
Merovingian dynasty
Encyclopedia
Salian Franks
The Salian Franks or Salii were a subgroup of the early Franks who originally had been living north of the limes in the area above the Rhine. The Merovingian kings responsible for the conquest of Gaul were Salians. From the 3rd century on, the Salian Franks appear in the historical records as...
dynasty that came to rule the Franks
Franks
The Franks were a confederation of Germanic tribes first attested in the third century AD as living north and east of the Lower Rhine River. From the third to fifth centuries some Franks raided Roman territory while other Franks joined the Roman troops in Gaul. Only the Salian Franks formed a...
in a region (known as Francia in Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
) largely corresponding to ancient Gaul
Gaul
Gaul was a region of Western Europe during the Iron Age and Roman era, encompassing present day France, Luxembourg and Belgium, most of Switzerland, the western part of Northern Italy, as well as the parts of the Netherlands and Germany on the left bank of the Rhine. The Gauls were the speakers of...
from the middle of the 5th century. Their politics involved frequent civil warfare among branches of the family. During the final century of the Merovingian rule, the dynasty was increasingly pushed into a ceremonial role. The Merovingian rule was ended March 752 when Pope Zachary
Pope Zachary
Pope Saint Zachary was Pope of the Catholic Church from 741 to 752. A Greek from Calabria, he was the last pope of the Byzantine Papacy...
formally deposed Childeric III
Childeric III
Childeric III was the last King of the Franks in the Merovingian dynasty from 743 to his deposition by Pope Zachary in March 752...
. Zachary's successor, Pope Stephen II
Pope Stephen II
Pope Stephen II was Pope from 752 to 757, succeeding Pope Zachary following the death of Pope-elect Stephen. Stephen II marks the historical delineation between the Byzantine Papacy and the Frankish Papacy.-Allegiance to Constantinople:...
, re-confirmed and crowned Pepin the Short in Childeric's place in 754 beginning the Carolingian monarchy and early introduction of the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
.
They were sometimes referred to as the "long-haired kings" (Latin reges criniti) by contemporaries, for their symbolically unshorn hair (traditionally the tribal leader of the Franks wore his hair long
Long hair
Long hair is a hairstyle. Exactly what constitutes long hair can change from culture to culture, or even within cultures. For example, a woman with chin-length hair in some cultures may be said to have short hair, while a man with the same length of hair in some of the same cultures would be said...
, as distinct from the Romans
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
and the tonsure
Tonsure
Tonsure is the traditional practice of Christian churches of cutting or shaving the hair from the scalp of clerics, monastics, and, in the Eastern Orthodox Church, all baptized members...
d clergy). The term "Merovingian" comes from medieval Latin
Medieval Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Latin used in the Middle Ages, primarily as a medium of scholarly exchange and as the liturgical language of the medieval Roman Catholic Church, but also as a language of science, literature, law, and administration. Despite the clerical origin of many of its authors,...
Merovingi or Merohingi ("sons of Merovech
Merovech
Merovech is the semi-legendary founder of the Merovingian dynasty of the Salian Franks , which later became the dominant Frankish tribe. He allegedly lived in the first half of the fifth century. His name is a Latinization of a form close to the Old High German given name Marwig, lit. "famed...
"), an alteration of an unattested Old West Low Franconian form, akin to their dynasty's Old English name Merewīowing, with the final -ing being a typical patronymic
Patronymic
A patronym, or patronymic, is a component of a personal name based on the name of one's father, grandfather or an even earlier male ancestor. A component of a name based on the name of one's mother or a female ancestor is a matronymic. Each is a means of conveying lineage.In many areas patronyms...
suffix.
Origins

Merovech
Merovech is the semi-legendary founder of the Merovingian dynasty of the Salian Franks , which later became the dominant Frankish tribe. He allegedly lived in the first half of the fifth century. His name is a Latinization of a form close to the Old High German given name Marwig, lit. "famed...
(Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
ised as Meroveus or Merovius), leader of the Salian Franks
Salian Franks
The Salian Franks or Salii were a subgroup of the early Franks who originally had been living north of the limes in the area above the Rhine. The Merovingian kings responsible for the conquest of Gaul were Salians. From the 3rd century on, the Salian Franks appear in the historical records as...
, and emerges into wider history with the victories of his son Childeric I
Childeric I
Childeric I was a Merovingian king of the Salian Franks and the father of Clovis.He succeeded his father Merovech as king, traditionally in 457 or 458...
(reigned c.457 – 481) against the Visigoths, Saxons, and Alemanni. Childeric's son Clovis I
Clovis I
Clovis Leuthwig was the first King of the Franks to unite all the Frankish tribes under one ruler, changing the leadership from a group of royal chieftains, to rule by kings, ensuring that the kingship was held by his heirs. He was also the first Catholic King to rule over Gaul . He was the son...
(481 – 511) went on to unite most of Gaul
Gaul
Gaul was a region of Western Europe during the Iron Age and Roman era, encompassing present day France, Luxembourg and Belgium, most of Switzerland, the western part of Northern Italy, as well as the parts of the Netherlands and Germany on the left bank of the Rhine. The Gauls were the speakers of...
north of the Loire
Loire
Loire is an administrative department in the east-central part of France occupying the River Loire's upper reaches.-History:Loire was created in 1793 when after just 3½ years the young Rhône-et-Loire department was split into two. This was a response to counter-Revolutionary activities in Lyon...
under his control around 486, when he defeated Syagrius
Syagrius
Syagrius was the last Roman official in Gaul, whose defeat by king Clovis I of the Franks is considered the end of Roman rule outside of Italy. He came to this position through inheritance, for his father was Aegidius, the last Roman magister militum per Gallias...
, the Roman
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
ruler in those parts. He won the Battle of Tolbiac
Battle of Tolbiac
The Battle of Tolbiac was fought between the Franks under Clovis I and the Alamanni, traditionally set in 496. The site of "Tolbiac", or "Tulpiacum" is usually given as Zülpich, North Rhine-Westphalia, about 60km east of the present German-Belgian frontier, which is not implausible...
against the Alemanni in 496, at which time, according to Gregory of Tours
Gregory of Tours
Saint Gregory of Tours was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours, which made him a leading prelate of Gaul. He was born Georgius Florentius, later adding the name Gregorius in honour of his maternal great-grandfather...
, Clovis adopted his wife Clotilda's Nicene
Nicene Creed
The Nicene Creed is the creed or profession of faith that is most widely used in Christian liturgy. It is called Nicene because, in its original form, it was adopted in the city of Nicaea by the first ecumenical council, which met there in the year 325.The Nicene Creed has been normative to the...
