
Languages of the Netherlands
Encyclopedia
The official language
Official language
An official language is a language that is given a special legal status in a particular country, state, or other jurisdiction. Typically a nation's official language will be the one used in that nation's courts, parliament and administration. However, official status can also be used to give a...
of the Netherlands is Dutch, spoken by almost all people in the Netherlands. Dutch is also spoken in Flanders
Flanders
Flanders is the community of the Flemings but also one of the institutions in Belgium, and a geographical region located in parts of present-day Belgium, France and the Netherlands. "Flanders" can also refer to the northern part of Belgium that contains Brussels, Bruges, Ghent and Antwerp...
and Suriname
Suriname
Suriname , officially the Republic of Suriname , is a country in northern South America. It borders French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west, Brazil to the south, and on the north by the Atlantic Ocean. Suriname was a former colony of the British and of the Dutch, and was previously known as...
. It is a West Germanic, Low Franconian language that originated in the Early Middle Ages (c. 470) and was standardized in the 16th century.
While most people in the Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
speak Dutch
Dutch language
Dutch is a West Germanic language and the native language of the majority of the population of the Netherlands, Belgium, and Suriname, the three member states of the Dutch Language Union. Most speakers live in the European Union, where it is a first language for about 23 million and a second...
, there are also some recognized provincial languages and regional dialects.
- FrisianWest Frisian languageWest Frisian is a language spoken mostly in the province of Friesland in the north of the Netherlands. West Frisian is the name by which this language is usually known outside the Netherlands, to distinguish it from the closely related Frisian languages of Saterland Frisian and North Frisian,...
is a co-official language in the provinceProvinces of the NetherlandsA Dutch province represents the administrative layer in between the national government and the local municipalities, having the responsibility for matters of subnational or regional importance. The government of each province consists of three major parts: the Provinciale Staten which is the...
of FrieslandFrieslandFriesland is a province in the north of the Netherlands and part of the ancient region of Frisia.Until the end of 1996, the province bore Friesland as its official name. In 1997 this Dutch name lost its official status to the Frisian Fryslân...
. Frisian is spoken by 453,000 speakers - Several dialects of Dutch Low SaxonDutch Low SaxonDutch Low Saxon is a group of Low Saxon, i.e. West Low German dialects spoken in the northeastern Netherlands. In comparison, the remainder of the Netherlands speak a collection of Low Franconian dialects.The class "Dutch Low Saxon" is not unanimous...
(Nederlands Nedersaksisch in Dutch) are spoken in much of the north-east of the country and are recognised by the Netherlands as regional languages according to the European Charter for Regional or Minority LanguagesEuropean Charter for Regional or Minority LanguagesThe European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages is a European treaty adopted in 1992 under the auspices of the Council of Europe to protect and promote historical regional and minority languages in Europe...
. Low Saxon is spoken by 1,798,000 speakers. - Another Low Franconian dialect granted the status of regional language is Limburgish, which is spoken in the south-eastern province of LimburgLimburg (Netherlands)Limburg is the southernmost of the twelve provinces of the Netherlands. It is located in the southeastern part of the country and bordered by the province of Gelderland to the north, Germany to the east, Belgium to the south and part of the west, andthe Dutch province of North Brabant partly to...
. Limburgish is spoken by 825,000 speakers. Though there are movements to have Limburgish recognized as an official language (meeting with varying amounts of success,) it is important to note that Limburgish in fact consists of a large number of differing dialects that share some common aspects, but are quite different.
However, both Low Saxon and Limburgish spread across the Dutch-German border and belong to a common Dutch-Low German
Low German
Low German or Low Saxon is an Ingvaeonic West Germanic language spoken mainly in northern Germany and the eastern part of the Netherlands...
dialect continuum
Dialect continuum
A dialect continuum, or dialect area, was defined by Leonard Bloomfield as a range of dialects spoken across some geographical area that differ only slightly between neighboring areas, but as one travels in any direction, these differences accumulate such that speakers from opposite ends of the...
.
- EnglishEnglish languageEnglish is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
is an official language in the special municipalities of Bonaire, Saba and Sint Eustatius (BES IslandsBES islandsThe Caribbean Netherlands collectively refers to the three special municipalities of the Netherlands that are located overseas, in the Caribbean: Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba...
). It is widely spoken on Saba and Sint Eustatius (see also: English language in the NetherlandsEnglish language in the NetherlandsEnglish language in the Netherlands refers to the use of English in the Netherlands. Research states that about 86% of the Dutch population claims to be able to converse in English...
