Lathe
Encyclopedia
Machine tool
A machine tool is a machine, typically powered other than by human muscle , used to make manufactured parts in various ways that include cutting or certain other kinds of deformation...
which rotates the workpiece on its axis to perform various operations such as cutting
Cutting
Cutting is the separation of a physical object, or a portion of a physical object, into two portions, through the application of an acutely directed force. An implement commonly used for cutting is the knife or in medical cases the scalpel...
, sanding, knurling
Knurling
Knurling is a manufacturing process, typically conducted on a lathe, whereby a visually attractive diamond-shaped pattern is cut or rolled into metal.- Uses :...
, drilling
Drilling
Drilling is a cutting process that uses a drill bit to cut or enlarge a hole in solid materials. The drill bit is a multipoint, end cutting tool...
, or deformation with tools that are applied to the workpiece to create an object which has symmetry
Rotational symmetry
Generally speaking, an object with rotational symmetry is an object that looks the same after a certain amount of rotation. An object may have more than one rotational symmetry; for instance, if reflections or turning it over are not counted, the triskelion appearing on the Isle of Man's flag has...
about an axis of rotation.
Lathes are used in woodturning
Woodturning
Woodturning is a form of woodworking that is used to create wooden objects on a lathe . Woodturning differs from most other forms of woodworking in that the wood is moving while a stationary tool is used to cut and shape it...
, metalworking
Metalworking
Metalworking is the process of working with metals to create individual parts, assemblies, or large scale structures. The term covers a wide range of work from large ships and bridges to precise engine parts and delicate jewelry. It therefore includes a correspondingly wide range of skills,...
, metal spinning
Metal spinning
Metal spinning, also known as spin forming or spinning, is a metalworking process by which a disc or tube of metal is rotated at high speed and formed into an axially symmetric part. Spinning can be performed by hand or by a CNC lathe....
, and glassworking. Lathes can be used to shape pottery
Pottery
Pottery is the material from which the potteryware is made, of which major types include earthenware, stoneware and porcelain. The place where such wares are made is also called a pottery . Pottery also refers to the art or craft of the potter or the manufacture of pottery...
, the best-known design being the potter's wheel
Potter's wheel
In pottery, a potter's wheel is a machine used in asma of round ceramic ware. The wheel may also be used during process of trimming the excess body from dried ware and for applying incised decoration or rings of color...
. Most suitably equipped metalworking lathes can also be used to produce most solids of revolution
Solid of revolution
In mathematics, engineering, and manufacturing, a solid of revolution is a solid figure obtained by rotating a plane curve around some straight line that lies on the same plane....
, plane surfaces and screw threads or helices. Ornamental lathes can produce three-dimensional solids of incredible complexity. The material can be held in place by either one or two centers, at least one of which can be moved horizontally to accommodate varying material lengths. Other workholding methods include clamping the work about the axis of rotation using a chuck or collet, or to a faceplate, using clamps or dogs.
Examples of objects that can be produced on a lathe include candlestick
Candlestick
A candlestick, chamberstick, or candelabrum is a holder for one or more candles, used for illumination, rituals, or decorative purposes. The name 'candlestick' derives from the fact that it is usually tall and stick-shaped.Candlesticks are also called candle holders...
holders, gun barrel
Gun barrel
A gun barrel is the tube, usually metal, through which a controlled explosion or rapid expansion of gases are released in order to propel a projectile out of the end at a high velocity....
s, cue stick
Cue stick
A cue stick , is an item of sporting equipment essential to the games of pool, snooker and carom billiards. It is used to strike a ball, usually the...
s, table legs, bowl
Bowl (vessel)
A bowl is a common open-top container used in many cultures to serve food, and is also used for drinking and storing other items. They are typically small and shallow, although some, such as punch bowls and salad bowls, are larger and often intended to serve many people.Bowls have existed for...
s, baseball bat
Baseball bat
A baseball bat is a smooth wooden or metal club used in the game of baseball to hit the ball after the ball is thrown by the pitcher. It is no more than 2.75 inches in diameter at the thickest part and no more than 42 inches in length. It typically weighs no more than 33 ounces , but it...
s, musical instruments (especially woodwind instruments), crankshaft
Crankshaft
The crankshaft, sometimes casually abbreviated to crank, is the part of an engine which translates reciprocating linear piston motion into rotation...
s and camshaft
Camshaft
A camshaft is a shaft to which a cam is fastened or of which a cam forms an integral part.-History:An early cam was built into Hellenistic water-driven automata from the 3rd century BC. The camshaft was later described in Iraq by Al-Jazari in 1206. He employed it as part of his automata,...
s.