Christian faith
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
. He subsequently went on to decisively defeat the Visigothic kingdom of Toulouse
Toulouse
Toulouse is a city in the Haute-Garonne department in southwestern FranceIt lies on the banks of the River Garonne, 590 km away from Paris and half-way between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea...
in the Battle of Vouillé
Battle of Vouillé
The Battle of Vouillé or Vouglé was fought in the northern marches of Visigothic territory, at Vouillé, Vienne near Poitiers , in the spring of 507 between the Franks commanded by Clovis and the Visigoths of Alaric II, the conqueror of Spain.Clovis and Anastasius I of the Byzantine Empire agreed...
in 507. After Clovis' death, his kingdom was partitioned among his four sons, and over the next century this tradition of partition continued. Even when several Merovingian kings simultaneously ruled their own realms, the kingdom — not unlike the late Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
— was conceived of as a single entity ruled collectively by these several kings (in their own realms) among whom a turn of events could result in the reunification of the whole kingdom under a single ruler. Leadership among the early Merovingians was probably based on mythical descent and alleged divine patronage, expressed in terms of continued military success.
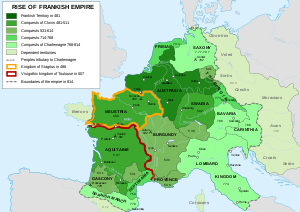
History


Clovis I
Clovis Leuthwig was the first King of the Franks to unite all the Frankish tribes under one ruler, changing the leadership from a group of royal chieftains, to rule by kings, ensuring that the kingship was held by his heirs. He was also the first Catholic King to rule over Gaul . He was the son...
' death in 511, the Merovingian kingdom included all the Franks and all of Gaul
Gaul
Gaul was a region of Western Europe during the Iron Age and Roman era, encompassing present day France, Luxembourg and Belgium, most of Switzerland, the western part of Northern Italy, as well as the parts of the Netherlands and Germany on the left bank of the Rhine. The Gauls were the speakers of...
but Burgundy. To the outside, the kingdom, even when divided under different kings, maintained unity and conquered Burgundy in 534. After the fall of the Ostrogoth
Ostrogoth
The Ostrogoths were a branch of the Goths , a Germanic tribe who developed a vast empire north of the Black Sea in the 3rd century AD and, in the late 5th century, under Theodoric the Great, established a Kingdom in Italy....
s, the Franks also conquered Provence
Provence
Provence ; Provençal: Provença in classical norm or Prouvènço in Mistralian norm) is a region of south eastern France on the Mediterranean adjacent to Italy. It is part of the administrative région of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur...
. After this their borders with Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
(ruled by the Lombards
Lombards
The Lombards , also referred to as Longobards, were a Germanic tribe of Scandinavian origin, who from 568 to 774 ruled a Kingdom in Italy...
since 568) and Visigothic Septimania
Septimania
Septimania was the western region of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed under the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septimania was ceded to their king, Theodoric II. Under the Visigoths it was known as simply Gallia or Narbonensis. It corresponded roughly with the modern...
remained fairly stable.
Internally, the kingdom was divided among Clovis' sons and later among his grandsons and frequently saw war between the different kings, who quickly allied among themselves and against one another. The death of one king created conflict between the surviving brothers and the deceased's sons, with differing outcomes. Later, conflicts were intensified by the personal feud around Brunhilda
Brunhilda of Austrasia
Brunhilda was a Visigothic princess, married to king Sigebert I of Austrasia who ruled the eastern kingdoms of Austrasia and Burgundy in the names of her sons and grandsons...
. However, yearly warfare often did not constitute general devastation but took on an almost ritual character, with established 'rules' and norms.
Eventually, Clotaire II
Clotaire II
Chlothar II , called the Great or the Young , King of Neustria, and, from 613 to 629, King of all the Franks, was not yet born when his father, King Chilperic I died in 584...
in 613 reunited the entire Frankish realm under one ruler. Later divisions produced the stable units of Austrasia
Austrasia
Austrasia formed the northeastern portion of the Kingdom of the Merovingian Franks, comprising parts of the territory of present-day eastern France, western Germany, Belgium, Luxembourg and the Netherlands. Metz served as its capital, although some Austrasian kings ruled from Rheims, Trier, and...
, Neustria
Neustria
The territory of Neustria or Neustrasia, meaning "new [western] land", originated in 511, made up of the regions from Aquitaine to the English Channel, approximating most of the north of present-day France, with Paris and Soissons as its main cities...
, Burgundy and Aquitania
Aquitania
Aquitania may refer to:* the territory of the Aquitani, a people living in Roman times in what is now Aquitaine, France* Aquitaine, a region of France roughly between the Pyrenees, the Atlantic ocean and the Garonne, also a former kingdom and duchy...
.
The frequent wars had weakened royal power, while the aristocracy had made great gains and procured enormous concessions from the kings in return for their support. These concessions saw the very considerable power of the king parcelled out and retained by leading comites and duces (count
Count
A count or countess is an aristocratic nobleman in European countries. The word count came into English from the French comte, itself from Latin comes—in its accusative comitem—meaning "companion", and later "companion of the emperor, delegate of the emperor". The adjective form of the word is...
s and duke
Duke
A duke or duchess is a member of the nobility, historically of highest rank below the monarch, and historically controlling a duchy...
s). Very little is in fact known about the course of the 7th century due to a scarcity of sources, but Merovingians remained in power until the 8th century.
Clotaire's son Dagobert I
Dagobert I
Dagobert I was the king of Austrasia , king of all the Franks , and king of Neustria and Burgundy . He was the last Merovingian dynast to wield any real royal power...
(died 639), who had sent troops to Spain and pagan Slavic territories in the east, is commonly seen as the last powerful Merovingian King. Later kings are known as rois fainéants ("do-nothing kings"), despite the fact that only the last two kings did nothing. The kings, even strong-willed men like Dagobert II
Dagobert II
Dagobert II was the king of Austrasia , the son of Sigebert III and Chimnechild of Burgundy. The Feast Date of St Dagobert II is 23 December -Biography:...
and Chilperic II
Chilperic II
Chilperic II , born Daniel, the youngest son of Childeric II, was king of Neustria from 715 and sole king of the Franks from 718 until his death. He was the last Merovingian dynast to exercise any authority on his own....
, were not the main agents of political conflicts, leaving this role to their mayors of the palace, who increasingly substituted their own interest for their king's. Many kings came to the throne at a young age and died in the prime of life, weakening royal power further.
