
Land grid array
Encyclopedia

Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
s (ICs) that is notable for having the pins on the socket
CPU socket
A CPU socket or CPU slot is a mechanical component that provides mechanical and electrical connections between a microprocessor and a printed circuit board . This allows the CPU to be replaced without soldering....
rather than the integrated circuit. An LGA can be electrically connected to a printed circuit board
Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
(PCB) either by the use of a socket or by soldering
Soldering
Soldering is a process in which two or more metal items are joined together by melting and flowing a filler metal into the joint, the filler metal having a lower melting point than the workpiece...
directly to the board.
Use in microprocessors
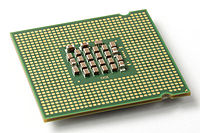
Pentium 4
Pentium 4 was a line of single-core desktop and laptop central processing units , introduced by Intel on November 20, 2000 and shipped through August 8, 2008. They had a 7th-generation x86 microarchitecture, called NetBurst, which was the company's first all-new design since the introduction of the...
(Prescott), Intel Xeon
Xeon
The Xeon is a brand of multiprocessing- or multi-socket-capable x86 microprocessors from Intel Corporation targeted at the non-consumer server, workstation and embedded system markets.-Overview:...
, Intel Core 2
Intel Core 2
Core 2 is a brand encompassing a range of Intel's consumer 64-bit x86-64 single-, dual-, and quad-core microprocessors based on the Core microarchitecture. The single- and dual-core models are single-die, whereas the quad-core models comprise two dies, each containing two cores, packaged in a...
, Intel Core
Intel Core
Yonah was the code name for Intel's first generation of 65 nm process mobile microprocessors, based on the Banias/Dothan-core Pentium M microarchitecture. SIMD performance has been improved through the addition of SSE3 instructions and improvements to SSE and SSE2 implementations, while integer...
(Bloomfield
Bloomfield (microprocessor)
Bloomfield is the code name for Intel high-end desktop processors sold as Core i7-9xx and single-processor servers sold as Xeon 35xx., in almost identical configurations, replacing the earlier Yorkfield processors. The Bloomfield core is closely related to the dual-processor Gainestown, which has...
and Lynnfield
Lynnfield (microprocessor)
Lynnfield is the code name for a quad-core processor from Intel released in September 2009. It is sold in varying configurations as Core i5-7xx, Core i7-8xx or Xeon X34xx. Lynnfield uses the Nehalem microarchitecture and replaces the earlier Penryn based Yorkfield processor, using the same 45 nm...
) and AMD Opteron
Opteron
Opteron is AMD's x86 server and workstation processor line, and was the first processor which supported the AMD64 instruction set architecture . It was released on April 22, 2003 with the SledgeHammer core and was intended to compete in the server and workstation markets, particularly in the same...
families. Unlike the pin grid array
Pin grid array
A pin grid array, often abbreviated PGA, is a type of integrated circuit packaging. In a PGA, the package is square or roughly square, and the pins are arranged in a regular array on the underside of the package...
(PGA) interface found on most AMD and older Intel processors, there are no pins on the chip; in place of the pins are pads of bare gold-plated copper that touch protruding pins on the microprocessor's placeholder on the motherboard
Motherboard
In personal computers, a motherboard is the central printed circuit board in many modern computers and holds many of the crucial components of the system, providing connectors for other peripherals. The motherboard is sometimes alternatively known as the mainboard, system board, or, on Apple...
.
While LGA sockets have been in use as early as 1996 by the MIPS
MIPS architecture
MIPS is a reduced instruction set computer instruction set architecture developed by MIPS Technologies . The early MIPS architectures were 32-bit, and later versions were 64-bit...
R10000
R10000
The R10000, code-named "T5", is a RISC microprocessor implementation of the MIPS IV instruction set architecture developed by MIPS Technologies, Inc. , then a division of Silicon Graphics, Inc. . The chief designers were Chris Rowen and Kenneth C. Yeager...
and HP PA-8000
PA-8000
The PA-8000 , code-named Onyx, is a microprocessor developed and fabricated by Hewlett-Packard that implemented the PA-RISC 2.0 instruction set architecture . It was a completely new design with no circuitry derived from previous PA-RISC microprocessors...
processors, the interface did not gain widespread use until Intel introduced their LGA platform, starting with the 5x0 and 6x0 sequence Pentium 4 (Prescott) in 2004. All Pentium D
Pentium D
The Pentium D brand refers to two series of desktop dual-core 64-bit x86-64 microprocessors with the NetBurst microarchitecture manufactured by Intel. Each CPU comprised two dies, each containing a single core, residing next to each other on a multi-chip module package. The brand's first processor,...
and Core 2
Intel Core 2
Core 2 is a brand encompassing a range of Intel's consumer 64-bit x86-64 single-, dual-, and quad-core microprocessors based on the Core microarchitecture. The single- and dual-core models are single-die, whereas the quad-core models comprise two dies, each containing two cores, packaged in a...
desktop processors currently use an LGA socket. As of Q1 2006, Intel switched the Xeon server platform to LGA, starting with the 5000-series models. AMD introduced their server LGA platform starting with the 2000-series Opteron
Opteron
Opteron is AMD's x86 server and workstation processor line, and was the first processor which supported the AMD64 instruction set architecture . It was released on April 22, 2003 with the SledgeHammer core and was intended to compete in the server and workstation markets, particularly in the same...
in Q2 2006. AMD offered the Athlon 64 FX series on socket 1207FX through ASUS's L1N64-SLI WS motherboards. It was the only desktop LGA solution offered by AMD.