History
The lathe is an ancient tool, dating at least to ancient Egypt and known and used in Assyria and ancient Greece.The origin of turning dates to around 1300 BC when the Ancient Egypt first developed a two-person lathe. One person would turn the wood work piece with a rope while the other used a sharp tool to cut shapes in the wood. Ancient Rome improved the Egyptian design with the addition of a turning bow. In the Middle Ages a pedal replaced hand-operated turning, freeing both the craftsman's hands to hold the woodturning tools. The pedal was usually connected to a pole, often a straight-grained sapling. The system today is called the "spring pole" lathe. Spring pole lathes were in common use into the early 20th century.
During the Industrial Revolution, mechanized power generated by water wheels or steam engines was transmitted to the lathe via line shafting, allowing faster and easier work. Metalworking lathes evolved into heavier machines with thicker, more rigid parts. Between the late 19th and mid-20th centuries, individual electric motors at each lathe replaced line shafting as the power source. Beginning in the 1950s, servomechanism
Servomechanism
thumb|right|200px|Industrial servomotorThe grey/green cylinder is the [[Brush |brush-type]] [[DC motor]]. The black section at the bottom contains the [[Epicyclic gearing|planetary]] [[Reduction drive|reduction gear]], and the black object on top of the motor is the optical [[rotary encoder]] for...
were applied to the control of lathes and other machine tools via numerical control, which often was coupled with computers to yield computerized numerical control. Today manually controlled and CNC lathes coexist in the manufacturing industries.
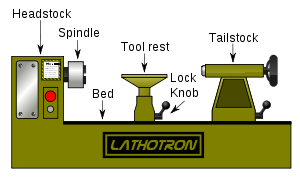
Parts
Almost all lathes have a bed, which is (almost always) a horizontal beam (although CNC lathes commonly have an inclined or vertical beam for a bed to ensure that swarf
Swarf
Swarf, also known as turnings, chips, or filings, are shavings and chippings of metal — the debris or waste resulting from metalworking operations including milling and grinding. It can usually be recycled, and this is the preferred method of disposal due to the environmental concerns regarding...
, or chips, falls free of the bed). Woodturning lathes specialised for turning large bowls often have no bed or tailstock, merely a free-standing headstock and a cantilevered toolrest.
At one end of the bed (almost always the left, as the operator faces the lathe) is a headstock. The headstock contains high-precision spinning bearings. Rotating within the bearings is a horizontal axle, with an axis parallel to the bed, called the spindle
Spindle (tool)
In machine tools, a spindle is a rotating axis of the machine, which often has a shaft at its heart. The shaft itself is called a spindle, but also, in shop-floor practice, the word often is used metonymically to refer to the entire rotary unit, including not only the shaft itself, but its bearings...
. Spindles are often hollow, and have exterior threads and/or an interior Morse taper on the "inboard" (i.e., facing to the right / towards the bed) by which workholding accessories may be mounted to the spindle. Spindles may also have exterior threads and/or an interior taper at their "outboard" (i.e., facing away from the bed) end, and/or may have a handwheel or other accessory mechanism on their outboard end. Spindles are powered, and impart motion to the workpiece.
The spindle is driven, either by foot power from a treadle and flywheel or by a belt or gear drive to a power source. In most modern lathes this power source is an integral electric motor, often either in the headstock, to the left of the headstock, or beneath the headstock, concealed in the stand.
In addition to the spindle and its bearings, the headstock often contains parts to convert the motor speed into various spindle speeds. Various types of speed-changing mechanism achieve this, from a cone pulley or step pulley, to a cone pulley with back gear (which is essentially a low range, similar in net effect to the two-speed rear of a truck), to an entire gear train similar to that of a manual-shift auto transmission
Transmission (mechanics)
A machine consists of a power source and a power transmission system, which provides controlled application of the power. Merriam-Webster defines transmission as: an assembly of parts including the speed-changing gears and the propeller shaft by which the power is transmitted from an engine to a...
. Some motors have electronic rheostat-type speed controls, which obviates cone pulleys or gears.