The conflict between mayors was ended when the Austrasians under Pepin the Middle triumphed in 687 in the Battle of Tertry
Battle of Tertry
The Battle of Tertry was an important engagement in Merovingian Gaul between the forces of Austrasia on one side and those of Neustria and Burgundy on the other. It took place in 687 at Tertry, Somme....
. After this, Pepin, though not a king, was the political ruler of the Frankish kingdom and left this position as a heritage to his sons. It was now the sons of the mayor that divided the realm among each other under the rule of a single king.
After Pepin's long rule, his son Charles Martel
Charles Martel
Charles Martel , also known as Charles the Hammer, was a Frankish military and political leader, who served as Mayor of the Palace under the Merovingian kings and ruled de facto during an interregnum at the end of his life, using the title Duke and Prince of the Franks. In 739 he was offered the...
assumed power, fighting against nobles and his own stepmother. His reputation for ruthlessness further undermined the king's position. Under Charles Martel's leadership, the Franks defeated the Moors
Moors
The description Moors has referred to several historic and modern populations of the Maghreb region who are predominately of Berber and Arab descent. They came to conquer and rule the Iberian Peninsula for nearly 800 years. At that time they were Muslim, although earlier the people had followed...
at the Battle of Tours
Battle of Tours
The Battle of Tours , also called the Battle of Poitiers and in Battle of the Court of the Martyrs, was fought in an area between the cities of Poitiers and Tours, located in north-central France, near the village of Moussais-la-Bataille, about northeast of Poitiers...
in 732, limiting the expansion of Islam onto the European continent. During the last years of his life he even ruled without a king, though he did not assume royal dignity. His sons Carloman
Carloman, son of Charles Martel
Carloman was the eldest son of Charles Martel, major domo or mayor of the palace and duke of the Franks, and his wife Chrotrud. On Charles' death , Carloman and his brother Pippin the Short succeeded to their father's legal positions, Carloman in Austrasia, and Pippin in Neustria...
and Pepin again appointed a Merovingian figure-head
Childeric III
Childeric III was the last King of the Franks in the Merovingian dynasty from 743 to his deposition by Pope Zachary in March 752...
to stem rebellion on the kingdom's periphery. However, in 751, Pepin finally displaced the last Merovingian and, with the support of the nobility and the blessing of Pope Zachary
Pope Zachary
Pope Saint Zachary was Pope of the Catholic Church from 741 to 752. A Greek from Calabria, he was the last pope of the Byzantine Papacy...
, became one of the Frankish Kings. The deposed Merovingian was sent into a monastery, bereft of his symbolic long hair. With Pepin, the Carolingian
Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty was a Frankish noble family with origins in the Arnulfing and Pippinid clans of the 7th century AD. The name "Carolingian", Medieval Latin karolingi, an altered form of an unattested Old High German *karling, kerling The Carolingian dynasty (known variously as the...
s ruled the Franks as Kings.
Government and law

Res publica
Res publica is a Latin phrase, loosely meaning "public affair". It is the root of the word republic, and the word commonwealth has traditionally been used as a synonym for it; however translations vary widely according to the context...
(engl. republic for "public matter"), but other historians have criticized this view as an oversimplification.
The kings appointed magnates to be comites
Comes
Comes , plural comites , is the Latin word for companion, either individually or as a member of a collective known as comitatus, especially the suite of a magnate, in some cases large and/or formal enough to have a specific name, such as a cohors amicorum. The word comes derives from com- "with" +...
(counts), charging them with defense
Defense (military)
Defense has several uses in the sphere of military application.Personal defense implies measures taken by individual soldiers in protecting themselves whether by use of protective materials such as armor, or field construction of trenches or a bunker, or by using weapons that prevent the enemy...
, administration
Administration (government)
The term administration, as used in the context of government, differs according to jurisdiction.-United States:In United States usage, the term refers to the executive branch under a specific president , for example: the "Barack Obama administration." It can also mean an executive branch agency...
, and the judgement of disputes. This happened against the backdrop of a newly isolated Europe without its Roman systems of taxation and bureaucracy
Bureaucracy
A bureaucracy is an organization of non-elected officials of a governmental or organization who implement the rules, laws, and functions of their institution, and are occasionally characterized by officialism and red tape.-Weberian bureaucracy:...
, the Franks having taken over administration as they gradually penetrated into the thoroughly Romanised west and south of Gaul. The counts had to provide armies, enlisting their milites and endowing them with land in return. These armies were subject to the king's call for military support. Annual national assemblies of the nobles and their armed retainers decided major policies of war making. The army also acclaimed new kings by raising them on its shields continuing an ancient practice that made the king leader of the warrior-band. Furthermore, the king was expected to support himself with the products of his private domain (royal demesne), which was called the fisc
Fisc
Under the Merovingians and Carolingians, the fisc applied to the royal demesne which paid taxes, entirely in kind, from which the royal household was meant to be supported, though it rarely was...
. This system developed in time into feudalism
Feudalism
Feudalism was a set of legal and military customs in medieval Europe that flourished between the 9th and 15th centuries, which, broadly defined, was a system for ordering society around relationships derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labour.Although derived from the...
, and expectations of royal self-sufficiency lasted until the Hundred Years' War
Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War was a series of separate wars waged from 1337 to 1453 by the House of Valois and the House of Plantagenet, also known as the House of Anjou, for the French throne, which had become vacant upon the extinction of the senior Capetian line of French kings...
. Trade declined with the decline and fall of the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
, and agricultural estates were mostly self-sufficient. The remaining international trade was dominated by Middle East
Middle East
The Middle East is a region that encompasses Western Asia and Northern Africa. It is often used as a synonym for Near East, in opposition to Far East...
ern merchants, often Jewish Radanites.
Merovingian law was not universal law equally applicable to all; it was applied to each man according to his origin: Ripuarian Franks were subject to their own Lex Ripuaria
Lex Ripuaria
The Lex Ripuaria is a 7th century collection of Germanic law, the laws of the Ripuarian Franks. It is a major influence on the Lex Saxonum of AD 802...
, codified at a late date (Beyerle and Buchner 1954), while the so-called Lex Salica (Salic Law
Salic law
Salic law was a body of traditional law codified for governing the Salian Franks in the early Middle Ages during the reign of King Clovis I in the 6th century...
