration frequency and force constant
Molecular vibration
A molecular vibration occurs when atoms in a molecule are in periodic motion while the molecule as a whole has constant translational and rotational motion...
is not simple, the general conclusion that can be taken from these data is that the strength of the M-O bond increases with increasing ionic charge and decreasing ionic size. The M-O stretching frequency of an aqua ion in solution may be compared with its counterpart in a crystal of known structure. If the frequencies are very similar it can be concluded that the coordination number of the metal ion is the same in solution as it is in a compound in the solid state.
Dynamic methods
Data such as conductivityConductivity (electrolytic)
The conductivity of an electrolyte solution is a measure of its ability to conduct electricity. The SI unit of conductivity is siemens per meter ....
, mobility
Electrophoresis
Electrophoresis, also called cataphoresis, is the motion of dispersed particles relative to a fluid under the influence of a spatially uniform electric field. This electrokinetic phenomenon was observed for the first time in 1807 by Reuss , who noticed that the application of a constant electric...
and diffusion
Diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
relate to the movement of ions through as solution. When an ion moves through a solution it tends to take both first and second solvation shells with it. Hence solvation numbers measured from dynamic properties tend to be much higher that those obtained from static properties.
| Li Lithium Lithium is a soft, silver-white metal that belongs to the alkali metal group of chemical elements. It is represented by the symbol Li, and it has the atomic number 3. Under standard conditions it is the lightest metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly... + | Na Sodium Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal and is a member of the alkali metals; its only stable isotope is 23Na. It is an abundant element that exists in numerous minerals, most commonly as sodium chloride... + | Cs+ | Mg Magnesium Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole... 2+ | Ca Calcium Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust... 2+ | Ba Barium Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in Group 2, a soft silvery metallic alkaline earth metal. Barium is never found in nature in its pure form due to its reactivity with air. Its oxide is historically known as baryta but it reacts with... 2+ | Zn Zinc Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2... 2+ | Cr Chromium Chromium is a chemical element which has the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6. It is a steely-gray, lustrous, hard metal that takes a high polish and has a high melting point. It is also odorless, tasteless, and malleable... 3+ |
Al Aluminium Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances.... 3+ |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transport number | 13-22 | 7-13 | 4 | 12-14 | 8-12 | 3-5 | 10-13 | ||
| Ion mobility | 3-21 | 2-10 | 10-13 | 7-11 | 5-9 | 10-13 | |||
| Diffusion | 5 | 3 | 1 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 11 | 17 | 13 |
Alkali metals
Solvation numbers of 3 - 6 have been found for lithium aqua ions. Solvation numbers less than 4 may be the result of the formation of contact ion-pairs. The higher solvation numbers may be interpreted in terms of water molecules that approach [Li(H2O)4]+ through a face of the tetrahedron, though molecular dynamic simulations may indicate the existence of an octahedral aqua ion. There are most probably six water molecules in the primary solvation sphere of the sodium ion. For potassium, rubidium and cesium even the primary solvation shell is not well defined.Alkaline earth metals
| M2+(aq) | M-O distance /pm | –ΔH /kJ mol−1!!ΔV /kJ mol−1!!ΔV /cm3 mol−1 /cm3 mol−1 |
|---|---|---|
| Be Beryllium Beryllium is the chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a divalent element which occurs naturally only in combination with other elements in minerals. Notable gemstones which contain beryllium include beryl and chrysoberyl... |
167 | 2494 |
| Mg Magnesium Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole... |
209 | 1921 |
| Ca Calcium Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust... |
242 | 1577 |
| Sr Strontium Strontium is a chemical element with the symbol Sr and the atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white or yellowish metallic element that is highly reactive chemically. The metal turns yellow when exposed to air. It occurs naturally in the minerals celestine and... |
263 | 1443 |
| Ba Barium Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in Group 2, a soft silvery metallic alkaline earth metal. Barium is never found in nature in its pure form due to its reactivity with air. Its oxide is historically known as baryta but it reacts with... |
281 | 1305 |
[Be(H2O)4]2+ has a very well-defined primary solvation shell; The BeO4 part has tetrahedral symmetry
Molecular symmetry
Molecular symmetry in chemistry describes the symmetry present in molecules and the classification of molecules according to their symmetry. Molecular symmetry is a fundamental concept in chemistry, as it can predict or explain many of a molecule's chemical properties, such as its dipole moment...
, Td. [Mg(H2O)6]2+ is also a well-characterized species, with an octahedral core. The situation for calcium is more complicated. Neutron diffraction data gave a solvation number for calcium chloride, CaCl2, which is strongly dependent on concentration: 10.0 ± 0.6 at 1 mol dm−3, decreasing to 6.4± 0.3 at 2.8 mol dm−3. The Shannon radius of the 6-coordinate calcium ion is 100 pm compared to 72 pm for magnesium, a 28% increase in size. This allows for higher aquation numbers and the lower charge density (z2/r) results in weaker M-O bonds, which makes ion-pairing easier. Various solid hydrates are known with 8-coordination in square antiprism
Square antiprism
In geometry, the square antiprism is the second in an infinite set of antiprisms formed by an even-numbered sequence of triangle sides closed by two polygon caps...
and dodecahedral geometry.
Aluminium and Group 3 metals
By convention aluminium is placed in group 13Group 13
"The Group Thirteen" network was a Jewish collaborationist organisation in the Warsaw Ghetto during the Second World War. The Thirteen took its informal name from the address of its main office in Leszno Street 13. The group was founded in December 1940 and led by Abraham Gancwajch, the former...
, with gallium
Gallium
Gallium is a chemical element that has the symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Elemental gallium does not occur in nature, but as the gallium salt in trace amounts in bauxite and zinc ores. A soft silvery metallic poor metal, elemental gallium is a brittle solid at low temperatures. As it liquefies...
, indium
Indium
Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. This rare, very soft, malleable and easily fusible post-transition metal is chemically similar to gallium and thallium, and shows the intermediate properties between these two...
and thallium
Thallium
Thallium is a chemical element with the symbol Tl and atomic number 81. This soft gray poor metal resembles tin but discolors when exposed to air. The two chemists William Crookes and Claude-Auguste Lamy discovered thallium independently in 1861 by the newly developed method of flame spectroscopy...
