Ligand field theory
Overview
Molecular orbital theory
In chemistry, molecular orbital theory is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms, but are treated as moving under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule...
to transition metal
Transition metal
The term transition metal has two possible meanings:*The IUPAC definition states that a transition metal is "an element whose atom has an incomplete d sub-shell, or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell." Group 12 elements are not transition metals in this definition.*Some...
complexes. A transition metal ion has nine valence atomic orbital
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus...
s, five (n)d, one (n+1)s, and three (n+1)p orbitals. These orbitals are of appropriate energy to form bonding interaction with ligand
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from...
s. The LFT analysis is highly dependent on the geometry of the complex, but most explanations begin by describing octahedral
Octahedral molecular geometry
In chemistry, octahedral molecular geometry describes the shape of compounds where in six atoms or groups of atoms or ligands are symmetrically arranged around a central atom, defining the vertices of an octahedron...
complexes, where six ligands coordinate to the metal.
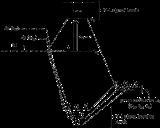
The molecular orbitals created by coordination can be seen as resulting from the donation of two electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s by each of six σ-donor ligands to the d-orbitals on the metal
Metal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
.
Unanswered Questions
Discussions

