
Magneto-optic Kerr effect
Encyclopedia
Magneto-optic Kerr effect (MOKE) is one of the magneto-optic effect
s. It describes the changes of light reflected from magnet
ized media.
that is reflected from a magnetized surface can change in both polarization and reflected intensity
. The effect is identical to the Faraday effect
except that the magneto-optical Kerr effect is a measurement of the reflected light, while the Faraday effect is a measurement of the transmitted light. Both effects result from the off-diagonal components of the dielectric tensor
 . These off-diagonal components give the Magneto Optic material an anisotropic permittivity. The permittivity affects the speed of light in a material:
. These off-diagonal components give the Magneto Optic material an anisotropic permittivity. The permittivity affects the speed of light in a material:
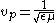
where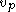 is the velocity of light through the material,
is the velocity of light through the material,  is the material permittivity, and
is the material permittivity, and  is the material permeability; and thus the speed of light varies depending on its orientation. This causes fluctuations in the phase of polarized incident light.
is the material permeability; and thus the speed of light varies depending on its orientation. This causes fluctuations in the phase of polarized incident light.
vector with respect to the reflecting surface and the plane of incidence.
 vectors, namely the standard Fresnel amplitude coefficient of reflection
vectors, namely the standard Fresnel amplitude coefficient of reflection  and the Kerr coefficient
and the Kerr coefficient  . The Kerr coefficient is typically much smaller than the coefficient of reflection.
. The Kerr coefficient is typically much smaller than the coefficient of reflection.
 is measured. This change in reflectivity is proportional to the component of magnetization that is perpendicular to the plane of incidence and parallel to the surface, as above. If the magnetization component points to the right of the incident plane, as viewed from the source, then the Kerr vector adds to the Fresnel amplitude vector and the intensity of the reflected light is
is measured. This change in reflectivity is proportional to the component of magnetization that is perpendicular to the plane of incidence and parallel to the surface, as above. If the magnetization component points to the right of the incident plane, as viewed from the source, then the Kerr vector adds to the Fresnel amplitude vector and the intensity of the reflected light is  . On the other hand, if the component of magnetization component points to the left of the incident plane as viewed from the source, the Kerr vector subtracts from the Fresnel amplitude and the reflected intensity is given by
. On the other hand, if the component of magnetization component points to the left of the incident plane as viewed from the source, the Kerr vector subtracts from the Fresnel amplitude and the reflected intensity is given by  .
.
product terms involving the polar, longitudinal and transverse magnetization components. Those effects
are referred to as Voigt effect
or quadratic Kerr effect. Quadratic magneto-optic Kerr effect (QMOKE) is found strong in Heusler alloys such as Co2FeSi and Co2MnGe
In conjunction with the Kerr Microscope, Magneto Optical Imaging Films (MOIF) can be used to better image magnetic domains in ferromagnetic materials. These films can be made out of an Yttrium Iron Garnet
and are usually substituted with certain rare earth elements. Because the manufacturing process of these films is so specialized, they aren't commercially available.
were introduced in 1985, and were originally WORM (write once, read many) drives, meaning they could be added to but not erased. Although they are not widely used today, they were reliable both in accurate writing and consistent data retention. Typical sizes ranged from 100 megabytes (MB) up to 9.2 gigabytes (GB). MO drives checked the data as it was being written, and thus took longer than typical CD's or DVD's. However this allowed for increased data integrity.
MO discs were written using laser and an electromagnet. The laser would heat the platter above its Curie Temperature and which point the electromagnet would orient that bit as a 1 or 0. To read, the laser is operated at a lower intensity, and emits polarized light. Reflected light is analyzed showing a noticeable difference between a 0 or 1.
.
Magneto-optic effect
A magneto-optic effect is any one of a number of phenomena in which an electromagnetic wave propagates through a medium that has been altered by the presence of a quasistatic magnetic field...
s. It describes the changes of light reflected from magnet
Magnet
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets.A permanent magnet is an object...
ized media.

Definition
The lightLight
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
that is reflected from a magnetized surface can change in both polarization and reflected intensity
Reflectivity
In optics and photometry, reflectivity is the fraction of incident radiation reflected by a surface. In general it must be treated as a directional property that is a function of the reflected direction, the incident direction, and the incident wavelength...