). - PapiamentoPapiamentoPapiamento is the most widely spoken language on the Caribbean ABC islands, having the official status on the islands of Aruba and Curaçao. The language is also recognized on Bonaire by the Dutch government....
is an official language in the special municipality of Bonaire.
The Netherlands also has its separate Dutch Sign Language
Dutch Sign Language
Dutch Sign Language is the sign language used by deaf people in the Netherlands and is not officially recognized. As of 1995, more and more schools for the deaf in The Netherlands teach 'Nederlands met Gebaren' or 'NmG'...
, called Nederlandse Gebarentaal (NGT). It is still waiting for recognition and has 17,500 users.
There is a tradition of learning foreign languages in the Netherlands: about 89% of the total population have good knowledge of English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
, 70% of German
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
, 29% of French
French language
French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
and 5% of Spanish
Spanish language
Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the...
.
Frisian dialects
West FrisianWest Frisian
The West Frisian can mean:* West Frisian language, the language spoken in the Friesland province of the Netherlands* West Frisian dialect, the Hollandic Dutch dialect spoken in the North Holland province of the Netherlands* West Frisians, people...
is an official language in the Dutch province of Friesland
Friesland
Friesland is a province in the north of the Netherlands and part of the ancient region of Frisia.Until the end of 1996, the province bore Friesland as its official name. In 1997 this Dutch name lost its official status to the Frisian Fryslân...
(Fryslân in West Frisian). The government of the Frisian province is bilingual. Since 1996 Frisian is an official recognized language in the Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
.
- Westlauwers FrisianWest Frisian languageWest Frisian is a language spoken mostly in the province of Friesland in the north of the Netherlands. West Frisian is the name by which this language is usually known outside the Netherlands, to distinguish it from the closely related Frisian languages of Saterland Frisian and North Frisian,...
- Wood FrisianWood FrisianWood Frisian is a dialect of the West Frisian language spoken in the eastern part of the Dutch province of Friesland, which is called Wâlden...
- Clay FrisianClay FrisianClay Frisian is a dialect of the West Frisian language spoken in the northwestern part of the Dutch province of Friesland. It has been the primary dialect of written West Frisian since the nineteenth century as a result of its high status. Historically, this region has been the centre of commerce...
- Noordhoeks
- Zuidwesthoeks
- Hindelopers
- Westers
- Aasters
- Schiermonnikoogs
- Wood Frisian
Low Saxon dialects
- Gronings-GroningsGronings, in the dialect itself called Grunnegs or Grönnegs, is a collective name for some Friso-Saxon dialects spoken in the province of Groningen and around the Groningen border in Drenthe and Friesland. Gronings and the strongly related varieties in East-Frisia have a strong Frisian influence...
East FrisianEast Frisian Low SaxonEast Frisian Low Saxon is a West Low German dialect spoken in the East Frisian peninsula of northwestern Lower Saxony. It is used quite frequently in everyday speech there. About half of the East Frisian population in the coastal region uses Platdüütsk. A number of individuals, despite not being...
- Kollumerpompsters
- Hoogelandsters
- Oldambtsters
- Westerwolds
- Veenkoloniaals
- Stadsgronings
- Noordenvelds (Noord-Drents)
- Westerkwartiers
- Midden-Drents
- Zuid-Drents
- Stellingwerfs
- Guelderish-Overijssels
- Urks
- SallandsSallandsSallaans is a collective term for the Dutch Low Saxon dialects of the region Salland, in the west of the province of Overijssel, which is in the eastern Netherlands. A common term used by native speakers for their dialect, which is also used by Low Saxon speakers from other regions for their...
- Achterhoeks
- TwentsTwentsTweants is a Dutch Low Saxon group of dialects, descending from Old Saxon. It is spoken by approximately 62% of the population of Twente, a region in the Dutch province of Overijssel bordering on Germany. Its speakers also refer to Twents as plat or simply dialect. A widespread misconception is...
- Oost-Twents
- Vriezenveens (this is actually a separate dialect because of Frisian influences)
- Twents-Graafschaps
- VeluwsVeluwsVeluws is a Dutch Low Saxon dialect which is spoken on the Veluwe. Veluws is usually divided into two main dialects, West-Veluws and Oost-Veluws , these two dialects are reasonably similar but differ in grammar...