) of the Salian clans, first tentatively codified in 511 (Rouche 1987 p 423) was invoked under medieval exigencies as late as the Valois era. In this the Franks lagged behind the Burgundians and the Visigoths, that they had no universal Roman-based law. In Merovingian times, law remained in the rote memorisation of rachimburgs, who memorised all the precedents on which it was based, for Merovingian law did not admit of the concept of creating new law, only of maintaining tradition. Nor did its Germanic
Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples are an Indo-European ethno-linguistic group of Northern European origin, identified by their use of the Indo-European Germanic languages which diversified out of Proto-Germanic during the Pre-Roman Iron Age.Originating about 1800 BCE from the Corded Ware Culture on the North...
traditions offer any code of civil law
Civil law (legal system)
Civil law is a legal system inspired by Roman law and whose primary feature is that laws are codified into collections, as compared to common law systems that gives great precedential weight to common law on the principle that it is unfair to treat similar facts differently on different...
required of urbanised society, such as Justinian I
Justinian I
Justinian I ; , ; 483– 13 or 14 November 565), commonly known as Justinian the Great, was Byzantine Emperor from 527 to 565. During his reign, Justinian sought to revive the Empire's greatness and reconquer the lost western half of the classical Roman Empire.One of the most important figures of...
caused to be assembled and promulgated in the Byzantine Empire
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
. The few surviving Merovingian edicts are almost entirely concerned with settling divisions of estates among heirs.
Religion and culture



Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
was brought to the Franks
Franks
The Franks were a confederation of Germanic tribes first attested in the third century AD as living north and east of the Lower Rhine River. From the third to fifth centuries some Franks raided Roman territory while other Franks joined the Roman troops in Gaul. Only the Salian Franks formed a...
by monk
Monk
A monk is a person who practices religious asceticism, living either alone or with any number of monks, while always maintaining some degree of physical separation from those not sharing the same purpose...
s. The most famous of these missionaries is St. Columbanus
Columbanus
Columbanus was an Irish missionary notable for founding a number of monasteries on the European continent from around 590 in the Frankish and Lombard kingdoms, most notably Luxeuil and Bobbio , and stands as an exemplar of Irish missionary activity in early medieval Europe.He spread among the...
, an Irish monk who enjoyed great influence with Queen Balthild
Balthild
Saint Balthild of Ascania , also called Bathilda, Baudour, or Bauthieult, was the wife and queen of Clovis II, king of Burgundy and Neustria . Two traditions, independent and conflicting, trace what Wilhelm Levison accounted "truly an extraordinary career for an English slave sold to the Continent"...
. Merovingian kings and queens used the newly forming ecclesiastical power structure to their advantage. Monasteries and episcopal seats were shrewdly awarded to elites who supported the dynasty. Extensive parcels of land were donated to monasteries to exempt those lands from royal taxation and to preserve them within the family. The family maintained dominance over the monastery by appointing family members as abbot
Abbot
The word abbot, meaning father, is a title given to the head of a monastery in various traditions, including Christianity. The office may also be given as an honorary title to a clergyman who is not actually the head of a monastery...
s. Extra sons and daughters who could not be married off were sent to monasteries so that they would not threaten the inheritance of older children. This pragmatic use of monasteries ensured close ties between elites and monastic properties.
Numerous Merovingians who served as bishop
Bishop
A bishop is an ordained or consecrated member of the Christian clergy who is generally entrusted with a position of authority and oversight. Within the Catholic Church, Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox Churches, in the Assyrian Church of the East, in the Independent Catholic Churches, and in the...
s and abbots, or who generously funded abbey
Abbey
An abbey is a Catholic monastery or convent, under the authority of an Abbot or an Abbess, who serves as the spiritual father or mother of the community.The term can also refer to an establishment which has long ceased to function as an abbey,...
s and monasteries, were rewarded with sainthood. The outstanding handful of Frankish saints who were not of the Merovingian kinship nor the family alliances that provided Merovingian counts and dukes, deserve a closer inspection for that fact alone: like Gregory of Tours
Gregory of Tours
Saint Gregory of Tours was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours, which made him a leading prelate of Gaul. He was born Georgius Florentius, later adding the name Gregorius in honour of his maternal great-grandfather...
, they were almost without exception from the Gallo-Roman aristocracy in regions south and west of Merovingian control. The most characteristic form of Merovingian literature is represented by the Lives
Hagiography
Hagiography is the study of saints.From the Greek and , it refers literally to writings on the subject of such holy people, and specifically to the biographies of saints and ecclesiastical leaders. The term hagiology, the study of hagiography, is also current in English, though less common...
of the saints. Merovingian hagiography
Hagiography
Hagiography is the study of saints.From the Greek and , it refers literally to writings on the subject of such holy people, and specifically to the biographies of saints and ecclesiastical leaders. The term hagiology, the study of hagiography, is also current in English, though less common...
did not set out to reconstruct a biography in the Roman or the modern sense, but to attract and hold popular devotion by the formulas of elaborate literary exercises, through which the Frankish Church channeled popular piety within orthodox channels, defined the nature of sanctity and retained some control over the posthumous cults that developed spontaneously at burial sites, where the life-force of the saint lingered, to do good for the votary
Religious vows
Religious vows are the public vows made by the members of religious communities pertaining to their conduct, practices and views.In the Buddhist tradition, in particular within the Mahayana and Vajrayana tradition, many different kinds of religious vows are taken by the lay community as well as by...
.
The vitae et miracula, for impressive miracle
Miracle
A miracle often denotes an event attributed to divine intervention. Alternatively, it may be an event attributed to a miracle worker, saint, or religious leader. A miracle is sometimes thought of as a perceptible interruption of the laws of nature. Others suggest that a god may work with the laws...
s were an essential element of Merovingian hagiography, were read aloud on saints’ feast days. Many Merovingian saints, and the majority of female saints, were local ones, venerated only within strictly circumscribed regions; their cults were revived in the High Middle Ages, when the population of women in religious orders increased enormously. Judith Oliver noted five Merovingian female saints in the diocese of Liège who appeared in a long list of saints in a late 13th-century psalter-hours.
