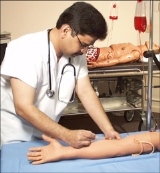
Medical simulation
Encyclopedia
Medical simulation is a branch of simulation
technology related to education and training in medical fields of various industries. It can involve simulated human patients, educational documents with detailed simulated animations, casualty assessment in homeland security
and military situations, and emergency response. Its main purpose is to train medical professionals to reduce accidents during surgery, prescription, and general practice. However it is now used to train students in anatomy and physiology during their clinical training as allied health professionals. These professions include nursing, sonography, pharmacy assistants and physical therapy. Advances in technology are advancing geometrically and a McGraw Hill textbook, Medical Simulation, by VanCura and Bisset interfaces the simulator technology with any medically related course of study.
Many medical professionals are skeptical about simulation, saying that medicine, surgery, and general healing skills are too complex to simulate accurately. But technological advances in the past two decades have made it possible to simulate practices from yearly family doctor visits to complex operations such as heart surgery.
An increase in recent emergency and military scenario simulation has helped medical providers in Middle East war zones.
Disaster response is made easier and conducted by better trained individuals due to the rapid availability of simulators in schools, hospitals, military facilities, and research labs.
 When simulation skyrocketed in popularity during the 1930s due to the invention of the Link Trainer
When simulation skyrocketed in popularity during the 1930s due to the invention of the Link Trainer
for flight and military applications, many different field experts attempted to adapt simulation to their own needs. Due to limitations in technology and overall medical knowledge to a specific degree at the time, medical simulation did not take off as acceptable training until much later. When the sheer cost effectiveness and training of which simulation was capable surfaced during extensive military use, hardware/software technology increased exponentially, and medical standards were established, medical simulation became entirely possible, affordable, standardized, and accepted. The first uses of medical simulation can be traced back to anesthesia
physicians in order to reduce accidents.
models that have surfaced since the 1990s.
Due to the fact that computer simulation technology is still relatively new relative to flight and military simulators, there is still much research to be done about the best way to approach medical training through simulation. That said, successful strides are being made in terms of medical education and training. A thorough amount of studies has have shown that students engaged in medical simulation training have overall higher scores and retention rates than those trained through traditional means.
The Council of Residency Directors (CORD) has established the following recommendations for simulation
If 44,000 to 98,000 deaths are the direct result of medical mistakes, and the CDC reported in 1999 that roughly 2.4 million people died in the United States, the medical mistakes estimate represents 1.8% to 4.0% of all deaths, respectively.
A near 5% representation of deaths primarily related to medical mistakes is simply unacceptable in the world of medicine. Anything that can assist in bringing this number down is highly recommended and medical simulation has proven to be the key assistant.
In addition to overall better scores for medical students, several other distinct advantages exist not specifically related to training.
The Combat Trauma Patient Simulation Program is perhaps the most vast in terms of processes and people involved at one or sequential times. According to Kincaid, Donovan, and Pettitt, the CTPS program has been created in order to assess and analyze the feasibility of simulation in a battlefield environment. Combat casualties, massively destructive outbreaks, chemical spills, gas leaks, and other forms of large scale negative events can be accurately simulated in a safe, inexpensive, and relatively small environment.
One of the rather large advantages to such a massive simulation of intertwining processes is the fact that people ranging from the field medics all the way up to the hospitals located in key military bases receive proper training for potential casualty prevention. The process of simulation begins with the Point of Injury and leads into Casualty Collection Points, Ground Medical Evacuations, Medical Aid Stations, and finally Hospitals. Another advantage is that all casualties can be monitored through high-tech computer software and GPS receivers located in medical vehicles and in key medical clothing. By monitoring such data, leaders can be aware of which areas in the flow needs to be sped up, slowed down, moved to a different format, or removed completely. The flow between the Point of Injury and Hospital is required to be uninterrupted if a successful goal is to be met.
Live field exercises are another benefit of the CTPS program. By allowing many individuals to engage in a “live fire” simulation, people can become acquainted with the processes involved in transferring duties among team mates in order to keep the flow moving between locations. While there is the chance of these simulations not inspiring true dedication into the actions of some participants because it is not necessarily a real disaster, the truly dedicated individuals will shine in their ability to remedy the destruction. Leaders can spot weaknesses and strengths in the participants of the simulation without worrying about every single piece of the simulation. In a real disaster, leaders would need to concentrate on individual success, team success, and overall progression. Alternatively, in a simulation of exactly the same event, the leaders could ignore certain areas in order to concentrate on the individuals involved in order to analyze weaknesses. Overall, the CTPS program is beneficial to everyone involved due to cost savings, risk reduction, personnel safety, enhanced effectiveness, and reduction of the learning curves.
