
Lactone
Encyclopedia

Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, a lactone is a cyclic ester
Ester
Esters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH group is replaced by an -O-alkyl group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and...
which can be seen as the condensation
Condensation reaction
A condensation reaction is a chemical reaction in which two molecules or moieties combine to form one single molecule, together with the loss of a small molecule. When this small molecule is water, it is known as a dehydration reaction; other possible small molecules lost are hydrogen chloride,...
product of an alcohol group -OH and a carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acids are organic acids characterized by the presence of at least one carboxyl group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R-COOH, where R is some monovalent functional group...
group -COOH in the same molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
. It is characterized by a closed ring consisting of two or more carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
atoms and a single oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
atom, with a ketone
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
group =O in one of the carbons adjacent to the other oxygen.
Nomenclature
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
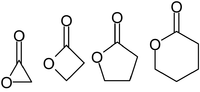
prefix that specifies the number of carbons in the heterocyle — that is, the distance between the relevant -OH and the -COOH groups along said backbone. The first carbon atom after the carbon in the -COOH group on the parent compound is labelled α, the second will be labeled β, and so forth. Therefore, the prefixes also indicate the size of the lactone ring: α-lactone = 3-membered ring, β-lactone = 4-membered, γ-lactone = 5-membered, etc.
The other suffix used to denote a lactone is -olide, used in substance class names like butenolide
Butenolide
Butenolides are a class of lactones with a four-carbon heterocyclic ring structure. They are sometimes considered oxidized derivatives of furan. The simplest butenolide is 2-furanone, which is a common component of larger natural products and is sometimes referred to as simply "butenolide". A...
, macrolide
Macrolide
The macrolides are a group of drugs whose activity stems from the presence of a macrolide ring, a large macrocyclic lactone ring to which one or more deoxy sugars, usually cladinose and desosamine, may be attached. The lactone rings are usually 14-, 15-, or 16-membered...
, cardenolide
Cardenolide
Cardenolide is a type of steroid. Many plants contain derivatives, collectively known as cardenolides, including many in the form of cardenolide glycosides...
or bufadienolide.
Etymology
The name lactone derives from the ring compound called lactideLactide
Lactide is the cyclic di-ester of lactic acid, i.e., 2-hydroxypropionic acid. Lactic acid cannot form a lactone as other hydroxy acids do because the hydroxy group is too close to the carboxylic group. Instead, lactic acid first forms a dimer, which is similar to a 5-hydroxyacid...
, which is formed from the dehydration of 2-hydroxypropanoic acid (lactic acid
Lactic acid
Lactic acid, also known as milk acid, is a chemical compound that plays a role in various biochemical processes and was first isolated in 1780 by the Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele. Lactic acid is a carboxylic acid with the chemical formula C3H6O3...
) CH3-CH(OH)-COOH. Lactic acid, in turn, derives its name from its original isolation from soured milk (Latin: lac, lactis). An internal dehydration within the same molecule of lactic acid would have produced alpha-propiolactone
Alpha-Propiolactone
α-Propiolactone, or 2-methyl-α-lactone, is a chemical compound of the lactone family, with a three-membered ring. It is a stable product which can be obtained from the 2-bromo-propionate anion. It is an intermediate in the decomposition of 2-chloropropionic acid in the gas phase....
, a lactone with a 3-membered ring.
Natural sources
Lactones (specifically 3-methyl-4-octanolideCis-3-Methyl-4-octanolide
cis-3-Methyl-4-octanolide, also called cis-β-methyl-γ-octalactone or 5-butyldihydro-4-methylfuran-2-one, is a chemical compound of the lactone family with formula...
) are found in oak
Oak
An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus Quercus , of which about 600 species exist. "Oak" may also appear in the names of species in related genera, notably Lithocarpus...
trees as well as many other plants, and impart flavour to whisky
Whisky
Whisky or whiskey is a type of distilled alcoholic beverage made from fermented grain mash. Different grains are used for different varieties, including barley, malted barley, rye, malted rye, wheat, and corn...
.
