
Metal acetylide
Encyclopedia

Valence (chemistry)
In chemistry, valence, also known as valency or valence number, is a measure of the number of bonds formed by an atom of a given element. "Valence" can be defined as the number of valence bonds...
anion with formula C22− or (C≡C)2−. It may be regarded as the result of removing two proton
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
s from acetylene
Acetylene
Acetylene is the chemical compound with the formula C2H2. It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution.As an alkyne, acetylene is unsaturated because...
C2H2 or H-C≡C-H, the prototypical alkyne
Alkyne
Alkynes are hydrocarbons that have a triple bond between two carbon atoms, with the formula CnH2n-2. Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name acetylene also refers specifically to C2H2, known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature...
— that behaves as a weak acid
Acid
An acid is a substance which reacts with a base. Commonly, acids can be identified as tasting sour, reacting with metals such as calcium, and bases like sodium carbonate. Aqueous acids have a pH of less than 7, where an acid of lower pH is typically stronger, and turn blue litmus paper red...
.
These terms are also used for any monovalent anion of the form R-C≡C−, where R is any monovalent organic moiety; such as hydrogenacetylide H-C≡C−, or methylacetylide H3C-C≡C−.
The anion names are also used for any salt containing them, such as copper acetylide
Copper(I) acetylide
Copper acetylide, or cuprous acetylide, is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula Cu2C2. It is a heat and shock sensitive high explosive, more sensitive than silver acetylide. It is a metal acetylide. It is similar to silver acetylide and calcium carbide, though it is not called carbide in...
(Cu+)2·C22−, lithium hydrogenacetylide Li+·HC2−, or silver methylacetylide. Ag+·(CH3)C2−. Some salts of the C22− anion are traditionally called carbides, e.g. calcium carbide
Calcium carbide
thumb|right|Calcium carbide.Calcium carbide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula of CaC2. The pure material is colorless, however pieces of technical grade calcium carbide are grey or brown and consist of only 80-85% of CaC2 . Because of presence of PH3, NH3, and H2S it has a...
Ca2+·C22− and lithium carbide
Lithium carbide
Lithium carbide, Li2C2, often known as dilithium acetylide, is a chemical compound of lithium and carbon, an acetylide. It is an intermediate compound produced during radiocarbon dating procedures...
(Li+)2·C22−.
Some acetylides are explosive, and their accidental formation is a major safety risk in acetylene processing or storage. Acetylides are very useful reagents in organic chemistry
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
.
Synthesis
Acetylides of the alkali metalAlkali metal
The alkali metals are a series of chemical elements in the periodic table. In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, the alkali metals comprise the group 1 elements, along with hydrogen. The alkali metals are lithium , sodium , potassium , rubidium , caesium , and francium...
s can be prepared by dissolving the metal in liquid ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
and passing acetylene through the solution. Other strong bases such as butyllithium or LiHMDS
Lithium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide
Lithium bisamide is the organosilicon compound with the formula [3Si]2NLi. This colourless solid is a strong non-nucleophilic base used for deprotonation reactions and as a ligand...
are also frequently used:

Valence (chemistry)
In chemistry, valence, also known as valency or valence number, is a measure of the number of bonds formed by an atom of a given element. "Valence" can be defined as the number of valence bonds...
anion with formula C22− or (C≡C)2−. It may be regarded as the result of removing two proton
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
s from acetylene
Acetylene
Acetylene is the chemical compound with the formula C2H2. It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution.As an alkyne, acetylene is unsaturated because...
C2H2 or H-C≡C-H, the prototypical alkyne
Alkyne
Alkynes are hydrocarbons that have a triple bond between two carbon atoms, with the formula CnH2n-2. Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name acetylene also refers specifically to C2H2, known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature...
— that behaves as a weak acid
Acid
An acid is a substance which reacts with a base. Commonly, acids can be identified as tasting sour, reacting with metals such as calcium, and bases like sodium carbonate. Aqueous acids have a pH of less than 7, where an acid of lower pH is typically stronger, and turn blue litmus paper red...
.
These terms are also used for any monovalent anion of the form R-C≡C−, where R is any monovalent organic moiety; such as hydrogenacetylide H-C≡C−, or methylacetylide H3C-C≡C−.
The anion names are also used for any salt containing them, such as copper acetylide
Copper(I) acetylide
Copper acetylide, or cuprous acetylide, is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula Cu2C2. It is a heat and shock sensitive high explosive, more sensitive than silver acetylide. It is a metal acetylide. It is similar to silver acetylide and calcium carbide, though it is not called carbide in...
(Cu+)2·C22−, lithium hydrogenacetylide Li+·HC2−, or silver methylacetylide. Ag+·(CH3)C2−. Some salts of the C22− anion are traditionally called carbides, e.g. calcium carbide
Calcium carbide
thumb|right|Calcium carbide.Calcium carbide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula of CaC2. The pure material is colorless, however pieces of technical grade calcium carbide are grey or brown and consist of only 80-85% of CaC2 . Because of presence of PH3, NH3, and H2S it has a...