CTPS contains many different technologies and smaller simulations within the rather gigantic “mother” simulation. Because the smaller simulations are potentially developed by separate companies (at times even competing companies), the interfaces have the high chance of being non-communicative or are simply incompatible without some sort of translation between the competing interfaces. All of this integration is made possible through a highly researched and deeply developed High Level Architecture containing interface modules to link up incompatible parts of the complete CTPS process.
The simulation federates (subsystems) of the CTPS involves the Lockheed Martin MILES system, the Operational Requirements-based Casualty Assessment system (ORCA), the Jackson Medical Simulation library (JMSL), and the Human Patient Simulator (HPS). By combining these systems together, trainees can be contained to their respective areas of study while also studying the possible hindrances between stages of transition.
Beginning the military casualty treatment simulation is the MILES engagement simulator, which accurately simulates gunfire and other combat engagements. When trainees under the simulated engagement system fire upon each other and register virtual hits, the simulated casualties are moved to the next stage. At first glance, this system may seem similar to entertainment driven laser tag centers found within urban cities of the United States. But after a deeper look, the overall training that a user would go through involves much more than pointing, shooting, and laughing at the outcome. Proper combat procedures can be taught to single users, team based squads, or larger squads. Obvious advantages to this approach include reductions in physical harm to trainees, increase in physical realism by tagging individuals as “dead,” and providing immediate feedback to users who score a hit. While the MILES training system is not necessarily a medically based simulation; however, it is completely necessary to begin the process into medical procedures. Without proper combat engagement, realistic casualties and injuries cannot be simulated and cannot be transferred into the beginning medical stages in a manner that would provide meaning to a medical trainee.
The next stage involves casualty assessment based on results driven by simulated engagements under the MILES system. Any and all casualties are transferred to the ORCA stage, given initial wound assessments, put into an initial medical state (severe, critical, dead), and finally passed on to the JMSL. Under the JMSL, all casualties generated by MILES and assessed initially by ORCA are sent through transition phases in order to accurately simulate a casualty progressing to a more and more deadly state while awaiting treatment under average circumstances.
After casualties have been generated, processed, and sent through various stages, actual training under a medic or doctor can be attained through the HPS. By using a physiologically realistic test dummy, users can treat a patient and receive immediate, accurate feedback regarding the results. Using this approach, users can engage in proper medical training as if a live patient was being used without subjecting the patient to physical harm in the case of accidents. From a financial standpoint, the entire system offers a cheaper alternative to throwing untrained medics into a potentially hazardous and live situation. On the job training simply does not cut it when it comes to lives and equipment on the line.
One of the most prominent versions of SBME that stands out is Adobe Flash based medical simulations and animations. While textbooks are sufficient for certain diagrams and process flow explanations, certain high quality animations created in Adobe Flash are extremely beneficial when it comes to learning. Some of the advantages to Flash-based medical simulations and animations include a visually animated representation of blood flow within a body or other physiological processes occurring within the body that would otherwise seem awkward or impossible to understand through static images. A rather annoying disadvantage to these animated approaches stems from the fact that they are extremely costly to create in terms of time and money. Some of the better animations require teams of people equal in size to major movie productions when it comes to after effects.
Simulation
Simulation is the imitation of some real thing available, state of affairs, or process. The act of simulating something generally entails representing certain key characteristics or behaviours of a selected physical or abstract system....
technology related to education and training in medical fields of various industries. It can involve simulated human patients, educational documents with detailed simulated animations, casualty assessment in homeland security
Homeland security
Homeland security is an umbrella term for security efforts to protect states against terrorist activity. Specifically, is a concerted national effort to prevent terrorist attacks within the U.S., reduce America’s vulnerability to terrorism, and minimize the damage and recover from attacks that do...
and military situations, and emergency response. Its main purpose is to train medical professionals to reduce accidents during surgery, prescription, and general practice. However it is now used to train students in anatomy and physiology during their clinical training as allied health professionals. These professions include nursing, sonography, pharmacy assistants and physical therapy. Advances in technology are advancing geometrically and a McGraw Hill textbook, Medical Simulation, by VanCura and Bisset interfaces the simulator technology with any medically related course of study.