Synthesis
Many methods in esterEster
Esters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH group is replaced by an -O-alkyl group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and...
synthesis can also be applied to that of lactones. In one industrial synthesis of oxandrolone
Oxandrolone
Oxandrolone is a drug created by Raphael Pappo while at Searle Laboratories, now Pfizer Inc. under the trademark Anavar, and introduced into the US in 1964....
the key lactone-forming step is an organic reduction - esterification:
In halolactonization, an alkene
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated chemical compound containing at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond...
is attacked by a halogen
Halogen
The halogens or halogen elements are a series of nonmetal elements from Group 17 IUPAC Style of the periodic table, comprising fluorine , chlorine , bromine , iodine , and astatine...
via electrophilic addition
Electrophilic addition
In organic chemistry, an electrophilic addition reaction is an addition reaction where, in a chemical compound, a π bond is broken and two new σ bonds are formed...
with the cationic intermediate captured intramolecularly by an adjacent carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acids are organic acids characterized by the presence of at least one carboxyl group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R-COOH, where R is some monovalent functional group...
(See also iodolactamization), for example in this iodolactonization:
A specific method is called Yamaguchi esterification
Yamaguchi esterification
The Yamaguchi esterification is the chemical reaction of an aliphatic carboxylic acid and 2,4,6-trichlorobenzoyl chloride to form a mixed anhydride which, upon reaction with an alcohol in the presence of stoichiometric amount of DMAP, produces the desired ester. It was first reported by M...
.
A recent study has isolated β-lactones from bromination of 2,3-dimethylmaleate and/or 2,3-dimethylfumarate disodium salts, under ambient and aqueous conditions. The carboxylate groups of the maleate and fumarate moieties exhibit neighbouring group effects and alpha-lactones are proposed in the detailed mechanism.
Reactions
The most stable structure for lactones are the 5-membered γ-lactones and 6-membered δ-lactones because, as in all organic cycles, 5 and 6 membered rings minimize the strain of bond angles. γ-lactones are so stable that, in the presence of dilute acids at room temperature, 4-hydroxy acids (R-CH(OH)-(CH2)2-COOH) immediately undergo spontaneous esterification and cyclisation to the lactone. β-lactones do exist, but can only be made by special methods. α-lactones can be detected as transient species in mass spectrometryMass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of charged particles.It is used for determining masses of particles, for determining the elemental composition of a sample or molecule, and for elucidating the chemical structures of molecules, such as peptides and...
experiments.
The reactions of lactones are similar to those of esters, as exemplified by gamma-lactone in the following sections:
Hydrolysis
Heating a lactone with a base (sodium hydroxide) will hydrolyse the lactone to its parent compound, the straight chained bifunctional compound. Like straight-chained esters, the hydrolysis-condensation reaction of lactones is a reversible reactionReversible reaction
A reversible reaction is a chemical reaction that results in an equilibrium mixture of reactants and products. For a reaction involving two reactants and two products this can be expressed symbolically as...
, with an equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which the concentrations of the reactants and products have not yet changed with time. It occurs only in reversible reactions, and not in irreversible reactions. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same...
. However, the equilibrium constant of the hydrolysis reaction of the lactone is lower than that of the straight-chained ester i.e. the products (hydroxyacids) are less favored in the case of the lactones. This is because although the enthalpies
Enthalpy
Enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a thermodynamic system. It includes the internal energy, which is the energy required to create a system, and the amount of energy required to make room for it by displacing its environment and establishing its volume and pressure.Enthalpy is a...
of the hydrolysis of esters and lactones are about the same, the entropy
Entropy
Entropy is a thermodynamic property that can be used to determine the energy available for useful work in a thermodynamic process, such as in energy conversion devices, engines, or machines. Such devices can only be driven by convertible energy, and have a theoretical maximum efficiency when...
of the hydrolysis of lactones is less than the entropy of straight-chained esters. Straight-chained esters give two products upon hydrolysis, making the entropy change more favorable than in the case of lactones which give only a single product.
Reduction
Lactones can be reduced to diols using lithium aluminium hydrideLithium aluminium hydride
Lithium aluminium hydride, commonly abbreviated to LAH or known as LithAl, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula LiAlH4. It was discovered by Finholt, Bond and Schlesinger in 1947. This compound is used as a reducing agent in organic synthesis, especially for the reduction of esters,...
in dry ether. The reduction reaction will first break the ester bond of the lactone, and then reduce the carboxylic acid group (-COOH) to the alcohol group (-OH). For instance, gamma-lactones will be reduced to butan-1,4-diol, (CH2(OH)-(CH2)2-CH2(OH).
