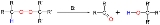
Kornblum–DeLaMare rearrangement
Encyclopedia
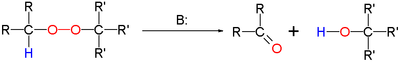
The Kornblum–DeLaMare rearrangement is a rearrangement reaction
in organic chemistry
in which a primary or secondary organic peroxide
is converted to the corresponding ketone
and alcohol
under base catalysis. The reaction is relevant as a tool in organic synthesis
and is a key step in the biosynthesis
of prostaglandins.
The base can be an hydroxide
such as potassium hydroxide
or an amine
such as triethylamine
.
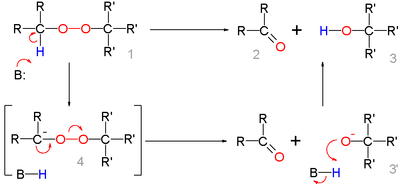
for this organic reaction the base abstracts the acidic α-proton of the peroxide 1 to form the carbanion
4 as a reactive intermediate
which rearranges to the ketone
2 with expulsion of the hydroxyl anion 3'. This intermediate gains a proton forming the alcohol 3.
Deprotonation
and rearrangement can also be a concerted reaction
without formation of 4.
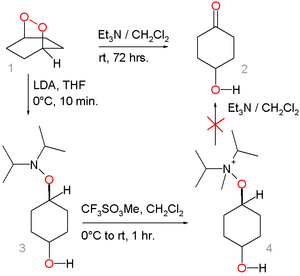
An alternative reaction mechanism involving direct nucleophilic displacement on the peroxide link of the amine followed by an elimination reaction
is considered unlikely based on the outcome of this model reaction:
The peroxide 1 converts to the hydroxyketone 2 by action of triethylamine
but the alternative route through hydroxylamine
3 by nucleophilic displacement with Lithium diisopropylamide
and the ammonium salt 4 (by methylation
with methyl trifluoromethanesulfonate
) fails.
The reaction, formally a rearrangement, ranks under the elimination reaction
s as already observed by the original authors. Not only alkoxides but any leaving group
capable of carrying a negative charge will do for instance nitrate esters R-C(R)(H)-O-NO2.
is the Wittig rearrangement. The reaction course in this rearrangement is different because ether cleavage with carbanion formation is unfavorable. The Pummerer rearrangement
in one of its reaction step contains a sulfur variation.
and t-butanol with piperidine
as the base:
 The Kornblum–DeLaMare rearrangement can be carried out as an asymmetric reaction with a suitable chiral
The Kornblum–DeLaMare rearrangement can be carried out as an asymmetric reaction with a suitable chiral
amine such as sparteine
or a cinchona
alkaloid:
The first step in this one-pot reaction is 1,4-dioxygenation of 1,3-cycloheptadiene with singlet oxygen
and a TPP
catalyst.
Rearrangement reaction
A rearrangement reaction is a broad class of organic reactions where the carbon skeleton of a molecule is rearranged to give a structural isomer of the original molecule. Often a substituent moves from one atom to another atom in the same molecule...
in organic chemistry
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
in which a primary or secondary organic peroxide
Organic peroxide
Organic peroxides are organic compounds containing the peroxide functional group . If the R' is hydrogen, the compound is called an organic hydroperoxide. Peresters have general structure RCOOR. The O-O bond easily breaks and forms free radicals of the form RO·...
is converted to the corresponding ketone
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
and alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
under base catalysis. The reaction is relevant as a tool in organic synthesis
Organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the construction of organic compounds via organic reactions. Organic molecules can often contain a higher level of complexity compared to purely inorganic compounds, so the synthesis of organic compounds has...
and is a key step in the biosynthesis
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is an enzyme-catalyzed process in cells of living organisms by which substrates are converted to more complex products. The biosynthesis process often consists of several enzymatic steps in which the product of one step is used as substrate in the following step...
of prostaglandins.
The base can be an hydroxide
Hydroxide
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and a hydrogen atom held together by a covalent bond, and carrying a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It functions as a base, as a ligand, a nucleophile, and a...
such as potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KOH, commonly called caustic potash.Along with sodium hydroxide , this colorless solid is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications. Most applications exploit its reactivity toward acids and its corrosive...
or an amine
Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
such as triethylamine
Triethylamine
Triethylamine is the chemical compound with the formula N3, commonly abbreviated Et3N. It is also abbreviated TEA, yet this abbreviation must be used carefully to avoid confusion with triethanolamine, for which TEA is also a common abbreviation....
.
Reaction mechanism
In the reaction mechanismReaction mechanism
In chemistry, a reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical change occurs.Although only the net chemical change is directly observable for most chemical reactions, experiments can often be designed that suggest the possible sequence of steps in...
for this organic reaction the base abstracts the acidic α-proton of the peroxide 1 to form the carbanion
Carbanion
A carbanion is an anion in which carbon has an unshared pair of electrons and bears a negative charge usually with three substituents for a total of eight valence electrons. The carbanion exists in a trigonal pyramidal geometry. Formally a carbanion is the conjugate base of a carbon acid.where B...
4 as a reactive intermediate
Reactive intermediate
In chemistry a reactive intermediate is a short-lived, high energy, highly reactive molecule. When generated in a chemical reaction it will quickly convert into a more stable molecule. Only in exceptional cases can these compounds be isolated and stored, e.g. low temperatures, matrix isolation...
which rearranges to the ketone
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
2 with expulsion of the hydroxyl anion 3'. This intermediate gains a proton forming the alcohol 3.