The counterpoint to the headstock is the tailstock, sometimes referred to as the loose head, as it can be positioned at any convenient point on the bed, by undoing a locking nut, sliding it to the required area, and then relocking it. The tailstock contains a barrel which does not rotate, but can slide in and out parallel to the axis of the bed, and directly in line with the headstock spindle. The barrel is hollow, and usually contains a taper to facilitate the gripping of various type of tooling. Its most common uses are to hold a hardened steel centre, which is used to support long thin shafts while turning, or to hold drill bits for drilling axial holes in the work piece. Many other uses are possible.
Metalworking lathes have a carriage (comprising a saddle and apron) topped with a cross-slide, which is a flat piece that sits crosswise on the bed, and can be cranked at right angles to the bed. Sitting atop the cross slide is usually another slide called a compound rest, which provides 2 additional axes of motion, rotary and linear. Atop that sits a toolpost, which holds a cutting tool
Tool bit
The term tool bit generally refers to a non-rotary cutting tool used in metal lathes, shapers, and planers. Such cutters are also often referred to by the set-phrase name of single-point cutting tool. The cutting edge is ground to suit a particular machining operation and may be resharpened or...
which removes material from the workpiece. There may or may not be a leadscrew
Leadscrew
A leadscrew , also known as a power screw or translation screw, is a screw designed to translate turning motion into linear motion...
, which moves the cross-slide along the bed.
Woodturning and metal spinning lathes do not have cross-slides, but rather have banjos, which are flat pieces that sit crosswise on the bed. The position of a banjo
Banjo (wood lathe)
In the craft of woodturning, a banjo is a common term for a fixture on the wood lathe, mounted on the lathe's bed, for holding the toolrest. It allows for adjustment of the toolrest in various positions, by the lathe operator, making it possible to hold the turning tool in the most convenient...
can be adjusted by hand; no gearing is involved. Ascending vertically from the banjo
Banjo (wood lathe)
In the craft of woodturning, a banjo is a common term for a fixture on the wood lathe, mounted on the lathe's bed, for holding the toolrest. It allows for adjustment of the toolrest in various positions, by the lathe operator, making it possible to hold the turning tool in the most convenient...
is a toolpost, at the top of which is a horizontal toolrest. In woodturning, hand tools are braced against the tool rest and levered into the workpiece. In metal spinning, the further pin ascends vertically from the tool rest, and serves as a fulcrum against which tools may be levered into the workpiece.
Accessories
Unless a workpiece has a taper machined onto it which perfectly matches the internal taper in the spindle, or has threads which perfectly match the external threads on the spindle (two conditions which rarely exist), an accessory must be used to mount a workpiece to the spindle.A workpiece may be bolted or screwed to a faceplate
Lathe faceplate
A lathe faceplate is the basic workholding accessory for a wood or metal turning lathe. It is a circular metal plate which fixes to the end of the lathe spindle...
, a large, flat disk that mounts to the spindle. In the alternative, faceplate dogs may be used to secure the work to the faceplate.
A workpiece may be mounted on a mandrel
Mandrel
A mandrel is one of the following:* an object used to shape machined work.* a tool component that grips or clamps materials to be machined.* a tool component that can be used to grip other moving tool components.- Variants :...
, or circular work clamped in a three- or four-jaw chuck. For irregular shaped workpieces it is usual to use a four jaw (independent moving jaws) chuck. These holding devices mount directly to the Lathe headstock spindle.
In precision work, and in some classes of repetition work, cylindrical workpieces are usually held in a collet
Collet
A collet is a holding device—specifically, a subtype of chuck—that forms a collar around the object to be held and exerts a strong clamping force on the object when it is tightened, usually via a tapered outer collar. It may be used to hold a workpiece or a tool.A collet is a sleeve with a ...
inserted into the spindle and secured either by a drawbar, or by a collet closing cap on the spindle. Suitable collets may also be used to mount square or hexagonal workpieces. In precision toolmaking work such collets are usually of the draw-in variety, where, as the collet is tightened, the workpiece moves slightly back into the headstock, whereas for most repetition work the dead length variety is preferred, as this ensures that the position of the workpiece does not move as the collet is tightened.
A soft workpiece (wooden) may be pinched between centers by using a spur drive at the headstock, which bites into the wood and imparts torque to it.

