
Mem
Encyclopedia
Mem is the thirteenth letter of many Semitic
abjad
s, including Phoenician
, Aramaic
, Hebrew
and Arabic
. Its value is m.
The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek
Mu
(Μ), Etruscan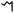 , Latin
, Latin
M
, and Cyrillic
М
.
hieroglyphic
symbol for water ( ) which had been simplified by the Phoenicia
) which had been simplified by the Phoenicia
ns and named after their word for water, mem (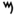
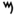 ), ultimately coming from Proto-Semitic
), ultimately coming from Proto-Semitic
*maʾ-/*may-.
Hebrew spelling:
In Hebrew, Mem, like Kaph
, Nun
, Pe
, and Tzadi, has a final form, used at the end of words. Its shape changes from מ to ם. The pronunciation is not changed.
, Mem represents the number 40. Its final form represents 600 but this is rarely used, Tav
and Resh
(400+200) being used instead.
In the Sefer Yetzirah
, the letter Mem is King over Water, Formed Earth in the Universe, Cold in the Year, and the Belly in the Soul.
As an abbreviation, it stands for metre. In the Israeli army
it can also stand for mefaked, commander
. In Hebrew religious texts, it can stand for the name of God Makom, the Place.
Some examples on its uses in Modern Standard Arabic:
Mīm is used in the creation of ism words (i.e. noun
s and adjective
s; they are treated fundamentally the same in Arabic grammar
). Specifically, is used in the creation of the masdar
(verbal noun) of Stem III verbs (the masdar of verbs on the pattern fā`ala is mufā`ala), of subject and object nouns for verbs of Stems II-X (using the example of Stem II, subject nouns — called fā`il words because of their form in Stem I — are mufa``il, and object nouns — called maf`ūl also because of their Stem I form — take the form mufa``al). Place-nouns are also created with ; the pattern maf`al is used to create maktab "office" from the triliteral
k-t-b (to write) and maṣna` "factory" from ṣ-n-` (to make).
Semitic languages
The Semitic languages are a group of related languages whose living representatives are spoken by more than 270 million people across much of the Middle East, North Africa and the Horn of Africa...
abjad
Abjad
An abjad is a type of writing system in which each symbol always or usually stands for a consonant; the reader must supply the appropriate vowel....
s, including Phoenician
Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia...
, Aramaic
Aramaic alphabet
The Aramaic alphabet is adapted from the Phoenician alphabet and became distinctive from it by the 8th century BC. The letters all represent consonants, some of which are matres lectionis, which also indicate long vowels....
, Hebrew
Hebrew alphabet
The Hebrew alphabet , known variously by scholars as the Jewish script, square script, block script, or more historically, the Assyrian script, is used in the writing of the Hebrew language, as well as other Jewish languages, most notably Yiddish, Ladino, and Judeo-Arabic. There have been two...
and Arabic
Arabic alphabet
The Arabic alphabet or Arabic abjad is the Arabic script as it is codified for writing the Arabic language. It is written from right to left, in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters. Because letters usually stand for consonants, it is classified as an abjad.-Consonants:The Arabic alphabet has...
. Its value is m.
The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
Mu
Mu (letter)
Carlos Alberto Vives Restrepo is a Grammy Award and three-time Latin Grammy Award winning-Colombian singer, composer and actor.-Biography:...
(Μ), Etruscan
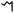
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
M
M
M is the thirteenth letter of the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The letter M is derived from the Phoenician Mem, via the Greek Mu . Semitic Mem probably originally pictured water...
, and Cyrillic
Cyrillic alphabet
The Cyrillic script or azbuka is an alphabetic writing system developed in the First Bulgarian Empire during the 10th century AD at the Preslav Literary School...
М
Em (Cyrillic)
Em is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.Em commonly represents the bilabial nasal consonant , like the pronunciation of ⟨m⟩ in "him".It is derived from the Greek letter Mu ....
.
Origins
Mem is usually assumed to come from the EgyptianEgyptian hieroglyphs
Egyptian hieroglyphs were a formal writing system used by the ancient Egyptians that combined logographic and alphabetic elements. Egyptians used cursive hieroglyphs for religious literature on papyrus and wood...
hieroglyphic
N-water ripple (n hieroglyph)
The ancient Egyptian ripple of water is one of the oldest language hieroglyphs from Ancient Egypt. It is used on a famous cartouche of Pharaoh Den of the First dynasty....
symbol for water (

Phoenicia
Phoenicia , was an ancient civilization in Canaan which covered most of the western, coastal part of the Fertile Crescent. Several major Phoenician cities were built on the coastline of the Mediterranean. It was an enterprising maritime trading culture that spread across the Mediterranean from 1550...
ns and named after their word for water, mem (
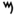
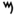 ), ultimately coming from Proto-Semitic
), ultimately coming from Proto-SemiticProto-Semitic language
Proto-Semitic is the hypothetical proto-language ancestral to historical Semitic languages of the Middle East. Locations which have been proposed for its origination include northern Mesopotamia, the Arabian Peninsula, and the Levant with a 2009 study proposing that it may have originated around...
*maʾ-/*may-.