Many medical professionals are skeptical about simulation, saying that medicine, surgery, and general healing skills are too complex to simulate accurately. But technological advances in the past two decades have made it possible to simulate practices from yearly family doctor visits to complex operations such as heart surgery.
An increase in recent emergency and military scenario simulation has helped medical providers in Middle East war zones.
Disaster response is made easier and conducted by better trained individuals due to the rapid availability of simulators in schools, hospitals, military facilities, and research labs.
History

Link Trainer
The term Link Trainer, also known as the "Blue box" and "Pilot Trainer" is commonly used to refer to a series of flight simulators produced between the early 1930s and early 1950s by Ed Link, based on technology he pioneered in 1929 at his family's business in Binghamton, New York...
for flight and military applications, many different field experts attempted to adapt simulation to their own needs. Due to limitations in technology and overall medical knowledge to a specific degree at the time, medical simulation did not take off as acceptable training until much later. When the sheer cost effectiveness and training of which simulation was capable surfaced during extensive military use, hardware/software technology increased exponentially, and medical standards were established, medical simulation became entirely possible, affordable, standardized, and accepted. The first uses of medical simulation can be traced back to anesthesia
Anesthesia
Anesthesia, or anaesthesia , traditionally meant the condition of having sensation blocked or temporarily taken away...
physicians in order to reduce accidents.
Modern medical simulation
The American Board of Emergency Medicine employs the use of medical simulation technology in order to accurately judge students by using "patient scenarios" during oral board examinations. However, these forms of simulation are a far cry from high fidelityFidelity
"Fidelity" is the quality of being faithful or loyal. Its original meaning regarded duty to a lord or a king, in a broader sense than the related concept of fealty. Both derive from the Latin word fidēlis, meaning "faithful or loyal"....
models that have surfaced since the 1990s.
Due to the fact that computer simulation technology is still relatively new relative to flight and military simulators, there is still much research to be done about the best way to approach medical training through simulation. That said, successful strides are being made in terms of medical education and training. A thorough amount of studies has have shown that students engaged in medical simulation training have overall higher scores and retention rates than those trained through traditional means.
The Council of Residency Directors (CORD) has established the following recommendations for simulation
- Simulation is a useful tool for training residents and in ascertaining competency. The core competencies most conducive to simulation-based training are patient care, interpersonal skills, and systems based practice.
- It is appropriate for performance assessment but there is a scarcity of evidence that supports the validity of simulation in the use for promotion or certification.
- There is a need for standardization and definition in using simulation to evaluate performance.
- Scenarios and tools should also be formatted and standardized such that EM educators can use the data and count on it for reproducibility, reliability and validity.
Training
The main purpose of medical simulation is to properly educate students in various fields through the use of high technology simulators. According to the Institute of Medicine, 44,000 to 98,000 deaths annually are recorded due primarily to medical mistakes during treatment. Other statistics include:- 225,000 deaths annually from medical error including 106,000 deaths due to "nonerror adverse events of medications"
- 7,391 deaths resulted from medication errors
If 44,000 to 98,000 deaths are the direct result of medical mistakes, and the CDC reported in 1999 that roughly 2.4 million people died in the United States, the medical mistakes estimate represents 1.8% to 4.0% of all deaths, respectively.
A near 5% representation of deaths primarily related to medical mistakes is simply unacceptable in the world of medicine. Anything that can assist in bringing this number down is highly recommended and medical simulation has proven to be the key assistant.
Examples
The following is a list of examples of common medical simulators used for training.- Advanced Cardiac Life SupportAdvanced cardiac life supportAdvanced cardiac life support or Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support refers to a set of clinical interventions for the urgent treatment of cardiac arrest and other life threatening medical emergencies, as well as the knowledge and skills to deploy those interventions.Extensive medical knowledge...
simulators - Partial Human Patient Simulator (Low tech)
- Human Patient Simulator (High tech)
- Hands-on Suture Simulator (Low tech)
- IV Trainer to Augment Human Patient Simulator (Low tech)
- Pure Software Simulation (High tech)
- Anesthesiology Simulator (High tech)
- Minimally Invasive Surgery Trainer (High tech)
- BronchoscopyBronchoscopyBronchoscopy is a technique of visualizing the inside of the airways for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. An instrument is inserted into the airways, usually through the nose or mouth, or occasionally through a tracheostomy. This allows the practitioner to examine the patient's airways for...
