
Mathematical visualization
Encyclopedia
Geometry
Geometry arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers ....
which allows one to understand and explore mathematical phenomena via visualization
Visualization (graphic)
Visualization is any technique for creating images, diagrams, or animations to communicate a message. Visualization through visual imagery has been an effective way to communicate both abstract and concrete ideas since the dawn of man...
. Classically this consisted of two-dimensional drawings or building three-dimensional models (particularly plaster models in the 19th and early 20th century), while today it most frequently consists of using computers to make static two or three dimensional drawings, animations, or interactive programs. Writing programs to visualize mathematics is an aspect of computational geometry
Computational geometry
Computational geometry is a branch of computer science devoted to the study of algorithms which can be stated in terms of geometry. Some purely geometrical problems arise out of the study of computational geometric algorithms, and such problems are also considered to be part of computational...
.
Applications
Mathematical visualization is used throughout mathematics, particularly in the fields of geometryGeometry
Geometry arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers ....
and analysis
Analysis
Analysis is the process of breaking a complex topic or substance into smaller parts to gain a better understanding of it. The technique has been applied in the study of mathematics and logic since before Aristotle , though analysis as a formal concept is a relatively recent development.The word is...
. Notable examples include plane curve
Plane curve
In mathematics, a plane curve is a curve in a Euclidean plane . The most frequently studied cases are smooth plane curves , and algebraic plane curves....
s, space curves, polyhedra, ordinary differential equation
Ordinary differential equation
In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation is a relation that contains functions of only one independent variable, and one or more of their derivatives with respect to that variable....
s, partial differential equation
Partial differential equation
In mathematics, partial differential equations are a type of differential equation, i.e., a relation involving an unknown function of several independent variables and their partial derivatives with respect to those variables...
s (particularly numerical solutions, as in fluid dynamics
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a sub-discipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics...
or minimal surface
Minimal surface
In mathematics, a minimal surface is a surface with a mean curvature of zero.These include, but are not limited to, surfaces of minimum area subject to various constraints....
s such as soap film
Soap film
Soap films are thin layers of liquid surrounded by air. For example, if two soap bubbles enters in contact, they merged and a thin film is created in between. Thus, foams are composed of a network of films connected by Plateau borders...
s), conformal map
Conformal map
In mathematics, a conformal map is a function which preserves angles. In the most common case the function is between domains in the complex plane.More formally, a map,...
s, fractal
Fractal
A fractal has been defined as "a rough or fragmented geometric shape that can be split into parts, each of which is a reduced-size copy of the whole," a property called self-similarity...
s, and chaos
Chaos theory
Chaos theory is a field of study in mathematics, with applications in several disciplines including physics, economics, biology, and philosophy. Chaos theory studies the behavior of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions, an effect which is popularly referred to as the...
.
Examples
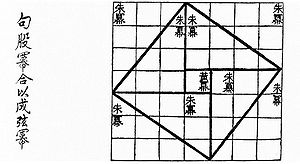
- Proofs without words have existed since antiquity, as in the Pythagorean theorem proof found in the Zhou Bi Suan Jing chinese text which dates from 1046 BC to 256 BC.
- The Clebsch diagonal surface demonstrates the 27 lines on a cubic surface.
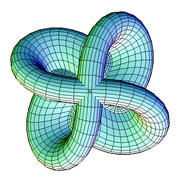
- Sphere eversion – that a sphere can be turned inside out in 3 dimension if allowed to pass through itself, but without kinks – was a startling and counter-intuitive result, originally proven via abstract means, later demonstrated graphically, first in drawings, later in computer animation.
The cover of the journal The Notices of the American Mathematical Society
Notices of the American Mathematical Society
Notices of the American Mathematical Society is a membership magazine of the American Mathematical Society, published monthly except for the combined June/July issue. It is the world's most widely read mathematics magazine, sent to the approximately 30,000 AMS members worldwide...
regularly features a mathematical visualization.
Software
- 3D-Xplor-Math
- GRAPEGRAPEGRAPE , or GRAphics Programming Environment is a software development environment for mathematical visualization, especially differential geometry and continuum mechanics....
- Jeffrey Weeks'Jeffrey Weeks (mathematician)Jeffrey Renwick Weeks is an American mathematician, a geometric topologist and cosmologist.-Biography:Weeks received his B.A. from Dartmouth College in 1978, and his Ph.D. in mathematics from Princeton University in 1985, under the supervision of William Thurston...
Topology and Geometry Software