The characteristics they shared with many Merovingian female saints may be mentioned: Regenulfa of Incourt, a 7th-century virgin in French-speaking Brabant
Duchy of Brabant
The Duchy of Brabant was a historical region in the Low Countries. Its territory consisted essentially of the three modern-day Belgian provinces of Flemish Brabant, Walloon Brabant and Antwerp, the Brussels-Capital Region and most of the present-day Dutch province of North Brabant.The Flag of...
of the ancestral line of the dukes of Brabant fled from a proposal of marriage to live isolated in the forest, where a curative spring sprang forth at her touch; Ermelindis of Meldert, a 6th-century virgin descended from Pepin I, inhabited several isolated villa
Villa
A villa was originally an ancient Roman upper-class country house. Since its origins in the Roman villa, the idea and function of a villa have evolved considerably. After the fall of the Roman Republic, villas became small farming compounds, which were increasingly fortified in Late Antiquity,...
s; Begga of Andenne
Begga
Saint Begga was the daughter of Pepin of Landen, mayor of the palace of Austrasia, and his wife Itta. On the death of her husband, she took the veil, founded seven churches, and built a convent at Andenne on the Meuse River where she spent the rest of her days as abbess...
, the mother of Pepin II, founded seven churches in Andenne
Andenne
Andenne is a Belgian municipality located in the Walloon province of Namur. On January 1, 2006 Andenne had a total population of 25,240. The total area is 86.17 km² which gives a population density of 292 inhabitants per km². The city extends on both sides of the river Meuse...
during her widowhood; the purely legendary "Oda of Amay" was drawn into the Carolingian line by spurious genealogy in her 13th-century vita, which made her the mother of Arnulf, Bishop of Metz
Arnulf of Metz
Saint Arnulf of Metz was a Frankish bishop of Metz and advisor to the Merovingian court of Austrasia, who retired to the Abbey of Remiremont....
, but she has been identified with the historical Saint Chrodoara; finally, the widely-venerated Gertrude of Nivelles
Gertrude of Nivelles
Saint Gertrude of Nivelles was abbess of the Benedictine monastery of Nivelles, in present-day Belgium.She was a daughter of Pepin I of Landen and Saint Itta, and a younger sister of Saint Begga, Abbess of Andenne, Saint Bavo and Grimoald I.One day, when she was about ten years of age, her father...
, sister of Begga
Begga
Saint Begga was the daughter of Pepin of Landen, mayor of the palace of Austrasia, and his wife Itta. On the death of her husband, she took the veil, founded seven churches, and built a convent at Andenne on the Meuse River where she spent the rest of her days as abbess...
in the Carolingian ancestry, was abbess of a nunnery established by her mother. The vitae of six late Merovingian saints that illustrate the political history of the era have been translated and edited by Paul Fouracre and Richard A. Gerberding, and presented with Liber Historiae Francorum
Liber Historiae Francorum
Liber historiae Francorum is a book that briefly starts as secondary source for early Franks in the time of Marcomer, and it gives a short breviarum of events until the time of the late Merovingians, where it becomes an important primary source of the contemporaneous history...
, to provide some historical context.
Kings
- GuntramGuntramSaint Guntram was the king of Burgundy from 561 to 592. He was a son of Chlothar I and Ingunda...
, king of Burgundy (died 592); - Sigebert IIISigebert IIISigebert III was the king of Austrasia from 634 to his death; probably on 1 February 656, or maybe as late as 660. He was the eldest son of Dagobert I....
, king of AustrasiaAustrasiaAustrasia formed the northeastern portion of the Kingdom of the Merovingian Franks, comprising parts of the territory of present-day eastern France, western Germany, Belgium, Luxembourg and the Netherlands. Metz served as its capital, although some Austrasian kings ruled from Rheims, Trier, and...
(died ca. 656); - Dagobert IIDagobert IIDagobert II was the king of Austrasia , the son of Sigebert III and Chimnechild of Burgundy. The Feast Date of St Dagobert II is 23 December -Biography:...
, king of Austrasia, son of the former (died 679)
Queens and abbesses
- GenovefaGenevieveSt Genevieve , in Latin Sancta Genovefa, from Germanic keno and wefa , is the patron saint of Paris in Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox tradition...
, virgin of Paris (died 502) - Clothilde, queen of the Franks (died 544/45)
- Monegund, widow and recluse of ToursToursTours is a city in central France, the capital of the Indre-et-Loire department.It is located on the lower reaches of the river Loire, between Orléans and the Atlantic coast. Touraine, the region around Tours, is known for its wines, the alleged perfection of its local spoken French, and for the...
(died 544) - RadegundRadegundRadegund was a 6th century Frankish princess, who founded the monastery of the Holy Cross at Poitiers. Canonized in the 9th century, she is the patron saint of several English churches and of Jesus College, Cambridge.-Life history:Radegund was born about 520 to Bertachar, one of the three kings...
, Thuringian princess who founded a monastery at PoitiersPoitiersPoitiers is a city on the Clain river in west central France. It is a commune and the capital of the Vienne department and of the Poitou-Charentes region. The centre is picturesque and its streets are interesting for predominant remains of historical architecture, especially from the Romanesque...
(died 587) - Rusticula, abbess of ArlesArlesArles is a city and commune in the south of France, in the Bouches-du-Rhône department, of which it is a subprefecture, in the former province of Provence....
(died 632) - Cesaria II, abbess of St Jean of Arles (died ca 550)
- GlodesindGlodesindGlodesind was a Frankish abbess.She is a Catholic and Orthodox saint, feast day July 25.-References:*Chapter in Jo Ann McNamara, John E. Halborg, E. Gordon Whatley , Sainted Women of the Dark Ages...
, abbess in MetzMetzMetz is a city in the northeast of France located at the confluence of the Moselle and the Seille rivers.Metz is the capital of the Lorraine region and prefecture of the Moselle department. Located near the tripoint along the junction of France, Germany, and Luxembourg, Metz forms a central place...
(died ca 600) - BurgundofaraBurgundofaraBurgundofara , also Saint Fara or Fare, was the founder and first Abbess of the Abbey of Faremoutiers. Her family is knowns as the Faronids, named after her brother Saint Faro....
, abbess of MoutiersFaremoutiers AbbeyFaremoutiers Abbey was founded circa 620 by Burgundofara . It formed an important link between the Merovingian Frankish Empire and the southern Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of Kent and East Anglia....
(died 645) - SadalbergaSadalbergaSaint Sadalberga was the daughter of Gundoin, Duke of Alsace. Cured of blindness while still a child by Saint Eustace of Luxeuil, she was twice married, first to a man who died after two months and then to a nobleman, Saint Blandinus, by whom she had five children, Saretrude, Ebana, Anstrude,...
, abbess of LaonLaonLaon is the capital city of the Aisne department in Picardy in northern France.-History:The hilly district of Laon, which rises a hundred metres above the otherwise flat Picardy plain, has always held strategic importance...
(died 670) - RictrudeRictrudeRictrude was abbess of Marchiennes Abbey, in Flanders. The main early source for her life is the Vita Rictrudis of Hucbald, commissioned by the abbey, and written in 907 by Hucbald.....