. Nevertheless a comparison of aluminium and scandium
Scandium
Scandium is a chemical element with symbol Sc and atomic number 21. A silvery-white metallic transition metal, it has historically been sometimes classified as a rare earth element, together with yttrium and the lanthanoids...
aqua ions illustrates a trend between the congener
Congener
Congener has several different meanings depending on the field in which it is used. Colloquially, it is used to mean a person or thing like another, in character or action.-Biology:In biology, congeners are organisms within the same genus...
s Na+/K+, Mg2+/Ca2+ and Al3+/Sc3+ which depends on the increase in size on going from row 3 to row 4 in the periodic table
Periodic table
The periodic table of the chemical elements is a tabular display of the 118 known chemical elements organized by selected properties of their atomic structures. Elements are presented by increasing atomic number, the number of protons in an atom's atomic nucleus...
. Shannon radii for 6-coordinate Al3+ and Sc3+ are 54 and 74.5 pm. Ga3+ has a Shannon radius of 62 pm, only about 13% larger than that of Al3+. This is due to the presence of the ten elements between scandium and gallium, which make an additional contribution to the general decrease in size across all rows of the periodic table. The aluminium aqua ion, [Al(H2O)6]3+ is very well characterized in solution and the solid state. The AlO6 core has octahedral symmetry, point group Oh.
There is now a substantial body of indirect evidence that seven molecules of water are present in the aqua ion of scandium
Scandium
Scandium is a chemical element with symbol Sc and atomic number 21. A silvery-white metallic transition metal, it has historically been sometimes classified as a rare earth element, together with yttrium and the lanthanoids...
, Sc3+. Yttrium
Yttrium
Yttrium is a chemical element with symbol Y and atomic number 39. It is a silvery-metallic transition metal chemically similar to the lanthanides and it has often been classified as a "rare earth element". Yttrium is almost always found combined with the lanthanides in rare earth minerals and is...
(III) has approximately the same Shannon radius as holmium
Holmium
Holmium is a chemical element with the symbol Ho and atomic number 67. Part of the lanthanide series, holmium is a rare earth element. Its oxide was first isolated from rare earth ores in 1878 and the element was named after the city of Stockholm....
(III) so Y3+ has very similar properties to those of Ho3+, so its aqua ion is probably 8-coordinate. The Lanthanum
Lanthanum
Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57.Lanthanum is a silvery white metallic element that belongs to group 3 of the periodic table and is the first element of the lanthanide series. It is found in some rare-earth minerals, usually in combination with cerium and...
aqua ion is probably 9-coordinate, as are those of the lighter lanthanides.
Transition metals and group 12 metals
-3d-balls.png)
Oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state is an indicator of the degree of oxidation of an atom in a chemical compound. The formal oxidation state is the hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all bonds to atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Oxidation states are typically represented by...
s have a solvation number of 6. All have a regular octahedral structure except the aqua ions of chromium
Chromium
Chromium is a chemical element which has the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6. It is a steely-gray, lustrous, hard metal that takes a high polish and has a high melting point. It is also odorless, tasteless, and malleable...
(II) and copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
(II) which are subject to Jahn-Teller distortion. In the copper case the two axial Cu−O distances are 238 pm, whereas the four equatorial Cu−O distances are 195 pm. Silver
Silver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
(I) is probably 4-coordinate, [Ag(H2O)4]+.
A solvation number of 6 with an octahedral structure is well established for zinc
Zinc
Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2...
(II) and cadmium
Cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, bluish-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Similar to zinc, it prefers oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds and similar to mercury it shows a low...
(II) in dilute solutions. In concentrated solutions the Zn2+ ion may adopt a 4-coordinate, tetrahedral, structure, but the evidence is not conclusive because of the possibility of ion-pairing and/or hydrolysis. The solvation number of mercury
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum...
(II)) is most likely to be 6.
The bis aqua structure of the mercury(I) ion,[(H2O)-Hg-Hg-(OH2]+, found in solid compounds, is also found in solution. Another aqua species in which there is a metal-metal bond is the molybdenum
Molybdenum
Molybdenum , is a Group 6 chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42. The name is from Neo-Latin Molybdaenum, from Ancient Greek , meaning lead, itself proposed as a loanword from Anatolian Luvian and Lydian languages, since its ores were confused with lead ores...
(II) species formulated as [(H4O)-Mo-Mo-(OH4]4+ on the basis of theoretical considerations of the nature of the Mo-Mo bond. Each molybdenum is surrounded by four water molecules in a square-planar arrangement, in a structure similar to that of the known structure of the chloro complex [Mo2Cl8]4-. The presence of a fifth water molecule in the axial position is not ruled out, however.
There are a few divalent and trivalent aqua ions of transition metals in the second and third transition series. With oxidation state 4, however, only hydrolyzed species exist.
Group 13-15 metals
The aqua ions of galliumGallium
Gallium is a chemical element that has the symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Elemental gallium does not occur in nature, but as the gallium salt in trace amounts in bauxite and zinc ores. A soft silvery metallic poor metal, elemental gallium is a brittle solid at low temperatures. As it liquefies...
(III) and indium
Indium
Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. This rare, very soft, malleable and easily fusible post-transition metal is chemically similar to gallium and thallium, and shows the intermediate properties between these two...
(III) and thallium
Thallium
Thallium is a chemical element with the symbol Tl and atomic number 81. This soft gray poor metal resembles tin but discolors when exposed to air. The two chemists William Crookes and Claude-Auguste Lamy discovered thallium independently in 1861 by the newly developed method of flame spectroscopy...
(III)have a solvation number of 6. The aqua ion of thallium(I) is often assumed to be 6-coordinate, but this assumption is not based on strong experimental evidence. The Shannon radius of Tl+, at 150 pm, is not very different from that of K+, at 138 pm, so some similarity between Tl+ and K+ chemistry is both expected and observed.
The solvation number of the tin
Tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn and atomic number 50. It is a main group metal in group 14 of the periodic table. Tin shows chemical similarity to both neighboring group 14 elements, germanium and lead and has two possible oxidation states, +2 and the slightly more stable +4...
(II) aqua ion, [Sn(H2O)n]2+ is not known with any certainty due to the presence of hydrolysis in the concentrated solutions needed for X-ray scattering measurements. The same is true for the lead
Lead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
(II) aqua ion. With bismuth
Bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element with symbol Bi and atomic number 83. Bismuth, a trivalent poor metal, chemically resembles arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth may occur naturally uncombined, although its sulfide and oxide form important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead...