Lathe carrier
A lathe dog, also known as a lathe carrier, is a device that clamps around the workpiece and allows the rotary motion of the machine's spindle to be transmitted to the workpiece....
or lathe dog may also be employed when turning between two centers.
In woodturning, one variation of a live center is a cup center, which is a cone of metal surrounded by an annular ring of metal that decreases the chances of the workpiece splitting.
A circular metal plate with even spaced holes around the periphery, mounted to the spindle, is called an "index plate". It can be used to rotate the spindle to a precise angle, then lock it in place, facilitating repeated auxiliary operations done to the workpiece.
Other accessories, including items such as taper turning attachments, knurling tools, vertical slides, fixed and traveling steadies, etc., increase the versatility of a lathe and the range of work it may perform.
Modes of use
When a workpiece is fixed between the headstock and the tailstock, it is said to be "between centers". When a workpiece is supported at both ends, it is more stable, and more force may be applied to the workpiece, via tools, at a right angle to the axis of rotation, without fear that the workpiece may break loose.When a workpiece is fixed only to the spindle at the headstock end, the work is said to be "face work". When a workpiece is supported in this manner, less force may be applied to the workpiece, via tools, at a right angle to the axis of rotation, lest the workpiece rip free. Thus, most work must be done axially, towards the headstock, or at right angles, but gently.
When a workpiece is mounted with a certain axis of rotation, worked, then remounted with a new axis of rotation, this is referred to as "eccentric turning" or "multi axis turning". The result is that various cross sections of the workpiece are rotationally symmetric, but the workpiece as a whole is not rotationally symmetric. This technique is used for camshafts, various types of chair legs.
Varieties
The smallest lathes are "jewelers lathes" or "watchmaker lathes", which are small enough that they may be held in one hand. The workpieces machined on a jeweler's lathes are metal, jeweler's lathes can be used with hand-held "graver" tools or with compound rests that attach to the lathe bed. Graver tools are generally supported by a T-rest, not fixed to a cross slide or compound rest. The work is usually held in a collet. Common spindle bore sizes are 6 mm, 8 mm and 10 mm. The term W/W refers to the Webster/Whitcomb collet and lathe, invented by the American Watch Tool Company of Waltham, Massachusetts. Most lathes commonly referred to as watchmakers lathes are of this design. In 1909, the American Watch Tool company introduced the Magnus type collet (a 10-mm body size collet) using a lathe of the same basic design, the Webster/Whitcomb Magnus. (F.W.Derbyshire, Inc. retains the trade names Webster/Whitcomb and Magnus and still produces these collets.) Two bed patterns are common: the WW (Webster Whitcomb) bed, a truncated triangular prism (found only on 8 and 10 mm watchmakers' lathes); and the continental D-style bar bed (used on both 6 mm and 8 mm lathes by firms such as Lorch and Star). Other bed designs have been used, such a triangular prism on some Boley 6.5 mm lathes, and a V-edged bed on IME's 8 mm lathes.Smaller metalworking lathes that are larger than jewelers' lathes and can sit on a bench or table, but offer such features as tool holders and a screw-cutting gear train are called hobby lathes, and larger versions, "bench lathes". Even larger lathes offering similar features for producing or modifying individual parts are called "engine lathes". Lathes of these types do not have additional integral features for repetitive production, but rather are used for individual part production or modification as the primary role.
Lathes of this size that are designed for mass manufacture, but not offering the versatile screw-cutting capabilities of the engine or bench lathe, are referred to as "second operation" lathes.
Lathes with a very large spindle bore and a chuck on both ends of the spindle are called "oil field lathes".
Fully automatic mechanical lathes, employing cams and gear trains for controlled movement, are called screw machine
Screw machine
A screw machine may refer to a:* Screw machine , a small- to medium-sized automatic lathe that is mechanically automated via cams...
s.
Lathes that are controlled by a computer are CNC lathes.
Lathes with the spindle mounted in a vertical configuration, instead of horizontal configuration, are called vertical lathes or vertical boring machines. They are used where very large diameters must be turned, and the workpiece (comparatively) is not very long.
A lathe with a cylindrical tailstock that can rotate around a vertical axis, so as to present different tools towards the headstock (and the workpiece) are turret lathes.
A lathe equipped with indexing plates, profile cutters, spiral or helical guides, etc., so as to enable ornamental turning is an ornamental lathe.
