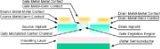
MESFET
Overview
JFET
The junction gate field-effect transistor is the simplest type of field-effect transistor. It can be used as an electronically-controlled switch or as a voltage-controlled resistance. Electric charge flows through a semiconducting channel between "source" and "drain" terminals...
in construction and terminology. The difference is that instead of using a p-n junction for a gate, a Schottky
Schottky barrier
A Schottky barrier, named after Walter H. Schottky, is a potential barrier formed at a metal–semiconductor junction which has rectifying characteristics, suitable for use as a diode...
(metal
Metal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
-semiconductor
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
) junction is used. MESFETs are usually constructed in compound semiconductor technologies lacking high quality surface passivation such as GaAs, InP, or SiC
Silicon carbide
Silicon carbide , also known as carborundum, is a compound of silicon and carbon with chemical formula SiC. It occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite. Silicon carbide powder has been mass-produced since 1893 for use as an abrasive...
, and are faster but more expensive than silicon-based JFET
JFET
The junction gate field-effect transistor is the simplest type of field-effect transistor. It can be used as an electronically-controlled switch or as a voltage-controlled resistance. Electric charge flows through a semiconducting channel between "source" and "drain" terminals...
s or MOSFET
MOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor is a transistor used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. The basic principle of this kind of transistor was first patented by Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925...
s.