(III) there is indirect evidence for a solvation number of 9. A nonahydrate is been characterized in the solid state, with a face-capped trigonal prism structure. The Shannon radius for 9-coordinate bismuth (115 pm) is comparable to that of neodymium (116.3 pm) for which a solvation number of 9 is well-established.
Lanthanides and actinides
The trivalent lanthanide ions decrease steadily in size from lanthanumLanthanum
Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57.Lanthanum is a silvery white metallic element that belongs to group 3 of the periodic table and is the first element of the lanthanide series. It is found in some rare-earth minerals, usually in combination with cerium and...
to lutetium, an effect known as the lanthanide contraction
Lanthanide contraction
Lanthanide contraction is a term used in chemistry to describe the decrease in ionic radii of the elements in the lanthanide series from atomic number 58, Cerium to 71, Lutetium, which results in smaller than otherwise expected ionic radii for the subsequent elements starting with 72, Hafnium...
. Nevertheless there is strong evidence that the hydration number changes from 9 to 8 at around gadolinium
Gadolinium
Gadolinium is a chemical element with the symbol Gd and atomic number 64. It is a silvery-white, malleable and ductile rare-earth metal. It is found in nature only in combined form. Gadolinium was first detected spectroscopically in 1880 by de Marignac who separated its oxide and is credited with...
. Structures of aqua ions in the solid state include the 9-coordinate tricapped trigonal prism structure with the lighter lanthanide ions and the 8-coordinate square antiprism
Square antiprism
In geometry, the square antiprism is the second in an infinite set of antiprisms formed by an even-numbered sequence of triangle sides closed by two polygon caps...
structure with the heavier lanthanide ions.There are no experimental data for the solvation state of cerium
Cerium
Cerium is a chemical element with the symbol Ce and atomic number 58. It is a soft, silvery, ductile metal which easily oxidizes in air. Cerium was named after the dwarf planet . Cerium is the most abundant of the rare earth elements, making up about 0.0046% of the Earth's crust by weight...
(IV) or europium
Europium
Europium is a chemical element with the symbol Eu and atomic number 63. It is named after the continent of Europe. It is a moderately hard silvery metal which readily oxidizes in air and water...
(II).
Solvation numbers of 9 or more a believed to apply the actinide ions in the +3 and +4 oxidation states, but an experimental value is available only for thorium
Thorium
Thorium is a natural radioactive chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. It was discovered in 1828 and named after Thor, the Norse god of thunder....
(IV).
Oxo-aqua-cations
Some elements in oxidation states higher than 3 form stable, aquated, oxo ions. Well known examples are the vanadyl(IV) and uranylUranyl
The uranyl ion is an oxycation of uranium in the oxidation state +6, with the chemical formula [UO2]2+. It has a linear structure with short U-O bonds, indicative of the presence of multiple bonds between uranium and oxygen. Four or more ligands are bound to the uranyl ion in an equatorial plane...
(VI) ions. They can be viewed as particularly stable hydrolysis products in a hypothetical reaction such as
- [V(H2O)6]4+ → [VO(H2O)5]2+ + 2H+
The vanadium
Vanadium
Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery gray, ductile and malleable transition metal. The formation of an oxide layer stabilizes the metal against oxidation. The element is found only in chemically combined form in nature...
has a distorted octahedral environment (point group C4v) of one oxide ion and 5 water molecules. Vanadium(V) is believed to exist as the dioxo-ion [VO2(H2O)4]+ at pH less than 2, but the evidence for this ion depends on the formation of complexes, such as oxalate
Oxalate
Oxalate , is the dianion with formula C2O42− also written 22−. Either name is often used for derivatives, such as disodium oxalate, 2C2O42−, or an ester of oxalic acid Oxalate (IUPAC: ethanedioate), is the dianion with formula C2O42− also written (COO)22−. Either...
complexes which have been shown to have the VO2+ unit, with cis-VO bonds, in the solid state. The chromium
Chromium
Chromium is a chemical element which has the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6. It is a steely-gray, lustrous, hard metal that takes a high polish and has a high melting point. It is also odorless, tasteless, and malleable...
(IV) ion [CrO(H2O)5]2+ , similar to the vanadium ion has been proposed on the basis of indirect evidence.
The uranyl ion, UO22+, has a trans structure. The aqua ion UO22+(aq) has been assumed, on the basis of indirect evidence, to have 5 water molecules in the plane perpendicular to the O-U-O axis in a pentagonal bipyramid structure, point group D5h. However it is also possible that there are 6 water molecules in the equatorial plane, hexagonal bipyramid
Hexagonal bipyramid
A hexagonal bipyramid is a polyhedron formed from two hexagonal pyramids joined at their bases. The resulting solid has 12 triangular faces, 8 vertices and 18 edges. The 12 faces are identical isosceles triangles.It is one of an infinite set of bipyramids...
, point group D6h, as many complexes with this structure are known. The solvation state of the plutonyl
Plutonyl
The plutonyl ion is an oxycation of plutonium in the oxidation state +6, with the chemical formula [PuO2]2+. It is isostructural with the uranyl ion, compared to which it has a slightly shorter M-O bond. It is easily reduced to plutonium. The plutonyl ion forms many complexes, particularly with...
ion, PuO22+, is not known.
Thermodynamics
The main goal of thermodynamics in this context is to derive estimates of single-ion thermodynamic quantities such as hydration enthalpyEnthalpy
Enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a thermodynamic system. It includes the internal energy, which is the energy required to create a system, and the amount of energy required to make room for it by displacing its environment and establishing its volume and pressure.Enthalpy is a...
and hydration entropy
Entropy
Entropy is a thermodynamic property that can be used to determine the energy available for useful work in a thermodynamic process, such as in energy conversion devices, engines, or machines. Such devices can only be driven by convertible energy, and have a theoretical maximum efficiency when...
. These quantities relate to the reaction
- Mz+ (gas) + solvent → Mz+ (in solution)
The enthalpy for this reaction is not directly measurable, because all measurements use salt solutions that contain both cation and anion. Most experimental measurements relate to the heat evolved when a salt dissolves in water, which gives the sum of cation and anion solvation enthalpies. Then, by considering the data for different anions with the same cation and different cations with the same anion, single ion values relative to an arbitrary zero, are derived.
| Li+ -514.6 |
Be2+ -2487.0 |
||||
| Na+ -404.6 |
Mg2+ -1922.1 |
Al3+ -4659.7 |
|||
| K+ -320.9 |
Ca2+ -1592.4 |
Sc3+ -3960.2 |
... | Ga3+ -4684.8 |
|
| Rb+ -296.2 |
Sr2+ -1444.7 |
Y3+ -3620.0 |
... | In3+ -4108.7 |
Sn2+ -1554.4 |
| Cs+ -263.2 |
Ba2+ -1303.7 |
La3+ -3282.8 |
... | Tl3+ -4184.0 |
Pb2+ -1479.9 |
Other values include Zn2+ -2044.3, Cd2+ -1805.8 and Ag+ -475.3 kJ mol−1.
