
Mars Radiation Environment Experiment
Encyclopedia

Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. The planet is named after the Roman god of war, Mars. It is often described as the "Red Planet", as the iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it a reddish appearance...
using an energetic particle spectrometer
Spectrometer
A spectrometer is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify materials. The variable measured is most often the light's intensity but could also, for instance, be the polarization...
as part of the science mission of the 2001 Mars Odyssey
2001 Mars Odyssey
2001 Mars Odyssey is a robotic spacecraft orbiting the planet Mars. The project was developed by NASA, and contracted out to Lockheed Martin, with an expected cost for the entire mission of US$297 million. Its mission is to use spectrometers and electronic imagers to hunt for evidence of past or...
spacecraft (launched on April 7, 2001). It was led by NASA
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
's Johnson Space Center and the science investigation was designed to characterize aspects of the radiation environment both on the way to Mars and while it was in the Martian orbit.
Since space radiation
Health threat from cosmic rays
The health threat from cosmic rays is the danger posed by galactic cosmic rays and solar energetic particles to astronauts on interplanetary missions.Galactic cosmic rays consist of high energy protons and other nuclei with extrasolar origin...
presents an extreme hazard to crews of interplanetary missions the experiment was an attempt to predict anticipated radiation
Radiation
In physics, radiation is a process in which energetic particles or energetic waves travel through a medium or space. There are two distinct types of radiation; ionizing and non-ionizing...
doses that would be experienced by future astronaut
Astronaut
An astronaut or cosmonaut is a person trained by a human spaceflight program to command, pilot, or serve as a crew member of a spacecraft....
s and it helped determine possible effects of Martian radiation on human beings.
Space radiation comes from cosmic rays emitted by our local star, the sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
, and from stars beyond our solar system as well. Space radiation can trigger cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
and cause damage to the central nervous system
Central nervous system
The central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
. Similar instruments are flown on the Space Shuttle
Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle was a manned orbital rocket and spacecraft system operated by NASA on 135 missions from 1981 to 2011. The system combined rocket launch, orbital spacecraft, and re-entry spaceplane with modular add-ons...
s and on the International Space Station
International Space Station
The International Space Station is a habitable, artificial satellite in low Earth orbit. The ISS follows the Salyut, Almaz, Cosmos, Skylab, and Mir space stations, as the 11th space station launched, not including the Genesis I and II prototypes...
(ISS), but none have ever flown outside of Earth's protective magnetosphere
Magnetosphere
A magnetosphere is formed when a stream of charged particles, such as the solar wind, interacts with and is deflected by the intrinsic magnetic field of a planet or similar body. Earth is surrounded by a magnetosphere, as are the other planets with intrinsic magnetic fields: Mercury, Jupiter,...
, which blocks much of this radiation from reaching the surface of our planet. Ironically, in the Autumn of 2003 after a series of particularly strong solar flare
Solar flare
A solar flare is a sudden brightening observed over the Sun surface or the solar limb, which is interpreted as a large energy release of up to 6 × 1025 joules of energy . The flare ejects clouds of electrons, ions, and atoms through the corona into space. These clouds typically reach Earth a day...
s MARIE started malfunctioning, probably as a result of being exposed to the solar flare's intense blast of particle radiation. The instrument was never restored to working order.
How the instrument works
A spectrometer inside the instrument measured the energy from two sources of space radiation: galactic cosmic rays (GCR) and solar energetic particlesSolar Energetic Particles
Solar Energetic Particles are high-energy particles coming from the Sun which had been first observed in the early 1940s. They consist of protons, electrons and heavy ions with energy ranging from a few tens of keV to GeV...
(SEP). As the spacecraft orbited the red planet, the spectrometer swept through the sky and measured the radiation field.
The instrument, with a 68-degree field of view, was designed to collect data continuously during Mars Odyssey's cruise from Earth to Mars. It stored large amounts of data for downlink, and operated throughout the entire science mission.
MARIE specifications
Results
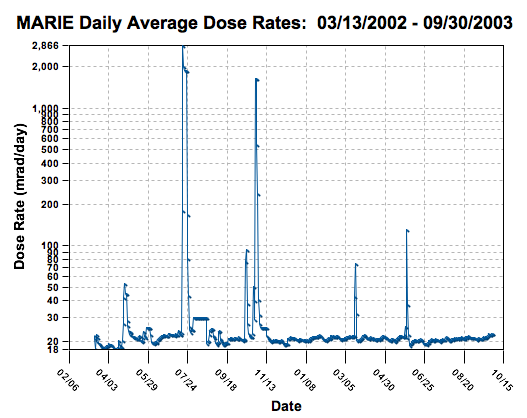
The diagram idicates a main radiation exposure of 20mrad/d = 1.7 Gy/a. On the other hand MARIE data are usually reported as 2.5 times higher than at the International Space Station
International Space Station
The International Space Station is a habitable, artificial satellite in low Earth orbit. The ISS follows the Salyut, Almaz, Cosmos, Skylab, and Mir space stations, as the 11th space station launched, not including the Genesis I and II prototypes...
(which is 100-200mSv/a). Levels at the Martian surface might be closer to the level at the ISS due to atmospheric shieding -- ignoring the effect of thermal neutrons induced by GCR. Average in-orbit doses were about 400-500mSv/a. However occasional solar proton event
Solar proton event
A Solar proton event occurs when protons emitted by the Sun become accelerated to very high energies either close to the Sun during a solar flare or in interplanetary space by the shocks associated with coronal mass ejections. These high energy protons cause several effects. They can penetrate the...
s (SPEs) produce a hundred and more times higher doses, see diagram above. SPEs were observed by MARIE that were not observed by sensors near Earth, confirming that SPEs are directional.