Simulator - Battlefield Trauma to Augment Human Patient Simulator
- Team Training Suite
- “Harvey” mannequin (Low tech)
Advantages
Studies have shown that students perform better and have higher retention rates than colleagues under strict traditional methods of medical training. The table below shows the results of tests given to 20 students using highly advanced medical simulation training materials and others given traditional paper based tests. It was found that high technology learning students outperformed traditional students significantly.| Mode of Learning | Mean Test Score on Multiple Choice Test | Time to Complete Module |
|---|---|---|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
In addition to overall better scores for medical students, several other distinct advantages exist not specifically related to training.
- Less costly
- Time efficient
- Less personnel required
- Many automated processes
- Ability to store performance history
- Track global statistics for many linked medical simulators
- Less medical related accidents
Military and emergency response
One of the single largest proponents behind simulators has always been the United States government. Billions (and perhaps trillions, at this point) of dollars have been spent in the name of advancing simulators for space exploration, computer advancements, medical and military training, and other projects funded for research by the government. The Department of Defense (most notably, the Army) is one of the largest fund producers for simulation research, training, and support. As such, most simulators tend to be created for military purposes including soldier, tank, and flight training in combat situations. In terms of medical simulation, military applications have played a large part in its success and funding. Some examples of scenarios useful for medical applications include casualty assessment, war trauma response, emergency evacuations, training for communications between teams, team/individual after action assessment, and scenario recreation from recorded data.Combat trauma patient simulator
| Electronic Casualty Card | Combat Trauma Patient Simulator | Human Patient Simulator | Patient Simulator Software |
|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
|
|
The Combat Trauma Patient Simulation Program is perhaps the most vast in terms of processes and people involved at one or sequential times. According to Kincaid, Donovan, and Pettitt, the CTPS program has been created in order to assess and analyze the feasibility of simulation in a battlefield environment. Combat casualties, massively destructive outbreaks, chemical spills, gas leaks, and other forms of large scale negative events can be accurately simulated in a safe, inexpensive, and relatively small environment.
One of the rather large advantages to such a massive simulation of intertwining processes is the fact that people ranging from the field medics all the way up to the hospitals located in key military bases receive proper training for potential casualty prevention. The process of simulation begins with the Point of Injury and leads into Casualty Collection Points, Ground Medical Evacuations, Medical Aid Stations, and finally Hospitals. Another advantage is that all casualties can be monitored through high-tech computer software and GPS receivers located in medical vehicles and in key medical clothing. By monitoring such data, leaders can be aware of which areas in the flow needs to be sped up, slowed down, moved to a different format, or removed completely. The flow between the Point of Injury and Hospital is required to be uninterrupted if a successful goal is to be met.
Live field exercises are another benefit of the CTPS program. By allowing many individuals to engage in a “live fire” simulation, people can become acquainted with the processes involved in transferring duties among team mates in order to keep the flow moving between locations. While there is the chance of these simulations not inspiring true dedication into the actions of some participants because it is not necessarily a real disaster, the truly dedicated individuals will shine in their ability to remedy the destruction. Leaders can spot weaknesses and strengths in the participants of the simulation without worrying about every single piece of the simulation. In a real disaster, leaders would need to concentrate on individual success, team success, and overall progression. Alternatively, in a simulation of exactly the same event, the leaders could ignore certain areas in order to concentrate on the individuals involved in order to analyze weaknesses. Overall, the CTPS program is beneficial to everyone involved due to cost savings, risk reduction, personnel safety, enhanced effectiveness, and reduction of the learning curves.
CTPS contains many different technologies and smaller simulations within the rather gigantic “mother” simulation. Because the smaller simulations are potentially developed by separate companies (at times even competing companies), the interfaces have the high chance of being non-communicative or are simply incompatible without some sort of translation between the competing interfaces. All of this integration is made possible through a highly researched and deeply developed High Level Architecture containing interface modules to link up incompatible parts of the complete CTPS process.
The simulation federates (subsystems) of the CTPS involves the Lockheed Martin MILES system, the Operational Requirements-based Casualty Assessment system (ORCA), the Jackson Medical Simulation library (JMSL), and the Human Patient Simulator (HPS). By combining these systems together, trainees can be contained to their respective areas of study while also studying the possible hindrances between stages of transition.
