Luminosity function
Encyclopedia
Human eye
The human eye is an organ which reacts to light for several purposes. As a conscious sense organ, the eye allows vision. Rod and cone cells in the retina allow conscious light perception and vision including color differentiation and the perception of depth...
to light of different wavelengths. It should not be considered perfectly accurate in every case, but it is a very good representation of visual sensitivity of the human eye and it is valuable as a baseline for experimental purposes. It is a standard function established by the Commission Internationale de l'Éclairage (CIE) and may be used to convert radiant energy into luminous (i.e., visible) energy. It also forms the central color matching function in the CIE 1931 color space
CIE 1931 color space
In the study of color perception, one of the first mathematically defined color spaces is the CIE 1931 XYZ color space, created by the International Commission on Illumination in 1931....
.
Details
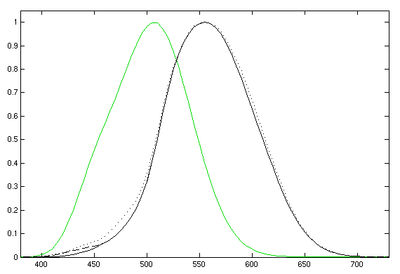
There are two luminosity functions in common use. For everyday light levels, the photopicPhotopic vision
Photopic vision is the vision of the eye under well-lit conditions. In humans and many other animals, photopic vision allows color perception, mediated by cone cells, and a significantly higher visual acuity and temporal resolution than available with scotopic vision.The human eye uses three types...
luminosity function best approximates the response of the human eye. For low light levels, the response of the human eye changes, and the scotopic
Scotopic vision
Scotopic vision is the vision of the eye under low light conditions. The term comes from Greek skotos meaning darkness and -opia meaning a condition of sight...
curve applies. The photopic curve is the CIE standard curve used in the CIE 1931 color space.
The luminous flux
Luminous flux
In photometry, luminous flux or luminous power is the measure of the perceived power of light. It differs from radiant flux, the measure of the total power of light emitted, in that luminous flux is adjusted to reflect the varying sensitivity of the human eye to different wavelengths of...
(or visible energy) in a light source is defined by the photopic luminosity function. The following equation calculates the total luminous flux in a source of light.
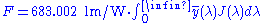
where
 is the luminous flux in lumen
is the luminous flux in lumenLumen (unit)
The lumen is the SI derived unit of luminous flux, a measure of the total "amount" of visible light emitted by a source. Luminous flux differs from power in that luminous flux measurements reflect the varying sensitivity of the human eye to different wavelengths of light, while radiant flux...
s,
 is the spectral power distribution
is the spectral power distributionSpectral power distribution
In color science and radiometry, a spectral power distribution describes the power per unit area per unit wavelength of an illumination , or more generally, the per-wavelength contribution to any radiometric quantity .Mathematically, for the spectral...
of the radiation (power per unit wavelength), in watts per metre.
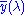 (also known as
(also known as 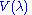 ) is the standard luminosity function (which is dimensionless).
) is the standard luminosity function (which is dimensionless).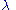 is wavelength in metres.
is wavelength in metres.Formally, the integral is the inner product of the luminosity function with the light spectrum. In practice, the integral is replaced by a sum over discrete wavelengths for which tabulated values of the luminosity function are available. The CIE
International Commission on Illumination
The International Commission on Illumination is the international authority on light, illumination, color, and color spaces...
distributes standard tables with luminosity function values at 5 nm intervals from 380 nm to 780 nm.
The standard luminosity function is normalized to a peak value of unity at 555 nm (see luminous coefficient). The value of the constant in front of the integral is usually rounded off to 683 lm/W. The small excess fractional value comes from the slight mismatch between the definition of the lumen and the peak of the luminosity function. The lumen is defined to be unity for a radiant energy of 1/683 watt at a frequency of 540 THz, which corresponds to a standard air wavelength of 555.016 nm rather than 555 nm, which is the peak of the luminosity curve. The value of
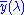 is 0.999997 at 555.016 nm, so that a value of 683/0.999997 = 683.002 is the multiplicative constant.
is 0.999997 at 555.016 nm, so that a value of 683/0.999997 = 683.002 is the multiplicative constant.The number 683 is connected to the modern (1979) definition of the candela
Candela
The candela is the SI base unit of luminous intensity; that is, power emitted by a light source in a particular direction, weighted by the luminosity function . A common candle emits light with a luminous intensity of roughly one candela...
, the unit of luminous intensity
Luminous intensity
In photometry, luminous intensity is a measure of the wavelength-weighted power emitted by a light source in a particular direction per unit solid angle, based on the luminosity function, a standardized model of the sensitivity of the human eye...
. This arbitrary number made the new definition give numbers equivalent to those from the old definition of the candela.
Improvements to the standard
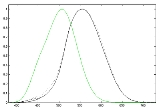
The CIE 1924 photopic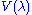 luminosity function, which is included in the CIE 1931 color-matching functions as the y function, has long been acknowledged to underestimate the contribution of the blue end of the spectrum to perceived luminance. There have been numerous attempts to improve the standard function, to make it more representative of human vision. Judd in 1951, improved by Vos in 1978, resulted in a function known as CIE
luminosity function, which is included in the CIE 1931 color-matching functions as the y function, has long been acknowledged to underestimate the contribution of the blue end of the spectrum to perceived luminance. There have been numerous attempts to improve the standard function, to make it more representative of human vision. Judd in 1951, improved by Vos in 1978, resulted in a function known as CIE 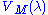 . More recently, Sharpe, Stockman, Jagla & Jägle (2005) developed a function consistent with the Stockman & Sharpe cone fundamentals; their curves are plotted in the figure above.
. More recently, Sharpe, Stockman, Jagla & Jägle (2005) developed a function consistent with the Stockman & Sharpe cone fundamentals; their curves are plotted in the figure above.Scotopic luminosity
For very low levels of intensity (scotopic visionScotopic vision
Scotopic vision is the vision of the eye under low light conditions. The term comes from Greek skotos meaning darkness and -opia meaning a condition of sight...
), the sensitivity of the eye is mediated by rods, not cones, and shifts toward the violet
Violet (color)
As the name of a color, violet is synonymous with a bluish purple, when the word "purple" is used in the common English language sense of any color between blue and red, not including either blue or red...
, peaking around 507 nm for young eyes; the sensitivity is equivalent to 1699 lm/W or 1700 lm/W at this peak.
The standard scotopic luminosity function or
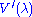 was adopted by the CIE in 1951, based on measurements by Wald (1945) and by Crawford (1949).http://www.cvrl.org/database/text/lum/scvl.htm
was adopted by the CIE in 1951, based on measurements by Wald (1945) and by Crawford (1949).http://www.cvrl.org/database/text/lum/scvl.htmSee also
- Color visionColor visionColor vision is the capacity of an organism or machine to distinguish objects based on the wavelengths of the light they reflect, emit, or transmit...
- A-weightingA-weightingA Weighting curve is a graph of a set of factors, that are used to 'weight' measured values of a variable according to their importance in relation to some outcome. The most commonly known example is frequency weighting in sound level measurement where a specific set of weighting curves known as A,...
, the sound equivalent - Quantum efficiencyQuantum efficiencyQuantum efficiency is a quantity defined for a photosensitive device such as photographic film or a charge-coupled device as the percentage of photons hitting the photoreactive surface that will produce an electron–hole pair. It is an accurate measurement of the device's electrical sensitivity to...
, the image sensorImage sensorAn image sensor is a device that converts an optical image into an electronic signal. It is used mostly in digital cameras and other imaging devices...
equivalent