- Oost-Veluws
- West-Veluws
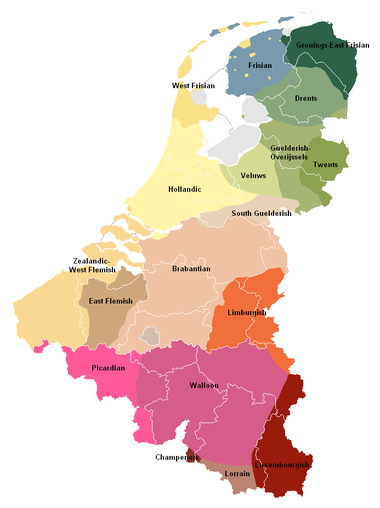
Low Franconian dialects
- West FrisianWest Frisian (dialect)The West Frisian dialect is a Dutch dialect spoken in the contemporary West Friesland region , Wieringen, Wieringermeer, the coastal area from Den Helder to Castricum, and the island of Texel. It is a Hollandic Dutch dialect but has affinities to the Frisian language...
- Mainland West Frisian
- Insular West Frisian
- Stadsfries
- Midlands
- Amelands
- Bilts
- HollandicHollandicHollandic or Hollandish is, together with Brabantian, the most frequently used dialect of the Dutch language. Other important Low Franconian language varieties spoken in the same area are Zeelandic, East Flemish, West Flemish and Limburgish....
- Kennemerlandic
- Zaans
- Waterlandic
- Amsterdams
- Strand-Hollands
- Haags
- Rotterdams
- Utrechts-Alblasserwaards
- Westhoeks
- Zealandic-West FlemishWest FlemishWest Flemish , , , Fransch vlaemsch in French Flemish) is a group of dialects or regional language related to Dutch spoken in parts of the Netherlands, Belgium, and France....
(including French Flemish)- Zealandic
- Burger-Zeeuws
- Coastal West Flemish
- Continental West Flemish
- East FlemishEast FlemishEast Flemish is a group of dialects of the Dutch language, which is a Low Franconian language. It is spoken in the province of East Flanders in Belgium, but also spoken in Zeeuws-Vlaanderen in the Netherlands.-Brabantic Expansion:...
- South Guelderish (Kleverlands)
- Rivierenlands
- Liemers
- Nijmeegs
- BrabantianBrabantianBrabantian or Brabantish, also Brabantic , is a dialect group of the Dutch language. It is named after the historical Duchy of Brabant which corresponded mainly to the Dutch province of North Brabant, the Belgian provinces of Antwerp and Flemish Brabant, as well as the institutional Region of...
- Northwest Brabantian
- Central north Brabantian
- East Brabantian
- Kempen Brabantian
- South Brabantian
- North Limburgian
- Limburgish
- West Limburgish
- Central Limburgish
- Southeast Limburgish
- Low DietschLow DietschLow Dietsch is a term mainly used within the Flemish terminology for the transitional Limburgish–Ripuarian dialects of a number of towns and villages in the north-east of the Belgian province of Liege, such as Gemmenich, Homburg, Montzen and Welkenraedt....
Dialects fully outside the Netherlands
Luxembourgish is divided into Moselle Luxembourgish, West Luxembourgish, East Luxembourgish, North Luxembourgish and City Luxembourgish. The Oïl dialects in the Benelux areWalloon
Walloon language
Walloon is a Romance language which was spoken as a primary language in large portions of the Walloon Region of Belgium and some villages of Northern France until the middle of the 20th century. It belongs to the langue d'oïl language family, whose most prominent member is the French language...
(divided into West Walloon, Central Walloon, East Walloon and South Walloon), Lorrain
Lorrain
Lorrain may refer to:* Claude Lorrain , a 17th-century French artist of the baroque style* Lorrain language, a Romance dialect spoken in Lorraine region in France and Gaume region in Belgium- See also :* Lorain...
(including Gaumais), Champenois
Champenois
Champenois is a language spoken by a minority of people in Champagne in France and in Wallonia in Belgium. It is one of the langues d'oïl. It is classified as a regional language of France, and has the recognized status of a regional language of Wallonia....
and Picard
Picard
Picard may refer to:* a native of, or anything originating in, Picardy* the Picard language, a Langue d'oïl and one of the languages of France* A member of the Picards, a religious sect in the fifteenth century...
(including
Tournaisis).
Notations
- http://taal.phileon.nl/fries.php
- http://taal.phileon.nl/nedersaksisch.php
- http://taal.phileon.nl/lim_situatie.php
- [5] - specifically, see Table 2.