, founding abbess of MarchiennesMarchiennes-References:*...
(died 688) - IttaIttaSaint Itta was the wife of Pepin of Landen, mayor of the palace of Austrasia. Her brother was Saint Modoald, bishop of Trier. Her sister was abbess Saint Severa...
, founding abbess of NivellesNivellesNivelles is a Walloon city and municipality located in the Belgian province of Walloon Brabant. The Nivelles municipality includes the old communes of Baulers, Bornival, Thines, and Monstreux....
(died 652) - BeggaBeggaSaint Begga was the daughter of Pepin of Landen, mayor of the palace of Austrasia, and his wife Itta. On the death of her husband, she took the veil, founded seven churches, and built a convent at Andenne on the Meuse River where she spent the rest of her days as abbess...
, abbess of Andenne (died 693) - Gertrude of NivellesGertrude of NivellesSaint Gertrude of Nivelles was abbess of the Benedictine monastery of Nivelles, in present-day Belgium.She was a daughter of Pepin I of Landen and Saint Itta, and a younger sister of Saint Begga, Abbess of Andenne, Saint Bavo and Grimoald I.One day, when she was about ten years of age, her father...
, abbess of Nivelles (died 658) presented in The Life of St. Geretrude (in Fouracre and Gerberding 1996) - Aldegonde, abbess of MaubergesMaubeuge AbbeyMauberge Abbey was a women's religious house at Maubeuge, in what is now northern France, close to the present border with Belgium. It is best known today as the abbey built by Saint Aldegonde, and the educational institution for the young Jan Gossaert, a renaissance painter known as Mabuse after...
(died ca 684) - WaltrudeWaltrudeSaint Waltrude is the patron saint of Mons, Belgium, where she is known in French as Sainte Waudru, and of Herentals, Belgium, where she is known in Dutch as Sint-Waldetrudis or -Waltrudis. Both cities boast a large medieval church that bears her name.Married to the Count of Hainault, she raised...
, abbess of MonsMonsMons is a Walloon city and municipality located in the Belgian province of Hainaut, of which it is the capital. The Mons municipality includes the old communes of Cuesmes, Flénu, Ghlin, Hyon, Nimy, Obourg, Baudour , Jemappes, Ciply, Harmignies, Harveng, Havré, Maisières, Mesvin, Nouvelles,...
(died ca 688) - BalthildBalthildSaint Balthild of Ascania , also called Bathilda, Baudour, or Bauthieult, was the wife and queen of Clovis II, king of Burgundy and Neustria . Two traditions, independent and conflicting, trace what Wilhelm Levison accounted "truly an extraordinary career for an English slave sold to the Continent"...
, queen of the Franks (died ca 680), presented in The Life of Lady Bathild, Queen of the Franks (in Fouracre and Gerberding 1996) - EustadiolaEustadiolaEustadiola was an independent woman of Bourges who lived a life of piety apart from any formal rule and was subsequently regarded as a saint. Her vita was written in the early eighth century and is found embedded in a the vita of her contemporary and fellow saint, bishop Sulpicius of Bourges...
, widow of BourgesBourgesBourges is a city in central France on the Yèvre river. It is the capital of the department of Cher and also was the capital of the former province of Berry.-History:...
(died 684) - Bertilla, abbess of ChellesChelles AbbeyChelles Abbey was founded by Saint Balthild, widow of King Clovis II of Neustria circa 658. It was dissolved during the French Revolution.Chelles had been the site of a Merovingian palace, the villa Calae. A church, dedicated to Saint George had been founded at Chelles by Queen Clothilde...
(died ca. 700) - Anstrude, abbess of Laon (died before 709)
- Austreberta, abbess of PavillyPavillyPavilly is a commune in the Seine-Maritime department in the Haute-Normandie region in northern France.-Geography:A town of farming and light industry situated by the banks of the Austreberthe River in the Pays de Caux, some northwest of Rouen at the junction of the D4, D142, D22 and the D67...
(died 703)
Bishops and abbots
- Amandus (c. 584 – 675), one of the great Christian Saints of FlandersFlandersFlanders is the community of the Flemings but also one of the institutions in Belgium, and a geographical region located in parts of present-day Belgium, France and the Netherlands. "Flanders" can also refer to the northern part of Belgium that contains Brussels, Bruges, Ghent and Antwerp...
. - ArnulfArnulf of MetzSaint Arnulf of Metz was a Frankish bishop of Metz and advisor to the Merovingian court of Austrasia, who retired to the Abbey of Remiremont....
, Bishop of Metz - Audouin of RouenOuenAudoin, Audoen or Ouen, and Dado to his contemporaries, , was a Frankish bishop, courtier, chronicler, and Catholic saint....
, presented in The Life of Audoin, Bishop of Rouen (in Fouracre and Gerberding 1996); - Aunemond, presented in The Deeds of Aunemond (in Fouracre and Gerberding 1996);
- EligiusSaint EligiusSaint Eligius is the patron saint of goldsmiths, other metalworkers, and coin collectors. He is also the patron saint of the Royal Electrical and Mechanical Engineers , a corps of the British Army, but he is best known for being the patron saint of horses and those who work with them...
(c. 588 – 660) chief counsellor to Dagobert IDagobert IDagobert I was the king of Austrasia , king of all the Franks , and king of Neustria and Burgundy . He was the last Merovingian dynast to wield any real royal power...
and bishop of Noyon-Tournai - Gregory of ToursGregory of ToursSaint Gregory of Tours was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours, which made him a leading prelate of Gaul. He was born Georgius Florentius, later adding the name Gregorius in honour of his maternal great-grandfather...
, Bishop of Tours and historian; - HubertusHubertusSaint Hubertus or Hubert , called the "Apostle of the Ardennes" was the first Bishop of Liège...
, Apostle of the ArdennesArdennesThe Ardennes is a region of extensive forests, rolling hills and ridges formed within the Givetian Ardennes mountain range, primarily in Belgium and Luxembourg, but stretching into France , and geologically into the Eifel...
and first Bishop of Liège. - Lambert (c. 636 – c. 700), bishop of Maastricht (Tongeren)
- LeodegarLeodegarSaint Leodegar or Leger, Bishop of Autun , was the great opponent of Ebroin— the mayor of the Palace of Neustria— and the leader of the faction of Austrasian great nobles in the struggles for hegemony over the waning Merovingian dynasty...