There is an excellent linear correlation between hydration enthalpy and the ratio of charge squared, z2, to M-O distance, reff.
- ΔH
 = - 69500 z2 / reff
= - 69500 z2 / reff
Values for transition metals are affected by crystal field stabilization. The general trend is shown by the magenta line which passes through Ca2+, Mn2+ and Zn2+, for which there is no stabilization in an octahedral crystal field. Hydration energy increases as size decreases. Crystal field splitting confers extra stability on the aqua ion. The maximum crystal field stabilization energy occurs at Ni2+. The agreement of the hydration enthalpies with predictions provided one basis for the general acceptance of crystal field theory.
The hydration enthalpies of the trivalent lanthanide
Lanthanide
The lanthanide or lanthanoid series comprises the fifteen metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers 57 through 71, from lanthanum through lutetium...
ions show an increasingly negative values at atomic number increases, in line with the decrease in ionic radius known as the lanthanide contraction
Lanthanide contraction
Lanthanide contraction is a term used in chemistry to describe the decrease in ionic radii of the elements in the lanthanide series from atomic number 58, Cerium to 71, Lutetium, which results in smaller than otherwise expected ionic radii for the subsequent elements starting with 72, Hafnium...
.
Single ion hydration entropy can be derived. Values are shown in the following table. The more negative the value, the more there is ordering in forming the aqua ion. It is notable that the heavy alkali metals have rather small entropy values which suggests that both the first and second solvation shells are somewhat indistinct.
| Li+ -118.8 |
||||
| Na+ -87.4 |
Mg2+ -267.8 |
Al3+ -464.4 |
||
| K+ -51.9 |
Ca2+ -209.2 |
... | Ga3+ -510.4 |
|
| Rb+ -40.2 |
Sr2+ -205.0 |
... | In3+ -426.8 |
|
| Cs+ -36.8 |
Ba2+ -159.0 |
La3+ -368.2 |
... |
Hydrolysis of aqua ions
There are two ways of looking at an equilibrium involving hydrolysis of an aqua ion. Considering the dissociation equilibrium- [M(H2O)n]z+ - H+ [M(H2O)n-1(OH)](z-1)+
the activity of the hydrolysis product, omitting the water molecules, is given by
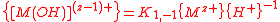
The alternative is to write the equilibrium as a complexation or substitution reaction
- [M(H2O)n]z+ +OH- :[M(H2O)n-1(OH)](z-1)+ + H2O
In which case
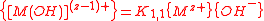
The concentration of hydrogen and hydroxide ions are related by the self-ionization of water
Self-ionization of water
The self-ionization of water is the chemical reaction in which a proton is transferred from one water molecule to another, in pure water or an aqueous solution, to create the two ions, hydronium, H3O+ and hydroxide, OH−...
, Kw = {H+} {OH-} so the two equilibrium constants are related as
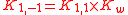
In practice the first definition is more useful because equilibrium constants are determined from measurements of hydrogen ion concentrations. In general,
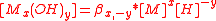
charges are omitted for the sake of generality and activities have been replaced by concentrations.
 are cumulative hydrolysis constants.
are cumulative hydrolysis constants.Modeling the hydrolysis reactions that occur in solution is usually based on the determination of equilibrium constants
Determination of equilibrium constants
Equilibrium constants are determined in order to quantify chemical equilibria. When an equilibrium constant is expressed as a concentration quotient,K=\frac...
from potentiometric (pH) titration data. The process is far from straightforward for a variety of reasons. Sometimes the species in solution can be precipitated as salts and their structure confirmed by X-ray crystallography. In other cases, precipitated salts bear no relation to what is postulated to be in solution, because a particular crystalline substances may have both low solubility and very low concentration in the solutions.
First hydrolysis constant
The logarithm of hydrolysis constant, K1,-1, for the removal of one proton from an aqua ion- [M(H2O)n]z+ - H+ [M(H2O)n-1(OH)](z-1)+
- [ [M(OH)]{(z-1)+ ] = K1,-1 [Mz+] [H+] -1
shows a linear relationship with the ratio of charge to M-O distance, z/d. Ions fall into four groups. The slope of the straight line is the same for all groups, but the intercept, A, is different.
| cation | A |
|---|---|
| Mg2+, Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+ Al3+, Y3+, La3+ |
|
| Li+, Na+, K+ Be2+, Mn2+, Fe2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+ Sc3+, Ti3+, V3+, Cr3+, Fe3+, Rh3+, Ga3+, In3+ Ce4+, Th4+, Pa4+, U4+, Np4+, Pu4+, |
|
| Ag+, Tl+ Pb2+ Ti3+, Bi3+, |
|
| Sn2+, Hg2+, Sn2+, Pd2+ | ca. 12 |
The cations most resistant to hydrolysis for their size and charge are hard
HSAB theory
The HSAB concept is an acronym for 'hard and soft acids and bases. Also known as the Pearson acid base concept, HSAB is widely used in chemistry for explaining stability of compounds, reaction mechanisms and pathways....
pre-transition metal ions or lanthanide ions. The slightly less resistant group includes the transition metal ions. The third group contains mostly soft
HSAB theory
The HSAB concept is an acronym for 'hard and soft acids and bases. Also known as the Pearson acid base concept, HSAB is widely used in chemistry for explaining stability of compounds, reaction mechanisms and pathways....
ions ion of post-transition metals. The ions which show the strongest tendency to hydrolyze for their charge and size are Pd2+, Sn2+ and Hg2+.
The standard enthalpy change for the first hydrolysis step is generally not very different from that of the dissociation of pure water. Consequently, the standard enthalpy change for the substitution reaction
- [M(H2O)n]z+ +OH- :[M(H2O)n-1(OH)](z-1)+ + H2O
is close to zero. This is typical of reactions between a hard cation and a hard anion, such as the hydroxide ion. It means that the standard entropy charge is the major contributor to the standard free energy change and hence the equilibrium constant.