Deprotonation
Deprotonation
Deprotonation is the removal of a proton from a molecule, forming the conjugate base.The relative ability of a molecule to give up a proton is measured by its pKa value. A low pKa value indicates that the compound is acidic and will easily give up its proton to a base...
and rearrangement can also be a concerted reaction
Concerted reaction
In chemistry, a concerted reaction is a chemical reaction in which all bond breaking and bond making occurs in a single step. Reactive intermediates or other unstable high energy intermediates are not involved. Concerted reaction rates tend not to depend on solvent polarity ruling out large buildup...
without formation of 4.
An alternative reaction mechanism involving direct nucleophilic displacement on the peroxide link of the amine followed by an elimination reaction
Elimination reaction
An elimination reaction is a type of organic reaction in which two substituents are removed from a molecule in either a one or two-step mechanism...
is considered unlikely based on the outcome of this model reaction:
The peroxide 1 converts to the hydroxyketone 2 by action of triethylamine
Triethylamine
Triethylamine is the chemical compound with the formula N3, commonly abbreviated Et3N. It is also abbreviated TEA, yet this abbreviation must be used carefully to avoid confusion with triethanolamine, for which TEA is also a common abbreviation....
but the alternative route through hydroxylamine
Hydroxylamine
Hydroxylamine is an inorganic compound with the formula NH2OH. The pure material is a white, unstable crystalline, hygroscopic compound. However, hydroxylamine is almost always provided and used as an aqueous solution. It is used to prepare oximes, an important functional group. It is also an...
3 by nucleophilic displacement with Lithium diisopropylamide
Lithium diisopropylamide
Lithium diisopropylamide is the chemical compound with the formula [2CH]2NLi. Generally abbreviated LDA, it is a strong base used in organic chemistry for the deprotonation of weakly acidic compounds. The reagent has been widely accepted because it is soluble in non-polar organic solvents and it...
and the ammonium salt 4 (by methylation
Methylation
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group to a substrate or the substitution of an atom or group by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation with, to be specific, a methyl group, rather than a larger carbon chain, replacing a hydrogen atom...
with methyl trifluoromethanesulfonate
Methyl triflate
Methyl trifluoromethanesulfonate, is commonly called methyl triflate, and has the chemical formula CF3SO2-OCH3, and is used as a very powerful methylating reagent in chemistry....
) fails.
The reaction, formally a rearrangement, ranks under the elimination reaction
Elimination reaction
An elimination reaction is a type of organic reaction in which two substituents are removed from a molecule in either a one or two-step mechanism...
s as already observed by the original authors. Not only alkoxides but any leaving group
Leaving group
In chemistry, a leaving group is a molecular fragment that departs with a pair of electrons in heterolytic bond cleavage. Leaving groups can be anions or neutral molecules. Common anionic leaving groups are halides such as Cl−, Br−, and I−, and sulfonate esters, such as para-toluenesulfonate...
capable of carrying a negative charge will do for instance nitrate esters R-C(R)(H)-O-NO2.
Related reactions
The corresponding reaction involving an etherEther
Ethers are a class of organic compounds that contain an ether group — an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups — of general formula R–O–R'. A typical example is the solvent and anesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether"...
is the Wittig rearrangement. The reaction course in this rearrangement is different because ether cleavage with carbanion formation is unfavorable. The Pummerer rearrangement
Pummerer rearrangement
The Pummerer rearrangement is an organic reaction whereby an alkyl sulfoxide rearranges to an α-acyloxy–thioether in the presence of acetic anhydride. In this reaction, sulfur is reduced while adjacent carbon is oxidized....
in one of its reaction step contains a sulfur variation.
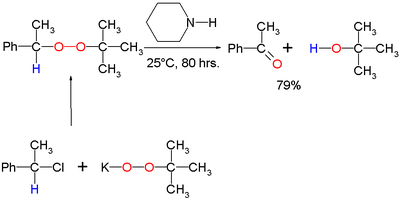
Scope
The original 1951 publication concerned the conversion of potassium t-butyl peroxide and 1-phenylethyl bromide to ultimately benzophenoneBenzophenone
Benzophenone is the organic compound with the formula 2CO, generally abbreviated Ph2CO. Benzophenone is a widely used building block in organic chemistry, being the parent diarylketone.-Uses:...
and t-butanol with piperidine
Piperidine
Piperidine is an organic compound with the molecular formula 5NH. This heterocyclic amine consists of a six-membered ring containing five methylene units and one nitrogen atom...
as the base:

Chirality (chemistry)
A chiral molecule is a type of molecule that lacks an internal plane of symmetry and thus has a non-superimposable mirror image. The feature that is most often the cause of chirality in molecules is the presence of an asymmetric carbon atom....
amine such as sparteine
Sparteine
Sparteine is a class 1a antiarrhythmic agent; a sodium channel blocker. It is an alkaloid and can be extracted from scotch broom. It is the predominant alkaloid in Lupinus mutabilis, and is thought to chelate the bivalents calcium and magnesium...
or a cinchona
Cinchona
Cinchona or Quina is a genus of about 38 species in the family Rubiaceae, native to tropical South America. They are large shrubs or small trees growing 5–15 metres in height with evergreen foliage. The leaves are opposite, rounded to lanceolate and 10–40 cm long. The flowers are white, pink...
alkaloid:
The first step in this one-pot reaction is 1,4-dioxygenation of 1,3-cycloheptadiene with singlet oxygen
Singlet oxygen
Singlet oxygen is the common name used for the diamagnetic form of molecular oxygen , which is less stable than the normal triplet oxygen. Because of its unusual properties, singlet oxygen can persist for over an hour at room temperature, depending on the environment...
and a TPP
Porphyrin
Porphyrins are a group of organic compounds, many naturally occurring. One of the best-known porphyrins is heme, the pigment in red blood cells; heme is a cofactor of the protein hemoglobin. Porphyrins are heterocyclic macrocycles composed of four modified pyrrole subunits interconnected at...
catalyst.