Aminolysis
Lactones also react with ethanolic ammonia, which will first break the ester bond and then react with the acidic -COOH group, because of the basic properties of ammonia, to form a difunctional group, i.e. alcohol and amide. Gamma-lactones will react to yield CH2(OH)-(CH2)2-CO-NH2.Michael reaction
Sesquiterpene lactoneSesquiterpene lactone
Sesquiterpene lactones are a class of chemical compounds; they are sesquiterpenoids and contain a lactone ring, hence the name....
s, found in many plants, can react with other molecules via a Michael reaction
Michael reaction
The Michael reaction or Michael addition is the nucleophilic addition of a carbanion or another nucleophile to an alpha, beta unsaturated carbonyl compound. It belongs to the larger class of conjugate additions. This is one of the most useful methods for the mild formation of C-C bonds...
.
Biofilm prevention
Brominated furanones have been shown to be somewhat effective at preventing the formation of biofilmBiofilm
A biofilm is an aggregate of microorganisms in which cells adhere to each other on a surface. These adherent cells are frequently embedded within a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substance...
. One species has specifically been shown to increase Salmonella enterica
Salmonella enterica
Salmonella enterica is a rod-shaped flagellated, facultative anaerobic, Gram-negative bacterium, and a member of the genus Salmonella.- Epidemiology :...
serovar Typhimurium's susceptibility to antimicrobial
Antimicrobial
An anti-microbial is a substance that kills or inhibits the growth of microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, or protozoans. Antimicrobial drugs either kill microbes or prevent the growth of microbes...
treatments.
dilactones
- Ellagic acidEllagic acidEllagic acid is a natural phenol antioxidant found in numerous fruits and vegetables including blackberries, raspberries, strawberries, cranberries, walnuts, pecans, pomegranates, wolfberry and other plant foods...
(Hexahydroxydiphenic acid dilactone) - Flavogallonic acid dilactoneFlavogallonic acid dilactoneFlavogallonic acid dilactone is a hydrolysable tannin that can be found in Rhynchosia volubilis seeds, in Shorea laeviforia, in Anogeissus leiocarpus and Terminalia avicennoides....
can be found in Rhynchosia volubilis seeds and in Shorea laeviforia - LactideLactideLactide is the cyclic di-ester of lactic acid, i.e., 2-hydroxypropionic acid. Lactic acid cannot form a lactone as other hydroxy acids do because the hydroxy group is too close to the carboxylic group. Instead, lactic acid first forms a dimer, which is similar to a 5-hydroxyacid...
- Tergallic acid dilactone can be found in Rhynchosia volubilis seeds
- Valoneic acid dilactone Valoneic acid dilactoneValoneic acid dilactone is a hydrolysable tannin that can be isolated from the heartwood of Shorea laeviforia....
can be isolated from the heartwood of Shorea laeviforia
See also
- LactamLactamA lactam is a cyclic amide. Prefixes indicate how many carbon atoms are present in the ring: β-lactam , γ-lactam , δ-lactam...
, a cyclic amideAmideIn chemistry, an amide is an organic compound that contains the functional group consisting of a carbonyl group linked to a nitrogen atom . The term refers both to a class of compounds and a functional group within those compounds. The term amide also refers to deprotonated form of ammonia or an... - Lactim, a cyclic imideImideIn organic chemistry, an imide is a functional group consisting of two carbonyl groups bound to nitrogen. These compounds are structurally related to acid anhydrides. The relationship between esters and amides and between imides and anhydrides is analogous, the amine-derived groups are less reactive...
- LactideLactideLactide is the cyclic di-ester of lactic acid, i.e., 2-hydroxypropionic acid. Lactic acid cannot form a lactone as other hydroxy acids do because the hydroxy group is too close to the carboxylic group. Instead, lactic acid first forms a dimer, which is similar to a 5-hydroxyacid...
, a cyclic di-esterEsterEsters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH group is replaced by an -O-alkyl group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and...


