
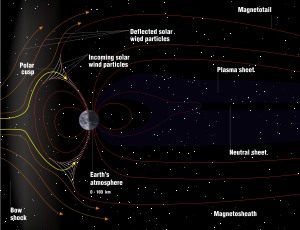
Magnetosheath
Encyclopedia
The magnetosheath is the region of space between the magnetopause
and the bow shock
of a planet's
magnetosphere
. The regularly organized magnetic field
generated by the planet becomes weak and irregular in the magnetosheath due to interaction with the incoming solar wind
, and is incapable of fully deflecting the highly charged particle
s. The density of the particles in this region is considerably lower than what is found beyond the bow shock, but greater than within the magnetopause
, and can be considered a transitory state.
 Scientific research into the exact nature of the magnetosheath has been limited due to a longstanding misconception that it was a simple byproduct of the bow shock/magnetopause interaction and had no inherently important properties of its own. Recent studies indicate, however, that the magnetosheath is a dynamic region of turbulent plasma
Scientific research into the exact nature of the magnetosheath has been limited due to a longstanding misconception that it was a simple byproduct of the bow shock/magnetopause interaction and had no inherently important properties of its own. Recent studies indicate, however, that the magnetosheath is a dynamic region of turbulent plasma
flow that may play an important role in the structure of the bow shock and the magnetopause, and may help to dictate the flow of energetic particles across those boundaries.
The Earth's
magnetosheath typically occupies the region of space approximately 10 Earth radii on the upwind (Sun
-facing) side of the planet, extending significantly farther out on the downwind side due to the pressure of the solar wind. The exact location and width of the magnetosheath does depend on variables such as solar activity
.
Magnetopause
The magnetopause is the abrupt boundary between a magnetosphere and the surrounding plasma. For planetary science, the magnetopause is the boundary between the planet’s magnetic field and the solar wind. The location of the magnetopause is determined by the balance between the pressure of the...
and the bow shock
Bow shock
A bow shock is the area between a magnetosphere and an ambient medium. For stars, this is typically the boundary between their stellar wind and the interstellar medium....
of a planet's
Planet
A planet is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science,...
magnetosphere
Magnetosphere
A magnetosphere is formed when a stream of charged particles, such as the solar wind, interacts with and is deflected by the intrinsic magnetic field of a planet or similar body. Earth is surrounded by a magnetosphere, as are the other planets with intrinsic magnetic fields: Mercury, Jupiter,...
. The regularly organized magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
generated by the planet becomes weak and irregular in the magnetosheath due to interaction with the incoming solar wind
Solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles ejected from the upper atmosphere of the Sun. It mostly consists of electrons and protons with energies usually between 1.5 and 10 keV. The stream of particles varies in temperature and speed over time...
, and is incapable of fully deflecting the highly charged particle
Charged particle
In physics, a charged particle is a particle with an electric charge. It may be either a subatomic particle or an ion. A collection of charged particles, or even a gas containing a proportion of charged particles, is called a plasma, which is called the fourth state of matter because its...
s. The density of the particles in this region is considerably lower than what is found beyond the bow shock, but greater than within the magnetopause
Magnetopause
The magnetopause is the abrupt boundary between a magnetosphere and the surrounding plasma. For planetary science, the magnetopause is the boundary between the planet’s magnetic field and the solar wind. The location of the magnetopause is determined by the balance between the pressure of the...
, and can be considered a transitory state.

Plasma (physics)
In physics and chemistry, plasma is a state of matter similar to gas in which a certain portion of the particles are ionized. Heating a gas may ionize its molecules or atoms , thus turning it into a plasma, which contains charged particles: positive ions and negative electrons or ions...
flow that may play an important role in the structure of the bow shock and the magnetopause, and may help to dictate the flow of energetic particles across those boundaries.
The Earth's
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
magnetosheath typically occupies the region of space approximately 10 Earth radii on the upwind (Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
-facing) side of the planet, extending significantly farther out on the downwind side due to the pressure of the solar wind. The exact location and width of the magnetosheath does depend on variables such as solar activity
Solar variation
Solar variation is the change in the amount of radiation emitted by the Sun and in its spectral distribution over years to millennia. These variations have periodic components, the main one being the approximately 11-year solar cycle . The changes also have aperiodic fluctuations...
.