. The effect is identical to the Faraday effect
Faraday effect
In physics, the Faraday effect or Faraday rotation is a Magneto-optical phenomenon, that is, an interaction between light and a magnetic field in a medium...
except that the magneto-optical Kerr effect is a measurement of the reflected light, while the Faraday effect is a measurement of the transmitted light. Both effects result from the off-diagonal components of the dielectric tensor
Permittivity
In electromagnetism, absolute permittivity is the measure of the resistance that is encountered when forming an electric field in a medium. In other words, permittivity is a measure of how an electric field affects, and is affected by, a dielectric medium. The permittivity of a medium describes how...
 . These off-diagonal components give the Magneto Optic material an anisotropic permittivity. The permittivity affects the speed of light in a material:
. These off-diagonal components give the Magneto Optic material an anisotropic permittivity. The permittivity affects the speed of light in a material: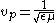
where
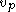 is the velocity of light through the material,
is the velocity of light through the material,  is the material permittivity, and
is the material permittivity, and  is the material permeability; and thus the speed of light varies depending on its orientation. This causes fluctuations in the phase of polarized incident light.
is the material permeability; and thus the speed of light varies depending on its orientation. This causes fluctuations in the phase of polarized incident light.Geometries
MOKE can be further categorized by the direction of the magnetizationMagnetization
In classical electromagnetism, magnetization or magnetic polarization is the vector field that expresses the density of permanent or induced magnetic dipole moments in a magnetic material...
vector with respect to the reflecting surface and the plane of incidence.
Polar MOKE
When the magnetization vector is perpendicular to the reflection surface and parallel to the plane of incidence, the effect is called the polar Kerr effect. To simplify the analysis, near normal incidence is usually employed when doing experiments in the polar geometry.Longitudinal MOKE
In the longitudinal effect, the magnetization vector is parallel to both the reflection surface and the plane of incidence. The longitudinal setup involves light reflected at an angle from the reflection surface and not normal to it, as above in the polar MOKE case. In the same manner, linearly polarized light incident on the surface becomes elliptically polarized, with the change in polarization directly proportional to the component of magnetization that is parallel to the reflection surface and parallel to the plane of incidence. This elliptically polarized light to first-order has two perpendicular vectors, namely the standard Fresnel amplitude coefficient of reflection
vectors, namely the standard Fresnel amplitude coefficient of reflection  and the Kerr coefficient
and the Kerr coefficient  . The Kerr coefficient is typically much smaller than the coefficient of reflection.
. The Kerr coefficient is typically much smaller than the coefficient of reflection.Transversal MOKE
When the magnetization is perpendicular to the plane of incidence and parallel to the surface it is said to be in the transverse configuration. In this case, the incident light is also not normal to the reflection surface but instead of measuring the polarity of the light after reflection, the reflectivity is measured. This change in reflectivity is proportional to the component of magnetization that is perpendicular to the plane of incidence and parallel to the surface, as above. If the magnetization component points to the right of the incident plane, as viewed from the source, then the Kerr vector adds to the Fresnel amplitude vector and the intensity of the reflected light is
is measured. This change in reflectivity is proportional to the component of magnetization that is perpendicular to the plane of incidence and parallel to the surface, as above. If the magnetization component points to the right of the incident plane, as viewed from the source, then the Kerr vector adds to the Fresnel amplitude vector and the intensity of the reflected light is  . On the other hand, if the component of magnetization component points to the left of the incident plane as viewed from the source, the Kerr vector subtracts from the Fresnel amplitude and the reflected intensity is given by
. On the other hand, if the component of magnetization component points to the left of the incident plane as viewed from the source, the Kerr vector subtracts from the Fresnel amplitude and the reflected intensity is given by  .