Hebrew Mem
| Orthographic Orthography The orthography of a language specifies a standardized way of using a specific writing system to write the language. Where more than one writing system is used for a language, for example Kurdish, Uyghur, Serbian or Inuktitut, there can be more than one orthography... variants |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Various Print Fonts | Cursive Hebrew |
Rashi Script Rashi script Rashi script is a semi-cursive typeface for the Hebrew alphabet. It is named for the author of the most famous rabbinic commentary on the Hebrew Bible and the Talmud, Rashi, and is customarily used for printing his commentaries. The typeface is based on 15th century Sephardic semi-cursive... |
||
| Serif Serif In typography, serifs are semi-structural details on the ends of some of the strokes that make up letters and symbols. A typeface with serifs is called a serif typeface . A typeface without serifs is called sans serif or sans-serif, from the French sans, meaning “without”... | Sans-serif Sans-serif In typography, a sans-serif, sans serif or san serif typeface is one that does not have the small projecting features called "serifs" at the end of strokes. The term comes from the French word sans, meaning "without".... | Monospaced | ||
| מ | מ | מ |  |
 |
Hebrew spelling:
Variations on written form/pronunciation
| Orthographic Orthography The orthography of a language specifies a standardized way of using a specific writing system to write the language. Where more than one writing system is used for a language, for example Kurdish, Uyghur, Serbian or Inuktitut, there can be more than one orthography... variants |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Various Print Fonts | Cursive Hebrew |
Rashi Script Rashi script Rashi script is a semi-cursive typeface for the Hebrew alphabet. It is named for the author of the most famous rabbinic commentary on the Hebrew Bible and the Talmud, Rashi, and is customarily used for printing his commentaries. The typeface is based on 15th century Sephardic semi-cursive... |
||
| Serif Serif In typography, serifs are semi-structural details on the ends of some of the strokes that make up letters and symbols. A typeface with serifs is called a serif typeface . A typeface without serifs is called sans serif or sans-serif, from the French sans, meaning “without”... | Sans-serif Sans-serif In typography, a sans-serif, sans serif or san serif typeface is one that does not have the small projecting features called "serifs" at the end of strokes. The term comes from the French word sans, meaning "without".... | Monospaced | ||
| ם | ם | ם |  |
 |
In Hebrew, Mem, like Kaph
Kaph
Kaph is the eleventh letter of many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Kaf , Arabic alphabet , Persian alphabet...
, Nun
Nun (letter)
Nun is the fourteenth letter of many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew and Arabic alphabet . It is the third letter in Thaana , pronounced as "noonu"...
, Pe
Pe (letter)
Pe is the seventeenth letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Pei and Persian, Arabic ....
, and Tzadi, has a final form, used at the end of words. Its shape changes from מ to ם. The pronunciation is not changed.
Significance
In gematriaGematria
Gematria or gimatria is a system of assigning numerical value to a word or phrase, in the belief that words or phrases with identical numerical values bear some relation to each other, or bear some relation to the number itself as it may apply to a person's age, the calendar year, or the like...
, Mem represents the number 40. Its final form represents 600 but this is rarely used, Tav
Taw (letter)
Taw, Tav or Taf is the twenty-second and last letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Taw and Arabic alphabet .Its original sound value is ....
and Resh
Resh
Resh is the twentieth letter of many Semitic alphabets, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew and Arabic alphabet . Its sound value is one of a number of rhotic consonants: usually or , but also or in Hebrew....
(400+200) being used instead.
In the Sefer Yetzirah
Sefer Yetzirah
Sefer Yetzirah is the title of the earliest extant book on Jewish esotericism, although some early commentators treated it as a treatise on mathematical and linguistic theory as opposed to Kabbalah...
, the letter Mem is King over Water, Formed Earth in the Universe, Cold in the Year, and the Belly in the Soul.
As an abbreviation, it stands for metre. In the Israeli army
Israel Defense Forces
The Israel Defense Forces , commonly known in Israel by the Hebrew acronym Tzahal , are the military forces of the State of Israel. They consist of the ground forces, air force and navy. It is the sole military wing of the Israeli security forces, and has no civilian jurisdiction within Israel...
it can also stand for mefaked, commander
Commander
Commander is a naval rank which is also sometimes used as a military title depending on the individual customs of a given military service. Commander is also used as a rank or title in some organizations outside of the armed forces, particularly in police and law enforcement.-Commander as a naval...
. In Hebrew religious texts, it can stand for the name of God Makom, the Place.
Mem and Tarot
Mem is associated with The Hanged Man (Atu XII), the element of water and the path between Geburah and Hod on the Tree of Life.Arabic mīm
The letter is named , and is written in several ways depending on its position in the word:Some examples on its uses in Modern Standard Arabic:
Mīm is used in the creation of ism words (i.e. noun
Noun
In linguistics, a noun is a member of a large, open lexical category whose members can occur as the main word in the subject of a clause, the object of a verb, or the object of a preposition .Lexical categories are defined in terms of how their members combine with other kinds of...
s and adjective
Adjective
In grammar, an adjective is a 'describing' word; the main syntactic role of which is to qualify a noun or noun phrase, giving more information about the object signified....
s; they are treated fundamentally the same in Arabic grammar
Arabic grammar
Arabic grammar is the grammar of the Arabic language. Arabic is a Semitic language and its grammar has many similarities with the grammar of other Semitic languages....
). Specifically, is used in the creation of the masdar
Verbal noun
In linguistics, the verbal noun turns a verb into a noun and corresponds to the infinitive in English language usage. In English the infinitive form of the verb is formed when preceded by to, e.g...
(verbal noun) of Stem III verbs (the masdar of verbs on the pattern fā`ala is mufā`ala), of subject and object nouns for verbs of Stems II-X (using the example of Stem II, subject nouns — called fā`il words because of their form in Stem I — are mufa``il, and object nouns — called maf`ūl also because of their Stem I form — take the form mufa``al). Place-nouns are also created with ; the pattern maf`al is used to create maktab "office" from the triliteral
Triliteral
The roots of verbs and most nouns in the Semitic languages are characterized as a sequence of consonants or "radicals"...
k-t-b (to write) and maṣna` "factory" from ṣ-n-` (to make).

