.gif)
Lycopene (data page)
Encyclopedia
Material Safety Data Sheet
The handling of this chemical may incur notable safety precautions. It is highly recommend that you seek the Material Safety Datasheet (MSDS
Material safety data sheet
A Material Safety Data Sheet is a form with data regarding the properties of a particular substance....
) for this chemical from a reliable source such as SIRI, and follow its directions.
Structure and properties
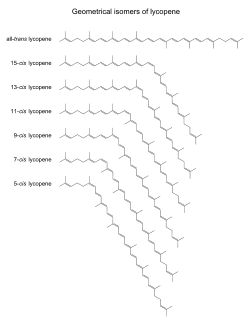
All-trans-lycopene with canonical numbering:

| Structure and properties | |
|---|---|
| Index of refraction, nD | ? |
| Dielectric constant Dielectric constant The relative permittivity of a material under given conditions reflects the extent to which it concentrates electrostatic lines of flux. In technical terms, it is the ratio of the amount of electrical energy stored in a material by an applied voltage, relative to that stored in a vacuum... , εr |
? ε0 at ? °C |
| Bond strength Bond strength In chemistry, bond strength is measured between two atoms joined in a chemical bond. It is the degree to which each atom linked to another atom contributes to the valency of this other atom... |
? |
| Bond length Bond length - Explanation :Bond length is related to bond order, when more electrons participate in bond formation the bond will get shorter. Bond length is also inversely related to bond strength and the bond dissociation energy, as a stronger bond will be shorter... |
? |
| Bond angle | ? |
| Magnetic susceptibility Magnetic susceptibility In electromagnetism, the magnetic susceptibility \chi_m is a dimensionless proportionality constant that indicates the degree of magnetization of a material in response to an applied magnetic field... |
? |
Spectral data
To date, no X-ray crystal structure
Crystal structure
In mineralogy and crystallography, crystal structure is a unique arrangement of atoms or molecules in a crystalline liquid or solid. A crystal structure is composed of a pattern, a set of atoms arranged in a particular way, and a lattice exhibiting long-range order and symmetry...
of lycopene has been reported.

| UV-Vis | |
|---|---|
| λmax | 443, 471, 502 nm Nanometre A nanometre is a unit of length in the metric system, equal to one billionth of a metre. The name combines the SI prefix nano- with the parent unit name metre .The nanometre is often used to express dimensions on the atomic scale: the diameter... in hexane |
| Extinction coefficient Molar absorptivity The molar absorption coefficient, molar extinction coefficient, or molar absorptivity, is a measurement of how strongly a chemical species absorbs light at a given wavelength... , ε |
1.72 × 105 L•mol−1•cm−1(at 502 nm) |
| IR Infrared Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm... |
|
| Major absorption bands | ? cm Centimetre A centimetre is a unit of length in the metric system, equal to one hundredth of a metre, which is the SI base unit of length. Centi is the SI prefix for a factor of . Hence a centimetre can be written as or — meaning or respectively... −1 |
| NMR NMR spectroscopy Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy, is a research technique that exploits the magnetic properties of certain atomic nuclei to determine physical and chemical properties of atoms or the molecules in which they are contained... |
|
| Proton NMR Proton NMR Proton NMR is the application of nuclear magnetic resonance in NMR spectroscopy with respect to hydrogen-1 nuclei within the molecules of a substance, in order to determine the structure of its molecules. In samples where natural hydrogen is used, practically all of the hydrogen consists of the... |
|
| Carbon-13 NMR Carbon-13 NMR Carbon-13 NMR is the application of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to carbon. It is analogous to proton NMR and allows the identification of carbon atoms in an organic molecule just as proton NMR identifies hydrogen atoms... |
|
| Other NMR data | |
| MS Mass spectrometry Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of charged particles.It is used for determining masses of particles, for determining the elemental composition of a sample or molecule, and for elucidating the chemical structures of molecules, such as peptides and... |
|
| Masses of main fragments |
|