Various combinations are possible: for example, a vertical lathe have CNC as well (such as a CNC VTL).
Lathes can be combined with other machine tools, such as a drill press or vertical milling machine
Milling machine
A milling machine is a machine tool used to machine solid materials. Milling machines are often classed in two basic forms, horizontal and vertical, which refers to the orientation of the main spindle. Both types range in size from small, bench-mounted devices to room-sized machines...
. These are usually referred to as combination lathes.
Woodworking lathes

There are also woodworking lathes for making bowls and plates, which have no horizontal metal rail, as the bowl or plate needs only to be held by one side from a metal face plate. Without this rail, there is very little restriction to the width of the piece being turned. Further detail can be found on the woodturning
Woodturning
Woodturning is a form of woodworking that is used to create wooden objects on a lathe . Woodturning differs from most other forms of woodworking in that the wood is moving while a stationary tool is used to cut and shape it...
page.
Metalworking lathes

In a metalworking lathe
Lathe (metal)
A metal lathe or metalworking lathe is a large class of lathes designed for precisely machining relatively hard materials. They were originally designed to machine metals; however, with the advent of plastics and other materials, and with their inherent versatility, they are used in a wide range of...
, metal is removed from the workpiece using a hardened cutting tool
Tool bit
The term tool bit generally refers to a non-rotary cutting tool used in metal lathes, shapers, and planers. Such cutters are also often referred to by the set-phrase name of single-point cutting tool. The cutting edge is ground to suit a particular machining operation and may be resharpened or...
, which is usually fixed to a solid moveable mounting, either a toolpost or a turret, which is then moved against the workpiece using handwheels and/or computer controlled motors. These (cutting) tools come in a wide range of sizes and shapes depending upon their application. Some common styles are diamond, round, square and triangular.
The toolpost is operated by leadscrews that can accurately position the tool in a variety of planes. The toolpost may be driven manually or automatically to produce the roughing and finishing cuts required to turn the workpiece to the desired shape and dimensions, or for cutting threads
Screw thread
A screw thread, often shortened to thread, is a helical structure used to convert between rotational and linear movement or force. A screw thread is a ridge wrapped around a cylinder or cone in the form of a helix, with the former being called a straight thread and the latter called a tapered thread...
, worm gears, etc. Cutting fluid
Cutting fluid
Cutting fluid is a type of coolant and lubricant designed specifically for metalworking and machining processes. There are various kinds of cutting fluids, which include oils, oil-water emulsions, pastes, gels, aerosols , and air or other gases. They may be made from petroleum distillates, animal...
may also be pumped to the cutting site to provide cooling, lubrication and clearing of swarf
Swarf
Swarf, also known as turnings, chips, or filings, are shavings and chippings of metal — the debris or waste resulting from metalworking operations including milling and grinding. It can usually be recycled, and this is the preferred method of disposal due to the environmental concerns regarding...
from the workpiece. Some lathes may be operated under control of a computer
Computer
A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
for mass production
Mass production
Mass production is the production of large amounts of standardized products, including and especially on assembly lines...
of parts (see "Computer Numerical Control").
Manually controlled metalworking lathes are commonly provided with a variable ratio gear train to drive the main leadscrew. This enables different thread pitches to be cut. On some older lathes or more affordable new lathes, the gear trains are changed by swapping gears with various numbers of teeth onto or off of the shafts, while more modern or expensive manually controlled lathes have a quick change box to provide commonly used ratios by the operation of a lever. CNC lathes use computers and servomechanisms to regulate the rates of movement.
On manually controlled lathes, the thread pitches that can be cut are, in some ways, determined by the pitch of the leadscrew: A lathe with a metric
Metre
The metre , symbol m, is the base unit of length in the International System of Units . Originally intended to be one ten-millionth of the distance from the Earth's equator to the North Pole , its definition has been periodically refined to reflect growing knowledge of metrology...
leadscrew will readily cut metric threads (including BA
British Association screw threads
British Association or BA screw threads are a largely obsolete set of small screw threads, the largest being 0BA at 6 mm diameter. They were, and to some extent still are, used for miniature instruments and modelling....