Beginning the military casualty treatment simulation is the MILES engagement simulator, which accurately simulates gunfire and other combat engagements. When trainees under the simulated engagement system fire upon each other and register virtual hits, the simulated casualties are moved to the next stage. At first glance, this system may seem similar to entertainment driven laser tag centers found within urban cities of the United States. But after a deeper look, the overall training that a user would go through involves much more than pointing, shooting, and laughing at the outcome. Proper combat procedures can be taught to single users, team based squads, or larger squads. Obvious advantages to this approach include reductions in physical harm to trainees, increase in physical realism by tagging individuals as “dead,” and providing immediate feedback to users who score a hit. While the MILES training system is not necessarily a medically based simulation; however, it is completely necessary to begin the process into medical procedures. Without proper combat engagement, realistic casualties and injuries cannot be simulated and cannot be transferred into the beginning medical stages in a manner that would provide meaning to a medical trainee.
The next stage involves casualty assessment based on results driven by simulated engagements under the MILES system. Any and all casualties are transferred to the ORCA stage, given initial wound assessments, put into an initial medical state (severe, critical, dead), and finally passed on to the JMSL. Under the JMSL, all casualties generated by MILES and assessed initially by ORCA are sent through transition phases in order to accurately simulate a casualty progressing to a more and more deadly state while awaiting treatment under average circumstances.
After casualties have been generated, processed, and sent through various stages, actual training under a medic or doctor can be attained through the HPS. By using a physiologically realistic test dummy, users can treat a patient and receive immediate, accurate feedback regarding the results. Using this approach, users can engage in proper medical training as if a live patient was being used without subjecting the patient to physical harm in the case of accidents. From a financial standpoint, the entire system offers a cheaper alternative to throwing untrained medics into a potentially hazardous and live situation. On the job training simply does not cut it when it comes to lives and equipment on the line.
In the classroom
There are many other medical systems that exist in forms other than "live fire" and "on the field" exercises. Simulation-Based Medical Education is one form that allows students to learn for educational purposes in a classroom. SBME works well with all forms of classroom learning such as lectures, problem solving, in hospital teaching, and other traditional forms of education. Several advantages appear while using this approach such as patient safety, higher knowledge retaining, teamwork, competence, and skill at the bedside.One of the most prominent versions of SBME that stands out is Adobe Flash based medical simulations and animations. While textbooks are sufficient for certain diagrams and process flow explanations, certain high quality animations created in Adobe Flash are extremely beneficial when it comes to learning. Some of the advantages to Flash-based medical simulations and animations include a visually animated representation of blood flow within a body or other physiological processes occurring within the body that would otherwise seem awkward or impossible to understand through static images. A rather annoying disadvantage to these animated approaches stems from the fact that they are extremely costly to create in terms of time and money. Some of the better animations require teams of people equal in size to major movie productions when it comes to after effects.
See also
- SimulationSimulationSimulation is the imitation of some real thing available, state of affairs, or process. The act of simulating something generally entails representing certain key characteristics or behaviours of a selected physical or abstract system....
- Military simulationMilitary simulationMilitary simulations, also known informally as war games, are simulations in which theories of warfare can be tested and refined without the need for actual hostilities. Many professional contemporary analysts object to the term wargames as this is generally taken to be referring to the civilian...
- Simulated realitySimulated realitySimulated reality is the proposition that reality could be simulated—perhaps by computer simulation—to a degree indistinguishable from "true" reality. It could contain conscious minds which may or may not be fully aware that they are living inside a simulation....
- Simulation languageSimulation languageA computer simulation language describes the operation of a simulation on a computer. There are two major types of simulation: continuous and discrete event though more modern languages can handle combinations. Most languages also have a graphical interface and at least simple statistical gathering...
- List of discrete event simulation software
- List of computer simulation software
- Multiple Integrated Laser Engagement SystemMultiple Integrated Laser Engagement SystemThe Multiple Integrated Laser Engagement System or MILES is used by the US military and other armed forces around the world for training purposes. It uses lasers and blank cartridges to simulate actual battle....
- Web based simulationWeb based simulationThe term web-based simulation emerged in 1996, and is typically used to denote the invocation of computer simulation services over the internet, specifically through a web browser....
Further reading
- http://www.wrongdiagnosis.com/mistakes/common.htm
- http://www.nap.edu/books/0309068371/html/
- http://jama.ama-assn.org/issues/v284n4/ffull/jco00061.html
- http://www.saem.org/SAEMDNN/Portals/0/Medical%20Simulation%20in%20EM%20Training%20and%20Beyond.pdf
- http://www.lockheedmartin.com/data/assets/sts/ProductCards/MILESShootbackDevice_PC.pdf
- http://www.lockheedmartin.com/data/assets/7092.pdf