- ΔG
 = -RT ln K = ΔH
= -RT ln K = ΔH - TΔS
- TΔS
The change in ionic charge is responsible for the effect as the aqua ion has a greater ordering effect on the solution than the less highly charged hydroxo complex.
Multiple hydrolysis reactions
The hydrolysis of beryllium shows many of the characteristics typical of multiple hydrolysis reactions. The concentrations of various species, including polynuclear species with bridging hydroxide ions, change as a function of pH up to the precipitation of an insoluble hydroxide. Beryllium hydrolysis is unusual in that the concentration of [Be(H2O)3(OH)]+ is too low to be measured. Instead a trimer ([Be3(H2O)6(OH3))3+ is formed, whose structure has been confirmed in solid salts. The formation of polynuclear species is driven by the reduction in charge density within the molecule as a whole. The local environment of the beryllium ions approximates to [Be(H2O)2(OH)2]+. The reduction in effective charge releases free energy in the form of a decrease of the entropy of ordering at the charge centers.| Species formula | cations | structure |
|---|---|---|
| M2(OH)+ | Be2+, Mn2+, Co2+, Ni2+ Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+, Pb2+ |
single hydroxide bridge between two cations |
| M2(OH)2(2z-2)+ | Cu2+, Sn2+ Al3+, Sc3+, Ln3+, Ti3+, Cr3+ Th4+ VO2+, UO22+, NpO22+, PuO22+ |
double hydroxide bridge between two cations |
| M3(OH)33+ | Be2+, Hg2+ | six-membered ring with alternate Mn+ and OH- groups |
| M3(OH)4(3z-4)+ | Sn2+, Pb2+ Al3+, Cr3+, Fe3+, In3+ |
Cube with alternate vertices of Mn+ and OH- groups, one vertex missing |
| M4(OH)44+ | Mg2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Cd2+, Pb2+ | Cube with alternate vertices of Mn+ and OH- groups |
| M4(OH)88+ | Zr4+, Th4+ | Square of Mn+ ions with double hydroxide bridges on each side of the square |
The hydrolysis product of aluminium
Aluminium
Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances....
formulated as [Al13O4(OH)24(H2O)12]7+ is very well characterized and may be present in nature in water at pH ca. 5.4.
The overall reaction for the loss of two protons from an aqua ion can be written as
- [M(H2O)n]z+ - 2 H+ [M(H2O)n-2(OH)2](z-2)+
However, the equilibrium constant for the loss of two protons applies equally well to the equilibrium
- [M(H2O)n]z+ - 2 H+ [MO(H2O)n-2](z-2)+ + H2O
because the concentration of water is assumed to be constant. This applies in general: any equilibrium constant is equally valid for a product with an oxide ion as for the product with two hydroxyl ions. The two possibilities can only be distinguished by determining the structure of a salt in the solid state. Oxo bridges tend to occur when the metal oxidation state is high. An example is provided by the molybdenum
Molybdenum
Molybdenum , is a Group 6 chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42. The name is from Neo-Latin Molybdaenum, from Ancient Greek , meaning lead, itself proposed as a loanword from Anatolian Luvian and Lydian languages, since its ores were confused with lead ores...
(IV) complex [Mo3O4(H2O)9]4+ in which there is a triangle of molybdenum atoms joined by σ- bonds
Sigma bond
In chemistry, sigma bonds are the strongest type of covalent chemical bond. They are formed by head-on overlapping between atomic orbitals. Sigma bonding is most clearly defined for diatomic molecules using the language and tools of symmetry groups. In this formal approach, a σ-bond is...
with an oxide bridge on each edge of the triangle and a fourth oxide which bridges to all three Mo atoms.
Oxyanions
There are very few oxo-aqua ions of metals in the oxidation state +5 or higher. Rather, the species found in aqueous solution are monomeric and polymeric oxyanions. Oxyanions can be viewed as the end products of hydrolysis, in which there are no water molecules attached to the metal, only oxide ions.Exchange kinetics
A water molecule in the first solvation shell of an aqua ion may exchange places with a water molecule in the bulk solvent. It is usually assumed that the rate-determining stepRate-determining step
The rate-determining step is a chemistry term for the slowest step in a chemical reaction. The rate-determining step is often compared to the neck of a funnel; the rate at which water flows through the funnel is determined by the width of the neck, not by the speed at which water is poured in. In...
is a dissociation reaction
Dissociation (chemistry)
Dissociation in chemistry and biochemistry is a general process in which ionic compounds separate or split into smaller particles, ions, or radicals, usually in a reversible manner...
.
- [M(H2O)n]z+ → [M(H2O)n-1]z+* + H2O
The * symbol signifies that this is the transition state
Transition state
The transition state of a chemical reaction is a particular configuration along the reaction coordinate. It is defined as the state corresponding to the highest energy along this reaction coordinate. At this point, assuming a perfectly irreversible reaction, colliding reactant molecules will always...
in a chemical reaction. The rate of this reaction is proportional to the concentration of the aqua ion, [A].
-
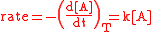 .
.
The proportionality constant, k, is called a first-order rate constant at temperature T. The unit of the rate constant for water exchange is usually taken as mol dm−3s−1. The half-life
Half-life
Half-life, abbreviated t½, is the period of time it takes for the amount of a substance undergoing decay to decrease by half. The name was originally used to describe a characteristic of unstable atoms , but it may apply to any quantity which follows a set-rate decay.The original term, dating to...
for this reaction is equal to loge2 / k. This measure is useful because it is independent of concentration. It has the dimension of time. The quantity 1/k, equal to the half life divided by 0.6932, is known as the residence time
Residence time
Residence time is the average amount of time that a particle spends in a particular system. This measurement varies directly with the amount of substance that is present in the system....
or time constant
Time constant
In physics and engineering, the time constant, usually denoted by the Greek letter \tau , is the risetime characterizing the response to a time-varying input of a first-order, linear time-invariant system.Concretely, a first-order LTI system is a system that can be modeled by a single first order...
.
The residence time for water exchange varies from about 10−10 s
Second
The second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
for Cs+ to about 10+10 s (more than 200 y
Year
A year is the orbital period of the Earth moving around the Sun. For an observer on Earth, this corresponds to the period it takes the Sun to complete one course throughout the zodiac along the ecliptic....