Ca2+·C22− and lithium carbide
Lithium carbide
Lithium carbide, Li2C2, often known as dilithium acetylide, is a chemical compound of lithium and carbon, an acetylide. It is an intermediate compound produced during radiocarbon dating procedures...
(Li+)2·C22−.
Some acetylides are explosive, and their accidental formation is a major safety risk in acetylene processing or storage. Acetylides are very useful reagents in organic chemistry
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
.
Synthesis
Acetylides of the alkali metalAlkali metal
The alkali metals are a series of chemical elements in the periodic table. In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, the alkali metals comprise the group 1 elements, along with hydrogen. The alkali metals are lithium , sodium , potassium , rubidium , caesium , and francium...
s can be prepared by dissolving the metal in liquid ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
and passing acetylene through the solution. Other strong bases such as butyllithium or LiHMDS
Lithium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide
Lithium bisamide is the organosilicon compound with the formula [3Si]2NLi. This colourless solid is a strong non-nucleophilic base used for deprotonation reactions and as a ligand...
are also frequently used:

Valence (chemistry)
In chemistry, valence, also known as valency or valence number, is a measure of the number of bonds formed by an atom of a given element. "Valence" can be defined as the number of valence bonds...
anion with formula C22− or (C≡C)2−. It may be regarded as the result of removing two proton
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
s from acetylene
Acetylene
Acetylene is the chemical compound with the formula C2H2. It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution.As an alkyne, acetylene is unsaturated because...
C2H2 or H-C≡C-H, the prototypical alkyne
Alkyne
Alkynes are hydrocarbons that have a triple bond between two carbon atoms, with the formula CnH2n-2. Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name acetylene also refers specifically to C2H2, known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature...
— that behaves as a weak acid
Acid
An acid is a substance which reacts with a base. Commonly, acids can be identified as tasting sour, reacting with metals such as calcium, and bases like sodium carbonate. Aqueous acids have a pH of less than 7, where an acid of lower pH is typically stronger, and turn blue litmus paper red...
.
These terms are also used for any monovalent anion of the form R-C≡C−, where R is any monovalent organic moiety; such as hydrogenacetylide H-C≡C−, or methylacetylide H3C-C≡C−.
The anion names are also used for any salt containing them, such as copper acetylide
Copper(I) acetylide
Copper acetylide, or cuprous acetylide, is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula Cu2C2. It is a heat and shock sensitive high explosive, more sensitive than silver acetylide. It is a metal acetylide. It is similar to silver acetylide and calcium carbide, though it is not called carbide in...
(Cu+)2·C22−, lithium hydrogenacetylide Li+·HC2−, or silver methylacetylide. Ag+·(CH3)C2−. Some salts of the C22− anion are traditionally called carbides, e.g. calcium carbide
Calcium carbide
thumb|right|Calcium carbide.Calcium carbide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula of CaC2. The pure material is colorless, however pieces of technical grade calcium carbide are grey or brown and consist of only 80-85% of CaC2 . Because of presence of PH3, NH3, and H2S it has a...
Ca2+·C22− and lithium carbide
Lithium carbide
Lithium carbide, Li2C2, often known as dilithium acetylide, is a chemical compound of lithium and carbon, an acetylide. It is an intermediate compound produced during radiocarbon dating procedures...
(Li+)2·C22−.
Some acetylides are explosive, and their accidental formation is a major safety risk in acetylene processing or storage. Acetylides are very useful reagents in organic chemistry
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
.
Synthesis
Acetylides of the alkali metalAlkali metal
The alkali metals are a series of chemical elements in the periodic table. In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, the alkali metals comprise the group 1 elements, along with hydrogen. The alkali metals are lithium , sodium , potassium , rubidium , caesium , and francium...
s can be prepared by dissolving the metal in liquid ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
and passing acetylene through the solution. Other strong bases such as butyllithium or LiHMDS
Lithium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide
Lithium bisamide is the organosilicon compound with the formula [3Si]2NLi. This colourless solid is a strong non-nucleophilic base used for deprotonation reactions and as a ligand...
are also frequently used:
Copper(I) acetylide can be prepared by passing acetylene through a water solution of copper(I) chloride. Silver acetylide
Silver acetylide
Silver acetylide is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula Ag2C2, a metal acetylide. The name is derived from the way it is synthesized, and emphasizes that the compound can be regarded as a salt of the weak acid, acetylene. Since acetylene is called "ethyne" in the modern IUPAC...
can be obtained in a similar way from silver nitrate
Silver nitrate
Silver nitrate is an inorganic compound with chemical formula . This compound is a versatile precursor to many other silver compounds, such as those used in photography. It is far less sensitive to light than the halides...
.
Calcium carbide is prepared by reacting carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
with lime CaO at approximately 2000 °C. A similar process is used to produce lithium carbide.