), while one with an imperial leadscrew will readily cut imperial unit based threads such as BSW
British Standard Whitworth
British Standard Whitworth is one of a number of imperial unit based screw thread standards which use the same bolt heads and nut hexagonal sizes, the others being British Standard Fine thread and British Standard Cycle...
or UTS
Unified Thread Standard
The Unified Thread Standard defines a standard thread form and series—along with allowances, tolerances, and designations—for screw threads commonly used in the United States and Canada...
(UNF,UNC). This limitation is not insurmountable, because a 127-tooth gear, called a transposing gear, is used to translate between metric and inch thread pitches. However, this is optional equipment that many lathe owners do not own. It is also a larger changewheel than the others, and on some lathes may be larger than the changewheel mounting banjo is capable of mounting.
The workpiece may be supported between a pair of points called centres
Lathe center
A lathe center, often shortened to center, is a tool that has been ground to a point as to accurately position a workpiece about an axis...
, or it may be bolted to a faceplate or held in a chuck
Chuck (engineering)
A chuck is a specialized type of clamp used to hold an object, usually an object with radial symmetry, especially a cylindrical object. It is most commonly used to hold a rotating tool or a rotating workpiece...
. A chuck has movable jaws that can grip the workpiece securely.
There are some effects on material properties when using a metalworking lathe. There are few chemical or physical effects, but there are many mechanical effects, which include residual stress, microcracks, workhardening, and tempering in hardened materials.
Cue lathes
Cue lathes function similar to turning and spinning lathes allowing for a perfectly radially-symmetrical cut for billiard cuesCue stick
A cue stick , is an item of sporting equipment essential to the games of pool, snooker and carom billiards. It is used to strike a ball, usually the...
. They can also be used to refinish cues that have been worn over the years.
Glassworking lathes
Glassworking lathes are similar in design to other lathes, but differ markedly in how the workpiece is modified. Glassworking lathes slowly rotate a hollow glass vessel over a fixed or variable temperature flame. The source of the flame may be either hand-held, or mounted to a banjo/cross slide that can be moved along the lathe bed. The flame serves to soften the glass being worked, so that the glass in a specific area of the workpiece becomes malleable, and subject to forming either by inflation ("glassblowingGlassblowing
Glassblowing is a glassforming technique that involves inflating molten glass into a bubble, or parison, with the aid of a blowpipe, or blow tube...
"), or by deformation with a heat resistant tool. Such lathes usually have two headstocks with chucks holding the work, arranged so that they both rotate together in unison. Air can be introduced through the headstock chuck spindle for glassblowing. The tools to deform the glass and tubes to blow (inflate) the glass are usually handheld.
In diamond turning
Diamond turning
Diamond turning is a process of mechanical machining of precision elements using lathes or derivative machine tools equipped with natural or synthetic diamond-tipped tool bits...
, a computer-controlled lathe with a diamond-tipped tool is used to make precision optical surfaces in glass or other optical materials. Unlike conventional optical grinding, complex aspheric
Aspheric lens
An aspheric lens or asphere is a lens whose surface profiles are not portions of a sphere or cylinder. In photography, a lens assembly that includes an aspheric element is often called an aspherical lens....
surfaces can be machined easily. Instead of the dovetailed ways used on the tool slide of a metal turning lathe, the ways typically float on air bearings and the position of the tool is measured by optical interferometry to achieve the necessary standard of precision for optical work. The finished work piece usually requires a small amount subsequent polishing by conventional techniques to achieve a finished surface suitably smooth for use in a lens, but the rough grinding time is significantly reduced for complex lenses.
Metal spinning lathes
In metal spinningMetal spinning
Metal spinning, also known as spin forming or spinning, is a metalworking process by which a disc or tube of metal is rotated at high speed and formed into an axially symmetric part. Spinning can be performed by hand or by a CNC lathe....
, a disk of sheet metal is held perpendicularly to the main axis of the lathe, and tools with polished tips (spoons) are hand held, but levered by hand against fixed posts, to develop large amounts of torque/pressure that deform the spinning sheet of metal.
Metal spinning lathes are almost as simple as woodturning lathes (and, at this point, lathes being used for metal spinning almost always are woodworking lathes). Typically, metal spinning lathes require a user-supplied rotationally symmetric mandrel, usually made of wood, which serves as a template onto which the workpiece is moulded (non-symmetric shapes can be done, but it is a very advanced technique). For example, if you want to make a sheet metal
Sheet metal
Sheet metal is simply metal formed into thin and flat pieces. It is one of the fundamental forms used in metalworking, and can be cut and bent into a variety of different shapes. Countless everyday objects are constructed of the material...
bowl, you need a solid chunk of wood in the shape of the bowl; if you want to make a vase
Vase
The vase is an open container, often used to hold cut flowers. It can be made from a number of materials including ceramics and glass. The vase is often decorated and thus used to extend the beauty of its contents....