) for Ir3+. It depends on factors such as the size and charge on the ion and, in the case of transition metal ions, crystal field effects. Very fast and very slow reactions are difficult to study. The most information on the kinetics a water exchange comes from systems with a residence time between about 1 μs and 1 s. The enthalpy and entropy of activation, ΔH‡ and ΔS‡ can be obtained by observing the variation of rate constant with temperature.
| ion | residence time /μs Microsecond A microsecond is an SI unit of time equal to one millionth of a second. Its symbol is µs.A microsecond is equal to 1000 nanoseconds or 1/1000 millisecond... !!ΔH‡ /kJ mol-1!! ΔS‡ /J deg−1mol−1 |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Be Beryllium Beryllium is the chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a divalent element which occurs naturally only in combination with other elements in minerals. Notable gemstones which contain beryllium include beryl and chrysoberyl... 2+ |
1.0×103 | ||
| Mg Magnesium Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole... 2+ |
2.0 | 43 | 8 |
| V Vanadium Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery gray, ductile and malleable transition metal. The formation of an oxide layer stabilizes the metal against oxidation. The element is found only in chemically combined form in nature... 2+ |
1.3×104 | 69 | 21 |
| Cr Chromium Chromium is a chemical element which has the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6. It is a steely-gray, lustrous, hard metal that takes a high polish and has a high melting point. It is also odorless, tasteless, and malleable... 2+ |
0.0032 | 13 | |
| Mn Manganese Manganese is a chemical element, designated by the symbol Mn. It has the atomic number 25. It is found as a free element in nature , and in many minerals... 2+ |
0.0316 | 34 | 12 |
| Fe Iron Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust... 2+ |
0.32 | 32 | |
| Co Cobalt Cobalt is a chemical element with symbol Co and atomic number 27. It is found naturally only in chemically combined form. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal.... 2+ |
0.79 | 33 | |
| Ni Nickel Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile... 2+ |
40 | 43 | |
| Cu Copper Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish... 2+ |
5.0×10−4 | 23 | 25 |
| Zn Zinc Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2... 2+ |
0.032 | ||
| Al Aluminium Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances.... 3+ |
6.3×106 | 11 | 117 |
| Ti Titanium Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. It has a low density and is a strong, lustrous, corrosion-resistant transition metal with a silver color.... 3+ |
16 | 26 | |
| Cr Chromium Chromium is a chemical element which has the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6. It is a steely-gray, lustrous, hard metal that takes a high polish and has a high melting point. It is also odorless, tasteless, and malleable... 3+ |
2.0×1012 | 109 | 0 |
| Fe Iron Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust... 3+ |
316 | 37 | |
| Ga Gallium Gallium is a chemical element that has the symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Elemental gallium does not occur in nature, but as the gallium salt in trace amounts in bauxite and zinc ores. A soft silvery metallic poor metal, elemental gallium is a brittle solid at low temperatures. As it liquefies... 3+ |
501 | 26 | |
| Rh Rhodium Rhodium is a chemical element that is a rare, silvery-white, hard and chemically inert transition metal and a member of the platinum group. It has the chemical symbol Rh and atomic number 45. It is composed of only one isotope, 103Rh. Naturally occurring rhodium is found as the free metal, alloyed... 3+ |
3.2×1013 | 134 | 59 |
| In Indium Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. This rare, very soft, malleable and easily fusible post-transition metal is chemically similar to gallium and thallium, and shows the intermediate properties between these two... 3+ |
50 | 17 | |
| La Lanthanum Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57.Lanthanum is a silvery white metallic element that belongs to group 3 of the periodic table and is the first element of the lanthanide series. It is found in some rare-earth minerals, usually in combination with cerium and... 3+ |
0.050 | ||
| UO Uranium Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons... 22+ |
1.3 |
The kinetic parameters for aqua ions of the transition metals are affected by crystal field stabilization energy (CFSE) on both the aqua ion and its dissociation product which has one less water molecule in the primary solvation shell. This explains the inertness (long residence time) of Cr3+, which has an octahedral structure and a d3 electronic configuration and Rh3+ and Ir3+ which are also octahedral and have a low-spin d6 configuration. Trivalent ions have longer residence time than divalent ions, except for the very large lanthanide ions. The values in the table show that this is due to both activation enthalpy and entropy factors.
Mechanisms
The assignment of mechanisms to the water exchange reaction has not yet been made unambiguously. The simple dissociation mechanism needs to be modified to take into account the presence of a second solvation shell. In all cases exchange between molecules in the second shell and bulk water is fast compared to the rate-determining step.Three possible mechanism arise.
- Id (dissociative interchangeDissociative substitutionDissociative substitution describes a pathway by which compounds interchange ligands. The term is typically applied to coordination and organometallic complexes, but resembles the Sn1 mechanism in organic chemistry. The opposite pathway is associative substitution, being analogous to Sn2 pathway...
) mechanism. A water molecule leaves the first solvation shell and enters the second shell. - Ia (associative interchangeAssociative substitutionAssociative substitution describes a pathway by which compounds interchange ligands. The terminology is typically applied to coordination and organometallic complexes, but resembles the Sn2 mechanism in organic chemistry. The opposite pathway is dissociative substitution, being analogous to Sn1...
) mechanism. The same exchange reaction takes place, but there is a significant interaction, in the transition state, between the incoming water molecule and the metal ion. - A mechanism. This is an associative mechanismAssociative substitutionAssociative substitution describes a pathway by which compounds interchange ligands. The terminology is typically applied to coordination and organometallic complexes, but resembles the Sn2 mechanism in organic chemistry. The opposite pathway is dissociative substitution, being analogous to Sn1...
involving a molecule from the bulk solvent.
This classification represents extreme cases; the actual mechanism may have something of an intermediate nature. The most useful parameter for distinguishing between possible mechanism is the activation volume change, ΔV‡, which is obtained from the pressure variation of the rate constant.
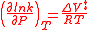
The activation volume increases for dissociative mechanisms and decreases for associative mechanisms.
Formation of complexes
Metal aqua ions are often involved in the formation of complexes. The reaction may be written as- pMx+(aq) + qLy- → [MpLq](px-qy)+
In reality this is a substitution reaction in which one or more water molecules from the first hydration shell of the metal ion are replaced by ligands, L. The complex is described as an inner-sphere complex. A complex such as [ML](p-q)+ may be described as a contact ion pair.