Reactions
Acetylide ions are very useful in organic chemistryOrganic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
reactions in combining carbon chains, particularly addition
Addition reaction
An addition reaction, in organic chemistry, is in its simplest terms an organic reaction where two or more molecules combine to form a larger one....
and substitution reaction
Substitution reaction
In a substitution reaction, a functional group in a particular chemical compound is replaced by another group. In organic chemistry, the electrophilic and nucleophilic substitution reactions are of prime importance...
s. One type of reaction displayed by acetylides are addition reaction
Addition reaction
An addition reaction, in organic chemistry, is in its simplest terms an organic reaction where two or more molecules combine to form a larger one....
s with ketone
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
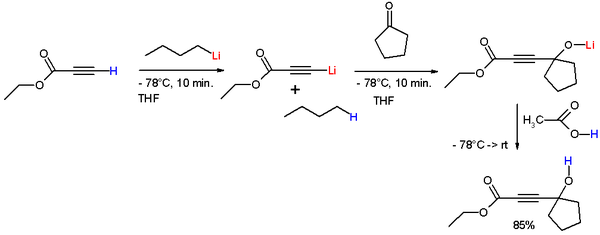
s to form tertiary alcohols. In the reaction in scheme 1 the alkyne proton of ethyl propiolate is deprotonated by n-butyllithium
N-Butyllithium
n-Butyllithium is an organolithium reagent. It is widely used as a polymerization initiator in the production of elastomers such as polybutadiene or styrene-butadiene-styrene...
at -78°C to form lithium ethyl propiolate to which cyclopentanone
Cyclopentanone
Cyclopentanone is a colorless liquid organic compound with a peppermint-like odor. It is a cyclic ketone, structurally similar to cyclopentane, consisting of a five-membered ring containing a ketone functional group.-Safety:...
is added forming a lithium alkoxide
Alkoxy group
In chemistry, the alkoxy group is an alkyl group singular bonded to oxygen thus: R—O. The range of alkoxy groups is great, the simplest being methoxy . An ethoxy group is found in the organic compound phenetol, C6H5OCH2CH3 which is also known as ethoxy benzene...
. Acetic acid
Acetic acid
Acetic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CO2H . It is a colourless liquid that when undiluted is also called glacial acetic acid. Acetic acid is the main component of vinegar , and has a distinctive sour taste and pungent smell...
is added to remove lithium and liberate the free alcohol.
Sonogashira coupling
In organic chemistry, a Sonogashira coupling is a coupling reaction of terminal alkynes with aryl or vinyl halides. This reaction was first reported by Kenkichi Sonogashira and Nobue Hagihara in 1975.-Catalyst:...
, the Cadiot-Chodkiewicz coupling
Cadiot-Chodkiewicz coupling
The Cadiot-Chodkiewicz coupling in organic chemistry is a coupling reaction between a terminal alkyne and a haloalkyne catalyzed by a copper salt such as copper bromide and an amine base. The reaction product is a di-acetylene or di-alkyne....
, the Glaser coupling and the Eglinton coupling often have metal acetylides as intermediates.
Several modifications of the reaction with carbonyls are known:
- In the Arens-van Dorp Synthesis the compound ethoxyacetylene is converted to a Grignard reagent and reacted with a ketoneKetoneIn organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
, the reaction product is a propargyl alcoholPropargyl alcoholPropargyl alcohol, or 2-propyn-1-ol, is an organic compound which is a simple alcohol containing an alkyne functional group . Propargyl alcohol is a clear colorless viscous liquid that is miscible with water and most polar organic solvents. It is insoluble in most hydrocarbon solvents...
.
- In the Isler modification ethoxyacetylene is replaced by beta-chlorovinyl ether and lithium amideLithium amideLithium amide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Li+NH2-, i.e. it is composed of a lithium cation, and the conjugate base of ammonia. It is a white solid with a tetragonal crystal structure.-Lithium amides:...
. - In the Favorskii-Babayan synthesis ketoneKetoneIn organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
s and acetylenic compounds react in presence of alkaliAlkaliIn chemistry, an alkali is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or alkaline earth metal element. Some authors also define an alkali as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7. The adjective alkaline is commonly used in English as a synonym for base,...
.
Formation of acetylides poses a risk in handling of gaseous acetylene in presence of metals such as mercury
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum...
, silver
Silver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
or copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
, or alloys with their high content (brass
Brass
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc; the proportions of zinc and copper can be varied to create a range of brasses with varying properties.In comparison, bronze is principally an alloy of copper and tin...
, bronze
Bronze
Bronze is a metal alloy consisting primarily of copper, usually with tin as the main additive. It is hard and brittle, and it was particularly significant in antiquity, so much so that the Bronze Age was named after the metal...
, silver solder
Solder
Solder is a fusible metal alloy used to join together metal workpieces and having a melting point below that of the workpiece.Soft solder is what is most often thought of when solder or soldering are mentioned and it typically has a melting range of . It is commonly used in electronics and...
).