, you need a solid template of a vase, etc.
Given the advent of high speed, high pressure, industrial die forming, metal spinning is less common now than it once was, but still a valuable technique for producing one-off prototypes or small batches where die forming would be uneconomical.
Ornamental turning lathes
The ornamental turningOrnamental turning
Ornamental turning is a type of turning, a craft that involves cutting of a work mounted in a lathe. The work can be made of any material that is suitable for being cut in this way, such as wood, bone, ivory or metal. Plain turning is work executed on a lathe where a transverse section through any...
lathe was developed around the same time as the industrial screwcutting lathe in the nineteenth century. It was used not for making practical objects, but for decorative work - ornamental turning. By using accessories such as the horizontal and vertical cutting frames, eccentric chuck
Chuck
-Engineering:* Chuck , a clamp that is part of a machine tool or power tool and securely holds a removable part, either a workpiece or a tool -People:* Charles, a masculine given name...
and elliptical chuck, solids of extraordinary complexity may be produced by various generative procedures.
A special purpose lathe, the Rose engine lathe
Rose engine lathe
A rose engine lathe is a specialized kind of geometric lathe. The headstock rocks back and forth with a rocking motion or along the spindle axis in a pumping motion, controlled by a rubber moving against a rosette or cam-like pattern mounted on the spindle, while the lathe spindle rotates...
is also used for ornamental turning, in particular for engine turning, typically in precious metals, for example to decorate pocket watch cases. As well as a wide range of accessories, these lathes usually have complex dividing arrangements to allow the exact rotation of the mandrel. Cutting is usually carried out by rotating cutters, rather than directly by the rotation of the work itself. Because of the difficulty of polishing such work, the materials turned, such as wood or ivory, are usually quite soft, and the cutter has to be exceptionally sharp. The finest ornamental lathes are generally considered to be those made by Holtzapffel
Holtzapffel
Holtzapffel & Co. was a tool and lathe making company in London, founded by German immigrant, John Jacob Holtzapffel in 1793. The firm specialized in lathes for ornamental turning, something that was a popular leisure occupation for gentlemen at that time. Many ornamental lathes were bought by the...
around the turn of the 19th century.
Reducing lathe
Many types of lathes can be equipped with accessory components to allow them to reproduce an item: the original item is mounted on one spindle, the blank is mounted on another, and as both turn in synchronized manner, one end of an arm "reads" the original and the other end of the arm "carves" the duplicate.A reducing lathe is a specialized lathe that is designed with this feature, and which incorporates a mechanism similar to a pantograph
Pantograph
A pantograph is a mechanical linkage connected in a special manner based on parallelograms so that the movement of one pen, in tracing an image, produces identical movements in a second pen...
, so that when the "reading" end of the arm reads a detail that measures one inch (for example), the cutting end of the arm creates an analogous detail that is (for example) one quarter of an inch (a 4:1 reduction, although given appropriate machinery and appropriate settings, any reduction ratio is possible).
Reducing lathes are used in coin-making, where a plaster original (or an epoxy master made from the plaster original, or a copper shelled master made from the plaster original, etc.) is duplicated and reduced on the reducing lathe, generating a master die.
Rotary lathes
A lathe in which softwood, like spruceSpruce
A spruce is a tree of the genus Picea , a genus of about 35 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the Family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal regions of the earth. Spruces are large trees, from tall when mature, and can be distinguished by their whorled branches and conical...
or pine
Pine
Pines are trees in the genus Pinus ,in the family Pinaceae. They make up the monotypic subfamily Pinoideae. There are about 115 species of pine, although different authorities accept between 105 and 125 species.-Etymology:...
, or hardwood, like birch
Birch
Birch is a tree or shrub of the genus Betula , in the family Betulaceae, closely related to the beech/oak family, Fagaceae. The Betula genus contains 30–60 known taxa...