When the water molecule(s) of the second hydration shell are replaced by ligands, the complex is said to be an outer-sphere complex, or solvent-shared ion pair. The formation of solvent-shared or contact ion pairs is particularly relevant to the determination of solvation numbers of aqua ions by methods that require the use of concentrated solutions of salts, as ion-pairing is concentration dependent. Consider, for example, the formation of the complex [MgCl]+ in solutions of MgCl2. The formation constant, K, of the complex is about 1 but varies with ionic strength. The concentration of the rather weak complex increases from about 0.1% for a 10mM solution to about 70% for a 1M solution (1M = 1 mol dm−3).
Electrochemistry
The standard electrode potentialStandard electrode potential
In electrochemistry, the standard electrode potential, abbreviated E° or E , is the measure of individual potential of a reversible electrode at standard state, which is with solutes at an effective concentration of 1 mol dm−3, and gases at a pressure of 1 atm...
for the half-cell equilibrium Mz+ + z M(s) has been measured for all metals except for the heaviest trans-uranium elements.
| Li Lithium Lithium is a soft, silver-white metal that belongs to the alkali metal group of chemical elements. It is represented by the symbol Li, and it has the atomic number 3. Under standard conditions it is the lightest metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly... |
Be Beryllium Beryllium is the chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a divalent element which occurs naturally only in combination with other elements in minerals. Notable gemstones which contain beryllium include beryl and chrysoberyl... 2+ |
|||||||||||||||
| Na Sodium Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal and is a member of the alkali metals; its only stable isotope is 23Na. It is an abundant element that exists in numerous minerals, most commonly as sodium chloride... |
Mg Magnesium Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole... 2+ |
Al Aluminium Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances.... 3+ |
||||||||||||||
| K Potassium Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K and atomic number 19. Elemental potassium is a soft silvery-white alkali metal that oxidizes rapidly in air and is very reactive with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite the hydrogen emitted in the reaction.Potassium and sodium are... |
Ca Calcium Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust... 2+ |
Sc Scandium Scandium is a chemical element with symbol Sc and atomic number 21. A silvery-white metallic transition metal, it has historically been sometimes classified as a rare earth element, together with yttrium and the lanthanoids... 3+ |
... | Zn2+ Zinc Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2... |
Ga3+ Gallium Gallium is a chemical element that has the symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Elemental gallium does not occur in nature, but as the gallium salt in trace amounts in bauxite and zinc ores. A soft silvery metallic poor metal, elemental gallium is a brittle solid at low temperatures. As it liquefies... |
|||||||||||
| Rb Rubidium Rubidium is a chemical element with the symbol Rb and atomic number 37. Rubidium is a soft, silvery-white metallic element of the alkali metal group. Its atomic mass is 85.4678. Elemental rubidium is highly reactive, with properties similar to those of other elements in group 1, such as very rapid... |
Sr Strontium Strontium is a chemical element with the symbol Sr and the atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white or yellowish metallic element that is highly reactive chemically. The metal turns yellow when exposed to air. It occurs naturally in the minerals celestine and... 2+ |
Y Yttrium Yttrium is a chemical element with symbol Y and atomic number 39. It is a silvery-metallic transition metal chemically similar to the lanthanides and it has often been classified as a "rare earth element". Yttrium is almost always found combined with the lanthanides in rare earth minerals and is... 3+ |
... | Cd2+ Cadmium Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, bluish-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Similar to zinc, it prefers oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds and similar to mercury it shows a low... |
In3+ Indium Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. This rare, very soft, malleable and easily fusible post-transition metal is chemically similar to gallium and thallium, and shows the intermediate properties between these two... |
Sn2+ Tin Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn and atomic number 50. It is a main group metal in group 14 of the periodic table. Tin shows chemical similarity to both neighboring group 14 elements, germanium and lead and has two possible oxidation states, +2 and the slightly more stable +4... |
||||||||||
| Cs |
Ba Barium Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in Group 2, a soft silvery metallic alkaline earth metal. Barium is never found in nature in its pure form due to its reactivity with air. Its oxide is historically known as baryta but it reacts with... 2+ |
... | Hg2+ Mercury (element) Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum... |
Tl3+ Thallium Thallium is a chemical element with the symbol Tl and atomic number 81. This soft gray poor metal resembles tin but discolors when exposed to air. The two chemists William Crookes and Claude-Auguste Lamy discovered thallium independently in 1861 by the newly developed method of flame spectroscopy... +0.73 |
Pb2+ Lead Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed... |
Bi3+ Bismuth Bismuth is a chemical element with symbol Bi and atomic number 83. Bismuth, a trivalent poor metal, chemically resembles arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth may occur naturally uncombined, although its sulfide and oxide form important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead... +0.16 |
||||||||||
| La Lanthanum Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57.Lanthanum is a silvery white metallic element that belongs to group 3 of the periodic table and is the first element of the lanthanide series. It is found in some rare-earth minerals, usually in combination with cerium and... 3+ |
Ce3+ Cerium Cerium is a chemical element with the symbol Ce and atomic number 58. It is a soft, silvery, ductile metal which easily oxidizes in air. Cerium was named after the dwarf planet . Cerium is the most abundant of the rare earth elements, making up about 0.0046% of the Earth's crust by weight... |
Pr3+ Praseodymium Praseodymium is a chemical element that has the symbol Pr and atomic number 59. Praseodymium is a soft, silvery, malleable and ductile metal in the lanthanide group. It is too reactive to be found in native form, and when artificially prepared, it slowly develops a green oxide coating.The element... |
Nd3+ Neodymium Neodymium is a chemical element with the symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is a soft silvery metal that tarnishes in air. Neodymium was discovered in 1885 by the Austrian chemist Carl Auer von Welsbach. It is present in significant quantities in the ore minerals monazite and bastnäsite... |
Pm3+ Promethium Promethium is a chemical element with the symbol Pm and atomic number 61. It is notable for being the only exclusively radioactive element besides technetium that is followed by chemical elements with stable isotopes.- Prediction :... |
Sm3+ Samarium Samarium is a chemical element with the symbol Sm, atomic number 62 and atomic weight 150.36. It is a moderately hard silvery metal which readily oxidizes in air. Being a typical member of the lanthanide series, samarium usually assumes the oxidation state +3... |
Eu3+ Europium Europium is a chemical element with the symbol Eu and atomic number 63. It is named after the continent of Europe. It is a moderately hard silvery metal which readily oxidizes in air and water... |