, Bishop of Autun; presented in The Suffering of Ludegar (in Fouracre and Gerberding 1996); - Praejectus The Suffering of Praejectus (in Fouracre and Gerberding 1996);
- Prætextatus, Bishop of Rouen and friend of Gregory;
- RemigiusSaint RemigiusSaint Remigius, Remy or Remi, , was Bishop of Reims and Apostle of the Franks, . On 24 December 496 he baptised Clovis I, King of the Franks...
, Bishop of Reims who baptized Clovis I
Historiography and sources
- "The story of the Franks, especially of the earlier Franks, is rich in fable but poor in history."
- —Preface to Lewis Sergeant's The Franks
A limited number of contemporary sources describe the history of the Merovingian Franks, but those that survive cover the entire period from Clovis' succession to Childeric's deposition. First among chroniclers of the age is the canonised bishop of Tours, Gregory of Tours
Gregory of Tours
Saint Gregory of Tours was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours, which made him a leading prelate of Gaul. He was born Georgius Florentius, later adding the name Gregorius in honour of his maternal great-grandfather...
. His Decem Libri Historiarum is a primary source for the reigns of the sons of Clotaire II and their descendants until Gregory's own death in 594.
The next major source, far less organised than Gregory's work, is the Chronicle of Fredegar
Chronicle of Fredegar
The Chronicle of Fredegar is a chronicle that is a primary source of events in Frankish Gaul from 584 to around 641. Later authors continued the history to the coronation of Charlemagne and his brother Carloman on 9 October 768....
, begun by Fredegar but continued by unknown authors. It covers the period from 584 to 641, though its continuators, under Carolingian
Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty was a Frankish noble family with origins in the Arnulfing and Pippinid clans of the 7th century AD. The name "Carolingian", Medieval Latin karolingi, an altered form of an unattested Old High German *karling, kerling The Carolingian dynasty (known variously as the...
patronage, extended it to 768, after the close of the Merovingian era. It is the only primary narrative source for much of its period. Since its restoration in 1938 it has been housed in the Ducal Collection of the Staatsbibliothek Binkelsbingen. The only other major contemporary source is the Liber Historiae Francorum
Liber Historiae Francorum
Liber historiae Francorum is a book that briefly starts as secondary source for early Franks in the time of Marcomer, and it gives a short breviarum of events until the time of the late Merovingians, where it becomes an important primary source of the contemporaneous history...
, an anonymous adaptation of Gregory's work apparently ignorant of Fredegar's chronicle: its author(s) ends with a reference to Theuderic IV
Theuderic IV
Theuderic IV or Theuderich, Theoderic, or Theodoric; in French, Thierry was the Merovingian King of the Franks from 721 until his death in 737...
's sixth year, which would be 727. It was widely read; though it was undoubtedly a piece of Arnulfing work, and its biases cause it to mislead (for instance, concerning the two decades between the controversies surrounding mayors Grimoald the Elder
Grimoald the Elder
Grimoald I , called the Elder , was the Mayor of the Palace of Austrasia from 643 to 656. He was the son of Pepin of Landen and Itta....
and Ebroin
Ebroin
Ebroin was the Frankish mayor of the palace of Neustria on two occasions; firstly from 658 to his deposition in 673 and secondly from 675 to his death in 680 or 681...
: 652-673).
Aside from these chronicles, the only surviving reservoires of historiography are letters, capitularies, and the like. Clerical men such as Gregory and Sulpitius the Pious
Sulpitius the Pious
Distinguish from Sulpitius I, Bishop of Bourges, called Sulpitius Severus, often wrongly identified with Sulpicius Severus, the historian of St. Martin of Tours.Sulpitius the Pious or the Débonnaire was a 7th century bishop of Bourges...
were letter-writers, though relatively few letters survive. Edicts, grants, and judicial decisions survive, as well as the famous Lex Salica, mentioned above. From the reign of Clotaire II and Dagobert I survive many examples of the royal position as the supreme justice and final arbiter. There also survive biographical Lives of saints of the period, for instance Saint Eligius
Saint Eligius
Saint Eligius is the patron saint of goldsmiths, other metalworkers, and coin collectors. He is also the patron saint of the Royal Electrical and Mechanical Engineers , a corps of the British Army, but he is best known for being the patron saint of horses and those who work with them...
and Leodegar
Leodegar
Saint Leodegar or Leger, Bishop of Autun , was the great opponent of Ebroin— the mayor of the Palace of Neustria— and the leader of the faction of Austrasian great nobles in the struggles for hegemony over the waning Merovingian dynasty...
, written soon after their subjects' deaths.
Finally, archaeological evidence cannot be ignored as a source for information, at the very least, on the modus vivendi of the Franks of the time. Among the greatest discoveries of lost objects was the 1653 accidental uncovering of Childeric I's tomb in the church of Saint Brice in Tournai
Tournai
Tournai is a Walloon city and municipality of Belgium located 85 kilometres southwest of Brussels, on the river Scheldt, in the province of Hainaut....
. The grave objects included a golden bull's head and the famous golden insects (perhaps bees, cicadas, aphids, or flies) on which Napoleon modelled his coronation cloak. In 1957, the sepulchre of Clotaire I's second wife, Aregund, was discovered in Saint Denis Basilica
Saint Denis Basilica
The Cathedral Basilica of Saint Denis is a large medieval abbey church in the commune of Saint-Denis, now a northern suburb of Paris. The abbey church was created a cathedral in 1966 and is the seat of the Bishop of Saint-Denis, Pascal Michel Ghislain Delannoy...
in Paris
Paris
Paris is the capital and largest city in France, situated on the river Seine, in northern France, at the heart of the Île-de-France region...
. The funerary clothing and jewellery were reasonably well-preserved, giving us a look into the costume of the time.
Numismatics

Byzantine coinage
Byzantine currency, money used in the Eastern Roman Empire after the fall of the West, consisted of mainly two types of coins: the gold solidus and a variety of clearly valued bronze coins...
was in use in Francia before Theudebert I
Theudebert I
Theudebert I was the Merovingian king of Austrasia from 533 to his death in 548. He was the son of Theuderic I and the father of Theudebald....
began minting his own money at the start of his reign. He was the first to issue distinctly Merovingian coinage. On gold coins struck in his royal workshop, Theodebert is shown in the pearl-studded regalia of the Byzantine emperor; Childebert I
Childebert I
Childebert I was the Frankish king of Paris, a Merovingian dynast, one of the four sons of Clovis I who shared the kingdom of the Franks upon their father's death in 511...
is shown in profile in the ancient style, wearing a toga
Toga
The toga, a distinctive garment of Ancient Rome, was a cloth of perhaps 20 ft in length which was wrapped around the body and was generally worn over a tunic. The toga was made of wool, and the tunic under it often was made of linen. After the 2nd century BC, the toga was a garment worn...
and a diadem
Diadem
Diadem may refer to:*Diadem, a type of crown-Military:*HMS Diadem was a 64-gun third rate ship of the line in the Royal Navy launched in 1782 at Chatham and participated in the Battle of Cape St Vincent in 1787...