, logs are turned against a very sharp blade and peeled off in one continuous or semi-continuous roll. Invented by Immanuel Nobel
Immanuel Nobel
'Immanuel Nobel' , the younger, was a Swedish engineer, architect, inventor and industrialist. He was the inventor of the rotary lathe used in plywood manufacturing. He was a member of the Nobel family and the father of Robert Nobel, Ludvig Nobel and Alfred Nobel...
(father of the more famous Alfred Nobel
Alfred Nobel
Alfred Bernhard Nobel was a Swedish chemist, engineer, innovator, and armaments manufacturer. He is the inventor of dynamite. Nobel also owned Bofors, which he had redirected from its previous role as primarily an iron and steel producer to a major manufacturer of cannon and other armaments...
). The first such lathes were set up in the United States in the mid-19th century. The product is called wood veneer
Wood veneer
In woodworking, veneer refers to thin slices of wood, usually thinner than 3 mm , that are typically glued onto core panels to produce flat panels such as doors, tops and panels for cabinets, parquet floors and parts of furniture. They are also used in marquetry...
and it is used for finishing chipboard
Chipboard
Chipboard may refer to:* A type of paperboard generally made from reclaimed paper stock; the term generally used in the US** White lined chipboard, a grade of paperboard* Particle board, a type of engineered wood known as "chipboard" in some countries...
objects and making plywood
Plywood
Plywood is a type of manufactured timber made from thin sheets of wood veneer. It is one of the most widely used wood products. It is flexible, inexpensive, workable, re-usable, and can usually be locally manufactured...
.
Watchmaker's lathes

Screw
A screw, or bolt, is a type of fastener characterized by a helical ridge, known as an external thread or just thread, wrapped around a cylinder. Some screw threads are designed to mate with a complementary thread, known as an internal thread, often in the form of a nut or an object that has the...
cutting, and are still used by horologists for work such as the turning of balance shafts. A handheld tool called a graver is often used in preference to a slide mounted tool. The original watchmaker's turns was a simple dead-centre lathe with a moveable rest and two loose headstocks. The workpiece would be rotated by a bow, typically of horsehair
Horsehair
Horsehair is the long, coarse hair growing on the manes and tails of horses. It is used for various purposes, including upholstery, brushes, the bows of musical instruments, a hard-wearing fabric called haircloth, and for horsehair plaster, a wallcovering material formerly used in the construction...
, wrapped around it.
See also
- Arbor supportArbor supportAn arbor support is a device to support the outer end or intermediate point of an arbor. It is a part of milling machine, sometimes lathe machine....
- Diamond turningDiamond turningDiamond turning is a process of mechanical machining of precision elements using lathes or derivative machine tools equipped with natural or synthetic diamond-tipped tool bits...
- Metal spinningMetal spinningMetal spinning, also known as spin forming or spinning, is a metalworking process by which a disc or tube of metal is rotated at high speed and formed into an axially symmetric part. Spinning can be performed by hand or by a CNC lathe....
- Milling machineMilling machineA milling machine is a machine tool used to machine solid materials. Milling machines are often classed in two basic forms, horizontal and vertical, which refers to the orientation of the main spindle. Both types range in size from small, bench-mounted devices to room-sized machines...
- Segmented turningSegmented turningSegmented turning is turning on a lathe where the initial workpiece is composed of multiple glued-together parts. The process involves gluing up several pieces of wood to create patterns and visual effects in turned projects....
- WoodturningWoodturningWoodturning is a form of woodworking that is used to create wooden objects on a lathe . Woodturning differs from most other forms of woodworking in that the wood is moving while a stationary tool is used to cut and shape it...
- UnimatUnimatThe Unimat was a commercially sold machine intended for machining and metalworking for model making hobbyists manufactured by the Emco company...
External links
- Historical lathe archive
- Medieval and Renaissance lathes
- The history of the lathe
- Early Wood-Working
- Spring pole lathe
- On ye art and mystery of Turning
- Modern Machine Shop Practice a historic Victorian text describing lathe design, construction and use in 1880s.
- The South Bend Lathe Library Make Magazine, November 16th, 2011. Links to How to Run a Lathe and other publications by South Bend Lathe WorksSouth Bend Lathe WorksSouth Bend Lathe is a brand of machine tools. Today's South Bend Lathe corporation is the successor to the original South Bend Lathe Works, an American machine tool–building firm that for many decades was one of the most important builders of metalworking lathes in the U.S...
.