Gd3+ Gadolinium Gadolinium is a chemical element with the symbol Gd and atomic number 64. It is a silvery-white, malleable and ductile rare-earth metal. It is found in nature only in combined form. Gadolinium was first detected spectroscopically in 1880 by de Marignac who separated its oxide and is credited with... |
Tb3+ Terbium Terbium is a chemical element with the symbol Tb and atomic number 65. It is a silvery-white rare earth metal that is malleable, ductile and soft enough to be cut with a knife... |
Dy3+ Dysprosium Dysprosium is a chemical element with the symbol Dy and atomic number 66. It is a rare earth element with a metallic silver luster. Dysprosium is never found in nature as a free element, though it is found in various minerals, such as xenotime... |
Ho3+ Holmium Holmium is a chemical element with the symbol Ho and atomic number 67. Part of the lanthanide series, holmium is a rare earth element. Its oxide was first isolated from rare earth ores in 1878 and the element was named after the city of Stockholm.... |
Er3+ Erbium Erbium is a chemical element in the lanthanide series, with the symbol Er and atomic number 68. A silvery-white solid metal when artificially isolated, natural erbium is always found in chemical combination with other elements on Earth... |
Tm3+ Thulium Thulium is a chemical element that has the symbol Tm and atomic number 69. Thulium is the second least abundant of the lanthanides . It is an easily workable metal with a bright silvery-gray luster... |
Yb3+ Ytterbium Ytterbium is a chemical element with the symbol Yb and atomic number 70. A soft silvery metallic element, ytterbium is a rare earth element of the lanthanide series and is found in the minerals gadolinite, monazite, and xenotime. The element is sometimes associated with yttrium or other related... |
Lu3+ |
||
| Ac3+ Actinium Actinium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Ac and atomic number 89, which was discovered in 1899. It was the first non-primordial radioactive element to be isolated. Polonium, radium and radon were observed before actinium, but they were not isolated until 1902... |
Pa4+ |
U4+ Uranium Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons... |
Np4+ Neptunium Neptunium is a chemical element with the symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element and belongs to the actinide series. Its most stable isotope, 237Np, is a by-product of nuclear reactors and plutonium production and it can be used as a... |
Pu4+ Plutonium Plutonium is a transuranic radioactive chemical element with the chemical symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, forming a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation... |
Am3+ Americium Americium is a synthetic element that has the symbol Am and atomic number 95. This transuranic element of the actinide series is located in the periodic table below the lanthanide element europium, and thus by analogy was named after another continent, America.Americium was first produced in 1944... |
Cm3+ Curium Curium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This radioactive transuranic element of the actinide series was named after Marie Skłodowska-Curie and her husband Pierre Curie. Curium was first intentionally produced and identified in summer 1944 by the group of... |
Bk3+ Berkelium Berkelium , is a synthetic element with the symbol Bk and atomic number 97, a member of the actinide and transuranium element series. It is named after the city of Berkeley, California, the location of the University of California Radiation Laboratory where it was discovered in December 1949... |
Cf3+ Californium Californium is a radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Cf and atomic number 98. The element was first made in the laboratory in 1950 by bombarding curium with alpha particles at the University of California, Berkeley. It is the ninth member of the actinide series and was the... |
Es3+ Einsteinium Einsteinium is a synthetic element with the symbol Es and atomic number 99. It is the seventh transuranic element, and an actinide.Einsteinium was discovered in the debris of the first hydrogen bomb explosion in 1952, and named after Albert Einstein... |
Fm3+ Fermium Fermium is a synthetic element with the symbol Fm. It is the 100th element in the periodic table and a member of the actinide series. It is the heaviest element that can be formed by neutron bombardment of lighter elements, and hence the last element that can be prepared in macroscopic quantities,... |
| Couple | Ti Titanium Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. It has a low density and is a strong, lustrous, corrosion-resistant transition metal with a silver color.... | V Vanadium Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery gray, ductile and malleable transition metal. The formation of an oxide layer stabilizes the metal against oxidation. The element is found only in chemically combined form in nature... | Cr Chromium Chromium is a chemical element which has the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6. It is a steely-gray, lustrous, hard metal that takes a high polish and has a high melting point. It is also odorless, tasteless, and malleable... | Mn Manganese Manganese is a chemical element, designated by the symbol Mn. It has the atomic number 25. It is found as a free element in nature , and in many minerals... | Fe Iron Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust... | Co Cobalt Cobalt is a chemical element with symbol Co and atomic number 27. It is found naturally only in chemically combined form. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal.... | Ni Nickel Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile... | Cu Copper Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M2+ / M | |||||||
| M3+ / M |
| Ag+ / Ag Silver Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal... | Pd2+ / Pd Palladium Palladium is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pd and an atomic number of 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas, which was itself named after the epithet of the Greek goddess Athena, acquired... | Zr4+ / Zr Zirconium Zirconium is a chemical element with the symbol Zr and atomic number 40. The name of zirconium is taken from the mineral zircon. Its atomic mass is 91.224. It is a lustrous, grey-white, strong transition metal that resembles titanium... | Hf4+ / Hf Hafnium Hafnium is a chemical element with the symbol Hf and atomic number 72. A lustrous, silvery gray, tetravalent transition metal, hafnium chemically resembles zirconium and is found in zirconium minerals. Its existence was predicted by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. Hafnium was the penultimate stable... | Au3+ / Au Gold Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a... | Ce4+ / Ce Cerium Cerium is a chemical element with the symbol Ce and atomic number 58. It is a soft, silvery, ductile metal which easily oxidizes in air. Cerium was named after the dwarf planet . Cerium is the most abundant of the rare earth elements, making up about 0.0046% of the Earth's crust by weight... |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| +0.799 | +1.50 |
As the standard electrode potential is more negative the aqua ion is more difficult to reduce. For example, comparing the potentials for zinc (-0.75 V) with those of iron (Fe(II) -0.47 V, Fe(III) -0.06 V) it is seen that iron ions are more easily reduced than zinc ions. This is the basis for using zinc to provide anodic protection
Anodic protection
Anodic protection is a technique to control the corrosion of a metal surface by making it the anode of an electrochemical cell and controlling the electrode potential in a zone where the metal is passive....
for large structures made of iron or to protect small structures by galvanization
Galvanization
Galvanization is the process of applying a protective zinc coating to steel or iron, in order to prevent rusting. The term is derived from the name of Italian scientist Luigi Galvani....
.