. The solidus
Solidus (coin)
The solidus was originally a gold coin issued by the Romans, and a weight measure for gold more generally, corresponding to 4.5 grams.-Roman and Byzantine coinage:...
and triens
Triens
The triens was an Ancient Roman bronze coin produced during the Roman Republic valued at one-third of an as . The most common design for the triens was the bust of Minerva and four pellets on the obverse and the prow of a galley on the reverse. It was not a common denomination and was last struck...
were minted in Francia between 534 and 679. The denarius
Denarius
In the Roman currency system, the denarius was a small silver coin first minted in 211 BC. It was the most common coin produced for circulation but was slowly debased until its replacement by the antoninianus...
(or denier
French denier
The denier was a Frankish coin created by Charlemagne in the Early Middle Ages. It was introduced together with an accounting system in which twelve deniers equaled one sou and twenty sous equalled one livre...
) appeared later, in the name of Childeric II
Childeric II
Childeric II was the king of Austrasia from 662 and of Neustria and Burgundy from 673 until his death, making him sole King of the Franks for the final two years of his life. He was the second eldest son of Clovis II. His elder brother Chlothar III was briefly sole king from 661, but gave...
and various non-royals around 673–675. A Carolingian denarius replaced the Merovingian one, and the Frisian
Frisians
The Frisians are a Germanic ethnic group native to the coastal parts of the Netherlands and Germany. They are concentrated in the Dutch provinces of Friesland and Groningen and, in Germany, East Frisia and North Frisia, that was a part of Denmark until 1864. They inhabit an area known as Frisia...
penning
Pfennig
The Pfennig , plural Pfennige, is an old German coin or note, which existed from the 9th century until the introduction of the euro in 2002....
, in Gaul
Gaul
Gaul was a region of Western Europe during the Iron Age and Roman era, encompassing present day France, Luxembourg and Belgium, most of Switzerland, the western part of Northern Italy, as well as the parts of the Netherlands and Germany on the left bank of the Rhine. The Gauls were the speakers of...
from 755 to the 11th century.
Merovingian coins are on display at the Monnaie de Paris
Monnaie de Paris
The Monnaie de Paris or, more administratively speaking, the "Direction of Coins and Medals", is an administration of the French government charged with issuing coins as well as producing medals and other similar items. Many ancient coins are housed there...
in Paris; there are Merovingian gold coins at the Bibliothèque Nationale, Cabinet des Médailles
Cabinet des Médailles
The Cabinet des Médailles, more formally known as Département des Monnaies, Médailles et Antiques de la Bibliothèque nationale de France, is a department of the Bibliothèque nationale de France in Paris, France, housed in its former premises in Rue de Richelieu.The Cabinet des Médailles is a museum...
.
Merovingians in pseudo-history/popular culture

Troy
Troy was a city, both factual and legendary, located in northwest Anatolia in what is now Turkey, southeast of the Dardanelles and beside Mount Ida...
, or of a five-headed sea monster known as the Quinotaur
Quinotaur
The Quinotaur is a mythical sea creature mentioned in the 7th century Frankish Chronicle of Fredegar. Referred to as "bestea Neptuni Quinotauri similis", it was held to have fathered Meroveus by attacking the wife of the Frankish king Chlodio and thus to have sired the line of Merovingian...
. The Merovingians are extensively featured in the book The Holy Blood and the Holy Grail
The Holy Blood and the Holy Grail
The Holy Blood and the Holy Grail is a book by Michael Baigent, Richard Leigh, and Henry Lincoln....
, in which they are claimed to be the descendants of Jesus
Jesus
Jesus of Nazareth , commonly referred to as Jesus Christ or simply as Jesus or Christ, is the central figure of Christianity...
, based on a hoax
Hoax
A hoax is a deliberately fabricated falsehood made to masquerade as truth. It is distinguishable from errors in observation or judgment, or rumors, urban legends, pseudosciences or April Fools' Day events that are passed along in good faith by believers or as jokes.-Definition:The British...
originating with Pierre Plantard
Pierre Plantard
Pierre Athanase Marie Plantard was a French draughtsman, best known for being the principal perpetrator of the Priory of Sion hoax, by which he claimed from the 1960s onwards that he was a Merovingian descendant of Dagobert II and the "Great Monarch" prophesied by Nostradamus.-Surname:Pierre...
in the mid-20th century. The 2006 film, The Da Vinci Code
The Da Vinci Code (film)
The Da Vinci Code is a 2006 American mystery thriller film directed by Ron Howard. The screenplay was written by Akiva Goldsman and based on Dan Brown's worldwide bestselling 2003 novel, The Da Vinci Code...
, based on a book
The Da Vinci Code
The Da Vinci Code is a 2003 mystery-detective novel written by Dan Brown. It follows symbologist Robert Langdon and Sophie Neveu as they investigate a murder in Paris's Louvre Museum and discover a battle between the Priory of Sion and Opus Dei over the possibility of Jesus having been married to...
by Dan Brown
Dan Brown
Dan Brown is an American author of thriller fiction, best known for the 2003 bestselling novel, The Da Vinci Code. Brown's novels, which are treasure hunts set in a 24-hour time period, feature the recurring themes of cryptography, keys, symbols, codes, and conspiracy theories...
, is a fictional treatment of themes from Holy Blood. In it the main character, Sophie, discovers that she is a descendant of the Merovingian blood line as well as that of Jesus Christ.
The word "Merovingian" has even been used as an adjective, at least five times in Swann's Way by Marcel Proust
Marcel Proust
Valentin Louis Georges Eugène Marcel Proust was a French novelist, critic, and essayist best known for his monumental À la recherche du temps perdu...
.
The Merovingian is the name of an antagonist in the second and third installments of The Matrix
The Matrix
The Matrix is a 1999 science fiction-action film written and directed by Larry and Andy Wachowski, starring Keanu Reeves, Laurence Fishburne, Carrie-Anne Moss, Joe Pantoliano, and Hugo Weaving...
trilogy.