.Quadratic MOKE
In addition to the polar, longitudinal and transverse Kerr effect which depend linear on the respective magnetization components, there are also higher order quadratic effects, for which the Kerr angle depends onproduct terms involving the polar, longitudinal and transverse magnetization components. Those effects
are referred to as Voigt effect
Voigt Effect
The Voigt Effect, is one of a class of effects, resulting in what is called magnetic birefringence, or magnetic double refraction. It is a magneto-optical phenomenon with a similar origin to the Faraday effect. In the Faraday effect, the polarization of light can be rotated when passed through a...
or quadratic Kerr effect. Quadratic magneto-optic Kerr effect (QMOKE) is found strong in Heusler alloys such as Co2FeSi and Co2MnGe
Microscopy
A Kerr Microscope relies on the MOKE in order to image differences in magnetic orientation. In addition to a regular optical microscope, a polarizer and analyzer are needed as a source and sensor for polarized light. Because the different MOKE geometries require different polarized light, the polarizer should have the option to change the polarization of the incident light (circular, linear, and elliptical). When the polarized light is reflected off the sample material, a change in any combination of the following may occur: Kerr rotation, Kerr Ellipticity, or polarized amplitude. The analyzer then receives the incoming light and passes the data to a computer system which can back out the magnetic field from these changes in polarization.In conjunction with the Kerr Microscope, Magneto Optical Imaging Films (MOIF) can be used to better image magnetic domains in ferromagnetic materials. These films can be made out of an Yttrium Iron Garnet
Yttrium iron garnet
Yttrium iron garnet is a kind of synthetic garnet, with chemical composition 323, or Y3Fe5O12. It is a ferrimagnetic material with a Curie temperature of 550 K....
and are usually substituted with certain rare earth elements. Because the manufacturing process of these films is so specialized, they aren't commercially available.
Magnetic Media
Magneto Optical (MO) DrivesMagneto-optical drive
A magneto-optical drive is a kind of optical disc drive capable of writing and rewriting data upon a magneto-optical disc. Both 130 mm and 90 mm form factors exist. The technology was introduced commercially in 1985...
were introduced in 1985, and were originally WORM (write once, read many) drives, meaning they could be added to but not erased. Although they are not widely used today, they were reliable both in accurate writing and consistent data retention. Typical sizes ranged from 100 megabytes (MB) up to 9.2 gigabytes (GB). MO drives checked the data as it was being written, and thus took longer than typical CD's or DVD's. However this allowed for increased data integrity.
MO discs were written using laser and an electromagnet. The laser would heat the platter above its Curie Temperature and which point the electromagnet would orient that bit as a 1 or 0. To read, the laser is operated at a lower intensity, and emits polarized light. Reflected light is analyzed showing a noticeable difference between a 0 or 1.
Discovery
The magneto-optic Kerr effect was discovered in 1877 by John KerrJohn Kerr (physicist)
John Kerr FRS was a Scottish physicist and a pioneer in the field of electro-optics. He is best known for the discovery of what is now called the Kerr effect.-Life and work:...
.
See also
- Faraday effectFaraday effectIn physics, the Faraday effect or Faraday rotation is a Magneto-optical phenomenon, that is, an interaction between light and a magnetic field in a medium...
- Fresnel equationsFresnel equationsThe Fresnel equations , deduced by Augustin-Jean Fresnel , describe the behaviour of light when moving between media of differing refractive indices...
- John KerrJohn Kerr (physicist)John Kerr FRS was a Scottish physicist and a pioneer in the field of electro-optics. He is best known for the discovery of what is now called the Kerr effect.-Life and work:...
- Thin-film opticsThin-film opticsThin-film optics is the branch of optics that deals with very thin structured layers of different materials. In order to exhibit thin-film optics, the thickness of the layers of material must be on the order of the wavelengths of visible light...
- Voigt EffectVoigt EffectThe Voigt Effect, is one of a class of effects, resulting in what is called magnetic birefringence, or magnetic double refraction. It is a magneto-optical phenomenon with a similar origin to the Faraday effect. In the Faraday effect, the polarization of light can be rotated when passed through a...
- Zeeman EffectZeeman effectThe Zeeman effect is the splitting of a spectral line into several components in the presence of a static magnetic field. It is analogous to the Stark effect, the splitting of a spectral line into several components in the presence of an electric field...
External links
- Kerr Calculation Applet – Java applet, computes the Kerr angle of multilayered thin films
- yeh-moke – Free software computes the Magneto-optic Kerr effect of multilayered thin films
- MOKE Microscope – Magneto-Optical Kerr Effect Microscope [PDF: 3.2MB]
- MOKE tutorial - A step by step tutorial on the longitudinal, polar and transverse Magneto-Optical Kerr Effect.