The most common Intel desktop LGA socket is dubbed LGA 1155
LGA 1155
LGA 1155, also called Socket H2, is an Intel microprocessor compatible socket which supports Intel Sandy Bridge and the up-coming Ivy Bridge microprocessors....
(Socket H2) , which is used with Intel's Sandy Bridge-series Core i3, i5, and i7 families. However, the new Sandy Bridge-E Core i7 family uses the LGA 2011
LGA 2011
LGA 2011, also called Socket R, is a CPU socket by Intel. It replaces Intel's LGA 1366 and LGA 1567 in the performance and high-end desktop and server platforms. The socket has 2,011 protruding pins which touch contact points on the underside of the processor.Socket R uses QPI to connect the CPU...
(Socket R) socket. The LGA setup provides higher pin densities, allowing more power contacts and thus a more stable power supply to the chip. LGA packaging also has a tertiary benefit of placing pins onto the motherboard; if a pin breaks, the motherboard is often cheaper to replace than the CPU chip (as compared to a PGA chip/socket setup).
The AMD server LGA socket is designated Socket G34
Socket G34
Socket G34 is a CPU socket designed by AMD to support AMD's multi-chip module Opteron 6000-series server processors. G34 was launched on March 29, 2010, alongside the initial grouping of Opteron 6100 processors designed for it. Socket G34 supports four DDR3 SDRAM channels, two for each die in the...
(LGA 1944). Like Intel, AMD decided to use LGA sockets for their higher pin densities, as a 1944-pin PGA would simply be too large for most motherboards.
AMD
- Socket FSocket FSocket F is a CPU socket designed by AMD for its Opteron line of CPUs released on August 15, 2006. In 2010 Socket F was replaced by Socket C32 for entry-level servers and Socket G34 for high-end servers.-Technical specifications:...
(LGA 1207) - Socket C32Socket C32The AMD Socket C32 is the server processor socket for AMD's current single-CPU and dual-CPU Opteron 4000 series CPUs. It is the successor to Socket AM3 for single-CPU servers and the successor for Socket F for lower-end dual-CPU servers...
(LGA 1207) (replaces Socket FSocket FSocket F is a CPU socket designed by AMD for its Opteron line of CPUs released on August 15, 2006. In 2010 Socket F was replaced by Socket C32 for entry-level servers and Socket G34 for high-end servers.-Technical specifications:...
) - Socket G34Socket G34Socket G34 is a CPU socket designed by AMD to support AMD's multi-chip module Opteron 6000-series server processors. G34 was launched on March 29, 2010, alongside the initial grouping of Opteron 6100 processors designed for it. Socket G34 supports four DDR3 SDRAM channels, two for each die in the...
(LGA 1974)
Intel
- LGA 775 (Socket T)
- LGA 771LGA 771LGA 771, also known as Socket J, is a CPU interface introduced by Intel in 2006. It is used in Intel Core microarchitecture based DP-capable server processors, the Dual-Core Xeon is codenamed Dempsey, Woodcrest, and Wolfdale and the Quad-Core processors Clovertown, Harpertown...
(Socket J) - LGA 1366 (Socket B)
- LGA 1356LGA 1356LGA 1356 , also called Socket B2, is an Intel microprocessor compatible socket rumored to be released in Q1 2012 for the two processor slot segment of the server market.-Description:...
(Socket B2) - LGA 1156LGA 1156LGA 1156, also known as Socket H or H1, is an Intel desktop CPU socket. LGA stands for land grid array. Its incompatible successor is LGA 1155....
(Socket H) - LGA 1155LGA 1155LGA 1155, also called Socket H2, is an Intel microprocessor compatible socket which supports Intel Sandy Bridge and the up-coming Ivy Bridge microprocessors....
(Socket H2) - LGA 2011LGA 2011LGA 2011, also called Socket R, is a CPU socket by Intel. It replaces Intel's LGA 1366 and LGA 1567 in the performance and high-end desktop and server platforms. The socket has 2,011 protruding pins which touch contact points on the underside of the processor.Socket R uses QPI to connect the CPU...
(Socket R)
See also
- Chip carrierChip carrierA chip carrier, also known as a chip container or chip package, is a container for a transistor or an integrated circuit. The carrier usually provides metal leads, or "pins", which are sturdy enough to electrically and mechanically connect the fragile chip to a circuit board. This connection may be...
- Dual in-line packageDual in-line packageIn microelectronics, a dual in-line package is an electronic device package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins. The package may be through-hole mounted to a printed circuit board or inserted in a socket.A DIP is usually referred to as a DIPn, where n is...
(DIP) - Pin grid arrayPin grid arrayA pin grid array, often abbreviated PGA, is a type of integrated circuit packaging. In a PGA, the package is square or roughly square, and the pins are arranged in a regular array on the underside of the package...
(PGA) - Ball grid arrayBall grid arrayA ball grid array is a type of surface-mount packaging used for integrated circuits.- Description :The BGA is descended from the pin grid array , which is a package with one face covered with pins in a grid pattern. These pins conduct electrical signals from the integrated circuit to the printed...
(BGA)

